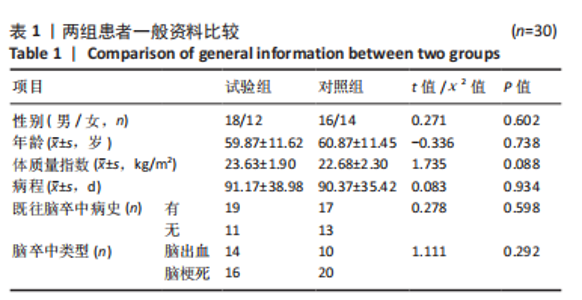
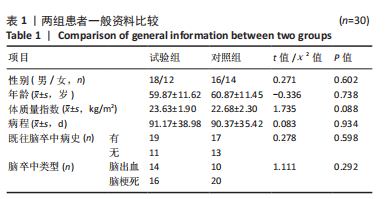
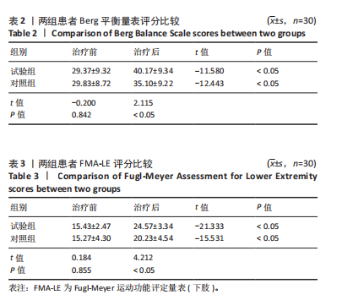
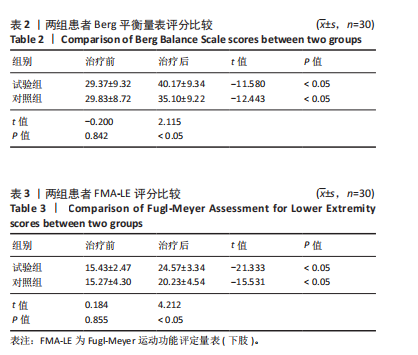
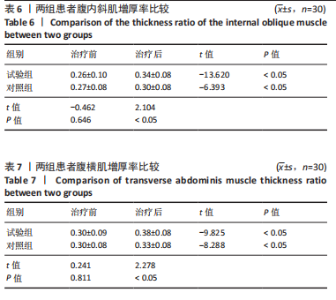
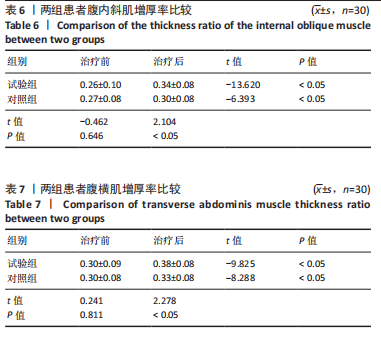
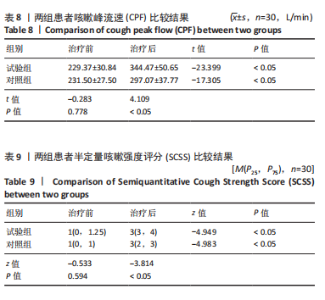
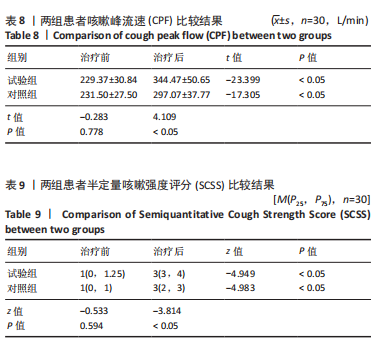
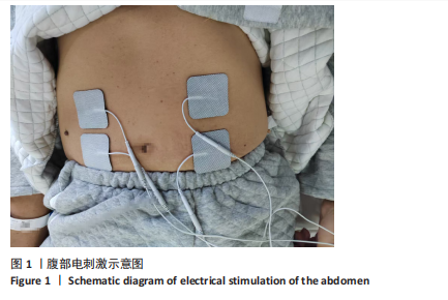
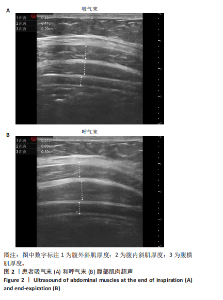
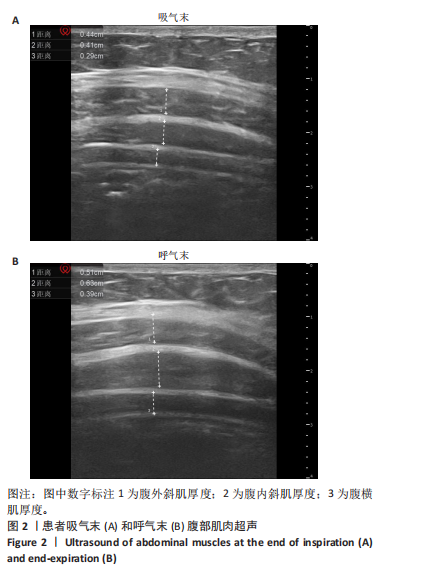
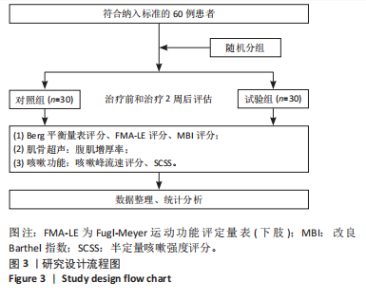
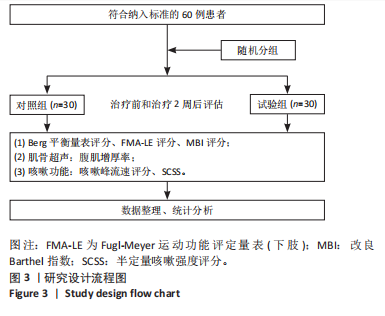
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2736-2744.doi: 10.12307/2026.076
Previous Articles Next Articles
Abdominal electrical stimulation combined with core stabilization training improves balance and cough function in patients with stroke pseudobulbar palsy
Gao Shiai1, Chen Jinhui1, Cao Xinyan1, Leng Xiaoxuan1, Liu Xihua2
- 1School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2025-02-25Accepted:2025-05-16Online:2026-04-18Published:2025-09-05 -
Contact:Liu Xihua, MD, Chief physician, Department of Rehabilitation, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Gao Shiai, MS candidate, School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China for the Youth, No. 81802239 (to LXH); Shandong Provincial Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Project, No. M-2023142 (to LXH); Shandong Provincial Medical Staff Science and Technology Innovation Program, No. SDYWZGKCJH2022024 (to LXH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Shiai, Chen Jinhui, Cao Xinyan, Leng Xiaoxuan, Liu Xihua. Abdominal electrical stimulation combined with core stabilization training improves balance and cough function in patients with stroke pseudobulbar palsy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2736-2744.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] AYCICEK HB, KARAKAYALI G, GURCAY E. Influence of core stabilization exercise on physical function and muscle thickness in patients with chronic stroke: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Scott Med J. 2024;69(4): 121-127. [2] 刘晶晶, 张小健, 郝春波, 等. 通督益脑化痰法针药并用治疗缺血性脑卒中假性球麻痹吞咽障碍临床研究[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2024, 51(1):171-175. [3] CHEN D, GUO H.Therapeutic effects of acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training on dysphagia in post-stroke pseudobulbar palsy. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2018;38(4):364-368. [4] 高爱民, 张月娥, 李丽杰, 等. 头针联合吞咽功能康复训练治疗中风后假性球麻痹吞咽障碍患者的临床观察[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2024,19(10):2012-2016. [5] 赵玉华, 罗文斓, 张旭, 等. 揿针为主治疗脑卒中假性球麻痹临床研究[J]. 四川中医,2021,39(10):179-182. [6] AL-BILTAGI M, BEDIWY AS, SAEED NK. Cough as a neurological sign: What a clinician should know. World J Crit Care Med. 2022;11(3):115-128. [7] 付常喜, 张秋阳. 核心稳定性训练对脑卒中偏瘫患者平衡功能和步行能力的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2016,36(21):5397-5398. [8] YELDAN I, CANAN GD, AKINCI B. Biofeedback Sensor vs. Physiotherapist Feedback During Core Stabilization Training in Patients with Chronic Nonspecific Low Back Pain. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2024; 49(1):103-113. [9] THIJS L, VOETS E, DENISSEN S, et al. Trunk training following stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023;3(3):Cd013712. [10] KARTHIKBABU S, GANESAN S, ELLAJOSYULA R, et al. Core Stability Exercises Yield Multiple Benefits for Patients With Chronic Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2022;101(4): 314-323. [11] HWANG UJ, KWON OY. Effect of electrical stimulation training and detraining on abdominal muscle function. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2023;36(4):831-843. [12] MCCAUGHEY EJ, BUTLER JE, MCBAIN RA, et al. Abdominal Functional Electrical Stimulation to Augment Respiratory Function in Spinal Cord Injury. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2019;25(2):105-111. [13] 李响, 张洪蕊, 刘陵鑫, 等. 腹部电刺激联合气道廓清技术对气管切开重症患者咳嗽能力及拔管成功率的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2024,39(10):1474-1480. [14] 中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国各类主要脑血管病诊断要点2019[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2019,52(9):710-715. [15] 黄樱, 钟善全. 神经病学[M]. 北京:化学工业出版社,2020:290. [16] 国家卫生健康委脑卒中防治工程委员会. 中国脑卒中防治指导规范[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2021:510. [17] JANG SH, LEE J, SEO JP. Pseudobulbar palsy due to bilateral injuries of corticobulbar tracts in a stroke patient. Int J Stroke. 2015;10(6): E53-54. [18] BIKMAL S, LIU F, MOON CH, et al. Microstructure of the residual corticofugal projection from primary motor cortex in chronic stroke. Brain Commun. 2025;7(1):fcaf016. [19] QI H, TIAN D, LUAN F, et al. Pathophysiological changes of muscle after ischemic stroke: a secondary consequence of stroke injury. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(4):737-746. [20] DE SIRE A, FERRILLO M, LIPPI L, et al. Sarcopenic Dysphagia, Malnutrition, and Oral Frailty in Elderly: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients. 2022;14(5):982. [21] 闫玉林, 于璐, 邵杨. 低频重复经颅磁刺激对脑卒中偏瘫患者下肢痉挛及平衡步态的影响[J]. 中国医药导报,2023,20(14):81-85. [22] SUH JH, LEE EC, KIM JS, et al. Association between trunk core muscle thickness and functional ability in subacute hemiplegic stroke patients: an exploratory cross-sectional study. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2022;29(3):163-172. [23] RODRIGUEZ-PORCEL F, SARVA H, JOUTSA J, et al. Current opinions and practices in post-stroke movement disorders: Survey of movement disorders society members. J Neurol Sci. 2024;458:122925. [24] ZHANG Y, WANG C, YANG J, et al. Comparing the Effects of Short-Term Liuzijue Exercise and Core Stability Training on Balance Function in Patients Recovering From Stroke: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Front Neurol. 2022;13:748754. [25] OLCZAK A. Importance of core stability for coordinated movement of the human body in stroke rehabilitation. Neurol Res. 2022;44(1):7-13. [26] LIU H, YIN H, YI Y, et al. Effects of different rehabilitation training on balance function in stroke patients: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Arch Med Sci. 2023;19(6):1671-1683. [27] MAHMOOD W, AHMED BURQ HSI, EHSAN S, et al. Effect of core stabilization exercises in addition to conventional therapy in improving trunk mobility, function, ambulation and quality of life in stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2022;14(1):62. [28] 刘建华, 魏清川, 胡秀茹, 等. 躯干控制训练联合肌内效贴对卒中后偏瘫患者躯干及平衡功能的临床疗效[J].中国康复,2020,35(11): 582-586. [29] SANTOS LTD, MATOS GSR, NOGUEIRA PC, et al. Effect of transcutaneous abdominal electrical stimulation in people with constipation due to spinal cord injuries: a pilot study. Rev Esc Enferm USP. 2022;56(spe): e20210449. [30] LIN S, WANG D, SANG H, et al. Predicting poststroke dyskinesia with resting-state functional connectivity in the motor network. Neurophotonics. 2023;10(2):025001. [31] YAMASHITA H, YAMAOKA T, SHIMOMURA R, et al. Therapeutic Intervention for Trunk Control Impairments in Central Nervous System Disorders: A Comprehensive Review of Methods and Efficacy. Prog Rehabil Med. 2025;10:20250002. [32] LI Z, GUO J, GE R, et al. Rehabilitation effect of core muscle training combined with functional electrical stimulation on lower limb motor and balance functions in stroke patients. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2024;37(2):347-354. [33] YOO HJ, PARK S, OH S, et al. Effects of electrical muscle stimulation on core muscle activation and physical performance in non-athletic adults: A randomized controlled trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(4): e32765. [34] HWANG UJ, KWON OY, JUNG SH, et al. Effect of neuromuscular electrical stimulation training for abdominal muscles on change of muscle size, strength, endurance and lumbopelvic stability. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2020;60(2):206-213. [35] KIM Y, KIM J, NAM H, et al. Ultrasound Imaging of the Trunk Muscles in Acute Stroke Patients and Relations With Balance Scales. Ann Rehabil Med. 2020;44(4):273-283. [36] BAYRAKTAR HEN, YALÇIN E, ŞIPAL MS, et al. The effect of electromyography triggered electrical stimulation to abdominal muscles on sitting balance, respiratory functions, and abdominal muscle thickness in complete spinal cord injury: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Rehabil Res. 2024;47(2):87-96. [37] 高丽萍, 邹恩苗, 屠文展. 超声联合肌电图检查在妊娠相关下腰痛康复评价中的应用[J]. 中国妇幼保健,2024,39(6):1146-1150. [38] LEE K, CHO JE, HWANG DY, et al. Decreased Respiratory Muscle Function Is Associated with Impaired Trunk Balance among Chronic Stroke Patients: A Cross-sectional Study. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2018; 245(2):79-88. [39] VILARDELL N, ROFES L, NASCIMENTO WV, et al. Cough reflex attenuation and swallowing dysfunction in sub-acute post-stroke patients: prevalence, risk factors, and clinical outcome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017;29(1). doi: 10.1111/nmo.12910. [40] 杜飞, 张龙举, 张李, 等. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者咳嗽相关生活质量与腹肌耐力、疲劳及抑郁的关系[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2019, 39(12):2904-2906. [41] SCHREIBER AF, BERTONI M, COIFFARD B, et al. Abdominal Muscle Use During Spontaneous Breathing and Cough in Patients Who Are Mechanically Ventilated: A Bi-center Ultrasound Study. Chest. 2021; 160(4):1316-1325. [42] 陈倩, 顾丽华, 沈梅芬, 等. 拔管前腹内压变化值对机械通气患者拔管失败的预测价值[J].中国急救医学,2021,41(11):938-942. [43] BRENNAN M, MCDONNELL MJ, DUIGNAN N, et al. The use of cough peak flow in the assessment of respiratory function in clinical practice- A narrative literature review. Respir Med. 2022;193: 106740. [44] NORISUE Y, KATAOKA J, HOMMA Y, et al. Increase in intra-abdominal pressure during airway suctioning-induced cough after a successful spontaneous breathing trial is associated with extubation outcome. Ann Intensive Care. 2018;8(1):61. [45] MURATA K, SHIMOYAMA K, TSURUYA T. Investigating the risk of reintubation by cough force assessment using cough peak expiratory flow: a single-center observational pilot study. BMC Pulm Med. 2024; 24(1):222. [46] PARK HY, HWANG UJ, KWON OY. Correlation between trunk rotation and lateral flexion range of motion, peak cough flow, and chest expansion in stroke patients. Physiother Res Int. 2023;28(1): e1970. [47] TERZI N, VAUGIER I, GUÉRIN C, et al. Comparison of Four Mechanical Insufflation-Exsufflation Devices: Effect of Simulated Airway Collapse on Cough Peak Flow. Respir Care. 2023;68(4):462-469. [48] JOPPIN V, JOURDAN A, BENDAHAN D, et al. Towards a better understanding of abdominal wall biomechanics: In vivo relationship between dynamic intra-abdominal pressure and magnetic resonance imaging measurements. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2025;121: 106396. [49] 胡正永, 马明, 杨玺, 等. 腹部电刺激联合高频胸壁振荡对气管切开重症患者气道廓清能力的效果[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2022, 28(2):232-241. [50] NADEEM I, BUTT SK, MUBEEN I, et al. Effects of core muscles strengthening exercises with routine physical therapy on trunk balance in stroke patients: A randomized controlled trial. J Pak Med Assoc. 2024;74(5):848-851. [51] 蔡锐, 白定群, 彭晓华. 咳嗽功能与脑卒中相关性肺炎发生风险的研究进展[J]. 现代医药卫生,2020,36(1):56-59. |
| [1] | Li Zhifei, Han Bin, Liu Qiuli, Zhang Zhanming, Wei Haokai, Zuo Kuangshi, Zhang Yisheng. Cervical motion characteristics in patients with cervical spondylotic radiculopathy based on motion capture technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2286-2293. |
| [2] | Wang Zheng, Cheng Ji, Yu Jinlong, Liu Wenhong, Wang Zhaohong, Zhou Luxing. Progress and future perspectives on the application of hydrogel materials in stroke therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2081-2090. |
| [3] | Gao Feng, Zhang Jun, Yu Wenjun, Chanyu Yujing, Zhao Le, Hu Yuting, Wang Junhua, Liu Yongfu. Effects of wrist-hand orthosis on hand dysfunction in stroke patients: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2124-2131. |
| [4] | Tao Daiju, Su Haiyu, Wang Yuqi, Shen Zhiqiang, He Bo . Construction and identification of stable PC12 cell lines with high/low expression of miR-122-5p [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1790-1799. |
| [5] | Wang Jie, Huang Rui, Zhang Ye, Shou Zhaoxi, Yao Jie, Liu Chenxi, Liao Jian. Role and mechanism of probiotics in peri-implantitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 901-907. |
| [6] | Jin Zhiyong, Wang Yufeng, Zhao Binjie, Xiong Minquan, Yan Li. Effects of inter-limb asymmetry on athletic performance from the perspective of bilateral limb control strategy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 949-963. |
| [7] | Yang Yuanyuan, Zhou Shanshan, Cheng Xiaofei, Feng Luye, Tang Jiqin. Network meta-analysis of non-invasive brain stimulation in the treatment of lower limb motor dysfunction after stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1008-1018. |
| [8] | Zhou Feng, Fu Pengfei, Qian Yufan, Xu Pingcheng, Guo Jiongjiong, Zhang Lei. Correlation between spinal sagittal imbalance and knee joint parameters detected by whole-body EOS imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 596-603. |
| [9] | Zhou Xinying, Sun Xinyue, Zhu Wenhao. Insulin-like growth factors and ischemic stroke: a genome-wide association analysis in European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2909-2919. |
| [10] |
Zhang Yueting, Li Jinglin, Fu Zhenyi, Yan Fei, Gao Yu, Liu Jiaxin.
Endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes ferroptosis and aggravates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2806-2813.
|
| [11] | Wang Degang, , Chen Guohua, , Mei Junhua, Wang Junli, Zheng Li. Effects of nocturnal sleep duration on new-onset cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in middle-aged and elderly patients with chronic comorbidities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2814-2822. |
| [12] | Li Tingwen, , Zhang Jianhua. Meta-analysis of the effects of aquatic exercise on balance function and motor ability in elderly patients with Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2560-2568. |
| [13] | Hu Xin, Wan Haili, Du Liang, Li Yongjie, Xia Yuan. Theta-stimulation for the treatment of motor function and daily activity ability in the lower extremities of stroke patients: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2576-2583. |
| [14] | Tian Meng, Lou Tianwei, Zhang Yongchen, Jia Hongling . Cathepsin F as a potential serum biomarker for stroke risk prediction: GWAS database data analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2662-2670. |
| [15] | Wang Zheng, Cheng Ji, Yu Jinlong, Liu Wenhong, Wang Zhaohong, Zhou Luxing. Progress and future perspectives on the application of hydrogel materials in stroke therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-10. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||