Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (27): 5845-5853.doi: 10.12307/2025.840
Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction of a risk prediction model for failure of proximal femoral nail antirotation fixation in intertrochanteric fractures
Tu Zesong, Xu Daxing, Luo Hongbin, Wang Yusheng, Feng Xinglun, Peng Zhonghua, Du Shaolong
- Department of Orthopedics, Sanshui Branch of Foshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Foshan 528100, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-06-26Accepted:2024-09-05Online:2025-09-28Published:2025-03-06 -
Contact:Xu Daxing, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Sanshui Branch of Foshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Foshan 528100, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Tu Zesong, MS, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Sanshui Branch of Foshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Foshan 528100, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Self-Financed Science and Technology Innovation Project in Foshan, No. 2220001004515 (to TZS); High-Level Medical Key Specialty Construction Project during the 14th Five-Year Plan in Foshan, Key Specialty Construction Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine during the 14th Five-Year Plan in Foshan, Medical Key Specialty Construction Project during the 14th Five-Year Plan in Sanshui (Department of Orthopedics, Sanshui Branch of Foshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), No. 202KJS09 (to TZS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tu Zesong, Xu Daxing, Luo Hongbin, Wang Yusheng, Feng Xinglun, Peng Zhonghua, Du Shaolong. Construction of a risk prediction model for failure of proximal femoral nail antirotation fixation in intertrochanteric fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5845-5853.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
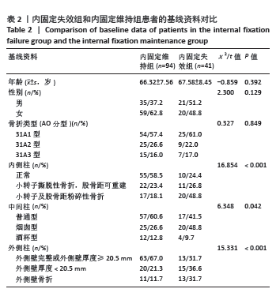
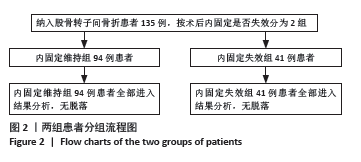
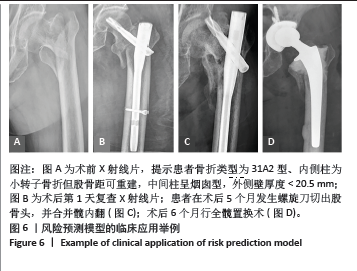
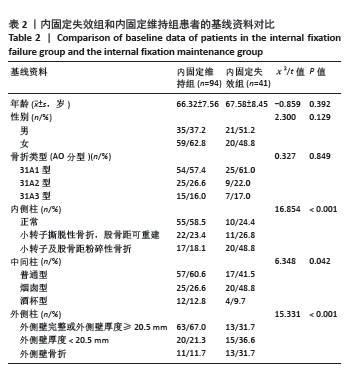
2.3 内固定失效组和维持组患者基线特征比较 如表2所示,135例患者中发生术后内固定失效患者41例,内固定维持组患者94例,内固定失效率为30.37%。内固定失效组患者平均年龄(67.58±8.45)岁,内固定维持组平均年龄(66.32±7.56)岁,两组比较差异无显著性意义(t=-0.859,P=0.392)。失效组患者男21例,女20例;维持组男35例,女59例,两组患者性别占比比较,差异无显著性意义(χ2=2.300,P=0.129)。两组患者的骨折分型分布比较,差异无显著性意义(χ2=0.327,P=0.849)。两组患者的“三柱”不同损伤情况及解剖形态比较,差异有显著性意义 (P < 0.05)。患者随访时间为6-12个月,平均(10.86±4.45)个月,其中内固定失效组患者中螺旋刀片切割股骨颈8例,髋内翻11例,螺旋刀片松动穿出股骨头2例,螺旋刀片退钉6例,骨折复位丢失9例,股骨颈短缩5例;二期手术翻修率为21.9%(9/41),其中7例因髋关节疼痛或不能负重行走,二期行股骨头置换术;2例患者行内固定重新翻修。"

2.4 股骨转子间骨折“三柱”分型筛选术后内固定失效的独立风险因素 将股骨转子间粉碎性骨折术后是否发生内固定失效为结局变量(是=1,否=0),内侧柱、中间柱和外侧柱的哑变量作为自变量分别赋值(赋值见表3)纳入多因素Logistic回归分析,采用向后-LR法进行影响因素的进一步筛选,结果显示,内侧柱(小转子及股骨距粉碎性骨折)[OR=5.385,95%CI(1.961,14.782),P=0.001]、中间柱(烟囱型)[OR=2.893,95%CI(1.167,7.173),P=0.022]、外侧柱(外侧壁厚度< 20.5 mm) [OR=2.804,95%CI(1.078,7.297),P=0.035] 及外侧柱(外侧壁骨折)[OR=4.278,95%CI(1.670,10.959),P=0.012]是股骨转子间骨折术后内固定失效的独立风险因素 (P < 0.05),见表4。"
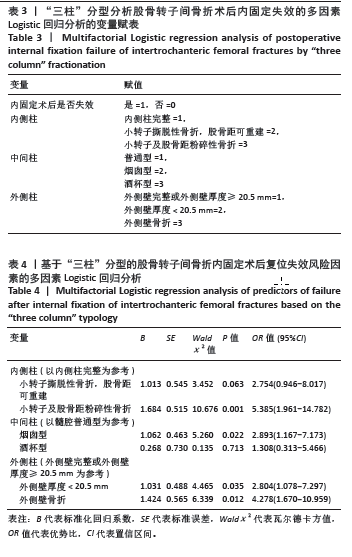
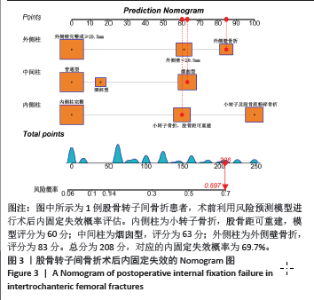
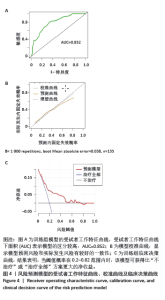
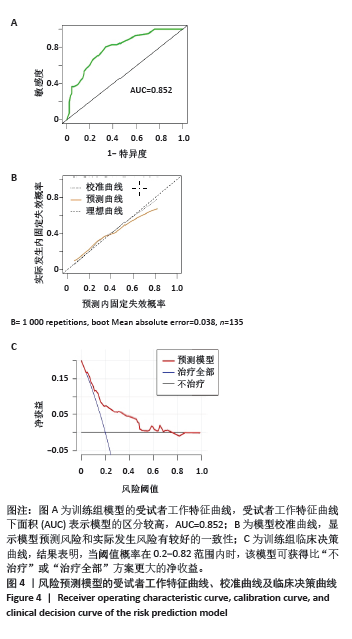
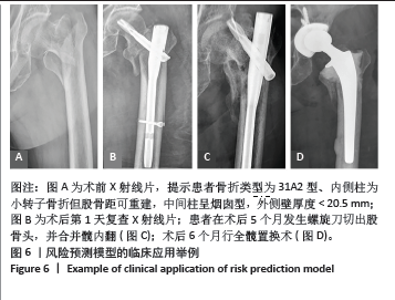
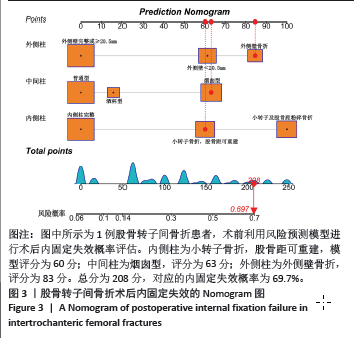
2.5 风险预测模型的构建 多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示“三柱”分型系统是股骨转子间骨折术后内固定失效的独立风险因素。基于“三柱”分型系统在Rstudio软件中利用逻辑回归方程构建风险预测模型。相应的回归方程为y=-2.664+1.684×(小转子及股骨距粉碎性骨折)+1.062×(烟囱型髓腔)+1.031×(外侧壁厚度< 20.5 mm)+1.424×(外侧壁骨折)。根据风险预测模型可以对每位患者术前进行“三柱”情况的分析判断,预测术后内固定失效的概率。实际应用时,将模型中纳入的风险因素把每部分的情况“投射”到顶部对应分数表中的分值,将总分相加,得到对应的术后内固定失效的风险概率。得到的分数越高,风险越大。 图3显示1例股骨转子间骨折患者,术前根据“三柱”理论评估骨折严重情况,小转子骨折,但股骨距可重建,髓腔呈烟囱型并外侧壁骨折,故根据模型的评分为85+63+60=208分,则术后内固定失效风险概率为69.7%。 2.6 风险预测模型的验证 内部验证用Bootstrap法重抽样1 000次,受试者工作特征曲线的曲线下面积为0.852[95%CI(0.837,0.922],证明模型有较好的区分度(图4A)。 模型的校准曲线证实模型预测风险和实际发生风险有较好的一致性(图4B)。临床决策曲线分析表明,当阈值概率在0.2-0.82范围内时,该模型可获得比“不治疗”或“治疗全部”方案更大的净收益,意味着模型有较好的临床适用性(图4C)。 "
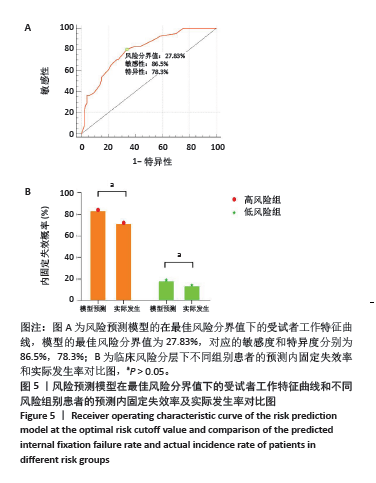
2.7 风险预测模型的临床风险分层 模型在风险分层的最佳分界值受试者工作特征曲线结果表明,内固定失效风险概率为27.83%时对应Youden指数最佳值为0.46,模型的敏感度和特异度分别为86.5%及78.3%(图5A)。因此,当内固定失效风险概率> 28%,归为高风险组;风险概率≤28%时,归为低风险组。将135例纳入研究的股骨转子间骨折患者根据最佳风险分界值分为高、低风险组。高风险组中,模型预测内固定失效概率与实际发生概率比较,差异无显著性意义(84% vs.72%,P > 0.05);低风险组中,模型预测内固定失效概率与实际发生概率比较,差异无显著性意义(19% vs. 14%,P > 0.05)(图5B)。表示模型风险分层下,预测内固定失效的准确率高。临床医生可根据患者不同的风险概率,制定个性化治疗方案。高风险组的患者应考虑通过不同的手术方式增强骨折断端的稳定性或髋关节置换术以防止内固定失效的发生;而低风险组应常规行PFNA手术治疗,以避免过度医疗带来的手术风险和高额费用。"
| [1] CAI C, TIAN L, CHEN Z, et al. Cementless bipolar hemiarthroplasty compared with proximal femoral nail anti-rotation of unstable intertrochanteric fractures in senile patients with osteoporosis: a retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):461. [2] LIANG Y, LIU S, LI L, et al. Proximal femoral nail antirotation versus external fixation for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients: A randomized controlled trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(28):e29384. [3] 武英楷,王瑞强,宁尚攀,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定股骨转子间骨折失败的因素[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(22):2050-2054. [4] RICCI WM. Stability of Intertrochanteric Femur Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2023;37(10S):S1-S4. [5] LEE Y, KIM J, PARK CH, et al. Analysis of risk factor for nail breakage in patients with mechanical failures after proximal femoral nail antirotation in intertrochanteric fractures. Medicine. 2022;101(25):e29436. [6] YOON Y, KIM J, CHO J, et al. Simple guidelines for evaluating intraoperative alignment after the reduction of intertrochanteric fractures. Asian J Surg. 2021;44(1):66-71. [7] KALIA RB, ARORA SS, SARKAR B, et al. A comprehensive 3D CT based classification of intertrochanteric fracture. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2022;30:101912. [8] WADA K, MIKAMI H, AMARI R, et al. A novel three-dimensional classification system for intertrochanteric fractures based on computed tomography findings. J Med Invest. 2019;66(3.4):362-366. [9] 张殿英. 支撑-牵张效应对股骨转子间骨折内固定稳定的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2022,42(2):77-83. [10] 洪加源, 缪建云, 康两期, 等. PFNA辅助微创锁定钢板治疗合并有外侧壁骨折的高龄老年股骨转子间骨折28例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019,27(1):45-46. [11] MIJDERWIJK HJ, BEEZ T, HANGGI D, et al. Clinical prediction models. Childs Nerv Syst. 2020;36(5):895-897. [12] DE JONG V, ROUSSET RZ, ANTONIO-VILLA NE, et al. Clinical prediction models for mortality in patients with covid-19: external validation and individual participant data meta-analysis. BMJ. 2022;378:e69881. [13] 中国脆性骨折联盟, 中国老年医学学会骨与关节分会创伤骨科学术工作委员会, 白求恩·骨科加速康复联盟, 等. 老年股骨转子间骨折诊疗指南[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(2):93-99. [14] 夏纪伍, 康斌, 王德利, 等. 股骨距骨密度变化对老年髋部骨折类型的影响研究[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020,13(4):295-298. [15] 杜心如, 卢世璧. 骨质疏松时股骨上段髓腔形态学特点及其临床意义[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2006,24(6):631-633. [16] 冯俊超, 高明暄, 骆文远. 股骨转子间骨折外侧壁与内侧壁的意义[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(5):436-440. [17] DORR LD, FAUGERE MC, MACKEL AM, et al. Structural and cellular assessment of bone quality of proximal femur. Bone. 1993;14(3):231-242. [18] LI S, SU ZH, ZHU JM, et al. The importance of the thickness of femoral lateral wall for treating intertrochanteric fractures: a finite elements analysis. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):12679. [19] 高永祥, 张晋昕. Logistic回归分析的样本量确定[J].循证医学, 2018,18(2):122-124. [20] VAN SMEDEN M, MOONS KG, DE GROOT JA, et al. Sample size for binary logistic prediction models: Beyond events per variable criteria. Stat Methods Med Res. 2019;28(8):2455-2474. [21] GLANS M, KEMPEN T, JAKOBSSON U, et al. Identifying older adults at increased risk of medication-related readmission to hospital within 30 days of discharge: development and validation of a risk assessment tool. BMJ Open. 2023;13(8):e70559. [22] SHIN WC, JANG JH, JUNG SJ, et al. Advantages and limitations of intramedullary nailing for the surgical treatment of ipsilateral intertrochanteric and femoral shaft fractures: a retrospective comparative study based on propensity score matching. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022;48(3):1779-1786. [23] De VINCENTIS A, BEHR AU, BELLELLI G, et al. Orthogeriatric co-management for the care of older subjects with hip fracture: recommendations from an Italian intersociety consensus. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021;33(9):2405-2443. [24] MUKHERJEE K, BROOKS SE, BARRACO RD, et al. Elderly adults with isolated hip fractures- orthogeriatric care versus standard care: A practice management guideline from the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020;88(2):266-278. [25] 聂少波, 张伟, 张里程, 等. 股骨转子间骨折术后内固定失效的危险因素研究进展[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2021,23(3):233-238. [26] JIANG QL, LI Y, BAI XW, et al. A novel computed tomography-based three-column MLP classification of intertrochanteric fracture. J Med Invest. 2023;70(3.4):524-529. [27] DO JH, KIM YS, LEE SJ, et al. Influence of fragment volume on stability of 3-part intertrochanteric fracture of the femur: a biomechanical study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23(4):371-377. [28] KULKARNI SG, BABHULKAR SS, KULKARNI SM, et al. Augmentation of intramedullary nailing in unstable intertrochanteric fractures using cerclage wire and lag screws: a comparative study. Injury. 2017;48 Suppl 2:S18-S22. [29] 李璐兵, 阿依丁·夏哈太, 李飞, 等. 老年髋关节术后发生假体周围骨折的危险因素研究[J].创伤外科杂志,2021,23(10):740-743. [30] 吴斗, 任鹏宇, 梁伟, 等. 老年股骨近端髓腔形态差异及其对股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定疗效的影响[J].中华创伤杂志,2018,34(6): 513-520. [31] WANG F, ZOU JL, SHANG J. Does matching degree matter for proximal femoral intramedullary nail on reoperation rate in intertrochanteric fractures? J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):573. [32] ZHENG L, WONG DW, CHEN X, et al. Risk of proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) implant failure upon different lateral femoral wall thickness in intertrochanteric fracture: a finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2022;25(5):512-520. [33] 周钰卓, 齐宇新, 马腾洋, 等. 老年股骨转子间骨折PFNA失败的危险因素分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(4):292-296. [34] ABRAM SG, POLLARD TC, ANDRADE AJ. Inadequate ‘three-point’ proximal fixation predicts failure of the Gamma nail. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(6):825-830. [35] 赵豪, 高山, 陈庭瑞. 外侧壁破裂股骨转子间骨折三种内固定有限元分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(6):538-542. [36] WANG R, ZHANG H, WEI Q, et al. Intramedullary nails in combination with reconstruction plate in the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures with lateral wall damage. Int Orthop. 2021;45(11):2955-2962. [37] ZHOU X, YANG J, FANG S. Comment on Shi et al.: Association of the lateral wall integrity with clinical outcomes in older patients with intertrochanteric hip fractures treated with the proximal femoral nail anti-rotation-Asia. Int Orthop. 2022;46(4):925-926. [38] CHEN WH, GUO WX, GAO SH, et al. Arthroplasty vs proximal femoral nails for unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures in elderly patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9(32):9878-9888. [39] JAWAD MJ. Evaluation of using PFN (proximal femoral nailing) in treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients. J Pak Med Assoc. 2021;71(Suppl 8)(12):S179-S184. [40] 陈漳鑫, 胡翠玉, 郑振华, 等. MIPPO重建外侧壁联合PFNA固定与单纯Intertan髓内钉固定治疗外侧壁不完整的股骨转子间骨折疗效比较[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(9):1085-1090. |
| [1] | Zhou Daobin, Wang Kehao, Xie Yang, Ning Rende. Biomechanical characteristics of volar locking plate only versus combined dorsal mini-plate fixation of distal radius fractures with dorsal ulnar fragment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2255-2261. |
| [2] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Wang Chaolu. High tibial osteotomy on a single plane: femorofibular angle as a reference marker for mechanical axis correction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 570-576. |
| [3] | Jia Yingao, Gao Shitao, Wang Fei. Application of 3D printed titanium cage cutting model in anterior cervical vertebrae subtotal decompression and bone graft fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 604-611. |
| [4] | Wang Jiangjing, Zhao Na, Hu Xiaona, Zhao Na . Safety of 3D printed titanium alloy bone trabecular cup prosthesis combined with modified Kidney Tonifying and Blood Activating Decoction for elderly hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 612-619. |
| [5] | Yu Weijie, Cao Dongdong, Guo Tianci, Niu Puyu, Yang Jialin, Wang Simin, Liu Aifeng. Risk prediction models of recurrence after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 749-759. |
| [6] | Wang Lei, Li Chengsong, Zhang Shenshen, Wang Qing. Finite element analysis of biomechanical characteristics of three internal fixation methods in treatment of inferior patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7048-7054. |
| [7] | Yang Wanzhong, Ma Rong, Guo Wei, Wang Zhiqiang, Yang Wei, Chen Zhen, Wang Zemin, Zhang Honglai, Ge Zhaohui. One-stage posterior hemivertebra resection and pedicle screw fixation in treatment of congenital scoliosis: a 2-year follow-up of correction effect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7173-7180. |
| [8] | Yan Jinlian, Xu Zhengquan, Wei Renjie, Wang Yehua. Hip joint function recovery and prediction model construction after proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7189-7195. |
| [9] | Cao Yong, Li Xin, Chen Zhigang, Gu Honglin, Lyu Shujun. Compensatory alignment changes of cervical and thoracic spine after correction of lumbar degenerative scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7196-7202. |
| [10] | Wang Yijun, Zheng Kai, Zhang Lianfang, Zhu Feng, Zhang Weicheng, Li Rongqun, Zhou Jun, Xu Yaozeng. Navigation-assisted total knee arthroplasty using functional alignment restores constitutional alignment and joint line obliquity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5810-5818. |
| [11] | Pan Hongyu, Li Hongtao, Xiao Changming, Li Sen. Biomechanical analysis on treatment of different types of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with individualized precise puncture vertebral augmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5773-5784. |
| [12] | Chen Zhen, Chen Xi, Li Xiaoting, Chen Daxin, Hong Weiwu. Comparison of medial-lateral and lateral-only fixation for pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5924-5932. |
| [13] | Qin Qi, Alimujiang·Yusufu, Liu Yuzhe, Liu Xiuxin, Ren Zheng, Ran Jian. Finite element analysis of intramedullary and extramedullary fixation of femoral neck base fractures: proximal femoral nail antirotation and femoral neck system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4407-4412. |
| [14] | Lyu Xiaodong, Gu Jinrui, Gao Jingyu, Ge Jianzhong. Total hip arthroplasty after failure of internal fixation for intertrochanteric fractures: model prediction of occult blood loss [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4506-4513. |
| [15] | Xu Daxing, Tu Zesong, Ji Muqiang, Xu Weipeng, Niu Wei. Machine learning prediction of the risk of secondary screw perforation after plate internal fixation for proximal humerus fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3179-3187. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||