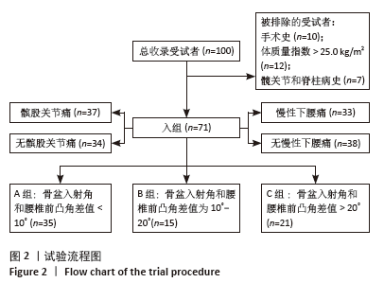
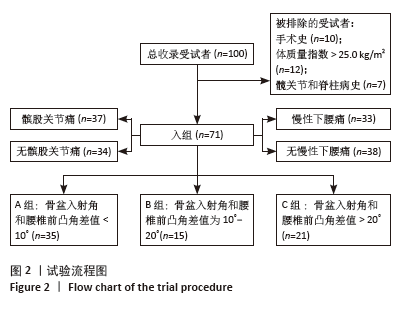
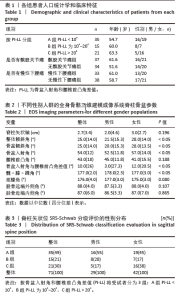
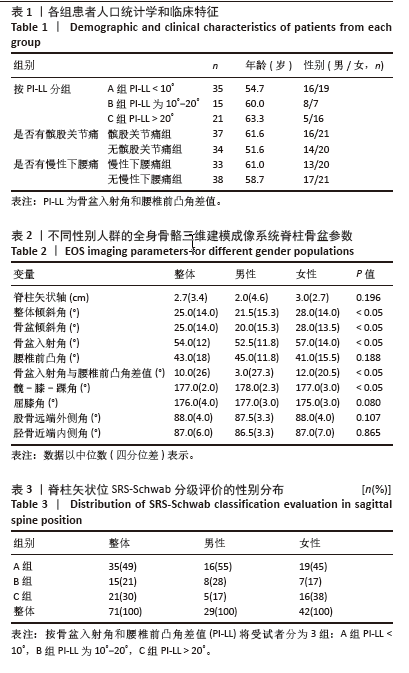
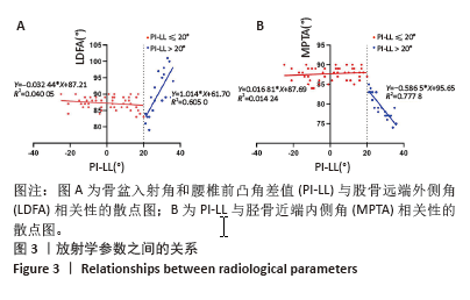
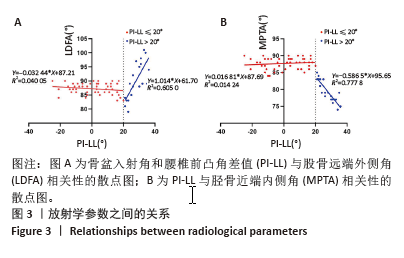
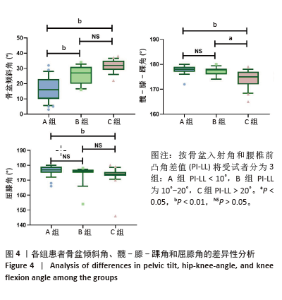
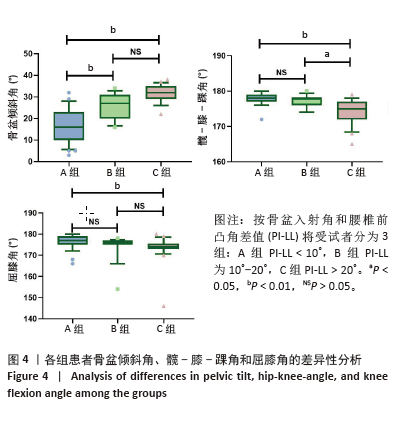
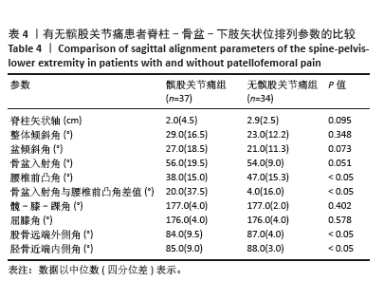
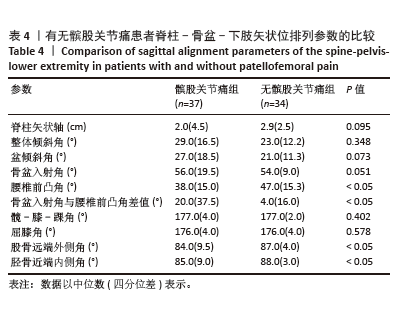
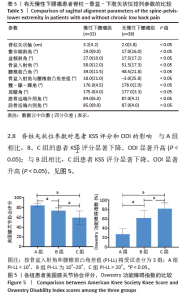
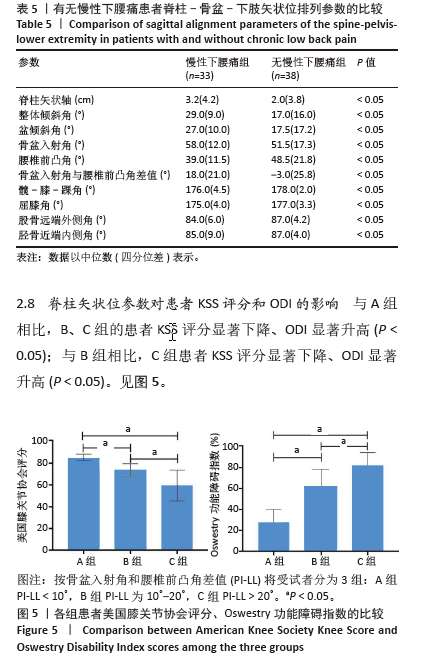
[1] HASEGAWA K, OKAMOTO M, HATSUSHIKANO S, et al. Standing sagittal alignment of the whole axial skeleton with reference to the gravity line in humans. J Anat. 2017;230(5):619-630.
[2] LE HUEC JC, SADDIKI R, FRANKE J, et al. Equilibrium of the human body and the gravity line: the basics. Eur Spine J. 2011;20 Suppl 5(Suppl 5): 558-563.
[3] IYER S, SHEHA E, FU MC, et al. Sagittal Spinal Alignment in Adult Spinal Deformity: An Overview of Current Concepts and a Critical Analysis Review. JBJS Rev. 2018;6(5):e2.
[4] GLASSMAN SD, BRIDWELL K, DIMAR JR, et al. The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(18):2024-2029.
[5] ITOI E. Roentgenographic analysis of posture in spinal osteoporotics. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991;16(7):750-756.
[6] CHA E, PARK JH. Spinopelvic Alignment as a Risk Factor for Poor Balance Function in Low Back Pain Patients. Global Spine J. 2023;13(8): 2193-2200.
[7] JANG HJ, PARK JY, KUH SU, et al. Comparison of Whole Spine Sagittal Alignment in Patients with Spinal Disease between EOS Imaging System versus Conventional Whole Spine X-ray. Yonsei Med J. 2022;63(11): 1027-1034.
[8] The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP publication 103. Ann ICRP. 2007;37(2-4): 1-332.
[9] BRENNER DJ. Estimating cancer risks from pediatric CT: going from the qualitative to the quantitative. Pediatr Radiol. 2002;32(4):228-221; discussion 242-224.
[10] PEETERS CMM, BOS G, KEMPEN DHR, et al. Assessment of spine length in scoliosis patients using EOS imaging: a validity and reliability study. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(12):3527-3535.
[11] MELHEM E, ASSI A, EL RACHKIDI R, et al. EOS(®) biplanar X-ray imaging: concept, developments, benefits, and limitations. J Child Orthop. 2016; 10(1):1-14.
[12] ILLES T, SOMOSKEOY S. The EOS imaging system and its uses in daily orthopaedic practice. Int Orthop. 2012;36(7):1325-1331.
[13] DESCHêNES S, CHARRON G, BEAUDOIN G, et al. Diagnostic imaging of spinal deformities: reducing patients radiation dose with a new slot-scanning X-ray imager. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(9):989-994.
[14] SMITH JA, STABBERT H, BAGWELL JJ, et al. Do people with low back pain walk differently? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sport Health Sci. 2022;11(4):450-465.
[15] HARAGUCHI N. Analysis of Whole Limb Alignment in Ankle Arthritis. Foot Ankle Clin. 2022;27(1):1-12.
[16] CHANG JS, KWON YH, KIM CS, et al. Differences of ground reaction forces and kinematics of lower extremity according to landing height between flat and normal feet. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2012;25(1):21-26.
[17] CROSS M, SMITH E, HOY D, et al. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(7):1323-1330.
[18] TAUCHI R, IMAGAMA S, MURAMOTO A, et al. Influence of spinal imbalance on knee osteoarthritis in community-living elderly adults. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2015;77(3):329-337.
[19] LEE CS, PARK SJ, CHUNG SS, et al. The effect of simulated knee flexion on sagittal spinal alignment: novel interpretation of spinopelvic alignment. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(5):1059-1065.
[20] BARREY C, ROUSSOULY P, PERRIN G, et al. Sagittal balance disorders in severe degenerative spine. Can we identify the compensatory mechanisms? Eur Spine J. 2011;20 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):626-633.
[21] OBEID I, HAUGER O, AUNOBLE S, et al. Global analysis of sagittal spinal alignment in major deformities: correlation between lack of lumbar lordosis and flexion of the knee. Eur Spine J. 2011;20 Suppl 5(Suppl 5): 681-685.
[22] MURATA Y, TAKAHASHI K, YAMAGATA M, et al. The knee-spine syndrome. Association between lumbar lordosis and extension of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85(1):95-99.
[23] WANG WJ, LIU F, ZHU YW, et al. Sagittal alignment of the spine-pelvis-lower extremity axis in patients with severe knee osteoarthritis: A radiographic study. Bone Joint Res. 2016;5(5):198-205.
[24] TSUJI T, MATSUYAMA Y, GOTO M, et al. Knee-spine syndrome: correlation between sacral inclination and patellofemoral joint pain. J Orthop Sci. 2002;7(5):519-523.
[25] CHALéAT-VALAYER E, MAC-THIONG JM, PAQUET J, et al. Sagittal spino-pelvic alignment in chronic low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2011;20 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):634-640.
[26] ROUSSOULY P, PINHEIRO-FRANCO JL. Biomechanical analysis of the spino-pelvic organization and adaptation in pathology. Eur Spine J. 2011;20 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):609-618.
[27] JACKSON RP, MCMANUS AC. Radiographic analysis of sagittal plane alignment and balance in standing volunteers and patients with low back pain matched for age, sex, and size. A prospective controlled clinical study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(14): 1611-1618.
[28] SMITH JS, KLINEBERG E, SCHWAB F, et al. Change in classification grade by the SRS-Schwab Adult Spinal Deformity Classification predicts impact on health-related quality of life measures: prospective analysis of operative and nonoperative treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38(19):1663-1671.
[29] SCHWAB F, UNGAR B, BLONDEL B, et al. Scoliosis Research Society-Schwab adult spinal deformity classification: a validation study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(12):1077-1082.
[30] KITAGAWA A, YAMAMOTO J, TODA M, et al. Spinopelvic Alignment and Low Back Pain before and after Total Knee Arthroplasty. Asian Spine J. 2021;15(1):9-16.
[31] HIYAMA A, KATOH H, SAKAI D, et al. Effects of preoperative sagittal spinal imbalance on pain after lateral lumbar interbody fusion. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):3001.
[32] ARAB AM, TALIMKHANI A, KARIMI N, et al. Change in lumbar lordosis during prone lying knee flexion test in subjects with and without low back pain. Chiropr Man Therap. 2015;23:18.
[33] LERCH TD, BOSCHUNG A, SCHMARANZER F, et al. Lower pelvic tilt, lower pelvic incidence, and increased external rotation of the iliac wing in patients with femoroacetabular impingement due to acetabular retroversion compared to hip dysplasia. Bone Jt Open. 2021;2(10): 813-824.
[34] FERRERO E, LIABAUD B, CHALLIER V, et al. Role of pelvic translation and lower-extremity compensation to maintain gravity line position in spinal deformity. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24(3):436-446.
[35] ERGüN T, LAKADAMYALı H, SAHIN MS. The relation between sagittal morphology of the lumbosacral spine and the degree of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2010; 44(4):293-299.
[36] GELB DE, LENKE LG, BRIDWELL KH, et al. An analysis of sagittal spinal alignment in 100 asymptomatic middle and older aged volunteers. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995;20(12):1351-1358.
[37] KEOROCHANA G, TAGHAVI CE, LEE KB, et al. Effect of sagittal alignment on kinematic changes and degree of disc degeneration in the lumbar spine: an analysis using positional MRI. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36(11):893-898.
[38] AMES C, GAMMAL I, MATSUMOTO M, et al. Geographic and Ethnic Variations in Radiographic Disability Thresholds: Analysis of North American and Japanese Operative Adult Spinal Deformity Populations. Neurosurgery. 2016;78(6):793-801.
[39] DIEBO BG, SHAH NV, BOACHIE-ADJEI O, et al. Adult spinal deformity. Lancet. 2019;394(10193):160-172.
[40] BREKKE AF, HOLSGAARD-LARSEN A, TORFING T, et al. Increased anterior pelvic tilt in patients with acetabular retroversion compared to the general population: A radiographic and prevalence study. Radiography (Lond). 2022;28(2):400-406. |