Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (32): 6821-6827.doi: 10.12307/2026.525
Deferoxamine alleviates the inhibitory effect of glucocorticoids on osteogenic differentiation
Tang Haoxu1, 2, Liang Yingjie1, Li Ce1, Ding Penglin1, Qian Minlong1, Yuan Lingli1
- 1Department of Orthopaedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu 233002, Anhui Province, China; 2Anhui Province key Laboratory of Tissue Transplantation, Bengbu 233000, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2024-10-08Accepted:2024-12-12Online:2025-11-18Published:2025-04-25 -
Contact:Yuan Lingli, Master, Associate professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopaedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu 233002, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Tang Haoxu, Master candidate, Department of Orthopaedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu 233002, Anhui Province, China; Anhui Province key Laboratory of Tissue Transplantation, Bengbu 233000, Anhui Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Research Project of Higher Education Institutions in Anhui Province, No. KJ2021A0756 (to YLL); Bengbu Medical University 2023 Graduate Student Research and Innovation Program, No. Byycxz23046 (to THX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tang Haoxu, Liang Yingjie, Li Ce, Ding Penglin, Qian Minlong, Yuan Lingli. Deferoxamine alleviates the inhibitory effect of glucocorticoids on osteogenic differentiation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6821-6827.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
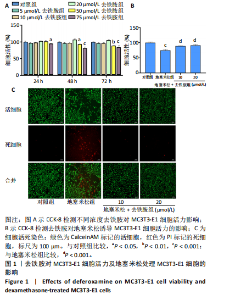
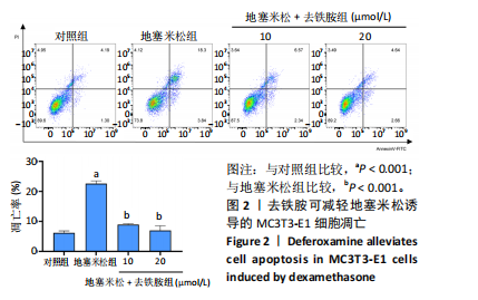
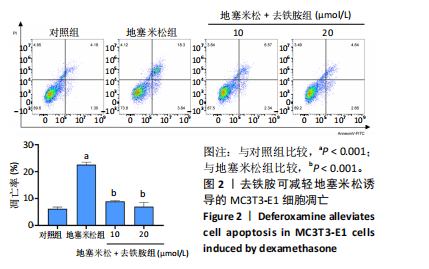
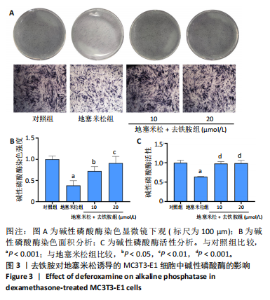
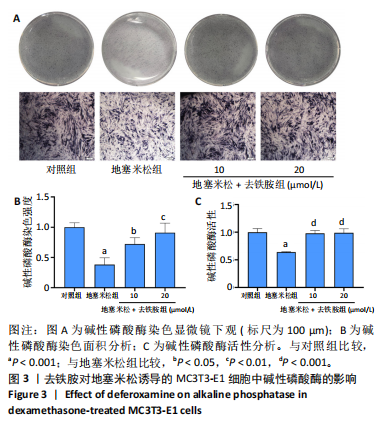
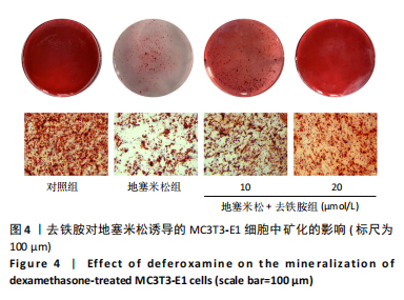
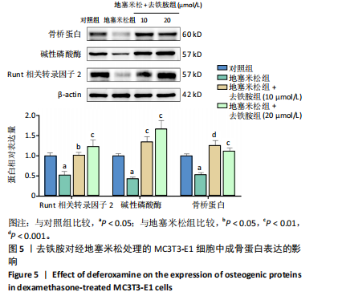
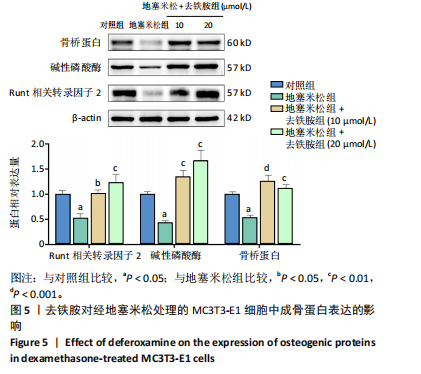
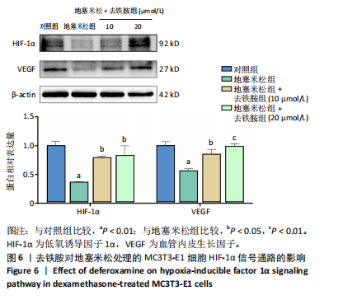
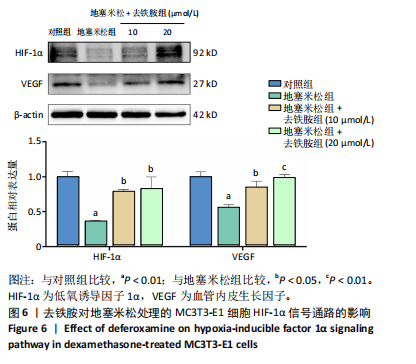
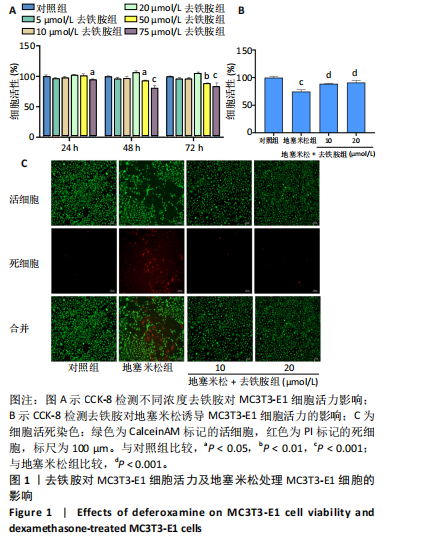
2.1 不同浓度去铁胺对MC3T3-E1成骨细胞活力的影响 为了研究去铁胺对细胞活力的影响,采用CCK-8法进行测定。在以5-75 μmol/L的递增剂量向MC3T3-E1细胞加入去铁胺干预24,48,72 h后,结果显示去铁胺浓度在5-20 μmol/L的范围内对细胞没有毒性作用(图1A)。因此,选择10 μmol/L和20 μmol/L浓度的去铁胺作为后续实验中的处理药物。 2.2 去铁胺改善地塞米松对MC3T3-E1成骨细胞增殖的抑制作用 采用CCK-8法观察去铁胺对地塞米松干预的MC3T3-E1成骨细胞增殖的影响。CCK-8检测结果显示,地塞米松与MC3T3-E1成骨细胞共孵育3 d后,细胞增殖明显受到抑制(P < 0.001),而联合应用去铁胺组(10 μmol/L和20 μmol/L)改善了地塞米松干预对MC3T3-E1成骨细胞的抑制作用(P < 0.001)(图1B)。 2.3 去铁胺增强地塞米松干预的MC3T3-E1细胞活性 采用CalceinAM/PI活死细胞双染法检测不同处理条件的MC3T3-E1细胞活性。其中绿色荧光细胞代表活细胞,红色荧光细胞代表死细胞,结果显示地塞米松干预MC3T3-E1细胞后出现大量的死细胞,而加入了去铁胺后死细胞的数量明显下降(图1C)。 2.4 去铁胺减轻地塞米松诱导的MC3T3-E1细胞凋亡 AnnexinV-FITC细胞凋亡检测结果提示,与对照组相比,地塞米松诱导的MC3T3-E1细胞发生凋亡的细胞数显著增多(P <"
| [1] XUE XH, FENG ZH, LI ZX, et al. Salidroside inhibits steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway: In vitro and in vivo studies. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(3):3751-3757. [2] QI B, LI C, CAI X, et al. Bioinformatics-Based Analysis of Key Genes in Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head That Are Associated with Copper Metabolism. Biomedicines. 2023;11(3):873. [3] CHANG C, GREENSPAN A, GERSHWIN ME. The pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical manifestations of steroid-induced osteonecrosis. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102460. [4] HUANG C, WEN Z, NIU J, et al. Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Novel Insight Into the Roles of Bone Endothelial Cells in Pathogenesis and Treatment. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:777697. [5] MOTTA F, TIMILSINA S, GERSHWIN ME, et al. Steroid-induced osteonecrosis. J Transl Autoimmun. 2022;5:100168. [6] WANG A, REN M, WANG J. The pathogenesis of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A systematic review of the literature. Gene. 2018;671:103-109. [7] WANG T, AZEDDINE B, MAH W, et al. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: genetic basis. Int Orthop. 2019;43(3):519-530. [8] ZHANG J, CAO J, LIU Y, et al. Advances in the Pathogenesis of Steroid-Associated Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Biomolecules. 2024;14(6):667. [9] HAN Y, YOU X, XING W, et al. Paracrine and endocrine actions of bone-the functions of secretory proteins from osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts. Bone Res. 2018;6:16. [10] SAWA N, FUJIMOTO H, SAWA Y, et al. Author Correction: Alternating Differentiation and Dedifferentiation between Mature Osteoblasts and Osteocytes. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):21788. [11] SUN F, ZHOU JL, LIU ZL, et al. Dexamethasone induces ferroptosis via P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;602:149-155. [12] ZHANG J, CAO J, LIU Y, et al. Advances in the Pathogenesis of Steroid-Associated Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Biomolecules. 2024;14(6):667. [13] MA Z, SUN J, JIANG Q, et al. Identification and analysis of mitochondria-related central genes in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head, along with drug prediction. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024;15:1341366. [14] YANG C, ZHONG ZF, WANG SP, et al. HIF-1: structure, biology and natural modulators. Chin J Nat Med. 2021;19(7):521-527. [15] MENG X, LIN Z, CAO S, et al. Estrogen-mediated downregulation of HIF-1α signaling in B lymphocytes influences postmenopausal bone loss. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):15. [16] LEE SY, KIM SJ, PARK KH, et al. Differential but complementary roles of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in the regulation of bone homeostasis. Commun Biol. 2024;7(1):892. [17] YI L, JU Y, HE Y, et al. Intraperitoneal injection of Desferal® alleviated the age-related bone loss and senescence of bone marrow stromal cells in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):45. [18] CHEN W, WU P, YU F, et al. HIF-1α Regulates Bone Homeostasis and Angiogenesis, Participating in the Occurrence of Bone Metabolic Diseases. Cells. 2022;11(22):3552. [19] GUO Q, YANG J, CHEN Y, et al. Salidroside improves angiogenesis-osteogenesis coupling by regulating the HIF-1α/VEGF signalling pathway in the bone environment. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;884:173394. [20] LIU Y, LIU J, CAI F, et al. Hypoxia During the Consolidation Phase of Distraction Osteogenesis Promotes Bone Regeneration. Front Physiol. 2022;13:804469. [21] GROSSO A, LUNGER A, BURGER MG, et al. VEGF dose controls the coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis in engineered bone. NPJ Regen Med. 2023; 8(1):15. [22] ZHA Y, LI Y, LIN T, et al. Progenitor cell-derived exosomes endowed with VEGF plasmids enhance osteogenic induction and vascular remodeling in large segmental bone defects. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):397-409. [23] LI B, LEI Y, HU Q, et al. Porous copper- and lithium-doped nano-hydroxyapatite composite scaffold promotes angiogenesis and bone regeneration in the repair of glucocorticoids-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Biomed Mater. 2021;16(6):10.1088/1748-605X/ac246e. [24] MA T, WANG Y, MA J, et al. Research progress in the pathogenesis of hormone-induced femoral head necrosis based on microvessels: a systematic review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):265. [25] ZHU Y, CHANG B, PANG Y, et al. Advances in Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Stabilizer Deferoxamine in Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2023;29(4):347-357. [26] YELLOWLEY CE, GENETOS DC. Hypoxia Signaling in the Skeleton: Implications for Bone Health. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2019;17(1):26-35. [27] CLINKENBEARD EL, HANUDEL MR, STAYROOK KR, et al. Erythropoietin stimulates murine and human fibroblast growth factor-23, revealing novel roles for bone and bone marrow. Haematologica. 2017;102(11):e427-e430. [28] ZHANG H, YANG F, CAO Z, et al. The influence of iron on bone metabolism disorders. Osteoporos Int. 2024;35(2):243-253. [29] CHENG W, DING Z, ZHENG X, et al. Injectable hydrogel systems with multiple biophysical and biochemical cues for bone regeneration. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(9): 2537-2548. [30] YAN Y, CHEN H, ZHANG H, et al. Vascularized 3D printed scaffolds for promoting bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2019;190-191:97-110. [31] YANG H, NIE S, ZHOU C, et al. Palliative effect of rotating magnetic field on glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats by regulating osteoblast differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024;725:150265. [32] LUO H, WEI J, WU S, et al. Elucidating the role of the GC/GR/GLUT1 axis in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A proteomic approach. Bone. 2024;183:117074. [33] REZUS E, TAMBA BI, BADESCU MC, et al. Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in Patients with Hypercoagulability-From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Implications. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(13):6801. [34] YOON BH, JONES LC, CHEN CH, et al. Etiologic Classification Criteria of ARCO on Femoral Head Osteonecrosis Part 1: Glucocorticoid-Associated Osteonecrosis.J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(1):163-168.e1. [35] HUANG C, QING L, XIAO Y, et al. Insight into Steroid-Induced ONFH: The Molecular Mechanism and Function of Epigenetic Modification in Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Biomolecules. 2023;14(1):4. [36] MALHOTRA R, GUPTA S, GUPTA V, et al. Risk Factors and Outcomes Associated with Intraoperative Fractures during Short-Stem Total Hip Arthroplasty for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Clin Orthop Surg. 2022;14(1):41-47. [37] MILADI M, VILLAIN B, MEBTOUCHE N, et al. Interest of short implants in hip arthroplasty for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: comparative study “uncemented short” vs “cemented conventional” femoral stems. Int Orthop. 2018;42(7):1669-1674. [38] MARTZ P, MACZYNSKI A, ELSAIR S, et al. Total hip arthroplasty with dual mobility cup in osteonecrosis of the femoral head in young patients: over ten years of follow-up. Int Orthop. 2017;41(3):605-610. [39] SCHEPPER JD, COLLINS F, RIOS-ARCE ND, et al. Involvement of the Gut Microbiota and Barrier Function in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(4):801-820. [40] XU S, GUO R, LI PZ, et al. Dexamethasone interferes with osteoblasts formation during osteogenesis through altering IGF-1-mediated angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(9):15167-15181. [41] KHOSHLAHNI N, SAGHA M, MIRZAPOUR T, et al. Dexamethasone interferes with osteoblasts formation during osteogenesis through altering IGF-1-mediated angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(9):15167-15181. [42] PENG L, WU F, CAO M, et al. Effects of different physical factors on osteogenic differentiation. Biochimie. 2023;207:62-74. [43] DORNELAS J, DORNELAS G, ROSSI A, et al. The Incorporation of Zinc into Hydroxyapatite and Its Influence on the Cellular Response to Biomaterials: A Systematic Review. J Funct Biomater. 2024;15(7):178. [44] MOLLENTZE J, DURANDT C, PEPPER MS. An In Vitro and In Vivo Comparison of Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:9919361. [45] KOMORI T. Whole Aspect of Runx2 Functions in Skeletal Development. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(10):5776. [46] HA SH, CHOUNG PH. Whole Aspect of Runx2 Functions in Skeletal Development. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(10):5776. [47] LIU Z, HUANG L, QI L, et al. Activating Angiogenesis and Immunoregulation to Propel Bone Regeneration via Deferoxamine-Laden Mg-Mediated Tantalum Oxide Nanoplatform. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(19):24384-24397. [48] PENG Y, WU S, LI Y, et al. Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeling. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):426-436. [49] GAO W, HE R, REN J, et al. Exosomal HMGB1 derived from hypoxia-conditioned bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells increases angiogenesis via the JNK/HIF-1α pathway. FEBS Open Bio. 2021;11(5):1364-1373. [50] WU D, LIU L, FU S, et al. Osteostatin improves the Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and enhances angiogenesis through HIF-1α under hypoxia conditions in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;606:100-107. [51] ZHANG Y, HAO Z, WANG P, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance fracture healing through HIF-1α-mediated promotion of angiogenesis in a rat model of stabilized fracture. Cell Prolif. 2019; 52(2):e12570. [52] HAMUSHAN M, CAI W, ZHANG Y, et al. High-purity magnesium pin enhances bone consolidation in distraction osteogenesis model through activation of the VHL/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling. J Biomater Appl. 2020;35(2):224-236. [53] LANG A, STEFANOWSKI J, PFEIFFENBERGER M, et al. MIF does only marginally enhance the pro-regenerative capacities of DFO in a mouse-osteotomy-model of compromised bone healing conditions. Bone. 2022;154:116247. |
| [1] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [2] | De Ji, Suo Langda, Wei Yuchen, Wang Bin, Awangcuoji, Renqingcuomu, Cui Jiuzeng, Zhang Lei, Ba Gui. Comprehensive analysis of genes related to endometrial receptivity and alternative splicing events in northwest Tibetan cashmere goats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1429-1436. |
| [3] | Sun Yuting, Wu Jiayuan, Zhang Jian. Physical factors and action mechanisms affecting osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1531-1540. |
| [4] | Chen Yuning, Jiang Ying, Liao Xiangyu, Chen Qiongjun, Xiong Liang, Liu Yue, Liu Tong. Buqi Huoxue Compounds intervene with the expression of related factors and autophagy related proteins in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1152-1158. |
| [5] | Ge Xiao, Zhao Zhuangzhuang, Guo Shuyu, Xu Rongyao. HOXA10 gene-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7701-7708. |
| [6] | Wang Yong, Li Hongyu, Liu Yuhang, Wang Fengxing. Knowledge map of surgical treatment for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a bibliometric analysis of data from 2005 to 2024 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7250-7260. |
| [7] | Zhou Lina, , Li Yun, , Liu Xixia, . Effects of different concentrations of hypertonic glucose in the repair of tendon injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6885-6892. |
| [8] | Liu Xun, Ouyang Hougan, Pan Rongbin, Wang Zi, Yang Fen, Tian Jiaxuan . Optimal parameters for physical interventions in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6727-6732. |
| [9] | Pan Yu, Zhao Renfeng, Li Xingping, Zhang Chengdong, Shi Feng, Pu Chao, Luo Xuwei, Xiao Dongqin. Iron overload induces ferroptosis in osteoblast precursor cells and inhibits osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6381-6390. |
| [10] | Wang Jianlei, He Peiliang, Sun Yongjian. A meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of intravenous glucocorticoids before lower limb joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 599-607. |
| [11] | Chai Jinlian, Sun Tiefeng, Li Wei, Zhang Bochun, Li Guangzheng, Zhou Zhongqi, Liang Xuezhen, Wang Ping. Therapeutic effect of Cornus Cervi Colla on steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rat models: fecal metabolomics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6187-6197. |
| [12] | Qiu Boyuan, Liu Fei, Tong Siwen, Ou Zhixue, Wang Weiwei. Bioinformatics identification and validation of aging key genes in hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5608-5620. |
| [13] | Chen Pinrui, Xue Yiyuan, Pei Xibo. Fe3O4@ZIF-8 nanoparticles affect osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under magnetic stimulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4841-4850. |
| [14] | Deng Yunyi, Chen Shichao, Luo Mingdong, Li Ruotong, Lan Xiaorong, Yu Ke, Li Guangwen. Gold nanoparticle @ mesoporous silica modified titanium implants promote osteogenic differentiation under high glucose conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4694-4701. |
| [15] | Wu Xiuli, Yan Xiaoxia, Ren Zhiqiang, Sun Nan, Li Jinju. Modeling methods and evaluation criteria in animal models of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4560-4567. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||