Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (19): 4161-4171.doi: 10.12307/2025.063
Previous Articles Next Articles
Action mechanism of Coptidis Rhizoma Alkaloids against cerebral ischemia based on transcriptome sequencing
Tian Liangliang1, 2, Zhou Rui3, Cao Guangzhao1, Zhang Jingjing1, 4
- 1Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China; 2Institute of Chinese Medicinal Sciences, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; 3School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; 4Chinese Institute for Brain Research, Beijing 102206, China
-
Received:2023-11-24Accepted:2024-04-15Online:2025-07-08Published:2024-09-13 -
Contact:Zhang Jingjing, PhD, Researcher, Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China; Chinese Institute for Brain Research, Beijing 102206, China -
About author:Tian Liangliang, Master candidate, Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China; Institute of Chinese Medicinal Sciences, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Project), No. 81974550 (to ZJJ); Innovation Project of China Acadenly of Chinese Medical Sciences, No. CI2021A04612 (to ZJJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tian Liangliang, Zhou Rui, Cao Guangzhao, Zhang Jingjing. Action mechanism of Coptidis Rhizoma Alkaloids against cerebral ischemia based on transcriptome sequencing[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(19): 4161-4171.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
2.1 实验动物数量分析 56只大鼠随机分为假手术组、缺血再灌注组、阳性药物组和黄连总碱组,每组14只。取材后每组6只行TTC染色;每组3只行病理染色及转录组测序;最后每组5只行ELISA检测。 2.2 黄连总碱含量测定结果 黄连碱含量为91.07 mg/g、盐酸小檗碱含量为222.07 mg/g、盐酸巴马汀含量为57.36 mg/g,表小檗碱含量为41.81 mg/g,四者在黄连总碱中共含有41.23%。 2.3 黄连总碱化学成分与潜在作用靶点 通过数据库筛选后获得palmatine作用靶点16个,berberine作用靶点16个,epiberberine作用靶点10个,coptisine作用靶点9个,columbamine作用靶点19个,jatrorrhizine作用靶点18个,magnoflorine作用靶点21个,ferulic acid作用靶点14个,groenlandicine作用靶点15个,berberrubine作用靶点12个,oxyberberine作用靶点18个,choline作用靶点1个,8-oxocoptisine作用靶点41个,合并后删除重复值共得到药物作用靶点87个,见表1。"

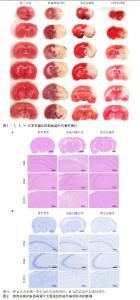
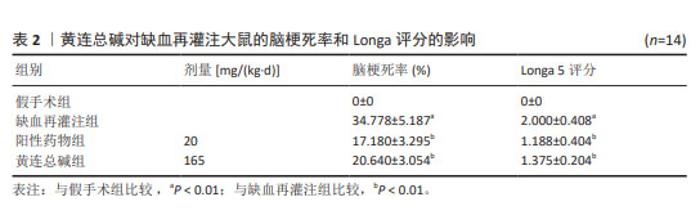
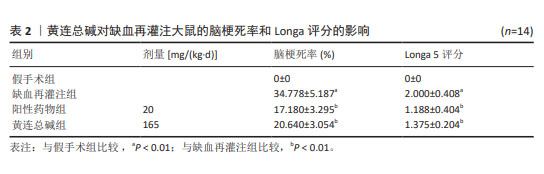
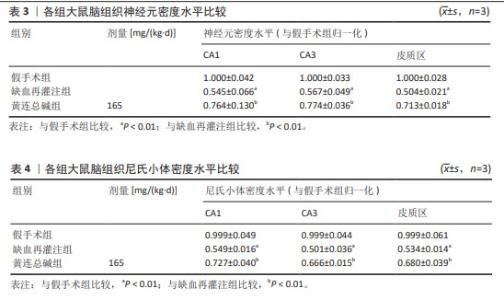
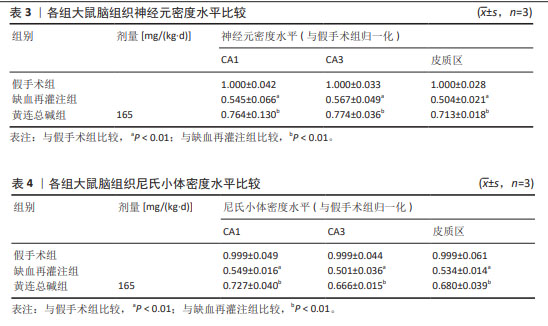
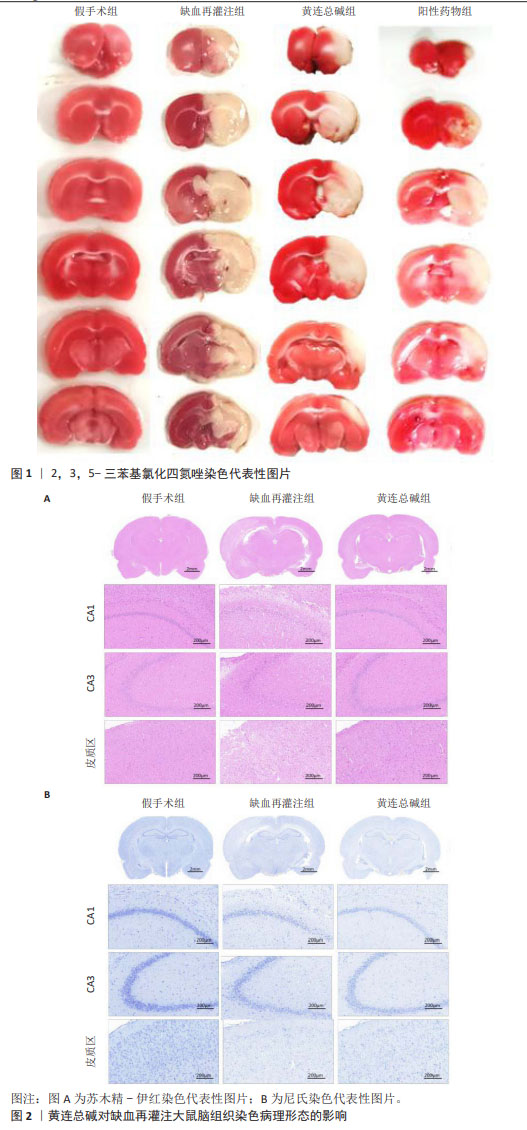
2.5 黄连总碱降低缺血再灌注大鼠脑梗死率 由TTC染色结果可知,与假手术组比较,缺血再灌注组大鼠脑梗死面积显著增大(P < 0.01);与缺血再灌注组大鼠比较,黄连总碱组和阳性药物组明显改善缺血再灌注大鼠脑梗死情况,降低脑梗死面积(P < 0.01),见表2及图1。 2.6 黄连总碱对缺血再灌注大鼠脑组织染色病理形态的影响 病理染色结果显示,假手术组大鼠大脑皮质轮廓清晰,形态完整,未见明显的空泡及细胞变性,海马神经元排列规则、紧密,细胞形态正常,胞浆丰富,核仁明显,尼氏小体着色较深且数量多;缺血再灌注组大鼠大脑皮质组织疏松,有明显空泡,海马神经元排列松散、紊乱,细胞间隙增宽,神经元细胞稀疏、数量少,部分丢失,细胞核固缩,与周围组织不紧密,尼氏小体颜色变浅;与缺血再灌注组相比较,黄连总碱组大鼠脑皮质轮廓较清晰,形态较完整,空泡明显减少,正常细胞多,海马神经元数量较多,尼氏小体数量较多,染色较均一,结构较完整,见图2及表3,4。"
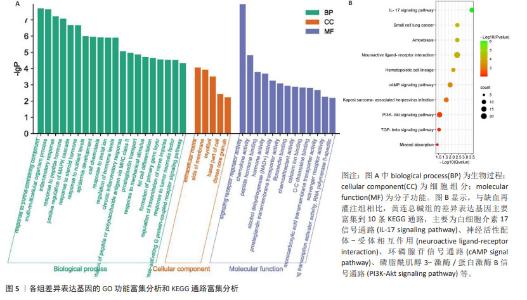
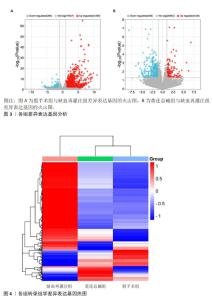
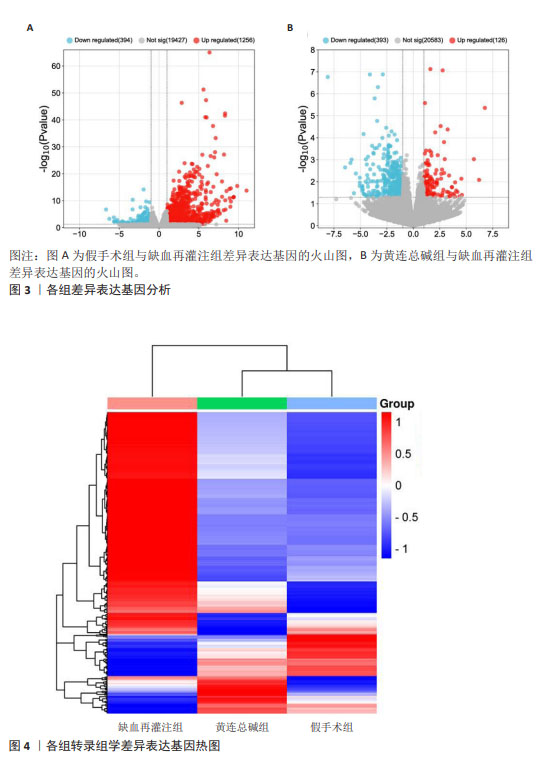
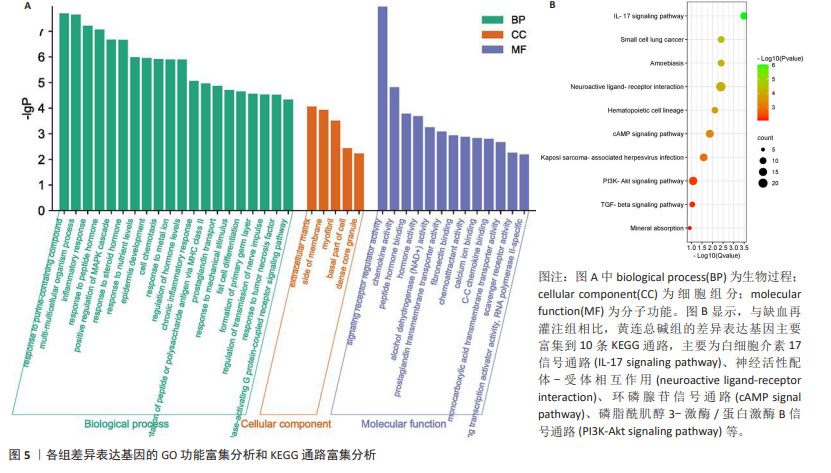
2.8 GO 功能富集分析和 KEGG 通路富集分析 与缺血再灌注组相比,黄连总碱组的差异表达基因主要富集到38个GO条目,其中生物过程20条,细胞组分5条,分子功能13条。排前5位的生物过程分别是对含嘌呤化合物的反应(response to purine- containing compound)、多细胞生物过程(multi-multicellular organism process)、炎症反应(inflammatory response)、对肽类激素的反应(response to peptide hormone)、分裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)级联的正调控(positive regulation of MAPK cascade);排前5位的细胞组分分别是细胞外基质(extracellular matrix)、膜侧(side of membrane)、肌原纤维(myofibril)、细胞基底部(basal part of cell)、致密核心颗粒(dense core granule);排前5位分子功能分别是信号受体调节活性(signaling receptor regulator activity)、趋化因子的活动(chemokine activity)、肽激素结合(peptide hormone binding)、激素的活动(hormone activity)、醇脱氢酶(NAD+)活性[alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity]。见图5A。 与缺血再灌注组相比,黄连总碱组的差异表达基因共富集到10条KEGG通路,主要为白细胞介素17信号通路(IL-17 signaling pathway)、神经活性配体-受体相互作用(neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction)、环磷腺苷信号通路(cAMP signal pathway)、磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路(PI3K-Akt signaling pathway)等,见图5B。"
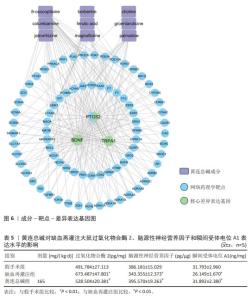
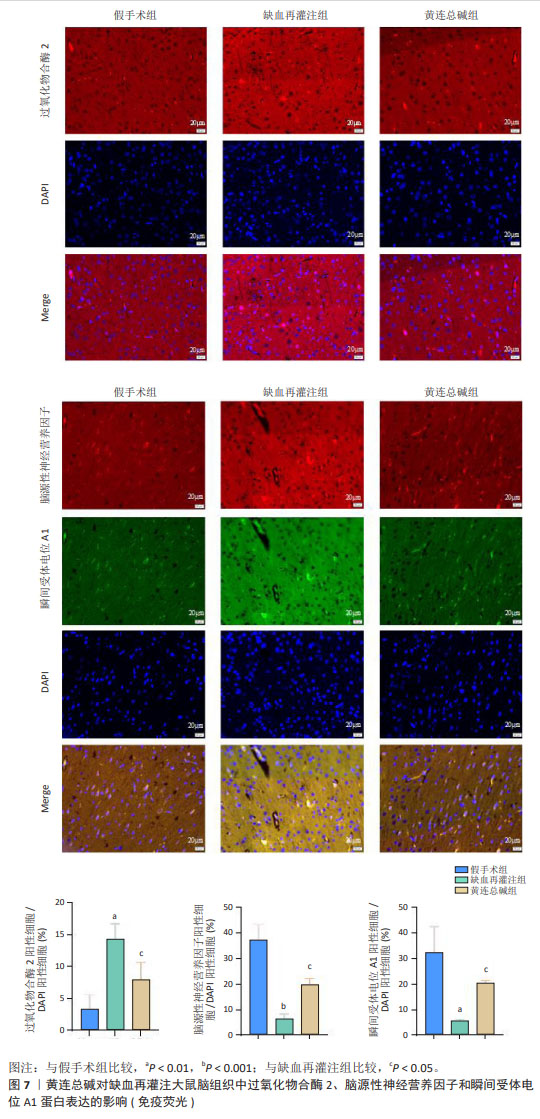
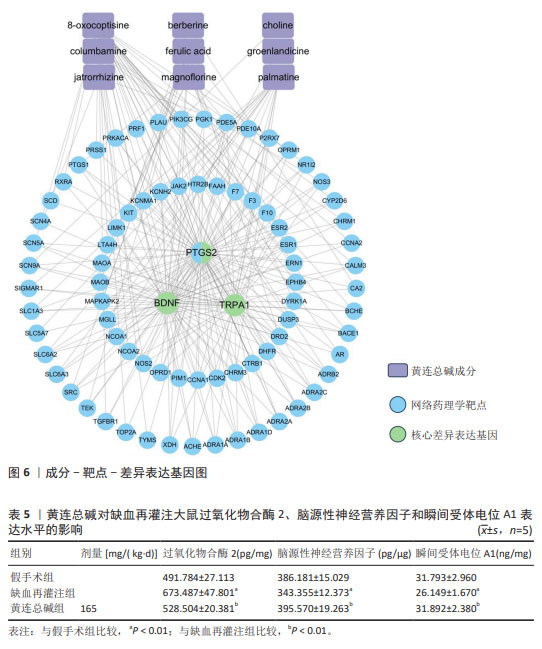
2.9 网络药理学分析 将转录组学黄连总碱组与缺血再灌注组的关键差异表达基因与网络药理学黄连总碱抗脑缺血预测的87个潜在作用靶点进行关联分析,构建成分-靶点-差异表达基因图,由图6可知,差异表达基因与预测的87个潜在作用靶点能较好关联,黄连总碱可能通过干预预测的87个潜在作用靶点而影响过氧化物合酶2、脑源性神经营养因子及瞬间受体电位A1发挥抗脑缺血 作用。 2.10 ELISA检测脑组织过氧化物合酶2、脑源性神经营养因子和瞬间受体电位A1表达水平 对黄连总碱干预脑缺血的关键靶点进行验证,结果表明,相较于假手术组,缺血再灌注组大鼠脑组织过氧化物合酶2表达水平显著升高(P < 0.01),脑源性神经营养因子和瞬间受体电位A1表达水平均明显降低(P < 0.01);相较于缺血再灌注组,黄连总碱组大鼠脑组织过氧化物合酶2表达水平显著降低(P < 0.01),脑源性神经营养因子和瞬间受体电位A1表达水平均明显升高(P < 0.01),见表5。"
| [1] ZHANG JJ,GUO FF, ZHOU R, et al. Proteomics and transcriptome reveal the key transcription factors mediating the protection of Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Phytomedicine. 2021;92:153613. [2] BOEHME AK, ESENWA C, ELKIND MS. Stroke Risk Factors, Genetics, and Prevention. Circ Res. 2017;120(3):472-495. [3] CAMPBELL BCV, DE SILVA DA, MACLEOD MR, et al. Ischaemic stroke. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019; 5(1):70. [4] FU Y, LIU Q, ANRATHER J, et al. Immune interventions in stroke. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015; 11(9):524-535. [5] SAINI V, GUADA L, YAVAGAL DR. Global Epidemiology of Stroke and Access to Acute Ischemic Stroke Interventions. Neurology. 2021;97(20 Supplement 2):S6-S16. [6] 石晓花, 莽靖, 徐忠信. 脑缺血再灌注损伤细胞死亡模式的研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版),2022,48(6):1635-1643. [7] ZHENG P, ZHANG N, REN D, et al. Integrated spatial transcriptome and metabolism study reveals metabolic heterogeneity in human injured brain. Cell Rep Med. 2023;4(6): 101057. [8] ZHENG K, LIN L, JIANG W, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals the transcriptional landscape in ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2022;42(1):56-73. [9] 丁实, 赵学荣, 赵亮, 等. 黄连素通过B细胞淋巴瘤-2/自噬相关基因复合体抑制自噬减轻脑缺血再灌注损伤的研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志,2021,37(9):1094-1097. [10] HU J, CHAI Y, WANG Y, et al. PI3K p55γ promoter activity enhancement is involved in the anti-apoptotic effect of berberine against cerebral ischemia–reperfusion. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012;674(2):132-142. [11] KIM M, KIM TW, KIM CJ, et al. Berberine Ameliorates Brain Inflammation in Poloxamer 407-Induced Hyperlipidemic Rats. Int Neurourol J. 2019;23(Suppl 2):S102-S110. [12] CHENG F, WANG Y, LI J, et al. Berberine improves endothelial function by reducing endothelial microparticles-mediated oxidative stress in humans. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167(3): 936-942. [13] SARNA LK, WU N, HWANG SY, et al. Berberine inhibits NADPH oxidase mediated superoxide anion production in macrophages. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010;88(3):369-378. [14] ZHOU R, GUO F, XIANG C, et al. Systematic Study of Crucial Transcription Factors of Coptidis rhizoma Alkaloids against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021;12(13):2308-2319. [15] CHEN HY, YE XL, CUI XL, et al. Cytotoxicity and antihyperglycemic effect of minor constituents from Rhizoma Coptis in HepG2 cells. Fitoterapia. 2012;83(1):67-73. [16] 李淑琴, 朱嘉宝, 武宇洲. 银杏叶提取物防治心脑血管疾病的研究进展[J]. 中国新药杂志,2016,25(1):76-81. [17] ZHANG JJ, GUO FF, ZHOU R, et al. Proteomics and transcriptome reveal the key transcription factors mediating the protection of Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Phytomedicine. 2021:153613. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153613. [18] ZHANG JJ, ZHOU R, CAO GZ, et al. Guhong Injection Prevents Ischemic Stroke-Induced Neuro-Inflammation and Neuron Loss Through Regulation of C5ar1. Front Pharmacol. 2022; 13:818245. [19] LIU R, DIAO J, HE S, et al. XQ-1H protects against ischemic stroke by regulating microglia polarization through PPARγ pathway in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;57:72-81. [20] XU D, HOU K, LI F, et al. XQ-1H alleviates cerebral ischemia in mice through inhibition of apoptosis and promotion of neurogenesis in a Wnt/β-catenin signaling dependent way. Life Sci. 2019;235:116844. [21] WANG Y, PEI DS, JI HX, et al. Protective effect of a standardized Ginkgo extract (ginaton) on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppressing the activation of JNK signal pathway. Phytomedicine. 2008;15(11):923-931. [22] LO EH, DALKARA T, MOSKOWITZ MA. Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4(5):399-415. [23] MOSKOWITZ MA, LO EH, IADECOLA C. The Science of Stroke: Mechanisms in Search of Treatments. Neuron. 2010;67(2):181-198. [24] 巩婷婷, 司凯, 刘会平, 等. MAPK级联调控细胞生长及其在免疫,炎症及癌症中作用的研究进展[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2022, 47(12):1721-1728. [25] 许川山, 余茜, 吴士明, 等. MAPK级联传导途径与脑缺血性损害[J]. 现代康复,2001 (13):62-63. [26] ZHANG M, GONG JX, WANG JL, et al. p38 MAPK Participates in the Mediation of GLT-1 Up-regulation During the Induction of Brain Ischemic Tolerance by Cerebral Ischemic Preconditioning. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;54(1): 1-14. [27] GELDERBLOM M, WEYMAR A, BERNREUTHER C, et al. Neutralization of the IL-17 axis diminishes neutrophil invasion and protects from ischemic stroke. Blood. 2012;120(18): 3793-3802. [28] SUN L, ZHANG H, WANG W, et al. Astragaloside IV Exerts Cognitive Benefits and Promotes Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Stroke Mice by Downregulating Interleukin-17 Expression via Wnt Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11: 421. [29] ZHANG Q, LUO T, YUAN D, et al. Retraction Note: Qilongtian ameliorate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice via inhibiting IL-17 signal pathway. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):11263. [30] 潘玲珍,闫智勇,左长英,等.长期使用地西泮对神经活性配体受体相互作用信号通路的影响[J]. 中国药科大学学报,2011, 42(5):443-446. [31] ZHANG S, WANG X, YANG Q, et al. Isopropyl 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxypropanoate plays an anti-hypoxic role through regulating neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction signaling pathway in larval zebrafish. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;161:114570. [32] ZAN XY, LI L. Construction of lncRNA-mediated ceRNA network to reveal clinically relevant lncRNA biomarkers in glioblastomas. Oncol Lett. 2019;17(5):4369-4374. [33] HU S, CAO Q, XU P, et al. Rolipram stimulates angiogenesis and attenuates neuronal apoptosis through the cAMP/cAMP-responsive element binding protein pathway following ischemic stroke in rats. Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(3):1005-1010. [34] LIU C, DU L, ZHANG S, et al. Network pharmacology and experimental study of phenolic acids in salvia miltiorrhiza bung in preventing ischemic stroke. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1108518. [35] WANG YL, ZHU XL, SUN MH, et al. Effects of astaxanthin onaxonal regeneration via cAMP/PKA signaling pathway in mice with focal cerebral infarction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(3 Suppl):135-143. [36] ZHOU XQ, ZENG XN, KONG H, et al. Neuroprotective effects of berberine on stroke models in vitro and in vivo. Neurosci Lett. 2008;447(1):31-36. [37] ZHU JR, LU HD, GUO C, et al. Berberine attenuates ischemia–reperfusion injury through inhibiting HMGB1 release and NF-κB nuclear translocation. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 2018;39(11):1706-1715. [38] JIN X, WANG RH, WANG H, et al. Brain protection against ischemic stroke using choline as a new molecular bypass treatment. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 2015;36(12):1416-1425. [39] WANG J, TANG M, XIE X, et al. Efficacy of ferulic acid in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke injury in rats: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2023; 14: 1278036. [40] ZHONG F, CHEN Y, CHEN J, et al. Jatrorrhizine: A Review of Sources, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics and Toxicity. Front Pharmacol. 2022;12:783127. [41] LIANG H, CHANG X, XIA R, et al. Magnoflorine attenuates cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal injury via autophagy/sirt1/AMPK signaling pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:2131561. [42] TANG C, HONG J, HU C, et al. Palmatine protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by activation of the AMPK/Nrf2 pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6660193. [43] PEREIRA JF, DE SOUSA NEVES JC, FONTELES AA, et al. Palmatine, a natural alkaloid, attenuates memory deficits and neuroinflammation in mice submitted to permanent focal cerebral ischemia. J Neuroimmunol. 2023;381:578131. [44] COLAIZZO D, FOFI L, TISCIA G, et al. The COX-2 G/C− 765 polymorphism may modulate the occurrence of cerebrovascular ischemia. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2006;17(2):93-96. [45] LIN W, WANG Y, CHEN Y, et al. Role of calcium signaling pathway-related gene regulatory networks in ischemic stroke based on multiple WGCNA and single-cell analysis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:8060477. [46] ZHOU Z, LU C, MENG S, et al. Silencing of PTGS2 exerts promoting effects on angiogenesis endothelial progenitor cells in mice with ischemic stroke via repression of the NF-κB signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(12):23448-23460. [47] CUI Q, ZHANG YL, MA YH, et al. A network pharmacology approach to investigate the mechanism of Shuxuening injection in the treatment of ischemic stroke. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;257:112891. [48] 尚津锋, 焦家康, 李倩楠, 等. 白杨素通过抑制铁死亡减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 中国中药杂志,2023,48(6): 597-1605. [49] REX D, DAGAMAJALU S, GOUDA MM, et al. A comprehensive network map of IL-17A signaling pathway. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023; 17(1):209-215. [50] LI JK, NIE L, ZHAO YP, et al. IL-17 mediates inflammatory reactions via p38/c-Fos and JNK/c-Jun activation in an AP-1-dependent manner in human nucleus pulposus cells. J Transl Med. 2016:14:77. [51] BALKAYA M, CHO S. Genetics of stroke recovery: BDNF val66met polymorphism in stroke recovery and its interaction with aging. Neurobiol Dis. 2019;126:36-46. [52] BÉJOT Y, MOSSIAT C, GIROUD M, et al. Circulating and Brain BDNF Levels in Stroke Rats. Relevance to Clinical Studies. PLOS ONE. 2011;6(12):e29405. [53] DI LAZZARO V, PELLEGRINO G, DI PINO G, et al. Val66Met BDNF gene polymorphism influences human motor cortex plasticity in acute stroke. Brain Stimul. 2015;8(1):92-96. [54] 何恩浩, 曾燕, 陈星星. Hap1在神经系统疾病中的研究进展[J]. 生命科学,2023,35(5): 592-600. [55] PLOUGHMAN M, ATTWOOD Z, WHITE N, et al. Endurance exercise facilitates relearning of forelimb motor skill after focal ischemia. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;25(11):3453-3460. [56] ZHAO D, ZHANG M, YANG L, et al. GPR68 improves nerve damage and myelination in an immature rat model induced by sevoflurane anesthesia by activating cAMP/CREB to mediate BDNF. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2022;13(3):423-431. [57] EARLEY S, GONZALES AL, CRNICH R. Endothelium-dependent cerebral artery dilation mediated by TRPA1 and Ca2+-Activated K+ channels. Circ Res. 2009;104(8):987-994. [58] PIRES PW, EARLEY S. Neuroprotective effects of TRPA1 channels in the cerebral endothelium following ischemic stroke. eLife. 2018;7:e35316. [59] PIRES PW, SULLIVAN MN, EARLEY S. Endothelial TRPA1 Channel is Protective Against Ischemia and Hemorrhagic Strokes in Mice. Stroke. 2016;47(suppl_1):A141-A141. |
| [1] | De Ji, Suo Langda, Wei Yuchen, Wang Bin, Awangcuoji, Renqingcuomu, Cui Jiuzeng, Zhang Lei, Ba Gui. Comprehensive analysis of genes related to endometrial receptivity and alternative splicing events in northwest Tibetan cashmere goats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1429-1436. |
| [2] | Yu Hui, Yang Yang, Wei Ting, Li Wenli, Luo Wenqian, Liu Bin. Gadd45b alleviates white matter damage in chronic ischemic rats by modulating astrocyte phenotype [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7797-7803. |
| [3] | Liu Ruojing, Zhao Xue, Zhu Yizhen, Fu Lingling, Zhu Junde. Ginsenoside Rb1 alleviates cerebral ischemic injury in mice by regulating microglial polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6219-6227. |
| [4] | Liu Yantong, Wang Shixuan, Zhao Shuangli, Wei Wei, Wang Donghai, Jiang Zongkun, Liu Hongfei. Transcriptional profiling and experimental validation of acupotomy for knee osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4239-4248. |
| [5] | Zhang Shuo, Cui Yinglin, Zhou Panpan, Li Yile, Wang Lei, Zou Qianqian. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress-autophagy in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4325-4332. |
| [6] | Wu Haiyang, Duan Mian, Li Chenglong, Zhang Junyu, Ji Haisheng, Wang Haitao, Mao Wei, Wang Ying. Neuroprotective mechanism of electroacupuncture in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3811-3818. |
| [7] | Wang Ruikun, Gao Weijuan, Zhang Haoran, Liu Yijie, Bu Jiaxin, Yuan Mei, Qin Yuxin, Zhang Yi. Effects of Buyang Huanwu Tang and its main components on pyroptosis in brain tissue of rats with middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3819-3825. |
| [8] | Sun Chengtao, Sun Guangjiang , Qi Xiaonan , Cheng Ming , Yao Xiaosheng. Applications and advances of single-cell transcriptome sequencing technology in osteoporosis research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2812-2821. |
| [9] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [10] | Liu Kexin, Song Lijuan, Wu Yige, Han Guangyuan, Miao Zhuyue, Wei Ruheng, Xiao Baoguo, Ma Cungen, Huang Jianjun. Hydroxysafflor yellow A intervenes astrocyte lipocalin 2 expression after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1063-1069. |
| [11] | Tang Lulu, Pan Xiaojia, Lai Yingtao, Wang Li. Regulatory mechanism of ferroptosis on pressure ulcers: bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5656-5661. |
| [12] | Yu Yanyan, Liu Juan, Yang Yue, Wang Qianhui, Li Shan, Jiang Jie. Moxibustion inhibits NLRP3/Caspase-1 pathway mediated cell pyroptosis and alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5473-5479. |
| [13] | Song Wenxue, Liao Yidong, Ming Jiang, He Longcai, Chen Guangtang, Chen Chen, Wang Zili, Xiong Mingsong, Cui Junshuan, Xu Kaya. Intracranial transplantation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviates rat brain ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 5036-5041. |
| [14] | Ma Jianglei, Zhang Huijie, Zhang Chenfang, Yang Xitong, Cheng Jianjie, Wang Guangming. Neuroprotective mechanism by which fenofibrate regulates superoxide dismutase 2 expression in transgenic C57BL/6J mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4547-4552. |
| [15] | Huang Ting, Liu Xia, Wang Zhu, Chen Ting, Chen Bin, Bai Guohui, Wu Jiayuan, Tian Yuan. Screening and analysis of differentially expressed genes for calcium homeostasis in ameloblasts with high fluoride intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2481-2487. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||