Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (23): 5013-5021.doi: 10.12307/2025.084
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hot topics on exosomes as drug delivery system in central nervous system diseases
Lin Huijie1, Huang Yun1, Huang Zhihua2, 3, Jiang Lixia2, 4
- 1First Clinical Medical School of Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China; 2Key Laboratory of Ministry of Education for Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China; 3School of Basic Medicine, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China; 4Clinical Laboratory of First Affiliated Hospital, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Received:2023-12-19Accepted:2024-05-17Online:2025-08-18Published:2024-09-30 -
Contact:Jiang Lixia, Master’s supervisor, Professor, Key Laboratory of Ministry of Education for Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China; Clinical Laboratory of First Affiliated Hospital, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Lin Huijie, Master candidate, First Clinical Medical School of Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:Open Project of Key Laboratory of Ministry of Education for Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases of Gannan Medical University, No. XN201921 (to JLX); Jiangxi Provincial Health Commission Project, No. 202130621 (to JLX); Graduate Innovation Special Fund Project, No. YC2023-S939 (to LHJ); Graduate Innovation Special Fund Project, No. YC2022-S964 (to HY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lin Huijie, Huang Yun, Huang Zhihua, Jiang Lixia. Hot topics on exosomes as drug delivery system in central nervous system diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 5013-5021.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
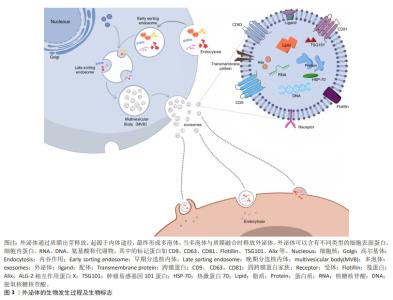
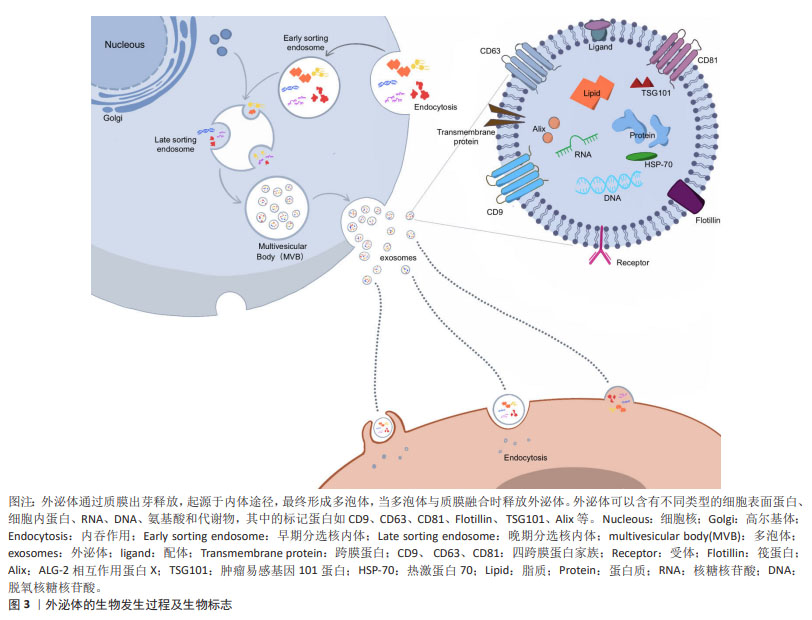
2.2 外泌体的生物学特性 外泌体直径在30-200 nm且具有与细胞相同的脂质双层膜结构,是富含特定蛋白质、脂质、核酸及各种代谢物的细胞外囊泡。外泌体合成首先是细胞膜内陷形成早期内泌体,早期内泌体进一步内陷包裹细胞质中的蛋白质、脂质和核酸,形成包含腔内囊泡的多泡体,当多泡体与质膜融合时,这些内部囊泡被释放为外泌体。外泌体与靶细胞特异性结合后通过内吞作用或膜融合被内化,这通常会影响细胞表型的变化。几乎所有的真核细胞都能分泌外泌体,外泌体携带其内容物调节受体细胞功能,并且在人类健康和疾病的许多方面都发挥着重要作用,包括发育、免疫、组织稳态、癌症和神经退行性疾病[19]。目前运用外泌体治疗更多还是基于内源性分泌的外泌体,可以潜在地作为无细胞疗法,用于产生耐受性免疫反应,以治疗自身免疫和中枢神经系统疾病[20]。由于具有治疗潜力,外泌体可以通过多种方式进行工程化设计,有效地将活性药物成分输送到各种靶器官、组织和细胞[21]。外泌体的发生及表面标志见图3。"
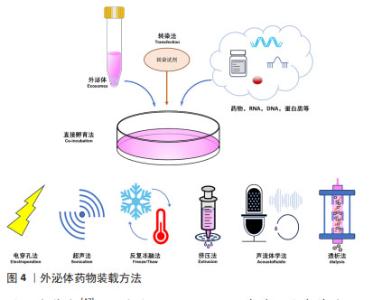
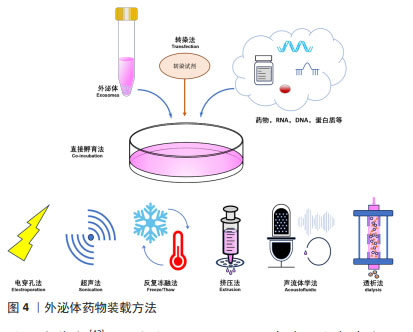
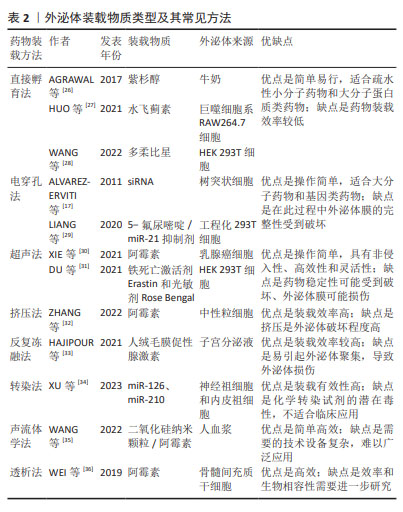
2.3 外泌体载药系统的构建 药物分子装载方法可分为内源装载和外源装载两大类,前者通过对亲本细胞进行修饰改造,而实现外泌体的药物装载;后者则是对纯化后外泌体通过物理以及化学等方法进行药物装载,具体包括直接孵育法、电穿孔法、超声法、挤压法、冻融法、转染、声流体学法和透析法等。内源装载是在收集纯化外泌体之前对亲本细胞进行干预,为外泌体的预培养,通常通过改变亲本细胞的培养条件将装载药物预先装载至亲本细胞,然后再收集处理过的细胞所产生的外泌体。孵育是最常见的方法,可用于外源性和内源性药物加载,这些疏水性或小分子药物可以直接与外泌体共孵育,而亲水性化合物不能被动通过脂质囊泡,因此,电穿孔、超声、挤压和冻融方法可以在外泌体膜上产生孔隙,以允许亲水性药物进入[22]。相较于外源装载,内源装载存在药物转染进入细胞的不确定性、药物浓度难以把控的问题,其应用普遍性不高。为了能更好地发挥外泌体载药后的治疗准确性,可以通过对外泌体进行工程化表面修饰来提高对中枢神经系统疾病的靶向性。外泌体载体的表面修饰分为基因工程、共价修饰、非共价修饰,通过短肽、响应性靶向及磁性靶向等修饰细胞外囊泡构建的外泌体载药系统[23-25],可以使其生物学功能及靶向更加稳定。外泌体装载药物类型及方法见表2及图4。"
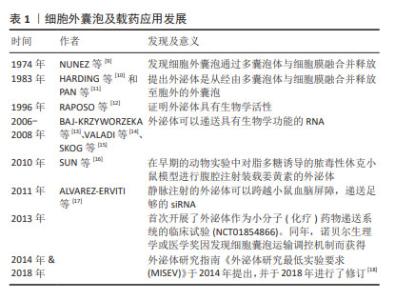
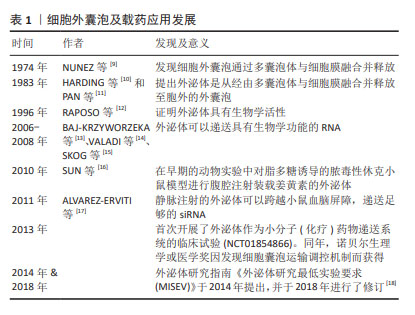
| [1] JIANG S, LIANG J, LI W, et al. The role of CXCL1/CXCR2 axis in neurological diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;120:110330. [2] FAN Y, CHEN Z, ZHANG M. Role of exosomes in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of central nervous system diseases. J Transl Med. 2022;20:291. [3] GUO M, WANG J, ZHAO Y, et al. Microglial exosomes facilitate alpha-synuclein transmission in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2020;143: 1476-1497. [4] ARIENTI G, CARLINI E, VERDACCHI R, et al. Prostasome to sperm transfer of CD13/aminopeptidase N (EC 3.4.11.2). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1336(3):533-538. [5] FRENETTE G, SULLIVAN R. Prostasome-like particles are involved in the transfer of P25b from the bovine epididymal fluid to the sperm surface. Mol Reprod Dev. 2001;59(1):115-121. [6] ZHOU H, YUEN PS, PISITKUN T, et al. Collection, storage, preservation, and normalization of human urinary exosomes for biomarker discovery. Kidney Int. 2006;69(8):1471-1476. [7] BATRAKOVA EV, KIM MS. Using exosomes, naturally-equipped nanocarriers, for drug delivery. J Control Release. 2015;219:396-405. [8] AHN SY, SUNG DK, KIM YE, et al. Brain-derived neurotropic factor mediates neuroprotection of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles against severe intraventricular hemorrhage in newborn rats. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021;10(3):374-384. [9] NUNEZ EA, WALLIS J, GERSHON MD. Secretory processes in follicular cells of the bat thyroid. 3. The occurrence of extracellular vesicles and colloid droplets during arousal from hibernation. Am J Anat. 1974;141(2):179-201. [10] HARDING C, HEUSER J, STAHL P. Receptor-mediated Endocytosis of Transferrin and of the Transferrin Receptor in Rat Reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983;97(2):329-339. [11] PAN BT, JOHNSTONE RM. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: selective externalization of the receptor. Cell. 1983;33(3):967-978. [12] RAPOSO G, NIJMAN HW, STOORVOGEL W, et al. B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med. 1996;183(3):1161-172. [13] BAJ-KRZYWORZEKA M, SZATANEK R, WEGLARCZYK K, et al. Tumour-derived microvesicles carry several surface determinants and mRNA of tumour cells and transfer some of these determinants to monocytes. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006;55(7):808-818. [14] VALADI H, EKSTRÖM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659. [15] SKOG J, WÜRDINGER T, VAN RIJN S, et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(12):1470-1476. [16] SUN D, ZHUANG X, XIANG X, et al. A Novel Nanoparticle Drug Delivery System: The Anti-inflammatory Activity of Curcumin Is Enhanced When Encapsulated in Exosomes. Mol Ther. 2010;18:1606-1614. [17] ALVAREZ-ERVITI L, SEOW Y, YIN H, et al. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(4):341-345. [18] THÉRY C, WITWER KW, AIKAWA E, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750. [19] PEGTEL DM, GOULD SJ. Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88: 487-514. [20] RIAZIFAR M, MOHAMMADI MR, PONE EJ, et al. Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as Nanotherapeutics for Autoimmune and Neurodegenerative Disorders. ACS Nano. 2019;13:6670-6688. [21] CHOI H, CHOI Y, YIM HY, et al. Biodistribution of Exosomes and Engineering Strategies for Targeted Delivery of Therapeutic Exosomes. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18:499-511. [22] MEHRYAB F, RABBANI S, SHAHHOSSEINI S, et al. Exosomes as a next-generation drug delivery system: An update on drug loading approaches, characterization, and clinical application challenges. Acta Biomater. 2020;113:42-62. [23] GUO L, HUANG Z, HUANG L, et al. Surface-modified engineered exosomes attenuated cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting the delivery of quercetin towards impaired neurons. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):141. [24] MA D, SHEN H, CHEN F, et al. Inflammatory Microenvironment-Responsive Nanomaterials Promote Spinal Cord Injury Repair by Targeting IRF5. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11:e2201319. [25] KIM HY, KUMAR H, JO MJ, et al. Therapeutic Efficacy-Potentiated and Diseased Organ-Targeting Nanovesicles Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Spinal Cord Injury Treatment. Nano Lett. 2018;18(8):4965-4975. [26] AGRAWAL AK, AQIL F, JEYABALAN J, et al. Milk-derived exosomes for oral delivery of paclitaxel. Nanomedicine. 2017;13(5):1627-1636. [27] HUO Q, SHI Y, QI Y, et al. Biomimetic silibinin-loaded macrophage-derived exosomes induce dual inhibition of Abeta aggregation and astrocyte activation to alleviate cognitive impairment in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;129: 112365. [28] WANG C, LI N, LI Y, et al. Engineering a HEK-293T exosome-based delivery platform for efficient tumor-targeting chemotherapy/internal irradiation combination therapy. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):247. [29] LIANG G, ZHU Y, ALI DJ, et al. Engineered exosomes for targeted co-delivery of miR-21 inhibitor and chemotherapeutics to reverse drug resistance in colon cancer. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):10. [30] XIE X, LIAN S, ZHOU Y, et al. Tumor-derived exosomes can specifically prevent cancer metastatic organotropism. J Control Release. 2021; 331:404-415. [31] DU J, WAN Z, WANG C, et al. Designer exosomes for targeted and efficient ferroptosis induction in cancer via chemo-photodynamic therapy. Theranostics. 2021;11:8185-8196. [32] ZHANG J, JI C, ZHANG H, et al. Engineered neutrophil-derived exosome-like vesicles for targeted cancer therapy. Sci Adv. 2022;8: eabj8207. [33] HAJIPOUR H, FARZADI L, ROSHANGAR L, et al. A human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) delivery platform using engineered uterine exosomes to improve endometrial receptivity. Life Sci. 2021;275: 119351. [34] XU X, ZHANG H, LI J, et al. Combination of EPC-EXs and NPC-EXs with miR-126 and miR-210 overexpression produces better therapeutic effects on ischemic stroke by protecting neurons through the Nox2/ROS and BDNF/TrkB pathways. Exp Neurol. 2023;359:114235. [35] WANG Z, RICH J, HAO N, et al. Acoustofluidics for simultaneous nanoparticle-based drug loading and exosome encapsulation. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2022;8:45. [36] WEI H, CHEN J, WANG S, et al. A Nanodrug Consisting Of Doxorubicin And Exosome Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells For Osteosarcoma Treatment In Vitro. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:8603-8610. [37] FEIGIN VL, STARK BA, JOHNSON CO, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20:795-820. [38] ZHOU M, WANG H, ZENG X, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2019;394:1145-1158. [39] BENJAMIN EJ, BLAHA MJ, CHIUVE SE, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;135:e146-e603. [40] CUN Y, JIN Y, WU D, et al. Exosome in Crosstalk between Inflammation and Angiogenesis: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Stroke. Mediators Inflamm. 2022;2022:7006281. [41] XIA Y, LING X, HU G, et al. Small extracellular vesicles secreted by human iPSC-derived MSC enhance angiogenesis through inhibiting STAT3-dependent autophagy in ischemic stroke. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):313. [42] FORRO T, BAJKO Z, BALASA A, et al. Dysfunction of the Neurovascular Unit in Ischemic Stroke: Highlights on microRNAs and Exosomes as Potential Biomarkers and Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):5621. [43] LI Y, TANG Y, YANG GY. Therapeutic application of exosomes in ischaemic stroke. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2021;6:483-495. [44] ZHANG Y, LIU J, SU M, et al. Exosomal microRNA-22-3p alleviates cerebral ischemic injury by modulating KDM6B/BMP2/BMF axis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:111. [45] YANG H, TU Z, YANG D, et al. Exosomes from hypoxic pre-treated ADSCs attenuate acute ischemic stroke-induced brain injury via delivery of circ-Rps5 and promote M2 microglia/macrophage polarization. Neurosci Lett. 2022;769:136389. [46] ZHANG H, WU J, WU J, et al. Exosome-mediated targeted delivery of miR-210 for angiogenic therapy after cerebral ischemia in mice. J Nanobiotechnology. 2019;17:29. [47] HU H, HU X, LI L, et al. Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Angiogenesis in Ischemic Stroke Mice via Upregulation of MiR-21-5p. Biomolecules. 2022;12(7):883. [48] TIAN T, ZHANG HX, HE CP, et al. Surface functionalized exosomes as targeted drug delivery vehicles for cerebral ischemia therapy. Biomaterials. 2018;150:137-149. [49] 雒慧钧,黄芷璇,史一杰.功能化外泌体载人参皂苷Rg1治疗缺血性脑卒中[J].生物工程学报,2023,39(1):275-285. [50] 齐梓彤,刘薇,雒慧钧,等.负载丹皮酚外泌体对缺血性脑卒中大鼠线粒体功能障碍的保护作用[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2023,39(4):615-621. [51] REZA-ZALDIVAR EE, HERNANDEZ-SAPIENS MA, GUTIERREZ-MERCADO YK, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote neurogenesis and cognitive function recovery in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14:1626-1634. [52] LOSURDO M, PEDRAZZOLI M, D’AGOSTINO C, et al. Intranasal delivery of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles exerts immunomodulatory and neuroprotective effects in a 3xTg model of Alzheimer’s disease. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020;9: 1068-1084. [53] CONE AS, YUAN X, SUN L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate Alzheimer’s disease-like phenotypes in a preclinical mouse model. Theranostics. 2021;11:8129-8142. [54] LEE M, BAN JJ, YANG S, et al. The exosome of adipose-derived stem cells reduces β-amyloid pathology and apoptosis of neuronal cells derived from the transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Research. 2018;1691:87-93. [55] LIU H, JIN M, JI M, et al. Hypoxic pretreatment of adipose-derived stem cell exosomes improved cognition by delivery of circ-Epc1 and shifting microglial M1 M2 polarization in an Alzheimer’s disease mice model. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(7):3070-3083. [56] WANG X, YANG G. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes reduce Abeta deposition and improve cognitive function recovery in mice with Alzheimer’s disease by activating sphingosine kinase/sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling pathway. Cell Biol Int. 2021; 45:775-784. [57] DING M, SHEN Y, WANG P, et al. Exosomes Isolated From Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Neuroinflammation and Reduce Amyloid-Beta Deposition by Modulating Microglial Activation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Res. 2018;43:2165-2177. [58] CUI GH, GUO HD, LI H, et al. RVG-modified exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells rescue memory deficits by regulating inflammatory responses in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Immun Ageing. 2019;16:10. [59] HUBER CC, CALLEGARI EA, PAEZ MD, et al. Heat Shock-Induced Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Neural Stem Cells Confer Marked Neuroprotection Against Oxidative Stress and Amyloid-beta-Caused Neurotoxicity. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59:7404-7412. [60] LI N, SHU J, YANG X, et al. Exosomes Derived From M2 Microglia Cells Attenuates Neuronal Impairment and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease Through the PINK1/Parkin Pathway. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:874102. [61] GE X, GUO M, HU T, et al. Increased Microglial Exosomal miR-124-3p Alleviates Neurodegeneration and Improves Cognitive Outcome after rmTBI. Mol Ther. 2020;28:503-522. [62] ZHAI L, SHEN H, SHENG Y, et al. ADMSC Exo-MicroRNA-22 improve neurological function and neuroinflammation in mice with Alzheimer’s disease. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:7513-7523. [63] WEI H, XU Y, CHEN Q, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-223 regulates neuronal cell apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:290. [64] HAO Y, SU C, LIU X, et al. Bioengineered microglia-targeted exosomes facilitate Aβ clearance via enhancing activity of microglial lysosome for promoting cognitive recovery in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomater Adv. 2022;136:212770. [65] WANG H, SUI H, ZHENG Y, et al. Curcumin-primed exosomes potently ameliorate cognitive function in AD mice by inhibiting hyperphosphorylation of the Tau protein through the AKT/GSK-3beta pathway. Nanoscale. 2019;11(15):7481-7496. [66] QI Y, GUO L, JIANG Y, et al. Brain delivery of quercetin-loaded exosomes improved cognitive function in AD mice by inhibiting phosphorylated tau-mediated neurofibrillary tangles. Drug Deliv. 2020;27:745-755. [67] DUTTA S, HORNUNG S, TAHA HB, et al. Biomarkers for parkinsonian disorders in CNS-originating EVs: promise and challenges. Acta Neuropathol. 2023;145(5):515-540. [68] CAI Y, ZHANG MM, WANG M, et al. Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Containing Gli1 Alleviate Microglial Activation and Neuronal Apoptosis In Vitro and in a Mouse Parkinson Disease Model by Direct Inhibition of Sp1 Signaling. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2022;81:522-534. [69] LI Y, LI Z, GU J, et al. Exosomes isolated during dopaminergic neuron differentiation suppressed neuronal inflammation in a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett. 2022;771:136414. [70] SUN T, DING ZX, LUO X, et al. Blood Exosomes Have Neuroprotective Effects in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:3807476. [71] XUE C, LI X, BA L, et al. MSC-Derived Exosomes can Enhance the Angiogenesis of Human Brain MECs and Show Therapeutic Potential in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Aging Dis. 2021;12:1211-1222. [732] REN X, ZHAO Y, XUE F, et al. Exosomal DNA Aptamer Targeting alpha-Synuclein Aggregates Reduced Neuropathological Deficits in a Mouse Parkinson’s Disease Model. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;17:726-740. [73] JIANG Y, LIU J, CHEN L, et al. Serum secreted miR-137-containing exosomes affects oxidative stress of neurons by regulating OXR1 in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 2019;1722:146331. [74] QU M, LIN Q, HUANG L, et al. Dopamine-loaded blood exosomes targeted to brain for better treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J Control Release. 2018;287:156-166. [75] MOBAHAT M, SADRODDINY E, NOOSHABADI VT, et al. Curcumin-loaded human endometrial stem cells derived exosomes as an effective carrier to suppress alpha-synuclein aggregates in 6OHDA-induced Parkinson’s disease mouse model. Cell Tissue Bank. 2023;24:75-91. [76] PENG H, LI Y, JI W, et al. Intranasal Administration of Self-Oriented Nanocarriers Based on Therapeutic Exosomes for Synergistic Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Nano. 2022;16:869-884. [77] MOBAHAT M, SADRODDINY E, NOOSHABADI VT, et al. Curcumin-loaded human endometrial stem cells derived exosomes as an effective carrier to suppress alpha-synuclein aggregates in 6OHDA-induced Parkinson’s disease mouse model. Cell Tissue Bank. 2022;24(1):75-91. [78] LUO S, SUN X, HUANG M, et al. Enhanced Neuroprotective Effects of Epicatechin Gallate Encapsulated by Bovine Milk-Derived Exosomes against Parkinson’s Disease through Antiapoptosis and Antimitophagy. J Agric Food Chem. 2021;69:5134-5143. [79] HUTSON TH, DI GIOVANNI S. The translational landscape in spinal cord injury: focus on neuroplasticity and regeneration. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15:732-745. [80] LI L, MU J, ZHANG Y, et al. Stimulation by Exosomes from Hypoxia Preconditioned Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Facilitates Mesenchymal Stem Cells Angiogenic Function for Spinal Cord Repair. ACS Nano. 2022;16:10811-10823. [81] SABAAWY HE, LANKFORD KL, ARROYO EJ, et al. Intravenously delivered mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes target M2-type macrophages in the injured spinal cord. PLoS One. 2018;13(1):e0190358. [82] HUANG JH, YIN XM, XU Y, et al. Systemic Administration of Exosomes Released from Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Attenuates Apoptosis, Inflammation, and Promotes Angiogenesis after Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. J Neurotrauma. 2017;34(24):3388-3396. [83] LI D, ZHANG P, YAO X, et al. Exosomes Derived From miR-133b-Modified Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Recovery After Spinal Cord Injury. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:845. [84] LAI X, WANG Y, WANG X, et al. miR-146a-5p-modified hUCMSC-derived exosomes facilitate spinal cord function recovery by targeting neurotoxic astrocytes. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):487. [85] RAN N, LI W, ZHANG R, et al. Autologous exosome facilitates load and target delivery of bioactive peptides to repair spinal cord injury. Bioact Mater. 2023;25:766-782. [86] QIN T, LI C, XU Y, et al. Local delivery of EGFR+NSCs-derived exosomes promotes neural regeneration post spinal cord injury via miR-34a-5p/HDAC6 pathway. Bioact Mater. 2024;33:424-443. [87] GUAN P, FAN L, ZHU Z, et al. M2 microglia-derived exosome-loaded electroconductive hydrogel for enhancing neurological recovery after spinal cord injury. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):8. [88] MCNEILL KA. Epidemiology of Brain Tumors. Neurol Clin. 2016;34(4): 981-998. [89] ZHU L, OH JM, GANGADARAN P, et al. Targeting and Therapy of Glioblastoma in a Mouse Model Using Exosomes Derived From Natural Killer Cells. Front Immunol. 2018;9:824. [90] SERPE C, MONACO L, RELUCENTI M, et al. Microglia-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Reduce Glioma Growth by Modifying Tumor Cell Metabolism and Enhancing Glutamate Clearance through miR-124. Cells. 2021;10;10(8):2066. [91] HUO H, YANG S, WU H, et al. Brain endothelial cells-derived extracellular vesicles overexpressing ECRG4 inhibit glioma proliferation through suppressing inflammation and angiogenesis. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;15(12):1162-1171. [92] WANG J, TANG W, YANG M, et al. Inflammatory tumor microenvironment responsive neutrophil exosomes-based drug delivery system for targeted glioma therapy. Biomaterials. 2021;273:120784. [93] KIMIZ-GEBOLOGLU I, ONCEL SS. Exosomes: Large-scale production, isolation, drug loading efficiency, and biodistribution and uptake. J Control Release. 2022;347:533-543. [94] SILVA AKA, MORILLE M, PIFFOUX M, et al. Development of extracellular vesicle-based medicinal products: a position paper of the group “Extracellular Vesicle translation to clinicaL perspectiVEs – EVOLVE France”. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;179:114001. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [3] | Su Xiaoyang, Chen Wenting, Fu Yidan, Zhao Yan, Lan Danfeng, Yang Qiuping. Correlation between Mer receptor tyrosine kinase and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Sprague-Dawley rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1593-1599. |
| [4] | Li Kaiying, Wei Xiaoge, Song Fei, Yang Nan, Zhao Zhenning, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng. Mechanism of Lijin manipulation regulating scar formation in skeletal muscle injury repair in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [5] | Li Jun, Gong Jingjing, Sun Guobin, Guo Rui, Ding Yang, Qiang Lijuan, Zhang Xiaoli, Fang Zhanhai . miR-27a-3p promotes the proliferation of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts by regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1609-1617. |
| [6] | Li Huayuan, Li Chun, Liu Junwei, Wang Ting, Li Long, Wu Yongli. Effect of warm acupuncture on PINK1/Parkin pathway in the skeletal muscle of rats with chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| [7] | Jing Ruyi, Chen Yingxin, Cao Lei . Prognosis of deep lamellar keratoplasty versus penetrating keratoplasty in the treatment of stromal corneal dystrophy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1626-1633. |
| [8] | Wang Xuanqiang, Zhang Wenyang, Li Yang, Kong Weiqian, Li Wei, Wang Le, Li Zhongshan, Bai Shi. Effects of chronic exposure to low-frequency pulsed magnetic fields on contractility and morphology of the quadriceps muscle in healthy adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1634-1642. |
| [9] | Zhang Yuxin, Yu Cong, Zhang Cui, Ding Jianjun, Chen Yan. Differences in postural control ability between older adults with mild cognitive impairment and those with normal cognition under different single-task and dual-task conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1643-1649. |
| [10] | Zhou Panpan, Cui Yinglin, Zhang Wentao, Wang Shurui, Chen Jiahui, Yang Tong . Role of cellular autophagy in cerebral ischemic injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [11] | Yu Jingbang, Wu Yayun. Regulatory effect of non-coding RNA in pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [12] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [13] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [14] | Yuan Weibo, Liu Chan, Yu Limei. Potential application of liver organoids in liver disease models and transplantation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [15] | Wang Yida, Liu Jun, Wang Xiaoling, Wang Liyan, Yang Chengru, Zhang Xuexiao. Effects of wearable electronic device-based interventions on physical activity and sedentary behavior in healthy adolescents: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1693-1704. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||