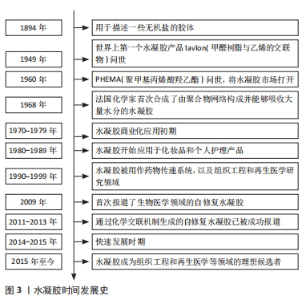
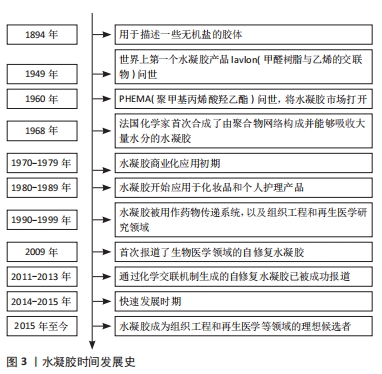
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (28): 6110-6117.doi: 10.12307/2025.478
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role of functional hydrogels in tissue repair after traumatic brain injury
Zhang Tong1, Wang Yan2, Yang Chunjia1, Yue Qingkun1, Wu Qingtian1
- 1School of Basic Medicine, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154007, Heilongjiang Province, China; 2Institute of Military Cognitive and Brain Sciences, Academy of Military Medical Sciences, Beijing 100039, China
-
Received:2024-07-13Accepted:2024-08-13Online:2025-10-08Published:2024-12-07 -
Contact:Wu Qingtian, PhD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Basic Medicine, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154007, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Zhang Tong, Master candidate, School of Basic Medicine, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154007, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:Jiamusi University "Dongji" Academic Team (Team Number: DJXSTD202404)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Tong, Wang Yan, Yang Chunjia, Yue Qingkun, Wu Qingtian. Role of functional hydrogels in tissue repair after traumatic brain injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6110-6117.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
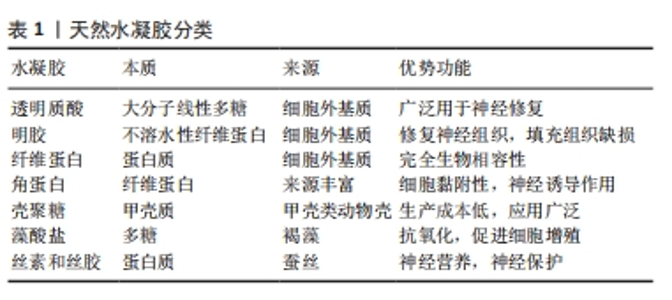
2.2 基于分子设计的功能水凝胶在神经修复领域的应用 水凝胶在其作为神经修复材料的应用中表现出几个优点。首先,作为一种理想的载体,可以负载细胞、药物、营养物质、生长因子和其他生物活性成分,以及长期保持其活性以促进神经修复;第二,拥有良好的生物降解性,可以在修复的初始阶段为新组织的生长提供支持,并通过逐渐降解为神经再生提供空间;第三,具有更高的含水量和更好的生物相容性,使其成为内源或移植细胞生长的合适基质;第四,具有可调的机械强度,可以灵活地适应受损神经组织的模量;最后,提供丰富的孔隙空间,有利于细胞生长和物质交换。因此,水凝胶在中枢神经组织修复领域的应用得到广泛研究。然而,它们在生物相容性、理化性能以及力学强度方面仍需要进一步优化,才能满足针对不同类型中枢神经系统创伤的组织修复需 要[18]。目前基于分子设计的功能水凝胶在神经修复领域研究应用较多的即天然水凝胶,文章简单介绍了基于分子设计的功能水凝胶分类,如表1所示。"
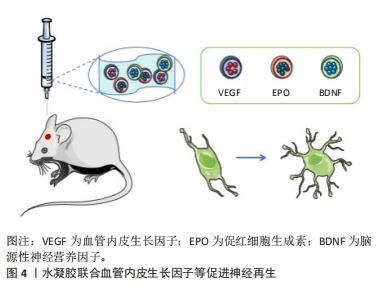
2.2.1 水凝胶模拟神经微结构促进再生修复 天然生物材料是在自然条件下生成的生物材料,通常以来源于动物、植物或人类的天然存在的大分子物质的形式存在,可通过水解、酶解等方法逐渐降解为存在于体内的小分子物质,通过代谢完全吸收或排泄,而不会对机体造成毒副作用。因此,已被广泛用作修复神经的水凝胶。最常用于治疗创伤性脑损伤并可单独发挥修复作用的主要有透明质酸和明胶,文中重点介绍这两种天然水凝胶。 透明质酸(HA)是一种大分子线性多糖,是细胞外基质的主要成分,在中枢系统中含量尤其丰富,参与多种细胞活动的调节,其独特的分子结构和理化性质赋予其在体内多种重要的生理功能。神经突起是从神经细胞(神经元)的细胞体延伸出来的细长部分,可以分为树突和轴突。树突是接收信息的入口,轴突是发出信息的出口。透明质酸参与炎症反应、血管生成和组织再生[19-20],促进神经突起再生,是最常用促进神经再生的水凝胶之一。赖氨酸(PDL)通常用作制备神经元培养物的涂层材料,将多聚赖氨酸涂覆到基质上是通过非共价结合,形成一种非永久性的修饰,有研究用赖氨酸修饰透明质酸,通过表面羟基与赖氨酸共价结合,模拟在基底上涂覆多聚赖氨酸,为创伤性脑损伤后分离的受损神经元轴突再生提供了合适的环境,促进了神经元再生[21]。 明胶水凝胶通过胶原蛋白的热变性获得,抗原性相对较低,在使用过程中可以减少机体的免疫系统反应。明胶水凝胶具有良好的生物相容性、可塑性和黏附性,有利于细胞黏附和活性,对神经愈合和重建具有显著效果,在医用修复生物材料领域得到广泛研究[22]。明胶水凝胶可作为神经导管的内部填充物修复断裂的神经组织,或作为独立的组织工程材料填充组织缺损[23-24]。有研究通过辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)和ChOx双酶交联的明胶水凝胶作为创伤性脑损伤小鼠模型中神经修复的神经支架,以搭载小鼠骨髓来源的间充质干细胞进行创伤性脑损伤治疗,发现明胶水凝胶可调节损伤局部炎症反应、抑制凋亡,促进神经再生,最终改善神经功能的重建和可塑性[25]。 天然生物材料具有良好的生物相容性,部分材料可能具有生物活性结构单元,这在一定程度上有利于神经修复。然而,由于天然生物材料多是从动物和植物中提取的,因此不同批次之间的性能略有差异,这限制其进一步应用于临床。因此,对于基于天然的生物材料来说,保持性能一致性是非常重要的。 2.2.2 水凝胶重塑神经血管单元促进血管再生 功能性微血管的血管生成和重建是促进神经损伤恢复的重要环节。血管内皮生长因子对运动神经元存活、神经元生存力和增殖具有促进作用。在缺血、缺氧或氧化应激等情况下,血管内皮生长因子在损伤后的神经系统中启动表达,通过信号转导增加组织灌注、抑制细胞凋亡、调节血管生成、诱导神经发生和神经突起生长,从而参与神经修复过程[26]。水凝胶联合表皮生长因子(EGF)和促红细胞生成素(EPO)可增强神经发生和改善功能恢复,以及递送脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)和血管内皮生长因子可有效调节神经保护、血管重塑和血脑屏障修复[27](如图4所示)。另有研究制备了3D打印的胶原蛋白/丝素蛋白携带缺氧预处理的人脐带间充质干细胞来源的外泌体支架,通过间充质干细胞的低氧刺激设计,能够显著促进神经再生和血管生成,并进一步抑制神经细胞凋亡和促炎因子,最终促进创伤性脑损伤的恢复。缺氧诱导外泌体的加入进一步表现出更好的生物相容性和神经再生能力,该支架具有良好的物理性能、合适的生物相容性和生物可降解性,是治疗创伤性脑损伤的有吸引力的候选材料[28]。"
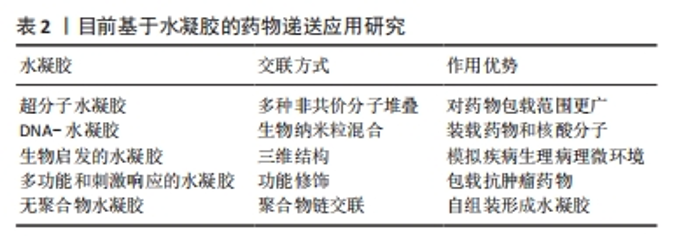
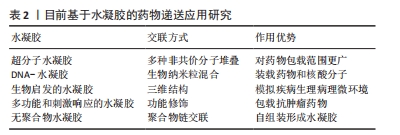
水凝胶的强负载特性使其成为所有场景的通用载体,如何平衡生理环境条件和水凝胶的理化性质,从而精确调控受损神经系统的理化参数以更好地促进神经修复,是该领域的一个重点研究方向。 2.3 基于药物递送的神经修复策略 在中枢神经系统再生研究中,广泛采用了生物分子递送的策略,以刺激内源性修复机制、靶向抑制因子、促进神经再生与功能重建[29]。但由于血脑屏障的低渗透性,传统给药策略可能会影响治疗药物的扩散,但全身给药又会导致治疗分子的非靶向分布,并可引发肿瘤形成和纤维化等不良副作用[30]。因此,提升药物穿过血脑屏障的策略是发挥创伤性脑损伤治疗效果的又一关键。 功能化水凝胶通过材料基因组设计能够具备与神经中枢系统相似的机械性能,可以通过建立微创的药物输送方法,实现药物的精准、靶向递送,并维持药物或生物制剂的活性,发挥显著的促神经发生、可塑性、轴突再生和神经保护等神经修复功能。目前基于水凝胶的药物递送应用研究概况见表2。"
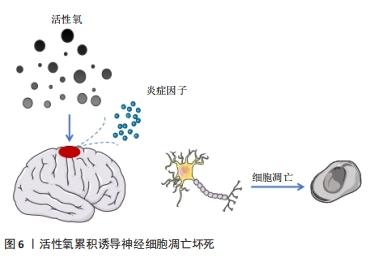
脑源性神经营养因子是一种特异性结合酪氨酸激酶B受体的神经营养因子,已被证明在发育过程中或损伤和疾病发作后促进中枢神经系统中神经元的分化、成熟和突触可塑性[31]。含有脑源性神经营养因子肽交联纳米结构的三维水凝胶能够促进细胞浸润,同时加速修复组织的功能成熟。脑源性神经营养因子为水凝胶提供了一种具有组织特异性的纳米结构生物活性基质,通过激活信号分子的呈递,诱导内源性细胞浸润并促进功能性神经元成熟[32-33]。另有研究显示,外源性硫化氢(H2S)在创伤性脑损伤后发挥了神经保护作用。为此,CHEN等[34]设计并研制了一种表面填充的可释放H2S的丝素蛋白(SF)水凝胶,通过小剂量局部给药,避免挥发性和毒副作用,减少组织损失和慢性神经炎症,促进神经恢复,在创伤性脑损伤后发挥神经保护作用。 神经营养因子可以调节中枢和周围神经系统的发育并抑制细胞凋亡,是促进神经可塑性损伤后神经元生长和存活的关键介质。WANG等[35]合成并优化了一种由半乳糖氧化酶(GalOx)和辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)原位双酶交联的可注射透明质酸水凝胶,研究了该水凝胶包裹骨髓间充质干细胞和神经生长因子对创伤性脑损伤小鼠的治疗作用,结果发现负载骨髓间充质干细胞和神经生长因子的复合水凝胶可通过神经生长因子释放和神经炎症调节促进内源性神经细胞的存活和增殖,从而改善创伤性脑损伤小鼠的神经功能恢复并加速修复过程。 2.3.2 水凝胶搭载药物促进神经再生 脑损伤后神经细胞的修复需要大量能量,往往会导致整个脑能量供需失衡。而损伤组织释放出大量的活性氧在创伤微环境中逐渐累积,使脑组织处于一个进行性加重的环境状态,释放出大量炎症因子,进一步诱导神经细胞凋亡和坏死[36-37],参与了继发性脑损伤的病理生理过程(如图6所示)。由于血脑屏障阻隔常规全身给药难以在创伤性脑损伤早期到达靶向区域,而通过理性设计的功能性水凝胶能够实现药物的定向、快速递送,从而达到促进神经再生的目的。"
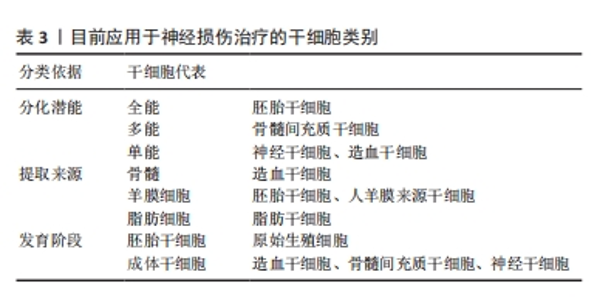
基于原花青素(PCs)具有强大的自由基清除能力,HUANG等[38]设计并制备了一种载有活性氧清除功能的原花青素水凝胶(GelMA-PPS/PC),通过激活免疫应答实现靶向创伤微环境的药物递送,体内外实验证明GelMA-PPS/PC水凝胶可以消耗活性氧,减轻脑水肿,保护血脑屏障的完整性,减轻神经炎症,促进神经功能的恢复。生物活性小分子没食子酸具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗菌、抗过敏、抗癌等多种活性,近年来越来越受到关注[39]。研究人员基于没食子酸共轭明胶(GGA)和氧化葡聚糖(Odex)的席夫碱反应,研制了一种用于创伤性脑损伤治疗的可注射性抗氧化水凝胶(GGA6Odex水凝胶),将复合水凝胶原位植入创伤性脑损伤小鼠后能够有效促进神经发生并提高了小鼠运动、学习和记忆能力;此外,此复合水凝胶通过激活Nrf2/HO-1途径以及调节炎症因子分泌和巨噬细胞/小胶质细胞极化来抑制氧化应激和炎症[40]。 要想实现水凝胶递送药物发挥预期的疗效,需要精确控制药物从水凝胶聚合物中释放的动力学。水凝胶的网络结构和药物分子大小之间的关系是预测特定水凝胶释放速率时的重要因素,如随着水凝胶浓度增大,网络密度增加,药物中小分子物质能够得到释放,但另一部分可能被截留在水凝胶基质中,直接影响药物释放速率[41]。通过药物和递送材料之间的耦合设计,对药物和生物材料之间的相互作用予以精确调控,有望实现功能性水凝胶搭载药物的可控释放。有研究显示,应用具有增加流体动力学模式的替代抗体,如scFv-Fc[42]、cIgG能够改善高度特异性单链抗体片段的长期释放模式[43],从而达到治疗目的。 2.4 搭载细胞的功能水凝胶靶向神经修复 随着神经修复研究的不断发展,干细胞替代疗法作为一种治疗多种神经退行性疾病的有前途的治疗策略而备受关注[44]。干细胞具有自我更新和分化为多种类型功能细胞的能力(具体分类见表3)。根据分化潜能和细胞来源,用于治疗中枢神经系统疾病的干细胞包括胚胎干细胞(ESCs)、诱导多能干细胞(iPSCs)、成体干细胞(ADASs)、间充质干细胞(MSCs)和神经干细胞(NSCs)等[45],除了直接的细胞替代疗法外,干细胞还可以通过分泌多种细胞因子和生长因子,发挥抗炎、神经细胞保护和诱导内源性恢复系统等各种有益的效果。尽管干细胞疗法是治疗创伤性脑损伤导致脑组织损伤的一种可行的选择,但是由于损伤局部的微环境不利于干细胞的分化发育,其应用受到了干细胞存活率低和分化效率的限制[46]。为了支持干细胞在组织植入部位的生理功能,采用水凝胶搭载干细胞实现体内递送是一种重要的方法。许多研究表明,设计良好的3D支架可以为调节体外和体内的细胞生物学功能提供物理支撑[47-49]。"
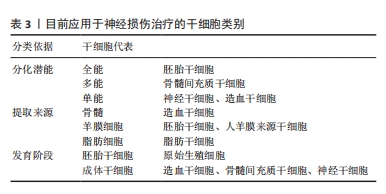

在多种能够用于开展脑损伤治疗的干细胞中,间充质干细胞因其来源广泛、免疫原性低、伦理争议少而备受关注。通过直接静脉途径或原位注射结合三维(3D)支架搭载干细胞植入创伤性脑损伤损伤区域,能够通过旁分泌或细胞替代的作用,明显加快脑结构重塑和神经功能恢复[50]。 骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体既结合了干细胞的优点,又避免了免疫排斥的风险。内源性神经干细胞迁移对中枢神经损伤的修复必不可少,复合水凝胶模拟大脑细胞外基质,为损伤后脑组织再生提供有利微环境,携带有干细胞衍生的外泌体诱导了神经干细胞的分化[51]。基质细胞衍生因子1及其受体CXCR4是调节干细胞存活、募集和分化的关键因素,研究合成了载有骨髓间充质干细胞的海藻酸钠/Ⅰ型胶原/基质细胞衍生因子1水凝胶,该复合性功能水凝胶在大鼠创伤性脑损伤中可以持续释放基质细胞衍生因子1,有利于骨髓间充质干细胞在体外的存活、迁移和神经元分化,显著减轻了运动和认知功能障碍,并缓解了焦虑和抑郁样行为。此外,骨髓间充质干细胞/海藻酸钠/Ⅰ型胶原/基质细胞衍生因子1联合应用减少了脑损伤和神经元细胞死亡,减轻了神经炎症,促进了损伤处骨髓间充质干细胞的迁移,并促进了神经发生[52]。 人脐带间充质干细胞与活化的星形胶质细胞直接共培养有利于人脐带间充质干细胞的体外增殖和神经元分化。有研究将人脐带间充质干细胞和活化的星形胶质细胞接种在RADA16-BDNF肽支架(R-B-SPH)中,形成自组装肽水凝胶,体内外实验结果显示人脐带间充质干细胞和活化星形胶质细胞的共培养促进了更多的脑源性神经营养因子分泌,促进神经细胞分化,为创伤性脑损伤的细胞替代疗法提供了一种有希望的治疗选择[53]。 与没有载体携带情况下的单纯细胞移植相比,水凝胶搭载干细胞移植到损伤部位后显著促进了细胞存活[54]。在大鼠创伤性脑损伤模型中,将重要的神经转录因子——神经元发生素2(Ngn2)基因转染入成熟人胎儿组织来源的神经干细胞后, 经透明质酸水凝胶搭载共同移植到创伤性脑损伤损伤部位,与未转染细胞相比,能更有效地促进人胎儿组织来源的神经干细胞分化为神经元谱系[55]。ZHEN等[56]研究制备了一种咪唑基团功能化的可注射水凝胶用于携带人脐带间充质干细胞治疗创伤性脑损伤,咪唑基团分子能够促进干细胞分化为神经细胞[57],从而达到治疗目的。此外,GAO等[58]构建出中性粒细胞免疫调节水凝胶,能够促进血管生成,提示水凝胶和细胞的联合应用有望成为一种备选的临床治疗策略,在创伤性脑损伤修复中发挥积极作用。目前,研究人员对功能性水凝胶在体内高效递送开展了深入研究,如将透明质酸结合到壳聚糖基自修复水凝胶中,制备了具有半互穿聚合物网络(semi-interpenetrating polymer network,SIPN)的自修复水凝胶,透明质酸成分使得水凝胶更容易进入创伤性脑损伤后的受损组织,并且增强了被包裹的神经干细胞在体外的铺展、迁移、增殖和分化[59]。另有现在比较流行的工程化水凝胶也有较多研究,如利用成骨诱导液培养人牙髓间充质干细胞获得工程化人牙髓间充质干细胞源细胞外囊泡,与水凝胶结合可增强材料的成骨矿化能力,同时具有血管生成和抗炎能力[60],但这种工程化水凝胶在创伤性脑损伤治疗中目前仍未有应用研究。 目前,干细胞移植被认为是神经修复中最有前途的方法之一。干细胞可以自我更新和分化为多种细胞。干细胞疗法的主要作用是再生轴突、防止细胞凋亡和取代丢失的细胞。基于干细胞的治疗正在迅速发展,目前研究开发的复合水凝胶具有良好的可注射性、稳定性、生物降解性,为创伤性脑损伤后神经再生治疗应用提供了坚实基础,研制并构建功能可调节的水凝胶神经修复材料是有利于干细胞靶向递送、精准归巢以及分化成熟的关键治疗策略。"

| [1] 陈一豪. CS-HEC-HA/GP温敏水凝胶的制备及其联合hUC-MSCs在TBI神经修复中的作用[D].郑州.郑州大学.2019. [2] BURDA JE, BERNSTEIN AM, SOFRONIEW MV. Astrocyte roles in traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2016;275 Pt 3(03):305-315. [3] SHAHROR RA, WU CC, CHIANG YH, et al. Genetically Modified Mesenchymal Stem Cells: The Next Generation of Stem Cell-Based Therapy for TBI. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(11):4051. [4] THAL SC, HEINEMANN M, LUH C, et al. Pioglitazone reduces secondary brain damage after experimental brain trauma by PPAR-γ-independent mechanisms. J Neurotrauma. 2011;28(6):983-993. [5] SICA A, MANTOVANI A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(3):787-795. [6] HU X, LEAK RK, SHI Y, et al. Microglial and macrophage polarization—new prospects for brain repair. Nat Nat Rev Neurol. 2015;11(1):56-64. [7] WANG G, ZHANG J, HU X, et al. Microglia/macrophage polarization dynamics in white matter after traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33(12):1864-1874. [8] MANGANAS LN, ZHANG X, LI Y, et al. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy identifies neural progenitor cells in the live human brain. Science. 2007;318(5852):980-985. [9] KADRY H, NOORANI B, CUCULLO L. A blood-brain barrier overview on structure, function, impairment, and biomarkers of integrity. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2020;17(1):69. [10] BAGCHI S, CHHIBBER T, LAHOOTI B, et al. In-vitro blood-brain barrier models for drug screening and permeation studies: an overview. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:3591-3605. [11] RUMON MMH, AKIB AA, SULTANAF, et al. Self-Healing Hydrogels: Development, Biomedical Applications, and Challenges. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(21):4539. [12] 王朝翔. ECM-SA复合水凝胶的制备及其在TBI后血管化的应用研究[D].南通:南通大学.2021. [13] XU J, HSU SH. Self-healing hydrogel as an injectable implant: translation in brain diseases. J Biomed Sci. 2023;30(1):43. [14] WANG L, JIAN Y, LE X, et al. Actuating and memorizing bilayer hydrogels for a self-deformed shape memory function. Chem Commun (Camb). 2018;54(10):1229-1232. [15] PRADHAN K, DAS G, KHAN J, et al. Neuro-Regenerative Choline-Functionalized Injectable Graphene Oxide Hydrogel Repairs Focal Brain Injury. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019;10(3):1535-1543. [16] YAO M, GAO F, XU R, et al. A dual-enzymatically cross-linked injectable gelatin hydrogel loaded with BMSC improves neurological function recovery of traumatic brain injury in rats. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(10): 4088-4098. [17] ROWLAND MJ, PARKINS CC, MCABEE JH, et al. An adherent tissue-inspired hydrogel delivery vehicle utilised in primary human glioma models. Biomaterials. 2018:179:199-208. [18] MA X, WANG M, RAN Y, et al. Design and Fabrication of Polymeric Hydrogel Carrier for Nerve Repair. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(8):1549. [19] GRAÇA MFP, MIGUEL SP, CABRAL CSD, et al. Hyaluronic acid-Based wound dressings: A review. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;241:116364. [20] CORTES H, CABALLERO-FLORÁN IH, MENDOZA-MUñOZ N, et al. Hyaluronic acid in wound dressings. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2020;66(4):191-198. [21] TIAN WM, HOU SP, MA J, et al. Hyaluronic acid-poly-D-lysine-based three-dimensional hydrogel for traumatic brain injury. Tissue Eng. 2005;11(3-4):513-525. [22] YE Q, ZHANG Y, DAI K, et al. Three dimensional printed bioglass/gelatin/alginate composite scaffolds with promoted mechanical strength, biomineralization, cell responses and osteogenesis. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020;31(9):77. [23] YOO J, PARK JH, KWON Y W, et al. Augmented peripheral nerve regeneration through elastic nerve guidance conduits prepared using a porous PLCL membrane with a 3D printed collagen hydrogel. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(22):6261-6271. [24] SALEHI M, NASERI-NOSAR M, EBRAHIMI-BAROUGH S, et al. Regeneration of sciatic nerve crush injury by a hydroxyapatite nanoparticle-containing collagen type I hydrogel. J Physiol Sci. 2018; 68(5):579-587. [25] LI J, ZHANG D, GUO S, et al. Dual-enzymatically cross-linked gelatin hydrogel promotes neural differentiation and neurotrophin secretion of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of moderate traumatic brain injury. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021:187:200-213. [26] GUO H, ZHOU H, LU J, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor: an attractive target in the treatment of hypoxic/ischemic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(1):174-179. [27] SAVIC I. Sex differences in the human brain, their underpinnings and implications. Preface. Prog Brain Res. 2010:186:vii-ix. [28] LIU X, WANG J, WANG P, et al. Hypoxia-pretreated mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes-loaded low-temperature extrusion 3D-printed implants for neural regeneration after traumatic brain injury in canines. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022:10:1025138. [29] ELLIOTT DONAGHUE I, TAM R, SEFTON MV, et al. Cell and biomolecule delivery for tissue repair and regeneration in the central nervous system. J Control Release. 2014;190:219-227. [30] LEE RJ, SPRINGER ML, BLANCO-BOSE WE, et al. VEGF gene delivery to myocardium: deleterious effects of unregulated expression. Circulation. 2000;102(8):898-901. [31] NAGAHARA AH, TUSZYNSKI MH. Potential therapeutic uses of BDNF in neurological and psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011; 10(3):209-219. [32] MARSHALL J, SZMYDYNGER-CHODOBSKA J, RIOULT-PEDOTTI MS, et al. TrkB-enhancer facilitates functional recovery after traumatic brain injury. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):10995. [33] EDELBROCK AN, ÀLVAREZ Z, SIMKIN D, et al. Supramolecular Nanostructure Activates TrkB Receptor Signaling of Neuronal Cells by Mimicking Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor. Nano Lett. 2018; 18(10):6237-6247. [34] CHEN X, HUANG X, LIU C, et al. Surface-fill H(2)S-releasing silk fibroin hydrogel for brain repair through the repression of neuronal pyroptosis. Acta Biomater. 2022:154:259-274. [35] WANG L, ZHANG D, REN Y, et al. Injectable hyaluronic acid hydrogel loaded with BMSC and NGF for traumatic brain injury treatment. Mater Today Bio. 2021:13:100201. [36] KHATRI N, THAKUR M, PAREEK V, et al. Oxidative Stress: Major Threat in Traumatic Brain Injury. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2018;17(9):689-695. [37] CHUANG JY, KAO TJ, LIN SH, et al. Specificity protein 1-zinc finger protein 179 pathway is involved in the attenuation of oxidative stress following brain injury. Redox Biol. 2017:11:135-143. [38] HUANG X, YE Y, ZHANG J, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging Functional Hydrogel Delivers Procyanidins for the Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice. A CS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c04930. [39] BAI J, ZHANG Y, TANG C, et al. Gallic acid: Pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms involved in inflammation-related diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;133:110985. [40] ZHANG D, CHANG R, REN Y, et al. Injectable and reactive oxygen species-scavenging gelatin hydrogel promotes neural repair in experimental traumatic brain injury. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;219: 844-863. [41] BERTZ A, WÖHL-BRUHN S, MIETHE S, et al. Encapsulation of proteins in hydrogel carrier systems for controlled drug delivery: influence of network structure and drug size on release rate. J Biotechnol. 2013; 163(2):243-249. [42] CARTER P J. Potent antibody therapeutics by design. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(5):343-357. [43] SCHIRRMANN T, MENZEL C, HUST M, et al. Oligomeric forms of single chain immunoglobulin (scIgG). MAbs. 2010;2(1):73-76. [44] YOO J, KIM HS, HWANG DY. Stem cells as promising therapeutic options for neurological disorders. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(4):743-753. [45] HSIEH FY, HSU SH. 3D bioprinting: A new insight into the therapeutic strategy of neural tissue regeneration. Organogenesis. 2015;11(4):153-158. [46] WU KH, MO XM, HAN ZC, et al. Stem cell engraftment and survival in the ischemic heart. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;92(5):1917-1925. [47] ENGLER AJ, SEN S, SWEENEY HL, et al. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. 2006;126(4):677-689. [48] FAN L, LIU C, CHEN X, et al. Directing Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Neural Stem Cell Fate with a Three-Dimensional Biomimetic Hydrogel for Spinal Cord Injury Repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(21):17742-17755. [49] WANG LS, BOULAIRE J, CHAN PP, et al. The role of stiffness of gelatin-hydroxyphenylpropionic acid hydrogels formed by enzyme-mediated crosslinking on the differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cell. Biomaterials. 2010;31(33):8608-8616. [50] DAS M, MAYILSAMY K, MOHAPATRA SS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for the treatment of traumatic brain injury: progress and prospects. Rev Neurosci. 2019;30(8):839-855. [51] LIU X, WU C, ZHANG Y, et al. Hyaluronan-based hydrogel integrating exosomes for traumatic brain injury repair by promoting angiogenesis and neurogenesis. Carbohydr Polym. 2023:306:120578. [52] MA S, ZHOU J, HUANG T, et al. Sodium alginate/collagen/stromal cell-derived factor-1 neural scaffold loaded with BMSCs promotes neurological function recovery after traumatic brain injury. Acta Biomater. 2021;131:185-197. [53] SHI W, HUANG CJ, XU XD, et al. Transplantation of RADA16-BDNF peptide scaffold with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells forced with CXCR4 and activated astrocytes for repair of traumatic brain injury. Acta Biomater. 2016:45:247-261. [54] LU P, WANG Y, GRAHAM L, et al. Long-distance growth and connectivity of neural stem cells after severe spinal cord injury. Cell. 2012;150(6):1264-1273. [55] LI X, TZENG SY, LIU X, et al. Nanoparticle-mediated transcriptional modification enhances neuronal differentiation of human neural stem cells following transplantation in rat brain. Biomaterials. 2016:84:157-166. [56] ZHENG Y, WU G, CHEN L, et al. Neuro-regenerative imidazole-functionalized GelMA hydrogel loaded with hAMSC and SDF-1α promote stem cell differentiation and repair focal brain injury. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(3):627-637. [57] ZHONG Q, LACO F, LIAO MC, et al. Influencing the Fate of Cardiac and Neural Stem Cell Differentiation Using Small Molecule Inhibitors of ALK5. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018;7(10):709-720. [58] GAO Z, YU Y, DAI K, et al. Engineering Neutrophil Immunomodulatory Hydrogels Promoted Angiogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022; 14(35):39746-39758. [59] LIU Y, HSU YH, HUANG AP, et al. Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Network of Hyaluronan and Chitosan Self-Healing Hydrogels for Central Nervous System Repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(36): 40108-40120. [60] WANG L, WEI X, HE X, et al. Osteoinductive Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Loaded Multifunctional Hydrogel for Bone Regeneration. ACS Nano. 2024;18(12):8777-8797. |
| [1] | Chang Jinxia, Liu Yufei, Niu Shaohui, Wang Chang, Cao Jianchun. Visualization analysis of macrophage polarization in tissue repair process [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1486-1496. |
| [2] | Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [3] | Zhang Yu, Xu Ruian, Fang Lei, Li Longfei, Liu Shuyan, Ding Lingxue, Wang Yuexi, Guo Ziyan, Tian Feng, Xue Jiajia. Gradient artificial bone repair scaffold regulates skeletal system tissue repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 846-855. |
| [4] | Yang Bin, Tao Guangyi, Yang Shun, Xu Junjie, Huang Junqing . Visualization analysis of research hotspots of artificial intelligence in field of spinal cord nerve injury and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 761-770. |
| [5] | Ren Bo, Tang Yongliang, Li Ni, Liu Bangding. Thermosensitive antibacterial hydrogel for treatment of infected bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7269-7277. |
| [6] | Wu Ziwei, Luo Yicai, Wei Yinge, Liao Hongbing. Application of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) copolymer in stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7393-7404. |
| [7] | Yan Rui, Wang Yiyu, Liu Xue, Jiang Yourong, Cheng Huanzhi, Ma Zhe. Application of exosome-loaded hydrogel in nerve injury regeneration and wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7439-7446. |
| [8] | Xiong Zhenghua, Zhou Jianghong, Shen Yi, Han Xuesong . Mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles in repair of endometrial injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6782-6791. |
| [9] | Liu Hanfei, Cai Zhencun, Zhou Xueting, Wen Hang, Chen Zhenjun. Mechanisms by which traumatic brain injury promotes bone callus formation and fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6260-6268. |
| [10] | Liu Xiaojun, Shang Yuqing, Guan Wenchao, Xu Linlin, Li Guicai. Oriented electrostatically spun polycaprolactone/silk fibroin scaffold loaded with calcium titanate promotes peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6070-6082. |
| [11] | Liu Yang, Yang Jilei, Wang Wenli, Cui Yingying, Sun Qihao, Li Yourui. Application characteristics of thermosensitive hydrogels in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6094-6100. |
| [12] | Chen Senlin, Zhu Zhou, Wan Qianbing. Application of Janus micro/nanoparticles in biomedicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6101-6109. |
| [13] | Guan Zhenjie, Li Wenyuan, Geng Rui, Wang Ying. Regulatory mechanisms of the corticospinal tract after spinal cord injury: combined therapeutic strategies targeting transcription factors and signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5158-5170. |
| [14] | Lin Huijie, Huang Yun, Huang Zhihua, Jiang Lixia. Hot topics on exosomes as drug delivery system in central nervous system diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 5013-5021. |
| [15] | Gao Simiao, Han Xue, Wu Xiaoguang, Zheng Jinyu, Gao Fangwen, Li Kuihua, Peng Yong, Liu Lanxiang. Effect of electroacupuncture combined with low-frequency transcranial ultrasound stimulation on the electroencephalographic signals of rats with traumatic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 402-408. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||