Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (28): 6101-6109.doi: 10.12307/2025.476
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of Janus micro/nanoparticles in biomedicine
Chen Senlin, Zhu Zhou, Wan Qianbing
- National Clinical Medical Research Center for Oral Diseases, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-06-11Accepted:2024-07-27Online:2025-10-08Published:2024-12-07 -
Contact:Wan Qianbing, PhD, Professor, National Clinical Medical Research Center for Oral Diseases, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Chen Senlin, Master candidate, National Clinical Medical Research Center for Oral Diseases, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China - General Project, No. 82371012 (to ZZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Senlin, Zhu Zhou, Wan Qianbing. Application of Janus micro/nanoparticles in biomedicine[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6101-6109.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
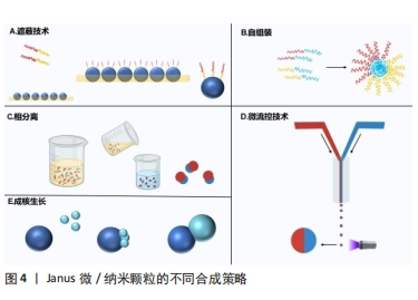
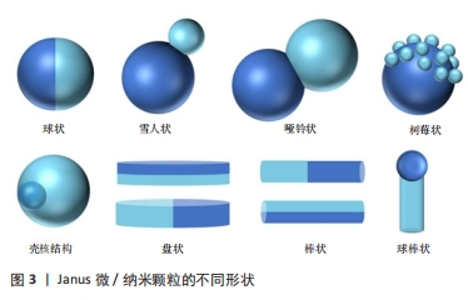
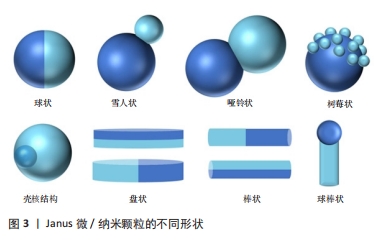
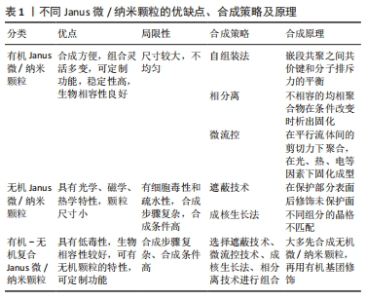
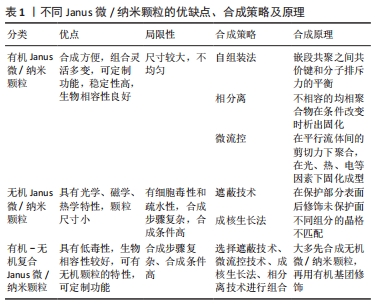
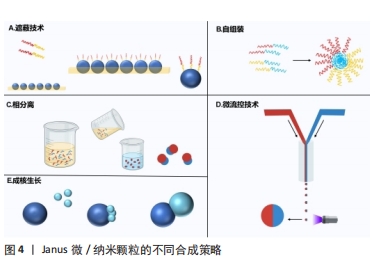
2.1.1 有机Janus微/纳米颗粒 有机Janus微/纳米颗粒由2种及以上的有机嵌段聚合物组成,如由不同类型的聚(乳酸-共乙醇酸)组成的Janus纳米颗粒能够在单个颗粒中负载疏水性药物紫杉醇和亲水性药物多柔比星,或由有机聚合物和脂质合成Janus微颗粒可负载用于肺癌吸入治疗的姜黄素和多柔比星药物,还有由不同水凝胶材料合成的Janus水凝胶微颗粒可用于负载不同生长因子来促进组织再生[25,31-32]。因Janus微/纳米颗粒有机聚合物可选范围广泛,所以其组合也更加灵活多变,并且可以根据研究目标设计,并拥有高度的稳定性和生物相容性。 2.1.2 无机Janus微/纳米颗粒 无机Janus微/纳米颗粒完全由不同无机材料组成,通常包括金、银、铁、铂、锰等金属材料和二氧化硅、石墨烯等非金属材料。金、铁、锰等金属或金属化合物组成的Janus纳米颗粒拥有光学、磁学、热学等特性,如铁、锰基Janus微/纳米颗粒因磁性和不对称性可增强MRI影像,而银基Janus微/纳米颗粒因易氧化性可广泛应用在生物传感方面,同时铂可通过催化过氧化氢分解为纳米马达提供动能[33-34]。而非金属材料如介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒,其高孔隙率和易修饰性是理想的药物载体[35]。 2.1.3 有机-无机复合Janus微/纳米颗粒 无机材料微/纳米颗粒的毒性和疏水性局限了它们的生物应用。有机-无机复合Janus微/纳米颗粒通过有机化合物修饰和包被无机颗粒后可以降低无机材料微/纳米颗粒的生物毒性,也能与组织细胞更好地结合和相互作用[2,17,25]。有机-无机复合Janus微/纳米颗粒将有机材料的良好生物亲和性和无机材料优异的物化特性结合在一起,拓宽了Janus微/纳米颗粒在生物医学领域应用的范围,例如:在无机Janus纳米颗粒上修饰透明质酸基团,可与肿瘤细胞过表达的CD44抗体靶向结合,实现肿瘤靶向给药;或让无机纳米颗粒负载光、声敏剂、酶、抗体,使Janus微/纳米颗粒可在特定环境中发挥作用[36-39]。 2.1.4 Janus微/纳米颗粒的主要合成策略 遮蔽技术:是将颗粒球半面用化学试剂遮蔽保护,或者当颗粒被限制在两相界面上时对无保护颗粒半面进行修饰或与其他颗粒的耦合,从而产生不对称性Janus颗粒(图4A)。通常包括以下步骤:暴露需修饰的半面和遮蔽保护颗粒半面或颗粒,如在两相界面处蒸发沉积和悬浮微/纳米颗粒,其中遮蔽材料可以是固体(例如石蜡)或液体(例如Pickering乳液)[30,35,40];对暴露面进行化学、官能团修饰;去除遮蔽,Janus微/纳米颗粒形成[25,41]。 自组装方法:最早主要用于合成有机Janus微/纳米颗粒,是将2种或2种以上有机嵌段聚合物同时或按顺序添加在一起,以不溶性嵌段物为中心,让嵌段有机聚合物通过分子间作用力(共价键和氢键)自动组装形成Janus结构[30](图4B)。有机Janus微/纳米颗粒的几何外观也与有机聚合物的物理化学性质及合成顺序有关[25]。 相分离技术:是先将2种不相容的嵌段聚合物在助溶剂的帮助下均匀混合后形成乳液,然后将混合乳液分散在另一不相容的液相中,在溶剂完全蒸发后析出具有优异胶体稳定性的Janus微/纳米颗粒[42](图4C)。还可根据嵌段聚合物或颗粒在溶液中溶解度不同,溶解度较低的首先从溶剂中分离出来并固化为前体,溶解度较高的聚合物可在较晚的时间在前体表面析出固化,从而生成Janus 微/纳米颗粒,这种方法类似成核生长技术[30]。前期的相分离体系主要是油/水、有机/水,而王瑞达等[43]、SONG等[44]通过水性三相体系的液-液相分离产生全水相哑铃型Janus液滴。 微流控技术:是将2种不同化学成分的流体在微流控系统中按程序控制流动,不同化学成分的液体在剪切力的作用下可形成Janus液体,最后通过紫外线照射、热固化或离子交联等处理形成Janus微/纳米颗粒[45](图4D)。微流控技术可通过控制反应时间、温度、浓度等合成条件使Janus微/纳米颗粒的形状和尺寸更加稳定,也可与磁性分选、电动流体动力喷射等技术创新性结合来合成尺寸稳定的Janus微/纳米颗粒[46-47]。 成核生长技术:以其中1个纳米颗粒或嵌段物充当种子或核心,在温度或其他反应条件的改变下,次级纳米颗粒或嵌段聚合物通过晶格匹配或化学键在种子表面成核和生长[30](图4E)。例如,以铂纳米颗粒为核心,表面沉积富含孔隙的硅纳米颗粒,生成可以基团修饰的Janus纳米马达[48]。"
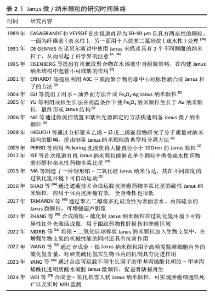
2.2 Janus微/纳米颗粒在生物医学的作用 Janus微/纳米颗粒的尺寸受多种因素影响,如基础材料的性质、合成策略以及合成过程中基础材料的体积比、合成条件等,例如:以无机材料为基础的Janus颗粒大多处于纳米级别,而有机Janus颗粒的尺寸控制对反应条件要求较高。微流控技术主要合成微米级颗粒[3,25,26],而对于细胞内递送药物、癌症治疗、生物传感、抗菌、生物影像等生物医学应用,纳米级Janus颗粒更受青睐,如Janus纳米颗粒对于组织细胞的穿透能力更强,对于体内环境的反应更加灵敏[23,30]。研究者可根据研究目的对Janus微/纳米颗粒进行个性化设计,拓宽其在生物医学领域的应用。Janus微/纳米颗粒的研究时间脉络见表2。"
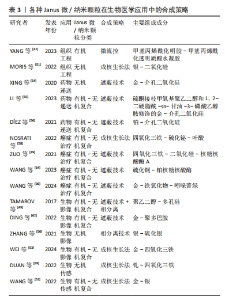
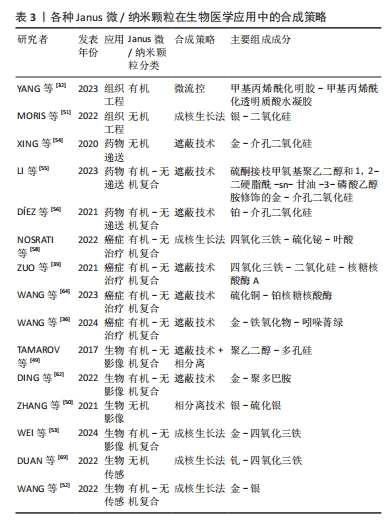
下面将从药物递送、癌症治疗、生物影像、生物传感、组织工程这五个方面阐述Janus微/纳米颗粒在生物医学中的应用。 2.2.1 药物递送 随着纳米技术的发展,已有许多研究来开发纳米材料用于药物递送,而相比于被动释放药物的单一性纳米颗粒,Janus纳米颗粒能通过其功能性部分在患病区域环境(pH值、酶、活性氧、光、温度、磁热、超声和小分子等)实现门控药物释放,从而靶向给药并减少药物抗性和毒副作用[2,47]。其中,介孔二氧化硅基Janus颗粒因孔隙丰富、生物相容好、可控释放和易修饰等特性深受纳米药物递送研究领域的青睐[35]。XING等[54]以金-介孔二氧化硅Janus纳米颗粒作为载体,其金粒子侧表面经硫醇-β-环糊精功能化后可容纳疏水性药物紫杉醇,而介孔二氧化硅侧负载亲水性药物多柔比星,从而实现负载不同性质药物用于治疗。LI等[55]设计出一个对肺纤维化活性氧环境特异性并负载吡非尼酮的硅基Janus纳米颗粒,该颗粒载有活性氧响应性的硫酮接枝甲氧基聚乙二醇和1,2-二硬脂酰-sn-甘油-3-磷酸乙醇胺2种不同的基团,1,2-二硬脂酰-sn-甘油-3-磷酸乙醇胺基团可使Janus纳米颗粒黏附于细胞表面,而硫酮接枝甲氧基聚乙二醇的修饰可抑制细胞内吞,因此,Janus纳米颗粒可在肺纤维化区域的细胞外微环境中释放药物吡非尼酮。尽管一些Janus纳米颗粒根据特殊环境输送药物的能力很强,但是也只能通过自由扩散的方式寻找合适位置释放药物,而Janus纳米马达可有更多的主动动力靶向给药。有研究者开发出具有门控释放药物和超快定向的铂-介孔二氧化硅Janus纳米马达,其铂侧面通过催化过氧化氢分解成水和氧气,氧气气泡可使纳米马达自主运动;而氧化还原敏感基团修饰的介孔二氧化硅可作为装载细胞毒性药物的容器,在细胞内感知氧化还原的环境时特异性释放细胞毒性药物[56]。 2.2.2 癌症治疗 在纳米技术不断提升的时代背景下,Janus微/纳米颗粒在癌症传统和新兴治疗方面有着广泛的研究。虽然传统的癌症治疗方式(如手术切除、放疗、化疗)取得了巨大的进步,但传统治疗措施仍有预后不明确和毒副作用大等问题,如化疗的不良反应是对健康组织器官的毒性,因此肿瘤细胞靶向毒性是减少正常器官和组织毒副作用的重要途径。SHAO等[16]将磁性氧化铁颗粒与载有抗肿瘤药物多柔比星的硅基颗粒通过遮蔽技术结合在一起形成磁性Janus纳米材料,其可在磁场作用下增加细胞内吞效率和pH值敏感性门控释放药物,同时在裸鼠原位和皮下移植肝肿瘤模型中证实了该纳米材料对癌细胞的选择性细胞毒性,同时全身毒性也很低。放射治疗辐射诱导肿瘤细胞的DNA损伤的同时,也让周围健康组织出现急性或晚期毒性,如纤维化、炎症和坏死[57]。因此,基于Janus纳米材料的放射增敏剂不仅能增强放疗辐射对肿瘤细胞的DNA损伤,也能减少健康组织的辐射毒性。NOSRATI等[58]开发出一种氧化铁-硫化铋-叶酸Janus型磁性纳米粒子,其不仅通过修饰基团叶酸增加肿瘤细胞内吞,也可通过X射线照射产生活性氧抑制和杀死肿瘤细胞。 除了通过增强传统放化疗效果和减轻毒副作用外,Janus微/纳米颗粒还被应用于肿瘤新兴的治疗方法中,如肿瘤免疫疗法、化学动力治疗、光动力治疗、肿瘤细胞铁死亡等。肿瘤免疫疗法是通过激活并维持机体对肿瘤免疫能力来促进肿瘤细胞的免疫原性细胞死亡,而肿瘤细胞的免疫原性不足和免疫应答率低限制了抗肿瘤免疫[57,59]。WANG等[38]开发出一种癌细胞膜涂层且负载光敏剂的磁性介孔二氧化硅Janus纳米颗粒,不仅通过癌细胞膜同源靶向作用聚集在乳腺癌细胞周围,还可在光照和交变磁场下产生光动力-磁热联合治疗,从而导致免疫原性细胞死亡和T淋巴细胞介导的抗癌免疫。Janus纳米颗粒也可用于运载蛋白质药物,以往的蛋白质药物因高度特异性和不产生药物抗性成为新的抗肿瘤措施之一,但肿瘤蛋白质药物治疗常因蛋白质药物的理化稳定性差和渗透能力弱而使肿瘤治疗效果差强人意。氧化铁-二氧化硅Janus纳米颗粒可表现出核糖核酸酶A高负载率和磁性靶向聚集能力,因核糖核酸酶A良好的细胞内吞现象和外部磁场干预,该Janus纳米颗粒可显著增强核糖核酸酶A在肿瘤区域聚集并发挥药效;此外,在交流磁场下,50 μg/mL的Janus纳米颗粒在30 min内可使细胞培养基温度从25 ℃上升到43 ℃,而不含Janus纳米颗粒的纯水或纯培养基仅升高6 ℃,从而有效地补充蛋白质治疗效果。体外和体内实验均证实了Janus磁性纳米颗粒负载蛋白质药物对乳腺癌有高抗癌结果和低不良反应[39]。 对于具有严重缺氧、富集过氧化氢、血管不均匀和间质致密等特点的复杂肿瘤微环境,许多纳米药物因无法到达肿瘤内部而限制了治疗效果。WANG等[60]设计出封装了光敏剂IR820 的硫化铜-铂 Janus纳米马达,铂可催化肿瘤内源性过氧化氢转化为氧气,不仅缓解了肿瘤缺氧状态,还为纳米马达提供推进力;在近红外光照射下,Janus纳米马达通过硫化铜高效的光热转换效率可增强其运动能力,而自主运动显著增强了纳米马达在肿瘤积累和向肿瘤内部更深的渗透;此外,富氧环境还促进了活性氧的产生,从而达到了令人满意的光热和光动力抗肿瘤效果。 细胞铁死亡现象也给予了研究者使用Janus微/纳米颗粒治疗癌症的新思路。细胞铁死亡是一种非凋亡形式的细胞死亡,依赖于细胞内铁的积累、活性氧和有毒脂质过氧化物升高以及谷胱甘肽的消耗[59]。因此,在短时间内提高细胞内铁和活性氧的水平至关重要。WANG等[36]合成含铁的超小型Janus纳米颗粒,其凭借透明质酸可靶向与肿瘤细胞过表达的CD44结合并进入肿瘤细胞实现铁累积,还可通过催化肿瘤微环境中过量的过氧化氢产生活性氧,从而引发肿瘤细胞铁死亡。除此之外,CHEN等[61]设计出超声波推进的Janus纳米马达,该纳米马达由金-铁氧化物和表面修饰的光敏吲哚菁绿染料组成,在超声波条件下不仅表现出良好的运动力加速细胞内化,还表现出良好的细胞内运动行为;再通过“芬顿样反应”和“光化学反应”的协同作用,该Janus纳米马达显示良好的细胞内活性氧生成性能,而且以主动方式诱导癌细胞铁死亡的效率比普通纳米马达高80%左右。 2.2.3 生物影像 医学生物影像是诊疗流程中重要的一环,如超声、CT、MRI,拥有无创、可视化等优点,也是医师评估诊断和良好医患沟通的基石。Janus微/纳米粒子不仅可以门控释放药物和增强癌症治疗,还可用于生物影像增强,例如:TAMAROV等[49]通过合成表面亲水和内部疏水的Janus多孔硅颗粒用于超声增强剂,在超声波的作用下其内部疏水结构因包含空气而产生微气泡,从而增强超声现象。还有用于光声成像的金基Janus纳米材、用于表面增强拉曼散射的银和磁共振成像的锰基Janus纳米材料[62-63]。ZHANG等[50]基于创伤和肿瘤富含活性氧等成分合成了银-硫化银Janus纳米颗粒,其在过氧化氢和第二近红外光(1 000-1 350 nm)环境下可特异性激活成像;WANG等[36]合成Janus结构的锰-氧化铁Janus纳米颗粒,不仅可消耗肿瘤微环境中的谷胱甘肽,加速肿瘤细胞的铁死亡,也可用作MRI对比剂,对T1和T2成像具有加速作用,用来监测肿瘤的治愈过程。WEI等[53]也设计出不对称的金-氧化铁Janus纳米颗粒来获得增强型T2 MRI影像。WANG等[64]制备了加载透明质酸(可靶向肿瘤细胞表面CD44受体)、IR780(可靶向线粒体)和线粒体己糖激酶抑制剂的Janus氧化钛-钆超小型纳米颗粒,超小尺寸的纳米颗粒具有很强的组织渗透性、肿瘤抑制性和体内代谢性,在超声环境下,氧化钛纳米颗粒和IR780可以产生协同效应来提高活性氧的生产效率和释放IR780靶向线粒体,线粒体己糖激酶抑制剂也可通过限制线粒体的活性来抑制肿瘤细胞的能量代谢,从而进一步加速细胞凋亡过程;所含的钆元素可以作为核磁共振成像对比剂,这表明合适的Janus纳米颗粒设计可以实现成像-诊断-治疗一体化。 2.2.4 组织工程 组织工程的目标在于促进患区组织的愈合和再生,因此其研究的主要领域有再生用途的干细胞、生物支架材料和生长因子。YANG等[32]开发出甲基丙烯酰化明胶-甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸Janus水凝胶微颗粒用作生长因子载体,其负载有磁性纳米颗粒和两种不同的生长因子——血管内皮生长因子和骨形态发生蛋白2,不仅能够通过磁性颗粒在磁场环境下聚集在骨缺损部位,还可将不同区域的生长因子释放出来促进骨再生。在组织损伤中细菌感染是组织愈合和再生的主要阻碍之一,因此抗菌成为了实现组织再生前必须解决的问题。LIU等[65]设计出一种无需载药的第二种近红外光驱动型Janus纳米马达,其由金纳米棒和铜硫化合物形成的不对称离子耦合体,可在第二近红外光的光声成像引导下产生定向运动、光热效应和光催化治疗细菌感染。因损伤组织的区域通常较大,用于组织再生的Janus结构大多设计成宏观的Janus水凝胶和Janus膜,但也有研究将Janus微/纳米颗粒与生物支架相结合来增加支架特性,从而促进组织愈合和再生。MORIS等[51]将支链淀粉、聚乙烯吡咯烷酮和银-二氧化硅Janus纳米颗粒混合,制备了具有Janus纳米颗粒的生物支架,该支架不仅具有良好的机械性能,也被赋予了银纳米颗粒的抗菌效能。GUI等[66]用3-氨基丙基三乙氧基硅烷修饰负载有阿莫西林的聚苯乙烯-硅Janus微颗粒,然后将该Janus微颗粒封装在乙二醇壳聚糖/双醛端聚乙二醇-藻酸盐双相水凝胶中,这样设计不仅增加了水凝胶的机械性能,也可使水凝胶具有温度响应力学性能和温度程序形状记忆性能,该水凝胶可以在伤口表面吸收热量并发生溶液-凝胶转变,不仅能够吸热镇痛,还能释放Janus微颗粒运载的抗菌药物,从而达到抗菌效果。 2.2.5 生物传感 纳米材料应用于生物传感领域已经很常见,拥有小尺寸、高表面积比和易修饰等特点,可增强传感器的灵敏度、传感速率和信噪比。Janus微/纳米颗粒不仅拥有纳米材料的所有特性,还能凭借不同基础材料和不对称结构拥有更好的信噪比和多种特性(如电学、磁学、光学和表面化学等)[23,67]。在光学传感方面,大多Janus微/纳米颗粒可以基于修饰荧光探针和比色来进行生物传感[17,68]。WAN等[37]建了一种基于金纳米团簇-二氧化硅组成并负载有葡萄糖氧化酶和甲胎蛋白抗体的Janus荧光微/纳米颗粒,该Janus纳米荧光探针实现了葡萄糖和甲胎蛋白的双重检测。DUAN等[69]也通过种子生成法合成哑铃型钯-氧化铁Janus纳米颗粒,其可作为一种过氧化物酶用于比色测量生物硫醇含量。使用拉曼光谱可对低浓度条件下的有机、无机小分子进行特异性检测。硫化氢是具有多种信号传导作用和生理作用的细胞内气体递质,WANG等[52]基于暗场光散射成像构建了各向异性金银 Janus等离子体纳米探针,在硫化氢存在下银颗粒容易氧化为硫化银,从而导致Janus纳米颗粒在纵向局域表面的等离子体共振性质发生变化,表现出显著且特异的散射颜色变化和光谱偏移,这种Janus纳米探针不仅表现出令人满意的抗干扰能力和线性关系,而且硫化氢检测限也低至0.11 nmol/L,这为细胞内硫化氢的等离子体检测和硫化氢相关的生物信号传导研究铺平了道路。 综上所述,Janus微/纳米颗粒可在药物递送、癌症治疗、组织工程、生物影像和传感广泛应用,而且以有机-无机复合颗粒为主,种类繁多,见表3,4。"
| [1] WANG QQ, ZHOU R, SUN JZ, et al. Naturally Derived Janus Cellulose Nanomaterials: Anisotropic Cellulose Nanomaterial Building Blocks and Their Assembly into Asymmetric Structures. ACS Nano. 2022; 16(9):13468-13491. [2] ZHANG X, FU Q, DUAN H, et al. Janus Nanoparticles: From Fabrication to (Bio)Applications. ACS Nano. 2021;15(4):6147-6191. [3] DUAN YP, ZHAO X, SUN MM, et al. Research Advances in The Synthesis, Application, Assembly, and Calculation of Janus Materials. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2021;60(3):1071-1095. [4] LIANG W, LE Z, DONG P, et al. Janus Bimetallic Materials as Efficient Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Oxidation and Evolution Reactions. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;625:128-135. [5] LI S, QIU F, XIA Y, et al. Integrating a Self-Floating Janus TPC@CB Sponge for Efficient Solar-Driven Interfacial Water Evaporation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022; 14(17):19409-19418. [6] ZHOU D, TANG X, GUO X, et al. Polyolefin-Based Janus Separator for Rechargeable Sodium Batteries. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020; 59(38):16725-16734. [7] AGABA A, MARRIAM I, TEBYETEKERWA M, et al. Janus Hybrid Sustainable All-cellulose Nanofiber Sponge for Oil-Water Separation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;185:997-1004. [8] ZHANG JJ, WANG CC, XING HW, et al. Advances in Asymmetric Wettable Janus Materials for Oil-Water Separation. Molecules. 2022;27(21):7470. [9] CHEN HB, YAN J, HU SY, et al. Janus Fibre/Sponge Composite Combined with IOPNs Promotes Haemostasis and Efficient Reconstruction in Oral Guided Bone Regeneration. Mater Des. 2022;222:111083. [10] JIANG YX, ZHU CH, MA XX, et al. Janus Hydrogels: Merging Boundaries in Tissue Engineering for Enhanced Biomaterials and Regenerative Therapies. Biomater Sci. 2024;12(10):2504-2520. [11] KIERULF A, ENAYATI M, YAGHOOBI M, et al. Starch Janus Particles: Bulk Synthesis, Self-Assembly, Rheology, and Potential Food Applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(51):57371-57386. [12] LIN J, HE Y, HE Y, et al. Janus Functional Electrospun Polyurethane Fibrous Membranes for Periodontal Tissue Regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11(38):9223-9236. [13] LV S, YUAN X, XIAO J, et al. Hemostasis-Osteogenesis Ntegrated Janus Carboxymethyl chitin/Hydroxyapatite Porous Membrane for Bone Defect Repair. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;313:120888. [14] ZHANG Q, ZHU J, FEI X, et al. A Janus Nanofibrous Scaffold Integrated with Exercise-driven Electrical Stimulation and Nanotopological Effect Enabling the Promotion of Tendon-to-Bone Healing. Nano Today. 2024;55. doi:10.1016/j.nantod.2024.102208 [15] ROCA AG, LOPEZ-BARBERA JF, LAFUENTE A, et al. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (Fe3O4, γ-Fe2O3 and FeO) as Photothermal Heat Mediators in The First, Second and Third Biological Windows. Phys Rep. 2023;1043:1-35. [16] SHAO D, LI J, ZHENG X, et al. Janus “Nano-Bullets” for Magnetic Targeting Liver Cancer Chemotherapy. Biomaterials. 2016;100:118-133. [17] MADADI M, KHOEE S. Magnetite-Based Janus Nanoparticles, Their Synthesis and Biomedical Applications. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2023;15(6):e1908. [18] LI Z, GAO Z, WANG C, et al. Recent Progress on Bioimaging Strategies Based on Janus Nanoparticles. Nanoscale. 2022;14(35):12560-12568. [19] HUANG YJ, LIU D, GUO RR, et al. Intelligent Jellyfish-Type Janus Nanoreactor Targeting Synergistic Treatment of Bacterial Infections. ACS Appl Bio Materi. 2023;6(6):2384-2393. [20] LIU C, HUANG J, XU T, et al. Powering Bioanalytical Applications in Biomedicine with Light-Responsive Janus Micro-/Nanomotors. Microchimica Acta. 2022;189(3):116. [21] YANG Z, WANG L, GAO Z, et al. Ultrasmall Enzyme-Powered Janus Nanomotor Working in Blood Circulation System. ACS Nano. 2023; 17(6):6023-6035. [22] MONTASERI H, ABRAHAMSE H. Targeted Photodynamic Therapy Technique of Janus Nanoparticles on Breast Cancer. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2024;52(1):270-277. [23] KARADKAR S, TIWARI A, CHASKAR AC. Recent Advancements in Janus Nanoparticle-Based Biosensing Platforms. Int Nano Lett. 2023;13(2): 93-115. [24] ALBERT SK, LEE S, DURAI P, et al. Janus Nanosheets with Face-Selective Molecular Recognition Properties from DNA-Peptide Conjugates. Small. 2021;17(12):e2006110. [25] LE TC, ZHAI J, CHIU WH, et al. Janus Particles: Recent Advances in The Biomedical Applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:6749-6777. [26] AZHDARI S, POST Y, TRÖEMER M, et al. Janus Nanoplates, -Bowls, and -Cups: Controlling Size and Curvature via Terpolymer/Homopolymer Blending in 3D Confinement. Nanoscale. 2023;15(36):14896-14905. [27] GEORGITSOPOULOU S, ANGELOPOULOU A, PAPAIOANNOU L, et al. Self-Assembled Janus Graphene Nanostructures with High Camptothecin Loading for Increased Cytotoxicity to Cancer Cells. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2022;67:102971. [28] DE LEON A, RODIER BJ, LUO QM, et al. Distinct Chemical and Physical Properties of Janus Nanosheets. Acs Nano. 2017;11(7):7485-7493. [29] YANG S, GUO F, KIRALY B, et al. Microfluidic Synthesis of Multifunctional Janus Particles for Biomedical Applications. Lab Chip. 2012;12(12): 2097-2102. [30] KAEWSANEHA C, TANGBORIBOONRAT P, POLPANICH D, et al. Janus Colloidal Particles: Preparation, Properties, and Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(6):1857-1869. [31] CHENG Q, CHEN J, WAN C, et al. Preparation of Janus Droplets and Hydrogels with Controllable Morphologies by An Aqueous Two-Phase System on The Superamphiphobic Surface. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(44):50434-50443. [32] YANG L, YANG W, XU W, et al. Bio-Inspired Janus Microcarriers with Sequential Actives Release for Bone Regeneration. Chem Eng J. 2023; 476:146797. [33] 鲍艳,项茹.功能性Janus纳米颗粒的研究进展[J].精细化工, 2024,41(4):697-706,39. [34] GUO J, LI Y, WANG B, et al. Self-Propelled Janus Nanomotor as Active Probe for Detection of Pepsinogen by Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Mikrochim Acta. 2022;189(12):468. [35] MILIAN YE, CLAROS M, USHAK S, et al. Silica Based Janus Nanoparticles: Synthesis Methods, Characterization, and Applications. Appl Mater Today. 2023;34:101901. [36] WANG J, WANG Z, LI L, et al. Ultra-Small Janus Nanoparticle-Induced Activation of Ferroptosis for Synergistic Tumor Immunotherapy. Acta Biomater. 2024;181:362-374. [37] WAN W, REN XL, TAN JR, et al. Preparation of Janus Fluorescent Probe Based on An Asymmetrical Silica and Its Application in Glucose and Alpha-fetoprotein Detection. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11(28):6664-6670. [38] WANG Z, ZHANG F, SHAO D, et al. Janus Nanobullets Combine Photodynamic Therapy and Magnetic Hyperthermia to Potentiate Synergetic Anti-Metastatic Immunotherapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019; 6(22):1901690. [39] ZUO S, WANG J, AN X, et al. Janus Magnetic Nanoplatform for Magnetically Targeted and Protein/Hyperthermia Combination Therapies of Breast Cance. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:763486. [40] ZHU X, LI K, LI J, et al. Physicochemical Properties and Antibacterial Property of Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Smart Janus Nanospheres. Food Chem. 2024;451:139413. [41] KHOEE S, BAKVAND PM. Synthesis of Dual-Responsive Janus Nanovehicle via PNIPAm Modified SPIONs Deposition on Crosslinked Chitosan Microparticles and Decrosslinking Process in The Core. Eur Polym J. 2019;114: 411-425. [42] URBAN M, FREISINGER B, GHAZY O, et al. Polymer Janus Nanoparticles with Two Spatially Segregated Functionalizations. Macromolecules. 2014;47(20):7194-7199. [43] 王端达,沈欣怡,宋永杨,等.新兴Janus颗粒在油水分离中的应用进展[J].化学学报,2023,81(9):1187-1195. [44] SONG Q, CHAO Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Controlled Formation of All-Aqueous Janus Droplets by Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation of an Aqueous Three-Phase System. J Phys Chem B. 2021;125(2):562-570. [45] SAQIB M, TRAN PA, ERCAN B, et al. Microfluidic Methods in Janus Particle Synthesis. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:4355-4366. [46] SAQIB M, ERCAN B, ERDEM EY. Synthesis of Anisotropic Magnetic Polymeric Janus Particles by In Situ Separation of Magnetic Nanoparticles in A Microfluidic Device. Langmuir. 2023;39(48):17080-17087. [47] FENG ZY, LIU TT, SANG ZT, et al. Microfluidic Preparation of Janus Microparticles with Temperature and pH Triggered Degradation Properties. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:756758. [48] CHEN K, PENG X, DANG M, et al. General Thermodynamic-Controlled Coating Method to Prepare Janus Mesoporous Nanomotors for Improving Tumor Penetration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(43): 51297-51311. [49] TAMAROV K, SVIRIDOV A, XU W, et al. Nano Air Seeds Trapped in Mesoporous Janus Nanoparticles Facilitate Cavitation and Enhance Ultrasound Imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(40):35234-35243. [50] ZHANG X, WANG W, SU L, et al. Plasmonic-Fluorescent Janus Ag/Ag2S Nanoparticles for In Situ H2O2-Activated NIR-II Fluorescence Imaging. Nano Lett. 2021;21(6):2625-2633. [51] MORIS H, GHAEE A, KARIMI M, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Pullulan-Based Nanocomposite Scaffold Incorporating Ag-Silica Janus Particles for Bone Tissue Engineering. Biomater Adv. 2022;135:212733. [52] WANG J, LUO D, CAI Y, et al. A Plasmonic Au-Ag Janus Nanoprobe for Monitoring Endogenous Hydrogen Sulfide Generation in Living Cells. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;213:114422. [53] WEI R, FU G, LI Z, et al. Au-Fe3O4 Janus Nanoparticles for Imaging-Guided Near Infrared-Enhanced Ferroptosis Therapy in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2024;663:644-655. [54] XING Y, ZHOU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Facile Fabrication Route of Janus Gold-Mesoporous Silica Nanocarriers with Dual-Drug Delivery for Tumor Therapy. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(3):1573-1581. [55] LI X, LI Y, YU C, et al. ROS-Responsive Janus Au/Mesoporous Silica Core/Shell Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Long-Term CT Imaging Tracking of MSCs in Pulmonary Fibrosis Treatment. ACS Nano. 2023; 17(7):6387-6399. [56] DÍEZ P, LUCENA-SÁNCHEZ E, ESCUDERO A, et al. Ultrafast Directional Janus Pt-Mesoporous Silica Nanomotors for Smart Drug Delivery. ACS Nano. 2021;15(3):4467-4480. [57] YU S, WANG Y, HE P, et al. Effective Combinations of Immunotherapy and Radiotherapy for Cancer Treatment. Front Oncol. 2022;12:809304. [58] NOSRATI H, GHAFFARLOU M, SALEHIABAR M, et al. Magnetite and Bismuth Sulfide Janus Heterostructures as Radiosensitizers for in Vivo Enhanced Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer. Biomater Adv. 2022;140: 213090. [59] ZHANG XY, GE HY, MA YL, et al. Engineered Anti-Cancer Nanomedicine for Synergistic Ferroptosis-Immunotherapy. Chem Eng J. 2023;455: 140688. [60] WANG WJ, MA EH, TAO PY, et al. Chemical-NIR Dual-Powered CuS/Pt Nanomotors for Tumor Hypoxia Modulation, Deep Tumor Penetration and Augmented Synergistic Phototherapy. J Mater Sci Technol. 2023; 148:171-185. [61] CHEN T, YANG J, ZHAO H, et al. Ultrasound-Propelled Nanomotors for Efficient Cancer Cell Ferroptosis. J Mater Chem B. 2024;12(3):667-677. [62] DING X, WANG T, BAI S, et al. Multifunction in One Nanoparticle for Anticancer Therapy: Bowl-Shaped Au@PDA Yolk-Shell NPs. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(24):27733-27742. [63] CHEN X, HOU M, ZHANG X, et al. Active Targeted Janus Theranostic Nanoplatforms Enable Chemo-Photothermal Therapy to Inhibit The Growth of Breast Cancer. Mol Pharm. 2023;20(11):5800-5810. [64] WANG ZF, WANG M, QIAN YR, et al. Dual-Targeted Nanoformulation with Janus Structure for Synergistic Enhancement of Sonodynamic Therapy and Chemotherapy. Chin Chem Lett. 2023;34(7):107853. [65] LIU L, LI S, YANG K, et al. Drug-Free Antimicrobial Nanomotor for Precise Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Infections. Nano Lett. 2023;23(9):3929-3938. [66] GUI H, YANG T, LI LL, et al. Temperature-Sensitive Anti-Inflammatory Organohydrogels Containing Janus Particle Stabilized Phase-Change Microinclusions. ACS Nano. 2022;16(6):9859-9870. [67] PANIAGUA G, VILLALONGA A, EGUíLAZ M, et al. Amperometric Aptasensor for Carcinoembryonic Antigen Based on The Use of Bifunctionalized Janus Nanoparticles as Biorecognition-Signaling Element. Anal Chim Acta. 2019;1061:84-91. [68] RUSSELL SM, ALBA-PATIÑO A, BORGES M, et al. Multifunctional Motion-to-Tolor Janus Transducers for The Rapid Detection of Sepsis Biomarkers in Whole Blood. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;140:154-160. [69] DUAN W, QIU Z, CAO S, et al. Pd-Fe3O4 Janus Nanozyme with Rational Design for Ultrasensitive Colorimetric Detection of Biothiols. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;196:113724. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Cao Yue, Ye Xinjian, Li Biyao, Zhang Yining, Feng Jianying. Effect of extracellular vesicles for diagnosis and therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1523-1530. |
| [3] | Sun Yuting, Wu Jiayuan, Zhang Jian. Physical factors and action mechanisms affecting osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1531-1540. |
| [4] | Li Shuai, Liu Hua, Shang Yonghui, Liu Yicong, Zhao Qihang, Liu Wen. Stress distribution on the maxilla when wearing the Twin-block appliance for Class II malocclusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 881-887. |
| [5] | Ding Zhili, Huang Jie, Jiang Qiang, Li Tusheng, Liu Jiang, Ding Yu. Constructing rabbit intervertebral disc degeneration models by different methods under X-ray guidance: a comparative study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 995-1002. |
| [6] | Xiao Fang, Huang Lei, Wang Lin. Magnetic nanomaterials and magnetic field effects accelerate bone injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 827-838. |
| [7] | Wang Sifan, He Huiyu, Yang Quan, Han Xiangzhen. miRNA-378a overexpression of macrophage cell line composite collagen sponge: anti-inflammation and tissue repair promotion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 789-799. |
| [8] | Li Mingzhe, Ye Xiangling, Wang Bing, Yu Xiang. Preparation and osteogenic properties of liquid crystal display light-cured polylactic acid scaffold loaded with nano-tantalum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 670-677. |
| [9] | Yu Shuangqi, Ding Fan, Wan Song, Chen Wei, Zhang Xuejun, Chen Dong, Li Qiang, Lin Zuoli. Effects of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer/lysine-grafted graphene oxide nanoparticle composite scaffolds on osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 707-712. |
| [10] | Dang Xiaowen, Huang Hailiang, Huang Lei, Wang Yajie . Research frontiers and hotspots of carbon nanomaterials in biomedical field over the past 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 752-760. |
| [11] | Ren Bo, Tang Yongliang, Li Ni, Liu Bangding. Thermosensitive antibacterial hydrogel for treatment of infected bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7269-7277. |
| [12] | Zhang Fei, Zuo Jun. Inhibition of hypertrophic scar in rats by beta-sitosterol-laden mesoporous silica nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7301-7309. |
| [13] | Pan Chun, Fan Zhencheng, Hong Runyang, Shi Yujie, Chen Hao. Effect and mechanism of polystyrene microplastics on prostate in male mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7353-7361. |
| [14] | Wang Guanyuan, Li Wenli, Liu Jinglin, Zhang Jie. Development and application of fully automated intelligent intravenous medication dispensing robot ML300 in Pharmacy Intravenous Admixture Services [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7362-7368. |
| [15] | Chen Jing, Zhang Nan, Meng Qinghua, Bao Chunyu. Material characterization of finite element computational models of knee joints at different ages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7369-7375. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||