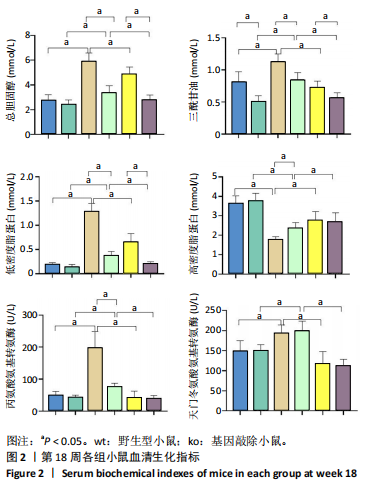
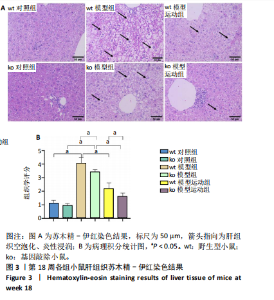
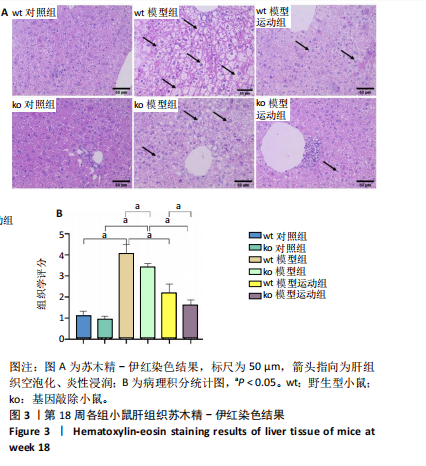
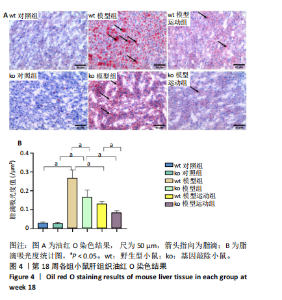
[1] CAO L, AN Y, LIU H, et al. Global epidemiology of type 2 diabetes in patients with NAFLD or MAFLD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2024;22(1):101.
[2] MELLEMKJAER A, KJAER MB, HALDRUP D, et al. Management of cardiovascular risk in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Eur J Intern Med. 2024;122:28-34.
[3] YANG Z, WANG L. Current, emerging, and potential therapies for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1152042.
[4] YANG Y, LI X, LIU Z, et al. Moderate Treadmill Exercise Alleviates NAFLD by Regulating the Biogenesis and Autophagy of Lipid Droplet. Nutrients. 2022;14(22):4910.
[5] HATTA K, GUO J, LUDKE A, et al. Expression of CNPY2 in mouse tissues: quantification and localization. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e111370.
[6] CHEN KQ, ZHANG YQ, WANG ZB, et al. Progress in Research on CNPY2 in Diseases. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(4):391-402.
[7] HONG F, LIN CY, YAN J, et al. Canopy Homolog 2 contributes to liver oncogenesis by promoting unfolded protein response-dependent destabilization of tumor protein P53. Hepatology. 2022;76(6):1587-1601.
[8] Hong F, Liu B, Wu BX, et al. CNPY2 is a key initiator of the PERK-CHOP pathway of the unfolded protein response. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017;24(10):834-839.
[9] SCHWABE RF, LUEDDE T. Apoptosis and necroptosis in the liver: a matter of life and death.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15(12):738-752.
[10] SHOJAIE L, IORGA A, DARA L. Cell Death in Liver Diseases: A Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9682.
[11] HOSSEINI SP, FARIVAR S, REZAEI R, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 2 reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in in-vitro Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease model. Daru. 2023;31(1):29-37.
[12] 王佳倩,李亚龙,蒋昌君,等. 有氧运动对AKT/GSK3β介导非酒精性脂肪肝肝细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 卫生研究,2023,52(2):246-252.
[13] DOU Y, LEI J Q, GUO SL, et al. The CNPY2 enhances epithelial-mesenchymal transition via activating the AKT/GSK3beta pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Biol Int. 2018;42(8):959-964.
[14] CHU M, LIU H, XIONG Z, et al. Canopy Fibroblast Growth Factor Signaling Regulator 2 (CNPY2) Inhibits Neuron Apoptosis in Parkinson’s Disease via the AKT/GSK3beta Pathway. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2021; 18(1):102-112.
[15] VAN HERCK MA, VONGHIA L, FRANCQUE SM. Animal Models of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-A Starter’s Guide. Nutrients. 2017; 9(10):1072.
[16] 潘磊,张金彪,崔荣岗,等.非酒精性脂肪肝C57BL/6小鼠模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(40):6054-6059.
[17] MARQUES CM, MOTTA VF, TORRES TS, et al.Beneficial effects of exercise training (treadmill) on insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat fed C57BL/6 mice. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2010;43(5):467-475.
[18] 张树玲,李军汉,王佳倩,等.有氧运动干预非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠肝脏 JAK2/STAT5 信号通路的变化 [J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(17):2690-2695.
[19] MAKRI E, GOULAS A, POLYZOS SA. Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Emerging Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Arch Med Res. 2021;52(1):25-37.
[20] AVTANSKI D, PAVLOV VA, TRACEY KJ, et al. Characterization of inflammation and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced male C57BL/6J mouse model of obesity. Animal Model Exp Med. 2019; 2(4):252-258.
[21] 马晓月,李钦钦,陆华贞,等.非酒精性脂肪肝动物模型及细胞模型研究进展[J].中国比较医学杂志,2023,33(6):120-127.
[22] KOHLI R, FELDSTEIN AE. NASH animal models: are we there yet?. J Hepatol. 2011;55(4):941-943.
[23] FANG T, WANG H, PAN X, et al. Mouse models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): pathomechanisms and pharmacotherapies. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(15):5681-5697.
[24] FLESSA CM, NASIRI-ANSARI N, KYROU I, et al. Genetic and Diet-Induced Animal Models for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Research. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(24):15791.
[25] GAUTHERON J, GORES GJ, RODRIGUES CMP. Lytic cell death in metabolic liver disease. J Hepatol. 2020;73(2):394-408.
[26] ZHANG Y, LIU Y, LIU X, et al. Exercise and Metformin Intervention Prevents Lipotoxicity-Induced Hepatocyte Apoptosis by Alleviating Oxidative and ER Stress and Activating the AMPK/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in db/db Mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:2297268.
[27] HAN JW, ZHAN XR, LI XY, et al. Impaired PI3K/Akt signal pathway and hepatocellular injury in high-fat fed rats. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16(48):6111-6118.
[28] ZHAO L, LI H, GAO Q, et al. Berberine Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Induced Neuronal Apoptosis by Down-Regulating the CNPY2 Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:609693.
[29] COOK JJ, WEI M, SEGOVIA B, et al. Endurance exercise-mediated metabolic reshuffle attenuates high-caloric diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann Hepatol. 2022;27(4):100709.
[30] HU Z, ZHANG H, WANG Y, et al. Exercise activates Sirt1-mediated Drp1 acetylation and inhibits hepatocyte apoptosis to improve nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2023;22(1):33.
[31] 刘倩倩,秦智,侯改霞,等.有氧运动对NAFLD大鼠肝细胞线粒体结构功能的影响[J].中国体育科技,2016,52(5):75-82+97.
[32] ZENG Y, ZHANG X, LUO W, et al. Effect of exercise intervention on clinical parameters in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;36(1):1-12. |