Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (23): 4868-4877.doi: 10.12307/2025.087
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for myocardial infarction in rats: effects of acute and chronic exercises
Feng Qiang1, Pi Yihua1, Huang Huasheng1, Huang Delun2, Zhang Yan1
- 1Department of Physical Education, 2Department of Physiology of College of Basic Medicine, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-12-27Accepted:2024-05-16Online:2025-08-18Published:2024-09-26 -
Contact:Zhang Yan, Master, Associate professor, Department of Physical Education, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Feng Qiang, Lecturer, Department of Physical Education, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Guangxi Education Science "Fourteenth Five-Year Plan" Key Project, No. 2023ZJY535 (to ZY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Feng Qiang, Pi Yihua, Huang Huasheng, Huang Delun, Zhang Yan. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for myocardial infarction in rats: effects of acute and chronic exercises[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4868-4877.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
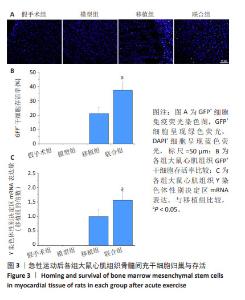
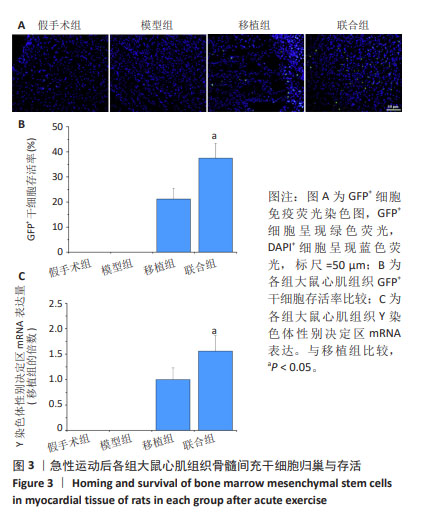
2.4 急性运动后各组大鼠实验指标检测结果 2.4.1 干细胞归巢与存活 GFP+细胞数量:免疫荧光染色结果显示,GFP+细胞呈现绿色荧光,DAPI+细胞呈现蓝色荧光。假手术组与模型组心肌组织内无GFP+细胞,移植组和联合组心肌组织内GFP+细胞显著增加,并且联合组干细胞GFP+细胞数量明显多于移植组(P < 0.05),见图3A,B。 Y染色体性别决定区mRNA表达:Y染色体性别决定区基因是雄性动物细胞Y染色体上所携带的特定基因,因此通过检测Y染色体性别决定区mRNA表达量间接反映干细胞存活量。检测结果显示,假手术组和模型组大鼠心肌组织未检测到Y染色体性别决定区mRNA表达;与移植组比较,联合组大鼠心肌组织Y染色体性别决定区mRNA表达升高(P < 0.05),见图3C。"
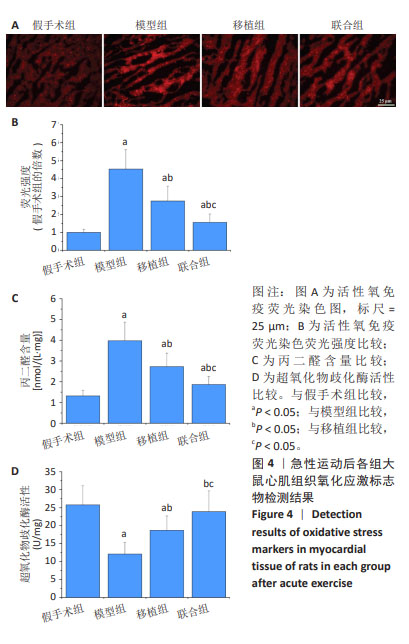
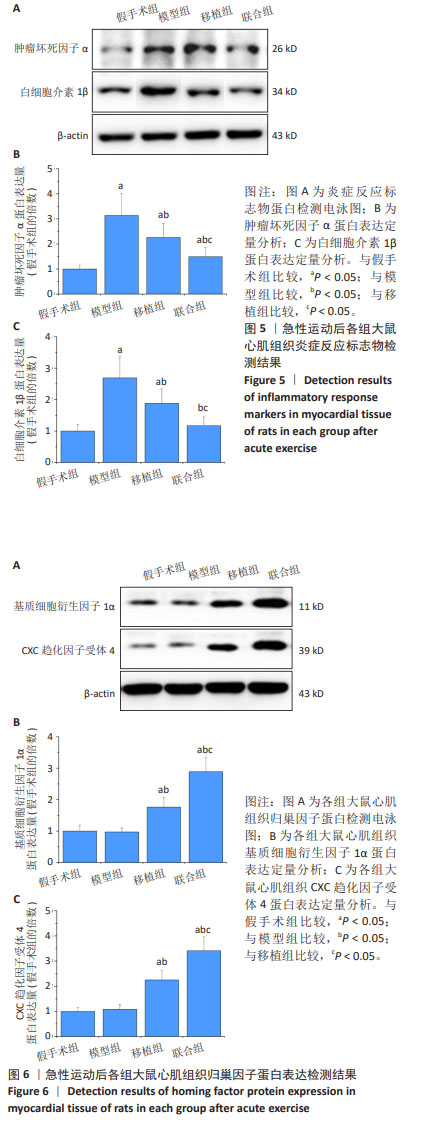
2.4.3 炎症反应标志物 与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠心肌组织肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,移植组和联合组大鼠心肌组织肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05);与移植组比较,联合组大鼠心肌组织肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05),见图5。 2.4.4 归巢因子蛋白表达 与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠心肌组织基质细胞衍生因子1α、CXC趋化因子受体4蛋白表达无明显变化(P > 0.05);与模型组比较,移植组和联合组大鼠心肌组织基质细胞衍生因子1α、CXC趋化因子受体4蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);与移植组比较,联合组大鼠心肌组织基质细胞衍生因子1α、CXC趋化因子受体4蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05),见图6。"

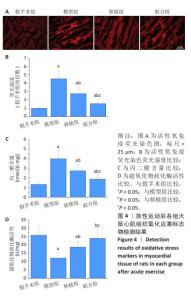
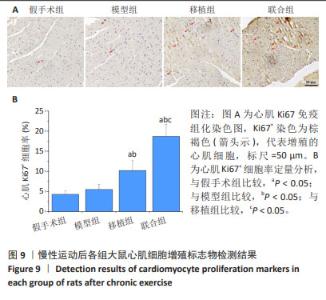
2.5.2 心肌组织学观察 苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,模型组心肌细胞排列紊乱无序,肌丝断裂、溶解,心肌细胞肥大;移植组、联合组心肌细胞形态和纤维排列明显改善,联合组改善更为明显,见图8A。 麦胚凝集素染色结果显示,与假手术组比较,模型组可见明显的心肌肥大,细胞横截面积增加(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,移植组心肌肥大减轻,细胞横截面积减少(P < 0.05),联合组心肌肥大程度无显著变化(P > 0.05);与移植组比较,联合组心肌细胞横截面积增加(P < 0.05),见图8B,C。 Masson染色结果显示,假手术组心肌间质仅有少量纤维组织;模型组出现心肌纤维化,胶原含量明显高于假手术组(P < 0.05);移植组和联合组心肌纤维化程度降低,胶原含量较模型组下降(P < 0.05);与移植组比较,联合组胶原含量进一步降低(P < 0.05),见图8D,E。"

| [1] BOLLI R. Cell therapy for acute myocardial infarction: Requiescat in pace. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(38):3711-3714. [2] WANG S, HU J, DONG G, et al. Effects of bone marrow cells transplantation for acute myocardial infarction on cardiac function, infarct size, and clinical events: a meta-analysis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2023;136(20):2518-2520. [3] LANG CI, DAHMEN A, VASUDEVAN P, et al. Cardiac cell therapies for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction in mice: systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytotherapy. 2023;25(6):640-652. [4] 孙维兴,赵永超,赵然尊.间充质干细胞移植治疗心肌梗死:问题、症结及新突破[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(19):3103-3109. [5] 杨佳炜,王宪云,王乐,等.间充质干细胞移植治疗心肌梗死的研究现状及优化策略[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2022,44(7): 1424-1432. [6] DIBBEN GO, FAULKNER J, OLDRIDGE N, et al. Exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation for coronary heart disease: a meta-analysis. Eur Heart J. 2023;44(6):452-469. [7] CARDOSO CG Jr, GOMIDES RS, QUEIROZ AC, et al. Acute and chronic effects of aerobic and resistance exercise on ambulatory blood pressure. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2010;65(3):317-325. [8] CHEN Y, HUANG Q, FENG Y. Exercise improves cardiac function in the aged rats with myocardial infarction. Physiol Res. 2023;72(1):27-35. [9] ESKANDARI A, SOORI R, CHOOBINEH S, et al. Exercise promotes heart regeneration in aged rats by increasing regenerative factors in myocardial tissue. Physiol Int. 2020;107(1):166-176. [10] MITSIOU G, KARATZANOS E, SMILIOS I, et al. Exercise promotes endothelial progenitor cell mobilization in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2022;28(18):e24-e27. [11] COSMO S, FRANCISCO JC, CUNHA RC, et al. Effect of exercise associated with stem cell transplantation on ventricular function in rats after acute myocardial infarction. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 2012;27(4):542-551. [12] LIAO Z, LI D, CHEN Y, et al. Early moderate exercise benefits myocardial infarction healing via improvement of inflammation and ventricular remodelling in rats. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(12):8328-8342. [13] FONG CY, PEH G, SUBRAMANIAN A, et al. The use of discontinuous density gradients in stem cell research and application. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2009;5(4):428-434. [14] 魏峰,马爱群,王亭忠,等.慢病毒载体介导GFP标记大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版),2010,31(3):288-292. [15] DE FREITAS JS, NEVES CA, DEL CARLO RJ, et al. Effects of exercise training and stem cell therapy on the left ventricle of infarcted rats. Rev Port Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2019;38(9):649-656. [16] LIESVELD JL, SHARMA N, ALJITAWI OS. Stem cell homing: From physiology to therapeutics. Stem Cells. 2020;38(10):1241-1253. [17] JIANG Q, HUANG K, LU F, et al. Modifying strategies for SDF-1/CXCR4 interaction during mesenchymal stem cell transplantation. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022;70(1):1-10. [18] OKUTSU M, ISHII K, NIU KJ, et al. Cortisol-induced CXCR4 augmentation mobilizes T lymphocytes after acute physical stress. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005;288(3):R591-599. [19] SANDRI M, ADAMS V, GIELEN S, et al. Effects of exercise and ischemia on mobilization and functional activation of blood-derived progenitor cells in patients with ischemic syndromes: results of 3 randomized studies. Circulation. 2005;111(25):3391-3399. [20] BREHM M, PICARD F, EBNER P, et al. Effects of exercise training on mobilization and functional activity of blood-derived progenitor cells in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Eur J Med Res. 2009;14(9): 393-405. [21] DUNCKER DJ, BACHE RJ. Regulation of coronary blood flow during exercise. Physiol Rev. 2008;88(3):1009-1086. [22] HICKS MR, PYLE AD. The emergence of the stem cell niche. Trends Cell Biol. 2023;33(2):112-123. [23] HANNA A, FRANGOGIANNIS NG. Inflammatory cytokines and chemokines as therapeutic targets in heart failure. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2020;34(6):849-863. [24] KHODAYARI S, KHODAYARI H, AMIRI AZ, et al. Inflammatory microenvironment of acute myocardial infarction prevents regeneration of heart with stem cells therapy. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;53(5): 887-909. [25] LEE CC, HIRASAWA N, GARCIA KG, et al. Stem and progenitor cell microenvironment for bone regeneration and repair. Regen Med. 2019;14(7):693-702. [26] LI H, HOU L. Regulation of melanocyte stem cell behavior by the niche microenvironment. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2018;31(5):556-569. [27] SUZUKI K, MURTUZA B, BEAUCHAMP JR, et al. Role of interleukin-1beta in acute inflammation and graft death after cell transplantation to the heart. Circulation. 2004;110(11 Suppl 1):II219-224. [28] DROWLEY L, OKADA M, BECKMAN S, et al. Cellular antioxidant levels influence muscle stem cell therapy. Mol Ther. 2010;18(10):1865-1873. [29] SCHMID M, KRöPFL JM, SPENGLER CM. Changes in circulating stem and progenitor cell numbers following acute exercise in healthy human subjects: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021;17(4):1091-1120. [30] PILLON BARCELOS R, FREIRE ROYES LF, GONZALEZ-GALLEGO J, et al. Oxidative stress and inflammation: liver responses and adaptations to acute and regular exercise. Free Radic Res. 2017;51(2):222-236. [31] 孙维兴,赵永超,赵然尊.间充质干细胞移植治疗心肌梗死:问题、症结及新突破[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(19):3103-3109. [32] 吕志伟. 有氧运动协同骨髓干细胞动员对心肌梗死后心电图和血流动力学指标的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(19): 2959-2964. [33] 吕志伟,芦忠文,马云霞,等.间歇有氧运动联合rhG-CSF可促进心肌组织Ang-1表达和血管再生[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2018,37(2):536-542. [34] FLAIM SF, MINTEER WJ, CLARK DP, et al. Cardiovascular response to acute aquatic and treadmill exercise in the untrained rat. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979;46(2):302-308. [35] XI Y, HAO M, LIANG Q, et al. Dynamic resistance exercise increases skeletal muscle-derived FSTL1 inducing cardiac angiogenesis via DIP2A-Smad2/3 in rats following myocardial infarction. J Sport Health Sci. 2021;10(5):594-603. [36] WU X, WANG L, WANG K, et al. ADAR2 increases in exercised heart and protects against myocardial infarction and doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Mol Ther. 2022;30(1):400-414. [37] LAVIE CJ, OZEMEK C, CARBONE S, et al. Sedentary behavior, exercise, and cardiovascular health. Circ Res. 2019;124(5):799-815. [38] 车琳,戴翠莲,刘伟静,等.心脏康复分级诊疗中国专家共识[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2022,30(8):561-572. [39] PEIXOTO TC, BEGOT I, BOLZAN DW, et al. Early exercise-based rehabilitation improves health-related quality of life and functional capacity after acute myocardial infarction: a randomized controlled trial. Can J Cardiol. 2015;31(3):308-313. [40] QIU Y, PAN X, CHEN Y, et al. Hallmarks of exercised heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022;164:126-135. [41] MARTIN TG, JUARROS MA, LEINWAND LA. Regression of cardiac hypertrophy in health and disease: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2023;20(5):347-363. [42] YAMADA Y, MINATOGUCHI S, KANAMORI H, et al. Stem cell therapy for acute myocardial infarction - focusing on the comparison between Muse cells and mesenchymal stem cells. J Cardiol. 2022; 80(1):80-87. [43] NADEEM S, HANNA MG, VISWANATHAN K, et al. Ki67 proliferation index in medullary thyroid carcinoma: a comparative study of multiple counting methods and validation of image analysis and deep learning platforms. Histopathology. 2023;83(6):981-988. |
| [1] | Lou Guo, Zhang Min, Fu Changxi. Exercise preconditioning for eight weeks enhances therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells in rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [2] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [3] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [4] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [5] | Zheng Rongfa, Mo Weibin, Huang Peng, Chen Junji, Liang Ting, Zi Fangyu, Li Guofeng. Effects of electroacupuncture on the expression of metabolic enzymes and autophagy genes in gastrocnemius muscle tissues of exercising rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1127-1136. |
| [6] | Gao Yang, Qin Hewei, Liu Dandan. ACSL4 mediates ferroptosis and its potential role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1239-1247. |
| [7] | Sun Xianjuan, Wang Qiuhua, Zhang Jinyi, Yang Yangyang, Wang Wenshuang, Zhang Xiaoqing. Adhesion, proliferation, and vascular smooth muscle differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on different electrospinning membranes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 661-669. |
| [8] | Han Mengjun, Xu Fang. Hematopoietic stem cell mobilization: advantages and disadvantages of different plans and improvements in predictive models and technologies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7863-7871. |
| [9] | Yang Dingyan, Yu Zhenqiu, Yang Zhongyu. Machine learning-based analysis of neutrophil-associated potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7909-7920. |
| [10] | Ge Xiao, Zhao Zhuangzhuang, Guo Shuyu, Xu Rongyao. HOXA10 gene-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7701-7708. |
| [11] | Zhang Xiongjinfu, Chen Yida, Cheng Xinyi, Liu Daihui, Shi Qin . Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of young rats to reverse senescence in aged rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7709-7718. |
| [12] | Sima Xinli, Liu Danping, Qi Hui. Effect and mechanism of metformin-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes on regulating chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7728-7734. |
| [13] | Liu Chengyuan, Guo Qianping. Differential effects of kartogenin on chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation of rat and rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7490-7498. |
| [14] | Wu Qingyun, Su Qiang. Antioxidant nanomedicine-mediated targeted therapy for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7431-7438. |
| [15] | Zhang Pulian, Liu Baoru, Yang Min . Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of aplastic anemia: inhibiting or activating relevant targets in its pathological evolution [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6800-6810. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||