Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (36): 7909-7920.doi: 10.12307/2025.523
Machine learning-based analysis of neutrophil-associated potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction
Yang Dingyan1, Yu Zhenqiu1, Yang Zhongyu2
- 1Department of Hypertension, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637100, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-17Accepted:2024-06-01Online:2025-12-28Published:2025-03-25 -
Contact:Yu Zhenqiu, Chief physician, Department of Hypertension, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Yang Dingyan, Master candidate, Department of Hypertension, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Fund Project of Guizhou Provincial Health Commission, No. gzwkjz2023-100 (to YZQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Dingyan, Yu Zhenqiu, Yang Zhongyu. Machine learning-based analysis of neutrophil-associated potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7909-7920.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
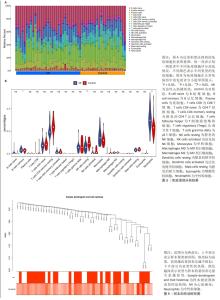
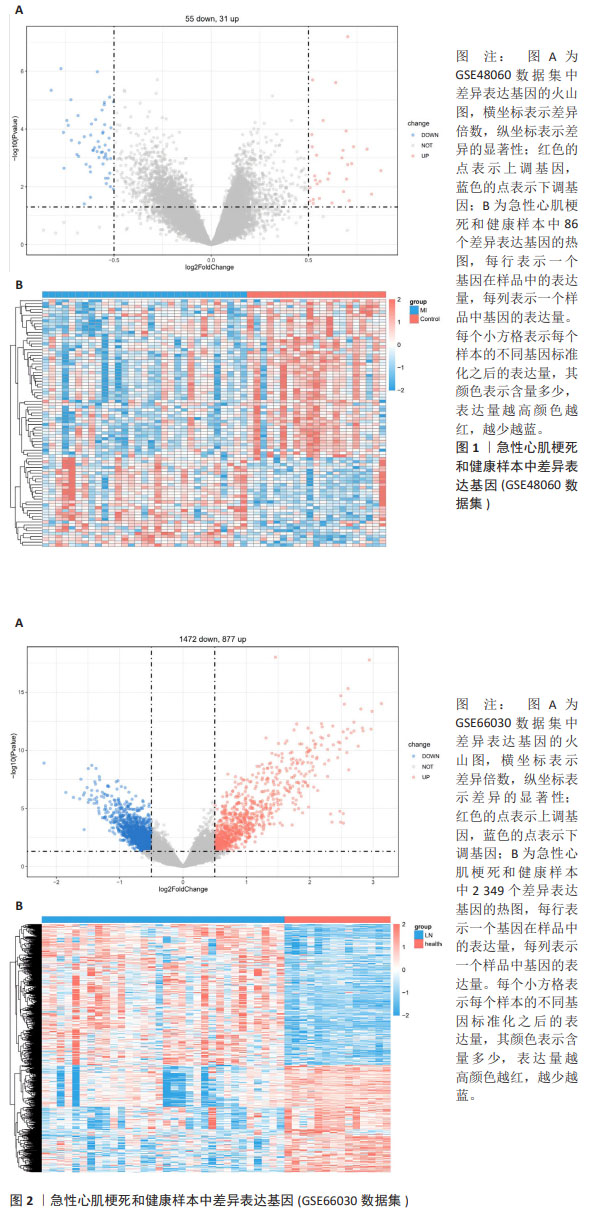
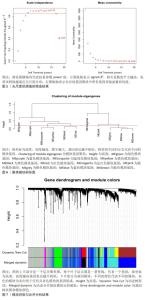
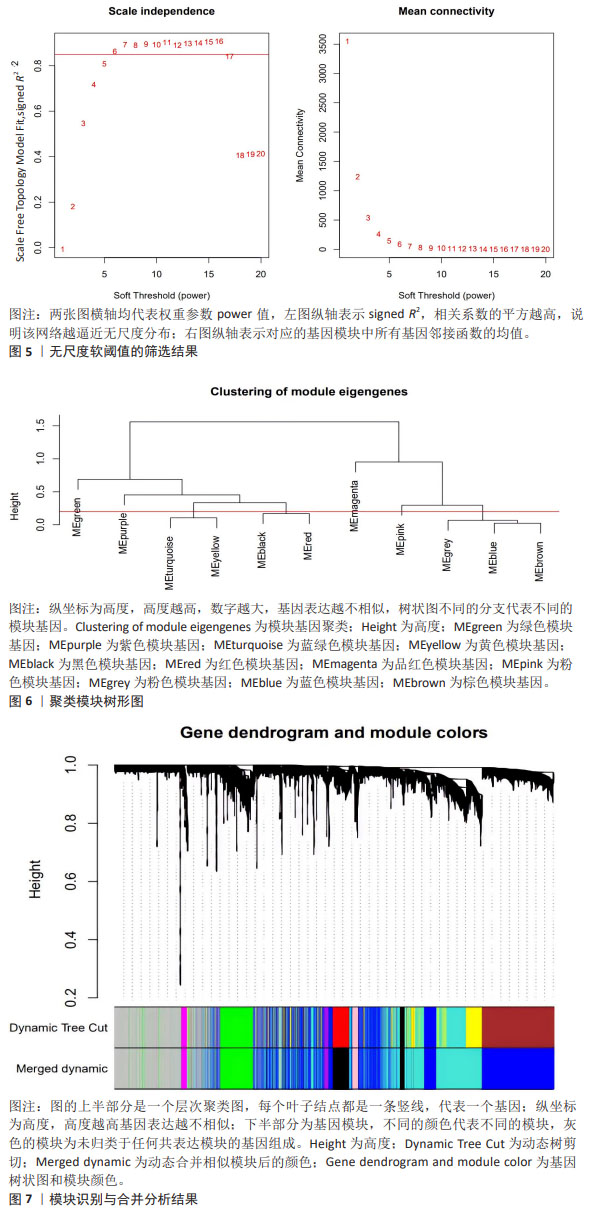
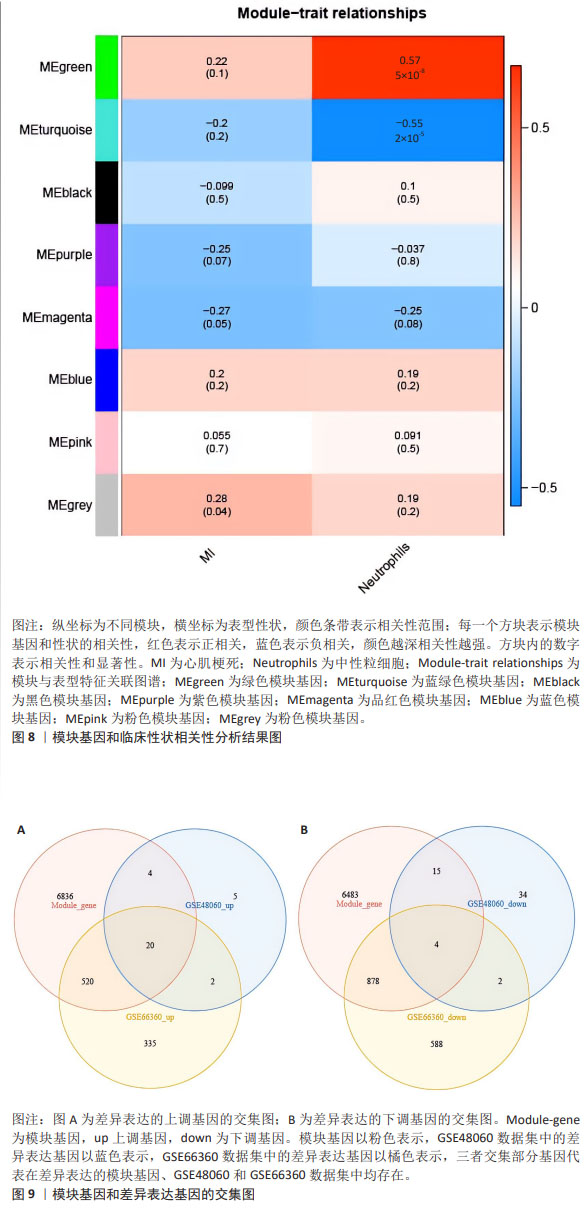
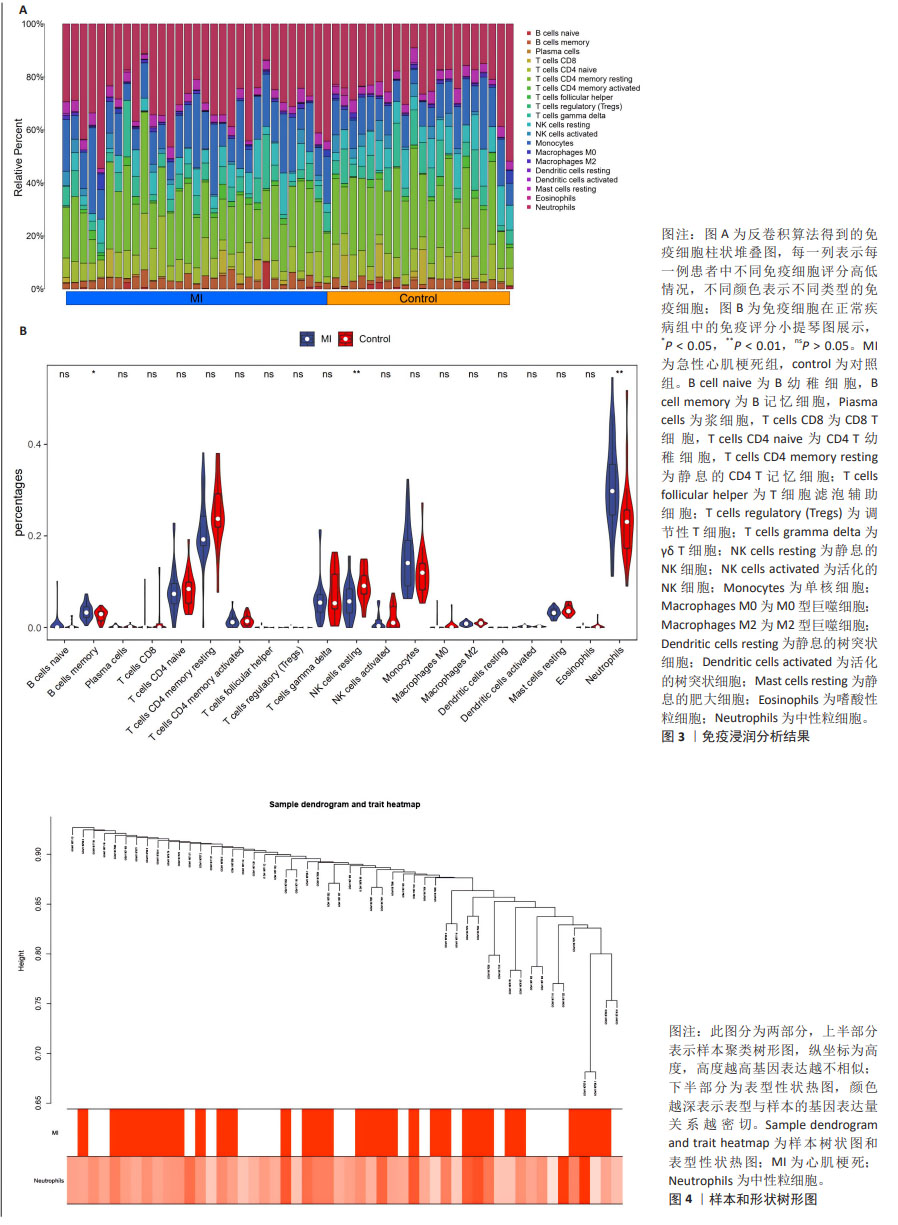
2.2 免疫浸润分析结果 图3A显示了每个样本中20种免疫细胞的丰度,M1型巨噬细胞和活化的肥大细胞丰度为0,故剔除。小提琴图表明记忆B细胞、静息的自然杀伤细胞和中性粒细胞的表达在急性心肌梗死组和对照组中存在显著差异,与对照组相比,中性粒细胞百分率显著升高,见图3B。 2.3 WGCNA分析结果 文章对GSE48060的样本进行聚类,在去除异常值后,绘制了一个样本聚类树,见图4。文章将软阈值设为6(R2=0.85)用以构建无标度网络,见图5。聚集了11个模块,见图6,模块过多,将相似性大的模块合并后共有7个模块,见图7。计算并绘制每个模块与急性心肌梗死和中性粒细胞之间的相关性,见图8。结果表明,ME green和ME turquoise与急性心肌梗死和中性粒细胞相关性最高(P < 0.05),被认为是关键模块进行后续分析。 "
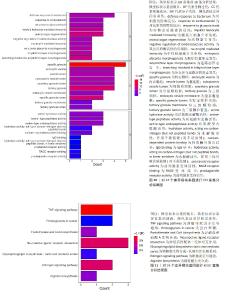
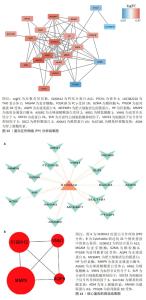
2.4 差异模块基因筛选及功能富集分析结果 2.4.1 差异模块基因筛选结果 使用Ven图展示GSE48060数据集、GSE66360数据集差异基因与模块基因的交集,结果显示上调组存在20个交集基因,下调组存在4个交集基因,见图9,将这24个基因作为后续分析的潜在基因。 2.4.2 模块差异基因功能富集分析结果 分别对24个差异模块基因进行基于KEGG和GO的富集分析,文章以P.adjust < 0.05 的条件对富集到的通路进行筛选,最终结果显示24个mRNA共富集到355个GO条目,如图10展示,Top前30条的条目,包括生物学过程、细胞组分和分子功能。生物学过程主要富集于炎症反应、对细菌的防御反应、中性粒细胞介导的免疫反应等方面;细胞组分主要富集于内吞囊泡膜、三级颗粒及特定颗粒流明等方面;分子功能富集于丝氨酸水解酶活性、丝氨酸型肽酶活性、RAGE受体结合等方面。KEGG富集结果显示富集到7条KEGG通路,如图11所示,肿瘤坏死因子信号通路、神经活性配体-受体相互作用及雌激素信号通路显著富集。 "

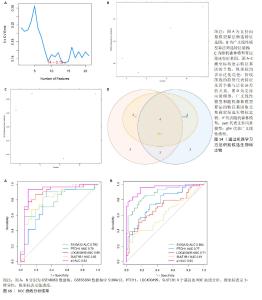
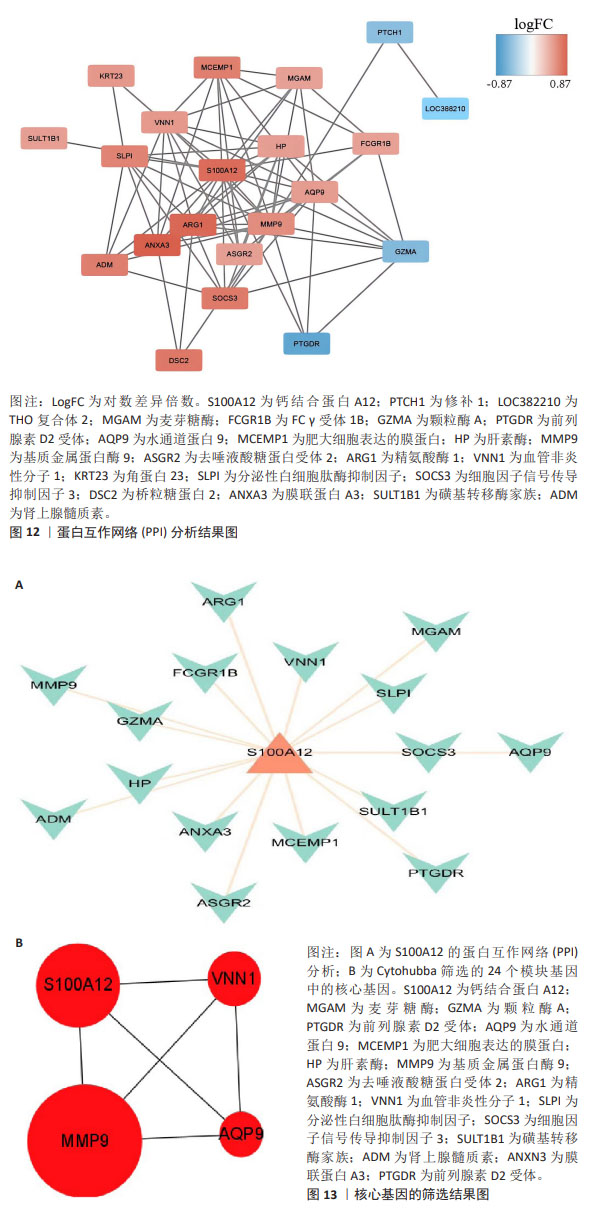
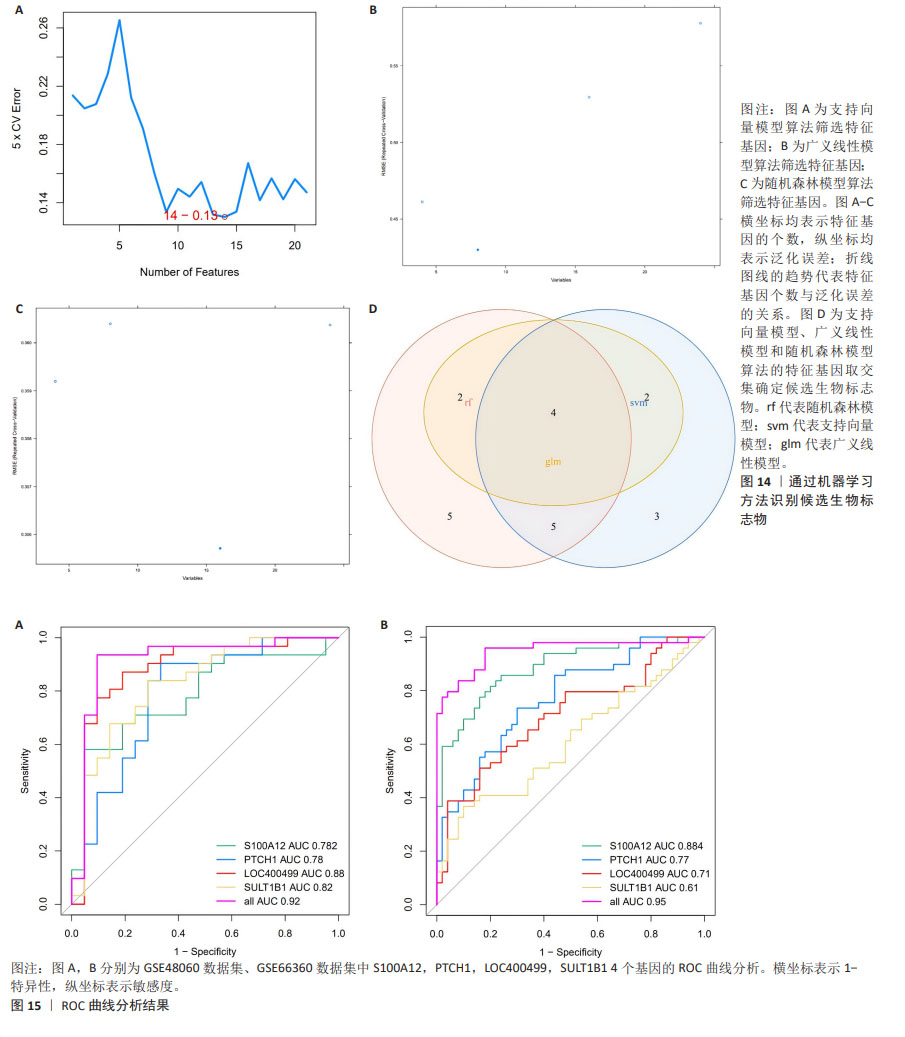
2.5 机器学习构建诊断模型 2.5.1 机器学习 如图14A-C所示,使用支持向量模型算法得到14个特征基因,分别为S100A12,PTCH1,DSC2,ADM,MGAM,LOC400499,HP,ANXA3,MMP9,SOCS3,SLPI,MCEMP1,SULT1B1,TDRD9,使用广义线性模型算法得到8个特征基因,分别为PTCH1,MGAM,SULT1B1,LOC400499,S100A12,GZMA,HP和SOCS3,使用随机森林模型算法得到16个特征基因,分别为LOC400499,ASGR2,PTCH1,PTGDR,ANXA3,SULT1B1,SOCS3,ARG1,GZMA,SLPI,FCGR1B,MCEMP1,DSC2,S100A12,B3GNT5和A2M_AS1。 2.5.2 特征基因取交集 将支持向量模型算法得到14个特征基因,广义线性模型算法得到8个特征基因,随机森林模型算法得到16个特征基因进行取交集后,得到的4个基因为在3种机器学习算法中同时存在的基因分别为S100A12,PTCH1,LOC400499和SULT1B1,见图14D,将其定为候选的生物标志物。 2.5.3 ROC 曲线验证关键核心基因的诊断能力 在GES48060数据集中分析急性心肌梗死和对照样本之间与中性粒细胞相关的候选标志物的表达,并构建ROC曲线。图15A中所有基因的AUC值都大于0.78,4个基因构建模型的AUC值为0.92,说明这4个基因对于区分疾病和对照样本具有一定的准确性。 2.5.4 模型基因ROC外部验证结果 在GSE66360数据集同样绘制4个基因的ROC曲线,结果见图15B,结果显示4个基因中S100A12,PTCH1和LOC400499基因的AUC值均大于0.7,综合模型的AUC值为0.95,说明S100A12,PTCH1和LOC400499这3个基因效果较为可靠,将这3个基因视为急性心肌梗死的潜在诊断生物标志物。"
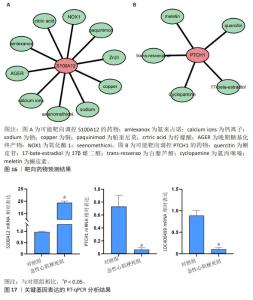
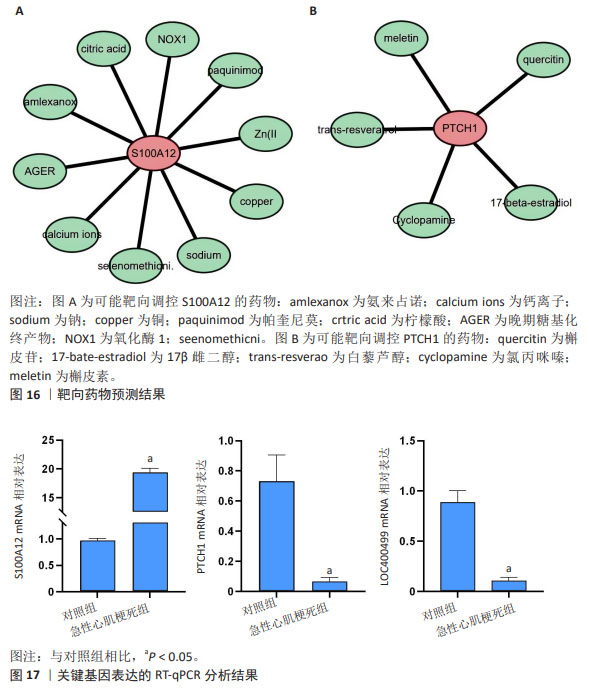
2.6 药物预测结果 S100A12基因输入STITCH数据库(http://stitch.embl.de/)后获得对应的药物靶点信息有10种,PTCH1 基因在STITCH数据库结果得到1个药物。随后将PTCH1基因输入到herb数据库(http://herb.ac.cn/)中得到5个药物,S100A12基因在herb 数据库结果得到1个药物。使用Cytoscape软件进行靶点-药物网络构建,如图16所示,Paquinimod,Amlexanox,quercitin及17-bate-estradiol等可能具有治疗急性心肌梗死的作用。 2.7 RT-qPCR验证关键基因表达结果 共收集了5例急性心肌梗死患者和5例对照组的外周血浆,为了验证数据集的可靠性,采用RT-qPCR来验证临床样本中上述3个基因的表达水平。结果显示,与正常对照组相比,急性心肌梗死患者中S100A12的表达上调(P < 0.05),见图17,PTCH1和LOC400499表达显著下调(P < 0.05),见图17。"
| [1] MEHTA LS, BECKIE TM, DEVON HA, et al. Acute myocardial infarction in women: a scientific statement from the american heart association. Circulation. 2016;133(9):916-947. [2] PAGIDIPATI NJ, GAZIANO TA. Estimating deaths from cardiovascular disease: a review of global methodologies of mortality measurement. Circulation. 2013; 127(6):749-756. [3] ALAOUR B, LIEW F, KAIER TE. Cardiac Troponin -diagnostic problems and impact on cardiovascular disease. Ann Med. 2018; 50(8):655-665. [4] THYGESEN K, ALPERT JS, JAFFE AS, et al. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). Circulation. 2018;138(20):e618-e651. [5] CLERICO A, ZANINOTTO M, PLEBANI M. Rapid rule-in and rule-out protocols of acute myocardial infarction using hs-cTnI and hs-cTnT methods. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2024;62(2):213-217. [6] PRABHU SD, FRANGOGIANNIS NG. The biological basis for cardiac repair after myocardial infarction: from inflammation to fibrosis. Circ Res. 2016;119(1):91-112. [7] EL KM, SHI H, VUONG S, et al. Nitroxides mitigate neutrophil-mediated damage to the myocardium after experimental myocardial infarction in rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7650. [8] DELEON-PENNELL KY, TIAN Y, ZHANG B, et al. CD36 Is a Matrix metalloproteinase-9 substrate that stimulates neutrophil apoptosis and removal during cardiac remodeling. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2016; 9(1):14-25. [9] HORCKMANS M, RING L, DUCHENE J, et al. Neutrophils orchestrate post-myocardial infarction healing by polarizing macrophages towards a reparative phenotype. Eur Heart J. 2017;38(3):187-197. [10] CURAJ A, SCHUMACHER D, RUSU M, et al. Neutrophils modulate fibroblast function and promote healing and scar formation after murine myocardial infarction. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):3685. [11] SREEJIT G, ABDEL-LATIF A, ATHMANATHAN B, et al. Neutrophil-derived s100a8/a9 amplify granulopoiesis after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2020;141(13): 1080-1094. [12] CHRISTIA P, BUJAK M, GONZALEZ-QUESADA C, et al. Systematic characterization of myocardial inflammation, repair, and remodeling in a mouse model of reperfused myocardial infarction. J Histochem Cytochem. 2013;61(8):555-570. [13] SWIRSKI FK, NAHRENDORF M. Leukocyte behavior in atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and heart failure. Science. 2013;339(6116):161-166. [14] KOLOGRIVOVA I, SHTATOLKINA M, SUSLOVA T, et al. Cells of the immune system in cardiac remodeling: main players in resolution of inflammation and repair after myocardial infarction. Front Immunol. 2021;12:664457. [15] ZHOU X, ZHANG C, WU X, et al. Dusp6 deficiency attenuates neutrophil-mediated cardiac damage in the acute inflammatory phase of myocardial infarction. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):6672. [16] RIDKER PM, MACFADYEN JG, GLYNN RJ, et al. Inhibition of interleukin-1beta by canakinumab and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71(21):2405-2414. [17] ZHENG PF, ZOU QC, CHEN LZ, et al. Identifying patterns of immune related cells and genes in the peripheral blood of acute myocardial infarction patients using a small cohort. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):321. [18] TORUN FM, VIRREIRA WS, DOLL S, et al. Transparent exploration of machine learning for biomarker discovery from proteomics and omics data. J Proteome Res. 2023;22(2):359-367. [19] MIAO M, CAO S, TIAN Y, et al. Potential diagnostic biomarkers: 6 cuproptosis- and ferroptosis-related genes linking immune infiltration in acute myocardial infarction. Genes Immun. 2023;24(4):159-170. [20] ALGOET M, JANSSENS S, HIMMELREICH U, et al. Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and the influence of inflammation. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2023;33(6):357-366. [21] CARVALHO A, LU J, FRANCIS JD, et al. S100A12 in digestive diseases and health: a scoping review. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2020;2020:2868373. [22] ZHAI H, HUANG L, GONG Y, et al. Human plasma transcriptome implicates dysregulated s100a12 expression: a strong, early-stage prognostic factor in st-segment elevated myocardial infarction: bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:874436. [23] ZHANG X, CHENG M, GAO N, et al. Utility of S100A12 as an early biomarker in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:747511. [24] ELLSWORTH DL, CROFT DJ, WEYANDT J, et al. Intensive cardiovascular risk reduction induces sustainable changes in expression of genes and pathways important to vascular function. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2014;7(2):151-160. [25] LI Q, DENG G, GAO Y. S100 calcium-binding protein A12 knockdown ameliorates hypoxia-reoxygenation-induced inflammation and apoptosis in human cardiomyocytes by regulating caspase-4-mediated non-classical pyroptosis. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2022;41(4):287-297. [26] HASANOVIC A, MUS-VETEAU I. Targeting the multidrug transporter ptch1 potentiates chemotherapy efficiency. Cells. 2018;7(8): 107. [27] DOHENY D, MANORE SG, WONG GL, et al. Hedgehog signaling and truncated GLI1 in cancer. Cells. 2020;9(9):2114. [28] POLA R, LING LE, SILVER M, et al. The morphogen Sonic hedgehog is an indirect angiogenic agent upregulating two families of angiogenic growth factors. Nat Med. 2001;7(6):706-711. [29] LI SH, ZHANG YY, SUN YL, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-802-5p inhibits myocardial apoptosis after myocardial infarction via Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway by targeting PTCH1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(1):326-334. [30] LAVINE KJ, KOVACS A, ORNITZ DM. Hedgehog signaling is critical for maintenance of the adult coronary vasculature in mice. J Clin Invest. 2008; 118(7):2404-2414. [31] YAN L, BJORK P, BUTUC R, et al. Beneficial effects of quinoline-3-carboxamide (ABR-215757) on atherosclerotic plaque morphology in S100A12 transgenic ApoE null mice. Atherosclerosis. 2013;228(1): 69-79. [32] ALBADRANI GM, BINMOWYNA MN, BIN-JUMAH MN, et al. Quercetin prevents myocardial infarction adverse remodeling in rats by attenuating TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling: different mechanisms of action. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021;28(5):2772-2782. [33] MO C, HAN H, TANG X, et al. Protein kinase TBK1/IKKepsilon inhibitor Amlexanox improves cardiac function after acute myocardial infarction in rats. Panminerva Med. 2023;65(3):343-350. |
| [1] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [2] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [3] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [4] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [5] | Wu Qingyun, Su Qiang. Antioxidant nanomedicine-mediated targeted therapy for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7431-7438. |
| [6] | Tian Yushi, Fu Qiang, Li Ji . Bioinformatics identification and validation of mitochondrial genes related to acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6697-6707. |
| [7] | Xie Yizi, Lin Xueying, Zhang Xinxin, Huang Xiufang, Zhan Shaofeng, Jiang Yong, Cai Yan. Biological mechanism of mitophagy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6708-6716. |
| [8] | Qiu Boyuan, Liu Fei, Tong Siwen, Ou Zhixue, Wang Weiwei. Bioinformatics identification and validation of aging key genes in hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5608-5620. |
| [9] | Hao Maochen, Ma Chao, Liu Kai, Liu Kexin, Meng Lingting, Wang Xingru, Wang Jianzhong. Bioinformatics screening of key genes for endoplasmic reticulum stress in osteoarthritis and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5632-5641. |
| [10] | Wang Lei, Wang Baiyan, Zhou Chunguang, Ren Xiaoyun, Dai Yueyou, Feng Shuying. Role of different cell-derived exosomal miRNAs in progression, diagnosis, and prognosis of gastric cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5434-5442. |
| [11] | Wang Zhifeng, Yang Jiao, Xi Yujiang, Xu Shuangfeng, Shi Ting, Lan Junfeng, Hao Zhihui, He Pengfen, Yang Aiming, Pan Pan, Wang Jian. Biomarkers affecting the progression of mild to moderate cognitive impairment after stroke: #br# a non-targeted metabolomics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5116-5126. |
| [12] | Wu Ao, Yu Peng, Teng Jiawen, Kong Peng, Bian Sishan. Analysis of oxidative stress-related genes and immune infiltration in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 302-311. |
| [13] | Zhu Kai, Liu Wanxin, Luo Haobing, Feng Shengyi, Wang Qiugen. Association between plasma proteins and osteoporosis and identification of potential therapeutic targets: information analysis based on the UK Biobank database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3948-3960. |
| [14] | Gu Xinbo, Liu Zemin, Sun Haiyu. Role of neutrophils in fracture healing and the promoting effect on healing after intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3235-3243. |
| [15] | Li Zhichao, Yang Zhenguo, Wang Lei, Wang Wenbo, Xue Jingcai, Liu Wenbin, Cao Hui. Role and clinical application progress of exosome-derived non-coding RNA in microenvironment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2784-2792. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||