Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (23): 4899-4906.doi: 10.12307/2025.095
Previous Articles Next Articles
Human leukocyte antigen matched sibling fresh cord blood transplantation for beta-thalassaemia major in children
Wen Jianyun, Chen Libai, He Yuelin, Feng Xiaoqin, Liu Xuan, Xu Xiaoxiao, Li Xiu, Liu Qiujun, Wu Xuedong
- Department of Pediatrics, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2023-12-07Accepted:2024-05-31Online:2025-08-18Published:2024-09-28 -
Contact:Wu Xuedong, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Pediatrics, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Wen Jianyun, Master, Attending physician, Department of Pediatrics, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund Enterprise Joint Fund Project of Guangdong Province, No. 2022A1515220153 (to WXD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wen Jianyun, Chen Libai, He Yuelin, Feng Xiaoqin, Liu Xuan, Xu Xiaoxiao, Li Xiu, Liu Qiujun, Wu Xuedong. Human leukocyte antigen matched sibling fresh cord blood transplantation for beta-thalassaemia major in children[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4899-4906.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
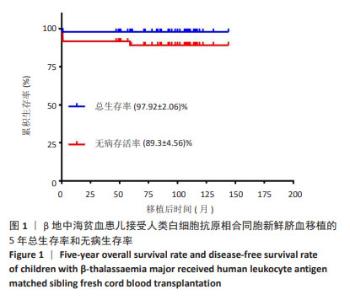
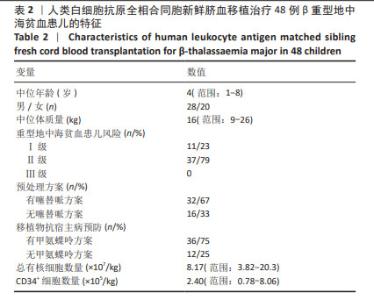
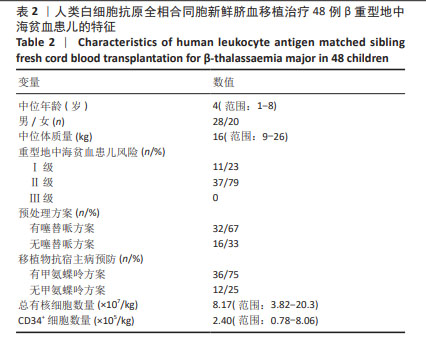
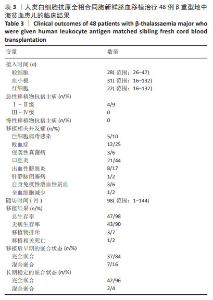
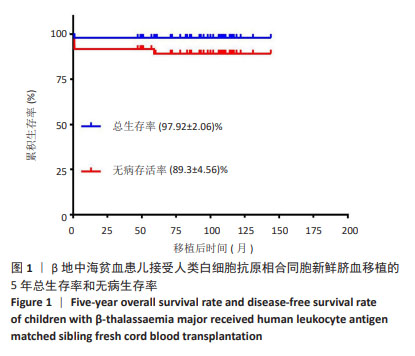
2.3.1 植入和植入失败 48例重型地中海贫血患儿回输的总有核细胞中位数为8.17×107/kg,CD34+细胞中位数为2.40×105/kg。48例患儿除去1例移植后不足1个月死亡,其中44例植入成功,中性粒细胞、血小板和红细胞植入中位时间分别为27,30,22 d;3例患儿发生原发性植入失败(7%),其回输的总有核细胞数分别为5.16×107/kg,5.28×107/kg,6.80×107/kg,回输的CD34+细胞数分别为0.87×105/kg,0.79×105/kg和1.62×105/kg,3例植入失败患儿回输的CD34+细胞数均较少,Logistic回归分析结果显示,CD34+细胞数不是影响移植物排斥的危险因素,这可能是样本数较少的原因,未来需进一步扩大样本量分析。3例植入失败的患儿均存活,1例于2019年3月即与第一次移植间隔43个月接受了同一同胞供者(供者43月龄)的外周血干细胞移植治疗,成功植入供者外周血干细胞,截至随访时患儿无病生存;另外2例患儿恢复重型地中海贫血状态。 48例患儿中,16例预处理方案无塞替哌,发生移植物排斥的3例患儿均未使用塞替哌,无塞替哌组移植物排斥率显著高于有塞替哌组(χ2=6.4,P=0.032)。预处理方案无塞替哌组(n=16)与有塞替哌组(n=32)对比,两组患儿的中位年龄、体质量、回输总有核细胞数和CD34+细胞数比较差异均无显著性意义(P=0.936,P=0.948,P=0.914,P=0.230)。Logistic回归分析结果显示,受者年龄、CD34+细胞数、总有核细胞数及有无使用甲氨蝶呤均不是影响移植物排斥的危险因素,这可能是样本数较少的原因。 44例植入成功的患儿,37例移植后植入证据检测为供者型完全嵌合,7例患儿(16%)在移植后早期检测为供受者稳定混合嵌合(范围:72%-92%的供者细胞),其中1度混合嵌合3例(7%),2度混合嵌合3例(7%),3度混合嵌合1例(2%)。对1度混合嵌合的患儿,每周动态监测植入证据或同时或调整抗排斥药剂量;对2度混合嵌合的患儿,予以减停免疫抑制药物;对于3度混合嵌合的患儿,予以调整抗排斥药和供者淋巴细胞输注2次后,复查植入证据供者细胞比例逐步升高。5例患儿(3例1度混合嵌合和2例2度混合嵌合)转化为完全供者嵌合,其中2例在移植后6个月内,3例在移植后1年内,其余2例儿童(1例2度混合嵌合和1例3度混合嵌合)在停用免疫抑制剂1年或以上后混合嵌合稳定(范围:89%-94%的供者细胞)。截至末次随访时间,最终完全嵌合状态42例,2例混合嵌合状态的患儿脱离输血,7例患儿均未发生原发性或继发性移植物失败。 在44例成功植入的患儿中,使用甲氨蝶呤对中性粒细胞恢复(P=0.259)和血小板恢复(P=0.349)均没有显著影响。 2.3.2 移植物抗宿主病 在44例植入成功的患儿中,4例发生急性移植物抗宿主病,分为Ⅰ级(n=2)和Ⅱ级(n=2),受累器官均为皮肤。长期随访后,未发生Ⅲ-Ⅳ级急性和慢性移植物抗宿主病。人类白细胞抗原同胞供者新鲜脐血移植后的急性和慢性移植物抗宿主病累积发生率非常低,分别为9%和0%。 2.3.3 移植相关的并发症 5例发生巨细胞病毒感染及激活,所有患儿经过更昔洛韦抢先治疗均转阴。12例出现败血症,其中6例为革兰阳性细菌感染(其中一半为感染金黄色葡萄球菌),6例为革兰阴性菌感染(其中4例为感染大肠杆菌),但没有患儿死于败血症。侵袭性真菌病发生3例,其中2例为真菌性肺部感染,1例为真菌性败血症合并真菌性心内膜炎。 口腔炎是移植过程中最常见的不良反应,48例患儿中有21例发生口腔炎。8例发生出血性膀胱炎,1例被诊断为肝静脉闭塞病,血清胆红素升高(> 20 mg/L)。供受者血型不合患儿输注新鲜脐血后均未发生溶血反应。3例患儿发生自身免疫性溶血性贫血,通过Coombs试验阳性确诊,其中2例来自ABO主要不相容供体,1例来自ABO相容供体,发病时间分别为造血干细胞移植后1,3,6个月,均接受了包括糖皮质激素、免疫抑制剂和静脉内注射免疫球蛋白在内的初始治疗,ABO血型相合患儿最初治疗1周后迅速恢复,2例ABO不相合患儿随后每周接受一次抗利妥昔单抗治疗,1例在3周后治愈,而另1例在使用利妥昔单抗治疗4周后反应不佳,在造血干细胞后8个月出现全血细胞减少,在移植1年后接受了来自同一同胞供者的骨髓移植治疗后治愈。 2.3.4 总生存率、无病生存率和移植相关死亡 48例患儿中,47例存活,1例在移植后28 d因重症肺炎合并急性心力衰竭死亡,43例无病存活,3例发生原发性植入失败,1例发生移植后全血细胞减少,5年总生存率和无病生存率分别为98%和89%(图1)。移植后1年时移植相关死亡的发病率为2%。"
| [1] KATTAMIS A, KWIATKOWSKI JL, AYDINOK Y. Thalassaemia. Lancet. 2022;399(10343):2310-2324. [2] LOCATELLI F, KABBARA N, RUGGERI A, et al. Outcome of patients with hemoglobinopathies given either cord blood or bone marrow transplantation from an HLAidentical sibling. Blood. 2013;122(6): 1072-1078. [3] 陆婧媛,林进宗,陈凌非,等.非冻存同胞脐血干细胞移植治疗儿童重型地中海贫血症9例[J].中华器官移植杂志,2022,43(3): 151-155. [4] WEN J, HAQUE Q, PEI F, et al. Transplant outcomes in beta-thalassemia major patients receiving combined granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-primed bone marrow and cord blood graft compared to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-primed bone marrow alone. Acta Haematol. 2018;140(1):20-29. [5] TANG X, FANG J, YU J, et al. Clinical outcomes of unrelated cord blood transplantation in children with malignant and non-malignant diseases: multicenter experience in China. Pediatr Transplant. 2018;22(1): e13090. [6] ZHU X, TANG B, SUN Z. Umbilical cord blood transplantation: Still growing and improving. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021;Suppl 2(Suppl 2): S62-S74. [7] CHEN G, YUE A, RUAN Z, et al. Comparison of the effects of different cryoprotectants on stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:1396783. [8] MCMANUS MP, WANG L, CALDER C, et al. Comparison of pre-cryopreserved and post-thaw-and-wash-nucleated cell count on major outcomes following unrelated cord blood transplant in children. Pediatr Transplant. 2012;16(5):438-442. [9] GALAMBRUN C, PONDARRÉ C, BERTRAND Y, et al. French multicenter 22- year experience in stem cell transplantation for beta-thalassemia major: lessons and future directions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19(1):62-68. [10] 康栋梁,谭永红,陈亚玫,等.不同年龄段地中海贫血患儿接受异基因造血干细胞移植后疗效的比较[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2022,30(2):539-542. [11] LI C, WU X, FENG X, et al. A novel conditioning regimen improves outcomes in β-thalassemia major patients using unrelated donor peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2012;120(19): 3875-3881. [12] HE Y, JIANG H, LI C, et al. Long-term results of the NF-08-TM protocol in stem cell transplant for patients with thalassemia major: A multi-center large-sample study. Am J Hematol. 2020;95(11):E297-E299. [13] SODANI P, GAZIEV D, POLCHI P, et al. New approach for bone marrow transplantation in patients with class 3 thalassemia aged younger than 17 years. Blood. 2004;104(4):1201-1203. [14] PRZEPIORKA D, WEISDORF D, MARTIN P, et al. 1994Consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995; 15(6):825-828. [15] SHAMSHAD GU, AHMED S, BHATTI FA, et al. Mixed donor chimerism in non-malignant haematological diseases after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2012;22(12):765-768. [16] FOUZIA NA, EDISON ES, LAKSHMI KM, et al. Long-term outcome of mixed chimerism after stem cell transplantation for thalassemia major conditioned with busulfan and cyclophosphamide. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018;53(2):169-174. [17] LI XY, SUN X, CHEN J, et al. Hematopoietie stem cell transplantation for children with beta-thalassemia major:muhicenter experience in China. World J Pediatr. 2018;14(1):92-99. [18] SUN Z, YAO B, XIE H, et al. Clinical Progress and Preclinical Insights Into Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation Improvement. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022;11(9):912-926. [19] 孙自敏.非血缘脐血移植的展望[J].国际输血及血液学杂志,2016, 39(6):461-465. [20] MAYANI H, WAGNER JE, BROXMEYER HE. Cord blood research, banking, and transplantation: achievements, challenges, and perspectives. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55(1):48-61. [21] RUGGERI A, EAPEN M, SCARAVADOU A, et al. Umbilical cord blood transplantation for children with thalassemia and sickle cell disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011;17(9):1375-1382. [22] FENG J, LEE V, LEUNG AWK, et al. Double-unit unrelated cord blood transplantation for thalassemia major: Comparison with HLA-identical sibling bone marrow transplantation. Pediatr Transplant. 2021;25(3): e13901. [23] MATZA LS, PARAMORE LC, STEWART KD, et al. Health state utilities associated with treatment for transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia. Eur J Health Econ. 2020;21(3):397-407. [24] IINO M, SATO T, SAKAMOTO Y. Minimum-Dose, Short-Term Methotrexate With Tacrolimus for Graft-vs-Host Disease Prophylaxis Following Unrelated Cord Blood Transplantation in Adults: A Retrospective Analysis at a Single Institution. Transplant Proc. 2021; 53(1):396-404. [25] PONCE DM, POLITIKOS I, ALOUSI A, et al. Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Graft-versus-Host Disease after Cord Blood Transplantation. Transplant Cell Ther. 2021;27(7):540-544. [26] LERTKOVIT O, ANURATHAPAN U, HONGENG S, et al. Chronic graft-versus-host disease in children and adolescents with thalassemia after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Int J Hematol. 2021; 113(4):556-565. [27] ANDREANI M, NESCI S, LUCARELLI G, et al. Long-term survival of ex-thalassemic patients with persistent mixed chimerism after bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000;25(4):401-404. [28] ANDREANI M, TESTI M, LUCARELLI G. Mixed chimerism in haemoglobinopathies: from risk of graft rejection to immune tolerance. Tissue Antigens. 2014;83(3):137-146. [29] MCCANN S, PASSWEG J, BACIGALUPO A, et al. The influence of cyclosporin alone, or cyclosporin and methotrexate, on the incidence of mixed haematopoietic chimaerism following allogeneic sibling bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anaemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007;39(2):109-114. [30] KAKO S, KANDA Y, ONIZUKA M, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for aplastic anemia with pre-transplant conditioning using fludarabine, reduced-dose cyclophosphamide, and low-dose thymoglobulin: A KSGCT prospective study. Am J Hematol. 2020;95(3):251-257. [31] LISINI D, ZECCA M, GIORGIANI G, et al. Donor/recipient mixed chimerism does not predict graft failure in children with beta-thalassemia given an allogeneic cord blood transplant from an HLA-identical sibling. Haematologica. 2008;93(12):1859- 1867. [32] BRUCKNER M, KATHERIA AC, SCHMÖLZER GM. Delayed cord clamping in healthy term infants: More harm or good? Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021;26(2):101221. |
| [1] | Ao Xiaojing, Li Kun, Liu Yuhang, Yang Xiaoxuan, Wang Xing, Li Zhijun, Ren Xiaoyan, Zhang Shaojie. Development and application of a three-dimensional digital visualization system for children’s neck acupoints [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1834-1840. |
| [2] | Sun Xiaojun, Wang Huaming, Zhang Dehong, Song Xuewen, Huang Jin, Zhang Chen, Pei Shengtai. Effect of finite element method in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1897-1904. |
| [3] | Zhang Pulian, Liu Baoru, Yang Min . Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of aplastic anemia: inhibiting or activating relevant targets in its pathological evolution [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6800-6810. |
| [4] | Yi Yuying, Sun Ruifen, Yin Zhaozheng, Li Lei, Zhang Fengzhen, Li Ziyu, Li Kun, Ren Xiaoyan, Wang Xing, Zhang Shaojie. Digital anatomical characteristics of morphological development of neurocentral synchondrosis of cervical vertebra in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3138-3146. |
| [5] | Xia Mengting, Sun Runjie, Fu Jiaqi, Li Suzhen, Yu Manya, Cui Xing. Mechanism by which Huangqintang regulates intestinal flora for treatment of intestinal acute graft-versus-host disease in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 95-102. |
| [6] | Kong Dai, Wang Xinkai, Zhang Wenhui, Pei Xiaohang, Lian Cheng, Niu Xiaona, Guo Honggang, Niu Junwei, Zhu Zunmin, Liu Zhongwen. Oral Herombopag Olamine and subcutaneous recombinant human thrombopoietin after haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 1-7. |
| [7] | Tu Meijuan, Zhang Chunli, Deng Li, Fang Bing, Sun Guangyu, Zhu Xiaoyu, Zhang Xinqiong. Characteristics of acute graft-versus-host disease of the intestine after unrelated cord blood transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 3955-3959. |
| [8] | Liu Yuhang, Sun Ruifen, Mu Rigen Jiya, Wang Xing, Li Zhijun, Liu Yanan, Hao Yunteng, Cai Yongqiang, Zhang Shaojie, Li Kun. Development of a three-dimensional digital children’s acupuncture point visualization system of Mongolian medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3223-3228. |
| [9] | Ye Xiaolong, Ma Yuan. Visualization analysis of magnetically controlled growing rod in treatment of spinal deformities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(15): 2323-2329. |
| [10] | Gao Siyu, Yao Lihong, Bian Zhilei, Zhang Suping, Li Li, Fan Jinpeng, Qin Jing, Peng Yingnan, Wan Dingming. Analysis of risk factors for short-term death after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2009-2016. |
| [11] | Zhang Wenhui, Pei Xiaohang, Kong Dai, Liu Zhongwen. Efficacy of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells replacing donor bone marrow cells in haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2042-2046. |
| [12] | Liu Yanan, Wang Xing, Li Kun, Sun Ruifen, Ma Xueying, Zhao Lei, Liu Yuhang, Yang Yang, Hao Yunteng, Li Ziyu, Zhang Shaojie, Li Zhijun. Digital characteristics of brainstem morphology and age-related development in young children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1730-1736. |
| [13] | Liang Xiao, Zhao Panchao, Li Jiahui, Ji Zhongqiu, Jiang Guiping. Gait and biomechanical characteristics of lower limbs in multi-task walking of 4-6-year-old children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 505-512. |
| [14] | Liu Qinghua, Cai Yongqiang, Jin Feng, Yu Jinghong, Wang Haiyan, Zhang Yunfeng, Wang Lidong, Li Jiawei, Wang Xing, He Yujie, Dai Lina, Wang Jianzhong, Wu Chao, Tong Ling, Kang Zhijie, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe. Finite element model of the 12-year-old child whole cervical spine: establishment and validity verification based on CT data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 500-504. |
| [15] | Qin Jing, Zhang Suping, Li Li, Zhang Ran, Peng Yingnan, Gao Siyu, Fan Jinpeng, Bian Zhilei, Wan Dingming. Analysis of risk factors for varicella-zoster virus infection after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5292-5297. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||