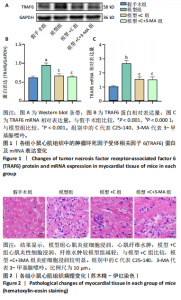
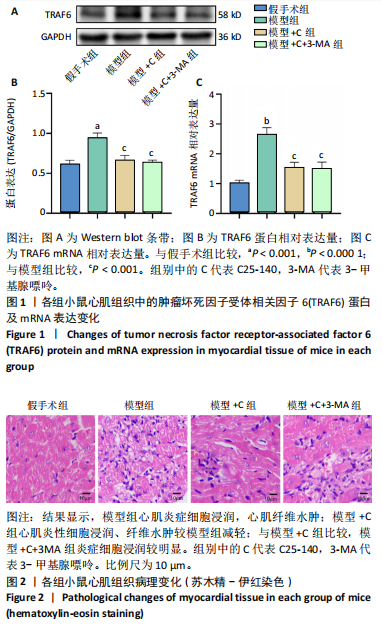
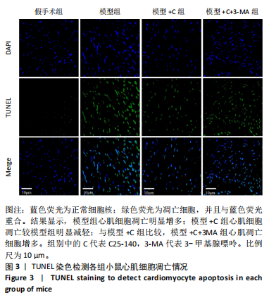
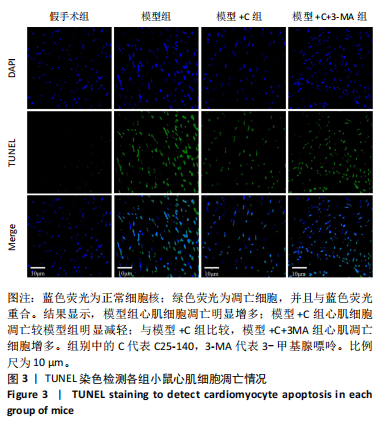
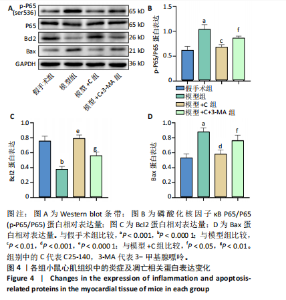
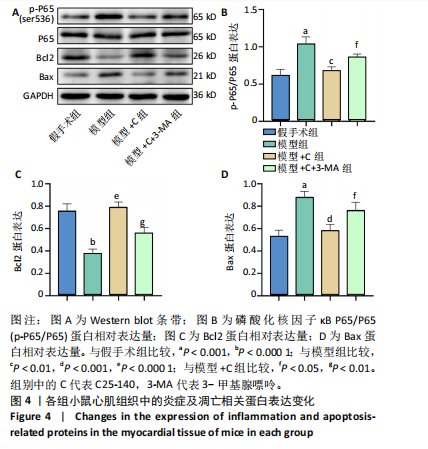
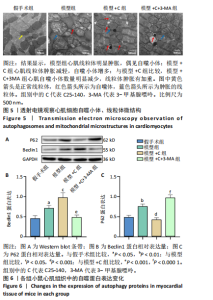
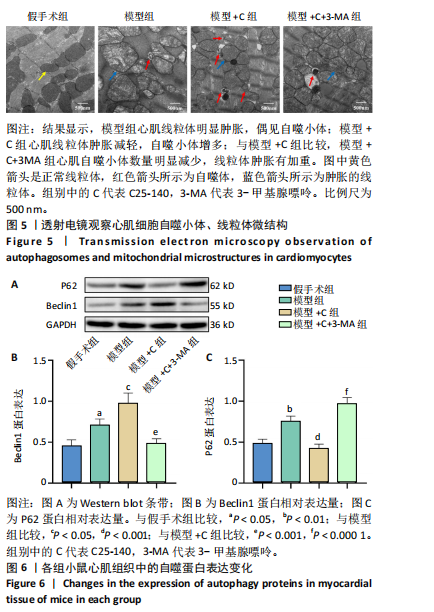
[1] L’HEUREUX M, STERNBERG M, BRATH L, et al. Sepsis-Induced Cardiomyopathy: a Comprehensive Review. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2020;22(5): 35.
[2] 中国中西医结合学会重症医学专业委员会, 中国医师协会中西医结合医师分会心脏介入专业委员会. 脓毒性心肌病中西医结合诊治专家共识[J]. 中国中西医结合急救杂志,2022,29(1):1-6.
[3] GUO Y, ZHANG X, LI J, et al. TRAF6 regulates autophagy and apoptosis of melanoma cells through c-Jun/ATG16L2 signaling pathway. MedComm (2020). 2023;4(4):e309.
[4] HUA T, YANG M, SONG H, et al. Huc-MSCs-derived exosomes attenuate inflammatory pain by regulating microglia pyroptosis and autophagy via the miR-146a-5p/TRAF6 axis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):324.
[5] WU C, ZENG L, YI W, et al. Echovirus induces autophagy to promote viral replication via regulating mTOR/ULK1 signaling pathway. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1162208.
[6] 周颖, 蒋大军, 田勇, 等. 抑制TRAF6调节炎症和自噬改善脓毒症小鼠的心肌损伤和心功能[J]. 实用医学杂志,2024,40(5):608-614.
[7] YAO H, LIU S, ZHANG Z, et al. A bibliometric analysis of sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction from 2002 to 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023;10: 1076093.
[8] KHALID N, PATEL PD, ALGHAREEB R, et al. The Effect of Sepsis on Myocardial Function: A Review of Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Criteria, and Treatment. Cureus. 2022;14(6):e26178.
[9] 宁海慧, 郭娜, 邢博民, 等. 炎症相关信号通路在脓毒症中的研究现状[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志,2022,38(7):744-747.
[10] LIU X, LIN Z, XU Y. Pellino1 promoted inflammation in lung injury model of sepsis by TRAF6/ NF-κB signal pathway. J Inflamm (Lond). 2021;18(1):11.
[11] FENG D, GUO R, LIAO W, et al. Plantamajoside alleviates acute sepsis-induced organ dysfunction through inhibiting the TRAF6/NF-κB axis. Pharm Biol. 2023;61(1):897-906.
[12] SHENG SY, LI J M, HU XY, et al. Regulated cell death pathways in cardiomyopathy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023;44(8):1521-1535.
[13] ZHU XG, ZHANG TN, WEN R, et al.Overexpression of miR-150-5p Alleviates Apoptosis in Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Depression. Biomed Res Int. 2020; 2020:3023186.
[14] XIAO Y, YU Y, HU L, et al. Matrine Alleviates Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Injury by Inhibiting Ferroptosis and Apoptosis. Inflammation. 2023;46(5):1684-1696.
[15] PRERNA K, DUBEY VK. Beclin1-mediated interplay between autophagy and apoptosis: New understanding. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;204:258-273.
[16] BI CF, LIU J, YANG LS, et al. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Sepsis Induced Myocardial Injury. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:4275-4290.
[17] WU B, SONG H, FAN M, et al. Luteolin attenuates sepsis‑induced myocardial injury by enhancing autophagy in mice. Int J Mol Med. 2020;45(5):1477-1487.
[18] WANG Z, XIAO D, JI Q, et al. Jujuboside A attenuates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by inhibiting inflammation and regulating autophagy. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;947:175451.
[19] SZWED A, KIM E, JACINTO E. Regulation and metabolic functions of mTORC1 and mTORC2. Physiol Rev. 2021;101(3):1371-426.
[20] BATTAGLIONI S, BENJAMIN D, WäLCHLI M, et al. mTOR substrate phosphorylation in growth control. Cell. 2022;185(11):1814-1836.
[21] TURCO E, FRACCHIOLLA D, MARTENS S. Recruitment and Activation of the ULK1/Atg1 Kinase Complex in Selective Autophagy. J Mol Biol. 2020;432(1): 123-134.
[22] CAI YY, LI L, ZHU XM, et al. The crucial role of the regulatory mechanism of the Atg1/ULK1 complex in fungi. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:1019543.
[23] LIU N, ZHAO H, ZHAO YG, et al. Atlastin 2/3 regulate ER targeting of the ULK1 complex to initiate autophagy. J Cell Biol. 2021;220(7):e202012091.
[24] LIU L, YAN L, LIAO N, et al. A Review of ULK1-Mediated Autophagy in Drug Resistance of Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(2):352.
[25] HOLCZER M, HAJDÚ B, LŐRINCZ T, et al. Fine-tuning of AMPK-ULK1-mTORC1 regulatory triangle is crucial for autophagy oscillation. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1): 17803.
[26] HOLLENSTEIN D M, KRAFT C. Autophagosomes are formed at a distinct cellular structure.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020;65:50-57.
[27] HAN S, LI X, WANG K, et al. PURPL represses autophagic cell death to promote cutaneous melanoma by modulating ULK1 phosphorylation. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(11):1070.
[28] RONG Z, ZHENG K, CHEN J, et al. Function and regulation of ULK1: From physiology to pathology. Gene. 2022;840:146772.
[29] LINARES JF, DURAN A, YAJIMA T, et al. K63 polyubiquitination and activation of mTOR by the p62-TRAF6 complex in nutrient-activated cells. Mol Cell. 2013;51(3):283-296.
[30] WU X, LIU JM, SONG HH, et al. Aurora-B knockdown inhibits osteosarcoma metastasis by inducing autophagy via the mTOR/ULK1 pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20(1):575. |