Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (28): 6094-6100.doi: 10.12307/2025.468
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application characteristics of thermosensitive hydrogels in bone tissue engineering
Liu Yang1, Yang Jilei2, Wang Wenli1, Cui Yingying1, Sun Qihao1, Li Yourui1
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China; 2Dezhou Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Dezhou 253000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-05-16Accepted:2024-07-20Online:2025-10-08Published:2024-12-07 -
Contact:Li Yourui, Associate chief physician, Department of Prosthodontics, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Liu Yang, Master candidate, Department of Prosthodontics, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Shandong Natural Science Foundation (General Project), No. ZR2023MH039 (to LYR); Dezhou Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Innovation Plan Project, No. DZZY2023015 (to YJL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Yang, Yang Jilei, Wang Wenli, Cui Yingying, Sun Qihao, Li Yourui. Application characteristics of thermosensitive hydrogels in bone tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6094-6100.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
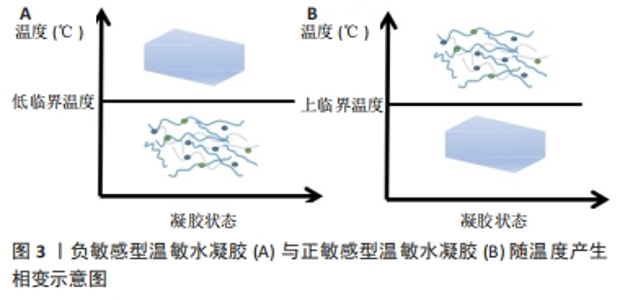
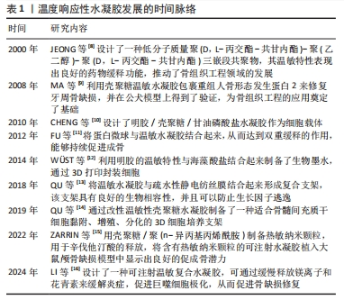
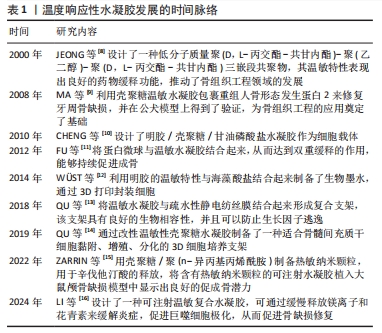
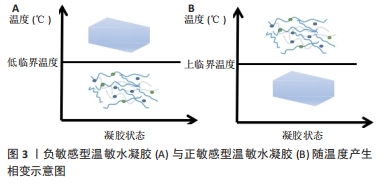
2000年,JEONG等[8]设计了一种低分子质量聚(D,L-丙交酯-共甘内酯)-聚(乙二醇)-聚(D,L-丙交酯-共甘内酯)三嵌段共聚物,其温敏特性表现出良好的药物缓释功能。此后,对于温度响应性水凝胶的研究进入了蓬勃发展阶段。2008年,MA等[9]利用壳聚糖温敏水凝胶包裹重组人骨形态发生蛋白2来修复牙周骨缺损,并在公犬模型上得到了验证,温敏水凝胶在骨组织工程领域得到了初步的应用。随着研究的深入,更多的温敏水凝胶通过细胞封装、药物缓释及生物支架作用来促进骨修复[10-11,13-14]。此外,随着3D打印技术的兴起,以温敏水凝胶制备的生物墨水及其3D打印支架已被广泛应用于骨组织工程[12]。近年来,通过改性制备复合温敏水凝胶,使其成为良好生物相容性、药物缓释功能的生物支架,促进了骨组织工程的发展[15-16]。 2.2 温度响应性水凝胶的凝胶化机制 温度响应性水凝胶的结构中一般同时具有疏水性结构和亲水性结构,而其所表现的温度变化转化特性便来源于2种结构之间的平衡变化。当温度发生变化时,温度响应性水凝胶中亲水与疏水结构之间的平衡发生转变,与水分子之间的作用也发生了改变,最终导致凝胶网络结构的溶解度增高或降低,产生溶胶-凝胶相的转变[17]。温度响应性水凝胶的成胶性能可通过温敏基团的微观机制来实现。温度响应性水凝胶根据其温敏结构可分为负敏感型和正敏感型。 2.2.1 负敏感型水凝胶 负敏感型水凝胶的温度降低到低临界温度以下时,分子链拉伸和打开,使凝胶充分吸收水分,膨胀成液相[17];当加热到低临界温度上方时,凝胶脱水[18],见图3A。YUAN等[19]设计合成的由聚乳酸-乙醇酸和聚乙二醇段合成的三嵌段聚合物[聚(D,L-丙交酯-共甘内酯)-聚(乙二醇)-聚(D,L-丙交酯-共甘内酯]符合上述反应机制,在水溶液中,聚(D,L-丙交酯-共甘内酯)-聚(乙二醇)-聚(D,L-丙交酯-共甘内酯)共聚物能够生成具有高度疏水核(聚乳酸-乙醇酸)和周围由聚乙二醇尾部组成的胶束状结构。通常,在室温下胶束被很好地分离和分布,体系处于溶胶状态,但在较高温度下,由于聚乳酸-乙醇酸段之间的疏水相互作用,胶束尺寸增大并开始聚集,导致凝胶形成。 2.2.2 正敏感型水凝胶 当温度低于某一临界温度时,水凝胶聚合物溶液呈凝胶状,这个阈值极限被定义为上临界温度[20]。在上临界温度附近,温敏聚合物发生相变;当温度低于上临界温度时,材料不溶解;而在上临界温度上方,材料溶解,见图3B。明胶便是正敏感型水凝胶的代表,其相变温度为30 ℃[21],当温度升高到30 ℃以上时呈液相;当温度降到30 ℃以下时,明胶溶液便转化为凝胶状[22]。因此,明胶相关大分子常为较稳定的化学交联,以避免在生理温度时液相化[23]。"
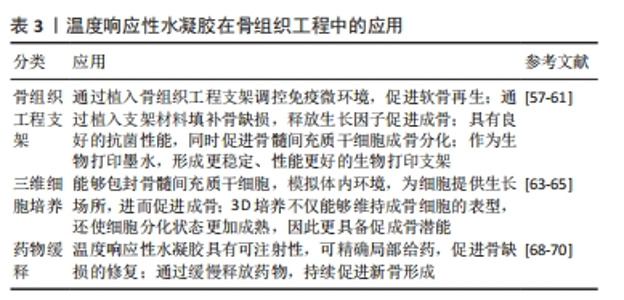
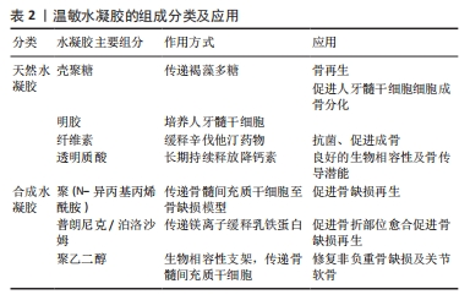
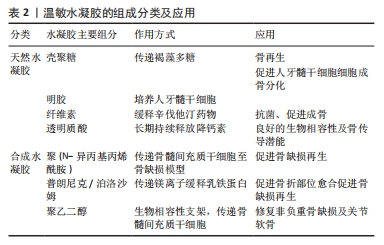
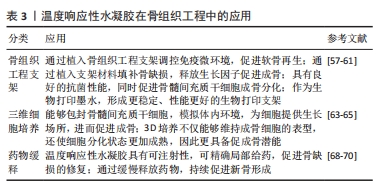
2.3.1 壳聚糖温敏水凝胶 壳聚糖是一种天然多糖,来源于甲壳类动物的外骨骼,本质是甲壳素的脱乙酰化衍生物[24-26]。壳聚糖具有良好的生物相容性、生物降解性和抗菌活性,为组织工程应用提供了广阔的前景。然而,壳聚糖本身并不是温度敏感的聚合物,温敏型凝胶往往是通过在壳聚糖溶液中加入β-甘油磷酸酯来实现的[27-28],该框架在室温下保持流体状态,而在生理温度和pH值下成为凝胶[29]。OHMES等[30]利用壳聚糖、胶原蛋白和β-甘油磷酸制备了一种可注射的温敏水凝胶,用于传递目标药物“褐藻多糖”至损伤部位,该壳聚糖基温敏水凝胶对人骨源间充质干细胞和人生长内皮细胞具有良好的生物相容性,因此可以作为良好的骨组织工程支架。 2.3.2 明胶温敏水凝胶 明胶来源于变性的胶原蛋白,其分子会随着温度的改变产生线圈到螺旋的变化,因此具备温度响应性[31]。SAMIEI等[32]将聚异丙基酰胺-壳聚糖共聚物和明胶混合形成一种可注射温敏水凝胶,结果发现明胶掺入量高的水凝胶的网状结构较其他水凝胶略松散,该温敏水凝胶对人牙髓干细胞具有较高的生物相容性;并且明胶含量高的水凝胶上骨钙素、骨形态发生蛋白2等晚期成骨基因表达量显著增高,可实现口腔组织工程所需的成骨分化。 2.3.3 纤维素温敏水凝胶 植物、海藻、甘蔗渣、被膜类、海藻和细菌是纤维素的主要来源[33]。纤维素具有良好的机械、物理和化学性能,如酸性条件下稳定性高、手性好、拉伸强度高、弹性模量好、密度低或质量轻、生物可降解性良好、表面有丰富的羟基官能团、可进行化学改性、润湿性好等[34]。LI等[35]研究显示,辛伐他汀负载热敏壳聚糖-甘油-羟丙基甲基纤维素水凝胶封装的二氧化钛纳米管是一种很有前景的骨科植入材料,具有良好的体内抗菌活性,同时在正常体温(37 ℃)下该水凝胶以溶胶态存在,有利于辛伐他汀的控释,促进MC3T3-E1成骨细胞的分化。 2.3.4 透明质酸温敏水凝胶 透明质酸是由d-葡萄糖醛酸和n-乙酰-d-葡萄糖胺重复双糖组成的长链无支链多糖。1934年,KARL MEYER和JOHN PALMER首次将其从牛眼的玻璃体中分离出来,但它的结构直到1970年才由LAURENT描述出来[36]。YU等[37]设计了一种由透明质酸和羟丙基几丁质复合而成的可注射温敏水凝胶,该水凝胶系统具有良好的生物相容性及药物缓释作用,其负载的降钙素可实现长达28 d的持续释放,因此具备良好的骨传导潜能。 2.3.5 聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺)温敏水凝胶 基于聚(n-异丙基丙烯酰胺)的水凝胶常被用于与各种天然聚合物相结合形成可注射的水凝胶。REN等[38]通过原子转移自由基聚合技术将聚(n-异丙基丙烯酰胺)与明胶结合在一起形成了可注射的温度响应性水凝胶,该水凝胶在生理温度时发生溶胶-凝胶转化,有利于修复不规则的骨缺损;同时,该水凝胶对骨髓间充质干细胞也具有良好的生物相容性,可有效地承载细胞,促进骨修复。 2.3.6 泊洛沙姆 泊洛沙姆又名普朗尼克,是由聚(环氧乙烷)和聚(环氧丙烷)单元组成的热敏、水溶性三嵌段共聚物,外区域由亲水的聚(环氧乙烷)单元组成,内芯由疏水的聚(环氧丙烷)单元组成,其在低温下更易溶解[39]。由于泊洛沙姆的两亲性,其可以同时携带疏水性和亲水性药物[40-41]。PERUMAL等[42]将镁颗粒和普朗尼克F127与半水硫酸钙和纳米羟基磷灰石结合,制备了一种可注射骨组织再生缺损填充材料,该纳米复合骨移植物对MG63骨肉瘤细胞具有良好的细胞相容性,使细胞提高成骨基因表达量两三倍。PARK等[43]利用泊洛沙默凝胶持续递送乳铁蛋白,该凝胶可缓慢释放乳铁蛋白达72 h,并且有或没有乳铁蛋白的泊洛沙姆均能在72 h提高成骨细胞的活力。 2.3.7 聚乙二醇基温敏水凝胶 亲水性聚乙二醇由于优良的生物相容性是设计和制造合成源的热响应性水凝胶的主要成分。通过将疏水段(如聚酯和多肽)引入聚乙二醇体系中,使得生物可降解和热敏性水凝胶的体内维护可调已得到发展[44]。 聚乙二醇-聚酯共聚物水凝胶:聚乙二醇-聚酯共聚物在低温下可溶于水,形成自由流动的溶胶,随着温度升高可自发形成半固态凝胶;随着温度的进一步升高,凝胶转变为可流动的悬浮体,最终发生宏观相分离[45]。NI等[46-47]先后开发了2种由甲氧基聚乙二醇-聚(?-己内酯)-甲氧基聚乙二醇/胶原/纳米羟基磷灰石和甲氧基聚乙二醇-聚(?-己内酯)-甲氧基聚乙二醇/脱细胞骨基质组成的可注射、可生物降解的水凝胶复合系统,用于修复非负重骨缺损,2种体系均保持了温度响应性的溶胶-凝胶过渡,并表现出良好的体内生物相容性。有报道称,聚(D,L-丙交酯-共甘内酯)-聚(乙二醇)-聚(D,L-丙交酯-共甘内酯)水凝胶包封骨髓间充质干细胞修复关节软骨损伤有效[48]。 聚乙二醇-多肽共聚物水凝胶:多肽基热敏聚合物是由聚乙二醇或聚氧乙烯-聚氧丙烯-聚氧乙烯聚合物作为亲水性成分,多肽如聚丙氨酸、聚丙氨酸-苯丙氨酸、聚γ-乙基-L-谷氨酸或聚(γ-乙基-L-谷氨酸-co-L谷氨酸)作为疏水性段组成[49-50]。QUADIR等[51]采用叠氮-炔环加成法将n -羧氢化物基开环聚合与后功能化反应合成了含胺链的聚乙二醇-多肽共聚物,合成的嵌段共聚物含有胺官能团的多肽段,可自组装成稳定的聚合体,并在一系列相关生物条件下以pH值反应方式降解,这些嵌段共聚物自组装产生纳米尺度的囊泡结构,能够在生理pH值下封装亲水性细胞毒剂(如阿霉素),但在细胞摄取后在核内体pH值水平下自动分解。 聚(有机磷腈)水凝胶:这类聚合物是一种包含聚有机磷腈的聚乙二醇类水凝胶,具有良好的温度响应特性及生物降解性[52]。SEO等[53]设计了一系列具有不同侧链的热敏聚有机磷腈水凝胶,用于连续供应骨形态发生蛋白2,带正电荷的骨形态发生蛋白2通过静电和疏水相互作用与带负电荷的载体聚合物络合,因此,通过改变聚合物水凝胶的性质可以很容易地调整骨形态发生蛋白2的释放行为。 2.4 温度响应性水凝胶在骨组织工程中的应用 支架、细胞、生长因子是骨组织工程成功所需要具备的3个因素[54]。水凝胶由于自身结构特性可注射至骨缺损区域修复不规则骨缺损,同时其内部的三维网格状结构也有利于引入细胞或生长因子,因此可以作为优秀的骨缺损修复支架材料[55]。水凝胶根据交联方式可分为传统水凝胶和刺激响应性水凝胶。传统水凝胶由较强的化学共价键结合而成,不受外界刺激的影响;刺激响应性水凝胶多由非共价相互作用组合而成,如氢键、p-p堆叠、供体-受体相互作用、金属配位和范德华相互作用[56]。以下将以温度响应性水凝胶为例介绍其在骨组织工程中的应用。 2.4.1 骨组织工程支架 温敏水凝胶因多孔结构、温度敏感性以及良好的注射性能广泛应用于骨组织工程。JI等[57]开发了一种巨噬细胞调节和可注射的“构建块”给药系统,由多孔壳聚糖(微球和羟丙基甲壳素(HPCH)水凝胶组成,其中二甲氧基丙烯基甘氨酸封装在热敏壳聚糖水凝胶中,kartogenin (KGN)偶联在多孔壳聚糖微球上,所研制的复合支架能有效调节缺损部位免疫微环境,实现局部巨噬细胞M2极化,从而促进软骨再生。TAN等[58]利用3种温敏壳聚糖水凝胶与碱性成纤维细胞生长因子以及胶原相结合,制备了不同种类的温敏水凝胶支架,分别植入大鼠牙周组织缺损模型,发现与对照组相比,实验组均有更好的成骨潜能。MAKVANDI等[59]以透明质酸为基础开发了一种新型的温度响应可注射水凝胶,该温敏水凝胶的凝胶温度接近人体体温,同时具有良好的抗菌能力和促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的能力,是一种很有潜力的骨组织工程支架材料。 由此可见,温度响应性水凝胶通过“支架”作用使药物及细胞在骨缺损部位得到良好释放,促进了骨的修复与形成。除此之外,随着近些年3D生物打印技术的发展,温度响应性水凝胶也逐渐应用到其中。DUTTA等[60]利用3D生物打印技术,以温度响应性泊洛沙姆407水凝胶为原材料,根尖牙乳头细胞作细胞填充,设计出了一种3D生物打印泊洛沙姆407水凝胶,该水凝胶在低频电磁场中可以有效促进口腔组织再生。然而,一些天然的温敏水凝胶由于力学性能较差难以单独当做生物墨水使用,因此常与其他化合物交联形成更加稳定的物质。MIAO等[61]采用无细胞3D打印法制备出一种甲基丙烯酰明胶、海藻酸钠和生物活性玻璃微球组成的多组分水凝胶,具备均匀的多孔结构及良好的膨胀性能,能够负载骨髓间充质干细胞以及生长因子,促进牙周组织再生。 2.4.2 3D细胞培养平台 水凝胶因自身类似于细胞外基质的结构,允许细胞、生长因子等可溶性因子通过[62];同时,温度响应性水凝胶由于自身的温敏性和可注射性,能适应骨缺损的各种形状,使细胞包埋其中,因此成为了3D细胞培养的良好平台。JI等[63]利用天然基温敏性水凝胶羟丙基几丁质水凝胶包埋培育间充质干细胞,并与3D打印出的聚己内酯支架相结合,制备出了具有高细胞相容性和良好力学性能的混合支架,该混合支架可以通过调节免疫反应促进巨噬细胞向M2型转化,从而达到抗炎、促进成骨的作用。间充质干细胞具有免疫调节能力,能够释放营养因子,但是由于炎症环境的存在,使其在支架上难以存活,而温敏水凝胶为细胞提供了生长的场所,由此可以看出温敏水凝胶是间充质干细胞的良好载体。RéTHORé等[64]通过对羟丙基甲基纤维素水凝胶硅烷化改性,并与硅烷壳聚糖联合制作出一种可注射温敏水凝胶来作为骨形成细胞的培养支架,使用4种不同的成骨细胞在水凝胶中进行3D培养,结果发现不仅保持了成骨细胞的表型,还使细胞获得了更为成熟的分化状态;同时包裹的软骨细胞在动物模型中可保持良好的活力和细胞外基质分泌活动。O’DONNELL等[65]利用光热敏感水凝胶甲基丙烯酸明胶创建了一个同时具有巨噬细胞和间充质干细胞的3D培养系统,相比于2D培养环境,3D培养的模式更能模仿体内环境,通过3D培养的模式也证明了巨噬细胞对骨形成有促进作用。 综上所述,温度响应性水凝胶因为温敏特性、可注射性、3D网络立体结构、良好的生物相容性、可降解性等特点,在3D细胞培养方面有独特的优势。 2.4.3 药物缓释系统 口服给药和静脉给药是临床上最常用的给药方法,但有些治疗药物具有首过效应,易被酶降解,口服起效慢;虽然全身静脉给药起效快,但药物直接流入血液,发生不良反应的概率高[66]。水凝胶具有良好的生物相容性和高度的物理化学调控性,可以通过改变网络的大小或降解速率来轻松控制分子的释放。一些天然或合成的水凝胶聚合物还可根据一定的环境刺激,通过扩散、肿胀或其他释放机制实现缓释给药,因此水凝胶在给药方面有很大的应用[67]。其中温敏水凝胶是一种温度刺激响应材料,它们随环境温度变化发生溶胶-凝胶状态的转变,从而达到缓释药物的效果。AKAY等[68]设计了一种含有催产素的聚(D,L -丙交酯-共甘内酯)缓释微球,然后将该微球加到泊洛沙姆与β-磷酸三钙和羟基磷灰石混合的温敏水凝胶中,形成一种合适的骨移植材料,将该骨移植材料加入到颅骨缺损大鼠模型中可使药缓慢物释放,显著提高新骨形成率与骨密度。PONTREMOLI等[69]通过将热敏聚氨酯基水凝胶与锶取代介孔生物活性玻璃相结合,开发了一种可注射的促进骨延迟愈合的交付平台,用于促成骨Sr2+离子和促进成骨分子n-乙酰半胱氨酸的长期和局部共交付,装载n-乙酰半胱氨酸的锶取代介孔生物活性玻璃保持了Sr2+离子和n-乙酰半胱氨酸的释放特性,显示出持续7 d的离子/药物共给药。FANG等[70]将非类固醇类抗炎药阿司匹林与β-磷酸三钙结合在一起,负载到温敏水凝胶聚n-异丙基丙烯酰胺上,所形成的混合支架通过缓慢释放阿司匹林达到了促进成骨的效果;同时,将混合支架注射到大鼠颅骨缺损模型中,也显示出该材料具有强大的促成骨潜力。 综上所述,通过体内和体外实验证明,温敏水凝胶能够成为一个很好的药物递送平台,可以利用其在接近人体体温时产生凝胶相变的特点,将药物或生长因子负载到水凝胶支架上注射到骨缺损部位,待凝胶化后缓慢释放药物,这样能够有效降低药物毒性,并且达到持续促进成骨的一个效果(表3)。"
| [1] KZHANG M, MATINLINNA JP, TSOI J, et al. Recent developments in biomaterials for long-bone segmental defect reconstruction: A narrative overview. J Orthop Translat. 2020;22:26-33. [2] HO-SHUI-LING A, BOLANDER J, RUSTOM LE, et al. Bone regeneration strategies: Engineered scaffolds, bioactive molecules and stem cells current stage and future perspectives. Biomaterials. 2018;180:143-162. [3] RODDY E, DEBAUN MR, DAOUD-GRAY A, et al. Treatment of critical-sized bone defects: clinical and tissue engineering perspectives. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018;28(3):351-362. [4] WUBNEH A, TSEKOURA EK, AYRANCI C, et al. Current state of fabrication technologies and materials for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2018;80:1-30. [5] CUI ZK, KIM S, BALJON JJ, et al. Microporous methacrylated glycol chitosan-montmorillonite nanocomposite hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):3523. [6] WU S, GAI T, CHEN J, et al. Smart responsive in situ hydrogel systems applied in bone tissue engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1389733. [7] XIAN S, WEBBER MJ. Temperature-responsive supramolecular hydrogels. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(40):9197-9211. [8] JEONG B, BAE YH, KIM SW. Drug release from biodegradable injectable thermosensitive hydrogel of PEG-PLGA-PEG triblock copolymers. J Control Release. 2000;63(1-2):155-163. [9] MA ZW, ZHANG YJ, WU ZF, et al. [A study on the effect of the chitosan thermosensitive hydrogel loading recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 on repairing periodontal defects]. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008;26(1):23-26. [10] CHENG YH, YANG SH, SU WY, et al. Thermosensitive chitosan-gelatin-glycerol phosphate hydrogels as a cell carrier for nucleus pulposus regeneration: an in vitro study. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(2):695-703. [11] FU Y, DU L, WANG Q, et al. In vitro sustained release of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 microspheres embedded in thermosensitive hydrogels. Pharmazie. 2012;67(4):299-303. [12] WUST S, GODLA ME, MULLER R, et al. Tunable hydrogel composite with two-step processing in combination with innovative hardware upgrade for cell-based three-dimensional bioprinting. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(2):630-640. [13] QU Y, WANG B, CHU B, et al. Injectable and Thermosensitive Hydrogel and PDLLA Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane Composites for Guided Spinal Fusion. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(5):4462-4470. [14] QU C, BAO Z, ZHANG X, et al. A thermosensitive RGD-modified hydroxybutyl chitosan hydrogel as a 3D scaffold for BMSCs culture on keloid treatment. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;125:78-86. [15] ZARRIN NK, MOTTAGHITALAB F, REIS RL, et al. Thermosensitive chitosan/poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) nanoparticles embedded in aniline pentamer/silk fibroin/polyacrylamide as an electroactive injectable hydrogel for healing critical-sized calvarial bone defect in aging rat model. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;213:352-368. [16] LI J, KE H, LEI X, et al. Controlled-release hydrogel loaded with magnesium-based nanoflowers synergize immunomodulation and cartilage regeneration in tendon-bone healing. Bioact Mater. 2024;36:62-82. [17] SUN Z, SONG C, WANG C, et al. Hydrogel-Based Controlled Drug Delivery for Cancer Treatment: A Review. Mol Pharm. 2020;17(2):373-391. [18] DEY M, OZBOLAT IT. 3D bioprinting of cells, tissues and organs. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):14023. [19] YUAN B, ZHANG Y, WANG Q, et al. Thermosensitive vancomycin@PLGA-PEG-PLGA/HA hydrogel as an all-in-one treatment for osteomyelitis. Int J Pharm. 2022;627:122225. [20] TAYLOR MJ, TOMLINS P, SAHOTA S. Thermoresponsive Gels. Gels. 2017; 3(1):4. [21] ANDREAZZA R, MORALES A, PIENIZ S, et al. Gelatin-Based Hydrogels: Potential Biomaterials for Remediation. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(4):1026. [22] MOHANTO S, NARAYANA S, MERAI KP, et al. Advancements in gelatin-based hydrogel systems for biomedical applications: A state-of-the-art review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;253(Pt 5):127143. [23] SAMIRANINEZHAD N, ASADI K, REZAZADEH H, et al. Using chitosan, hyaluronic acid, alginate, and gelatin-based smart biological hydrogels for drug delivery in oral mucosal lesions: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;252:126573. [24] QIN Y, LI P, GUO Z. Cationic chitosan derivatives as potential antifungals: A review of structural optimization and applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;236:116002. [25] ZHAO J, QIU P, WANG Y, et al. Chitosan-based hydrogel wound dressing: From mechanism to applications, a review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;244: 125250. [26] GHOLAP AD, ROJEKAR S, KAPARE HS, et al. Chitosan scaffolds: Expanding horizons in biomedical applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2024;323:121394. [27] DEHGHAN-BANIANI D, CHEN Y, WANG D, et al. Injectable in situ forming kartogenin-loaded chitosan hydrogel with tunable rheological properties for cartilage tissue engineering. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;192:111059. [28] ZHOU HY, JIANG LJ, CAO PP, et al. Glycerophosphate-based chitosan thermosensitive hydrogels and their biomedical applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2015;117:524-536. [29] DENG A, KANG X, ZHANG J, et al. Enhanced gelation of chitosan/beta-sodium glycerophosphate thermosensitive hydrogel with sodium bicarbonate and biocompatibility evaluated. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;78:1147-1154. [30] OHMES J, SAURE LM, SCHUTT F, et al. Injectable Thermosensitive Chitosan-Collagen Hydrogel as A Delivery System for Marine Polysaccharide Fucoidan. Mar Drugs. 2022;20(6):402. [31] CAO H, WANG J, HAO Z, et al. Gelatin-based biomaterials and gelatin as an additive for chronic wound repair. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1398939. [32] SAMIEI M, DALIR AE, AMIRYAGHOUBI N, et al. Injectable thermosensitive chitosan/gelatin hydrogel for dental pulp stem cells proliferation and differentiation. Bioimpacts. 2023;13(1):63-72. [33] ABDELHAMID HN, MATHEW AP. Cellulose-Based Nanomaterials Advance Biomedicine: A Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(10):5405. [34] SUN Z, KUANG Y, AHMAD M, et al. Enhanced osmotic energy conversion through bacterial cellulose based double-network hydrogel with 3D interconnected nanochannels. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;305:120556. [35] LI B, ZHANG L, WANG D, et al. Thermosensitive -hydrogel-coated titania nanotubes with controlled drug release and immunoregulatory characteristics for orthopedic applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;122:111878. [36] ABATANGELO G, VINDIGNI V, AVRUSCIO G, et al. Hyaluronic Acid: Redefining Its Role. Cells. 2020;9(7):1743. [37] YU P, XIE J, CHEN Y, et al. A thermo-sensitive injectable hydroxypropyl chitin hydrogel for sustained salmon calcitonin release with enhanced osteogenesis and hypocalcemic effects. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(2): 270-281. [38] REN Z, WANG Y, MA S, et al. Effective Bone Regeneration Using Thermosensitive Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Grafted Gelatin as Injectable Carrier for Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2015,7(34):19006-19015. [39] RUSSO E, VILLA C. Poloxamer Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11(12):671. [40] ABDELTAWAB H, SVIRSKIS D, SHARMA M. Formulation strategies to modulate drug release from poloxamer based in situ gelling systems. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020;17(4):495-509. [41] ABDELTAWAB H, SVIRSKIS D, BOYD BJ, et al. Injectable thermoresponsive gels offer sustained dual release of bupivacaine hydrochloride and ketorolac tromethamine for up to two weeks. Int J Pharm. 2021;604: 120748. [42] PERUMAL G, RAMASAMY B, NANDKUMAR AM, et al. Influence of magnesium particles and Pluronic F127 on compressive strength and cytocompatibility of nanocomposite injectable and moldable beads for bone regeneration. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;88:453-462. [43] PARK YE, CHANDRAMOULI K, WATSON M, et al. Sustained Delivery of Lactoferrin Using Poloxamer Gels for Local Bone Regeneration in a Rat Calvarial Defect Model. Materials (Basel). 2021;15(1):212. [44] LIU J, ZHANG Y, LI Q, et al. Development of injectable thermosensitive polypeptide hydrogel as facile radioisotope and radiosensitizer hotspot for synergistic brachytherapy. Acta Biomater. 2020;114:133-145. [45] PIAO L, XIANG P, ZHOU Y, et al. Thermo-sensitive PLGA-PEG-PLGA hydrogel for sustained release of EGF to inhibit cervical cancer recurrence. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2024;236:113795. [46] NI P, DING Q, FAN M, et al. Injectable thermosensitive PEG-PCL-PEG hydrogel/acellular bone matrix composite for bone regeneration in cranial defects. Biomaterials. 2014;35(1):236-248. [47] FU S, NI P, WANG B, et al. Injectable and thermo-sensitive PEG-PCL-PEG copolymer/collagen/n-HA hydrogel composite for guided bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2012;33(19):4801-4809. [48] GUREL PG, ABAY AN, CUMBUL A, et al. Investigation of Vasculogenesis Inducing Biphasic Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(4):1526-1538. [49] WANG KH, LIU CH, TAN DH, et al. Block Sequence Effects on the Self-Assembly Behaviors of Polypeptide-Based Penta-Block Copolymer Hydrogels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(5):6674-6686. [50] YU S, ZHANG D, HE C, et al. Injectable Thermosensitive Polypeptide-Based CDDP-Complexed Hydrogel for Improving Localized Antitumor Efficacy. Biomacromolecules. 2017;18(12):4341-4348. [51] QUADIR MA, MORTON SW, DENG ZJ, et al. PEG-polypeptide block copolymers as pH-responsive endosome-solubilizing drug nanocarriers. Mol Pharm. 2014;11(7):2420-2430. [52] JIN GW, REJINOLD NS, CHOY JH. Polyphosphazene-Based Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(24):15993. [53] SEO BB, KOH JT, SONG SC. Tuning physical properties and BMP-2 release rates of injectable hydrogel systems for an optimal bone regeneration effect. Biomaterials. 2017;122:91-104. [54] ZHANG W, WANG N, YANG M, et al. Periosteum and development of the tissue-engineered periosteum for guided bone regeneration. J Orthop Translat. 2022;33:41-54. [55] JURCZAK P, LACH S. Hydrogels as Scaffolds in Bone-Related Tissue Engineering and Regeneration. Macromol Biosci. 2023;23(11):e2300152. [56] SAUNDERS L, MA PX. Self-Healing Supramolecular Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Macromol Biosci. 2019;19(1):e1800313. [57] JI X, SHAO H, LI X, et al. Injectable immunomodulation-based porous chitosan microspheres/HPCH hydrogel composites as a controlled drug delivery system for osteochondral regeneration. Biomaterials. 2022;285: 121530. [58] TAN Z, LUO Y, YANG L. Basic fibroblast growth factor/chitosan derivatives/collagen composite thermosensitive hydrogel promotes perio-dontal tissue regeneration in rats. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2023;41(1):21-28. [59] MAKVANDI P, ALI GW, DELLA SF, et al. Hyaluronic acid/corn silk extract based injectable nanocomposite: A biomimetic antibacterial scaffold for bone tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;107:110195. [60] DUTTA SD, BIN J, GANGULY K, et al. Electromagnetic field-assisted cell-laden 3D printed poloxamer-407 hydrogel for enhanced osteogenesis. RSC Adv. 2021;11(33):20342-20354. [61] MIAO G, LIANG L, LI W, et al. 3D Bioprinting of a Bioactive Composite Scaffold for Cell Delivery in Periodontal Tissue Regeneration. Biomolecules. 2023;13(7):1062. [62] LANGHANS SA. Three-Dimensional in Vitro Cell Culture Models in Drug Discovery and Drug Repositioning. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:6. [63] JI X, YUAN X, MA L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-loaded thermosensitive hydroxypropyl chitin hydrogel combined with a three-dimensional-printed poly(epsilon-caprolactone) /nano-hydroxyapatite scaffold to repair bone defects via osteogenesis, angiogenesis and immunomodulation. Theranostics. 2020;10(2):725-740. [64] RETHORE G, BOYER C, KOUADIO K, et al. Silanization of Chitosan and Hydrogel Preparation for Skeletal Tissue Engineering. Polymers (Basel). 2020;12(12):2823. [65] O’DONNELL BT, AL-GHADBAN S, IVES CJ, et al. Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells Retain Their Adipocyte Differentiation Potential in Three-Dimensional Hydrogels and Bioreactors (dagger). Biomolecules. 2020; 10(7):1070. [66] DIMATTEO R, DARLING NJ, SEGURA T. In situ forming injectable hydrogels for drug delivery and wound repair. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;127:167-184. [67] ZHU J, TANG X, JIA Y, et al. Applications and delivery mechanisms of hyaluronic acid used for topical/transdermal delivery - A review. Int J Pharm. 2020;578:119127. [68] AKAY AS, ARISAN V, CEVHER E, et al. Oxytocin-loaded sustained-release hydrogel graft provides accelerated bone formation: An experimental rat study. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(8):1676-1687. [69] PONTREMOLI C, BOFFITO M, LAURANO R, et al. Mesoporous Bioactive Glasses Incorporated into an Injectable Thermosensitive Hydrogel for Sustained Co-Release of Sr(2+) Ions and N-Acetylcysteine. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(9):1890. [70] FANG X, LEI L, JIANG T, et al. Injectable thermosensitive alginate/beta-tricalcium phosphate/aspirin hydrogels for bone augmentation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(5):1739-1751. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Cai Yaohao, Lang Lyu, Li Hong. Assessing the bone mass of the residual alveolar ridge in the first molar for implant placement by cone-beam computed tomography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1572-1577. |
| [3] | He Longcai, Song Wenxue, Ming Jiang, Chen Guangtang, Wang Junhao, Liao Yidong, Cui Junshuan, Xu Kaya. An experimental method for simultaneous extraction and culture of primary cortical neurons and microglial cells from SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1395-1400. |
| [4] | Li Shuai, Liu Hua, Shang Yonghui, Liu Yicong, Zhao Qihang, Liu Wen. Stress distribution on the maxilla when wearing the Twin-block appliance for Class II malocclusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 881-887. |
| [5] | Xiao Fang, Huang Lei, Wang Lin. Magnetic nanomaterials and magnetic field effects accelerate bone injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 827-838. |
| [6] | Li Mingzhe, Ye Xiangling, Wang Bing, Yu Xiang. Preparation and osteogenic properties of liquid crystal display light-cured polylactic acid scaffold loaded with nano-tantalum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 670-677. |
| [7] | Yu Shuangqi, Ding Fan, Wan Song, Chen Wei, Zhang Xuejun, Chen Dong, Li Qiang, Lin Zuoli. Effects of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer/lysine-grafted graphene oxide nanoparticle composite scaffolds on osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 707-712. |
| [8] | Liu Haoyang, Xie Qiang, Shen Mengran, Ren Yansong, Ma Jinhui, Wang Bailiang, Yue Debo, Wang Weiguo . Application, research hotspots, and shortcomings of degradable zinc-based alloys in bone defect repair and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 839-845. |
| [9] | Zhang Yu, Xu Ruian, Fang Lei, Li Longfei, Liu Shuyan, Ding Lingxue, Wang Yuexi, Guo Ziyan, Tian Feng, Xue Jiajia. Gradient artificial bone repair scaffold regulates skeletal system tissue repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 846-855. |
| [10] | Ge Xiao, Zhao Zhuangzhuang, Guo Shuyu, Xu Rongyao. HOXA10 gene-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7701-7708. |
| [11] | Ren Bo, Tang Yongliang, Li Ni, Liu Bangding. Thermosensitive antibacterial hydrogel for treatment of infected bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7269-7277. |
| [12] | Zhao Jianwei, Li Xunsheng, Lyu Jinpeng, Zhou Jue, Jiang Yidi, Yue Zhigang, Sun Hongmei. Deer antler stem cell exosome composite hydrogel promotes the repair of burned skin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7344-7352. |
| [13] | Yi Xiaoding, Zhang Di, Guo Hong, Qing Liang, Zhao Tianyu. Decellularized tendon scaffold: a biomedical material for tendon injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7385-7392. |
| [14] | Wu Ziwei, Luo Yicai, Wei Yinge, Liao Hongbing. Application of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) copolymer in stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7393-7404. |
| [15] | Li Zhongzheng, Chen Zhenghao, Tang Ziyou, Lou Kaiyang, Zhang Rui, Liu Qi, Zhao Na, Yang Kun. Effects of scaffold materials combined with biological factors on biological characteristics of dental follicle cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7405-7414. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||