Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (16): 2481-2487.doi: 10.12307/2024.309
Previous Articles Next Articles
Screening and analysis of differentially expressed genes for calcium homeostasis in ameloblasts with high fluoride intervention
Huang Ting1, Liu Xia1, Wang Zhu2, Chen Ting2, Chen Bin2, Bai Guohui1, Wu Jiayuan1, Tian Yuan1
- 1Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2023-02-14Accepted:2023-04-24Online:2024-06-08Published:2023-07-29 -
Contact:Tian Yuan, Chief physician, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Huang Ting, Master, Physician, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960198 (to TY); Zunyi Municipal Research and Development Innovation Talent Team Program for Oral Disease Immunoprevention and Medical Biomaterials, No. [2022]1 (to BGH); Oral Infectious and Malignant Diseases Etiology and Prevention Team Program of Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, No. HZ(2020) (to WJY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Ting, Liu Xia, Wang Zhu, Chen Ting, Chen Bin, Bai Guohui, Wu Jiayuan, Tian Yuan. Screening and analysis of differentially expressed genes for calcium homeostasis in ameloblasts with high fluoride intervention[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2481-2487.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
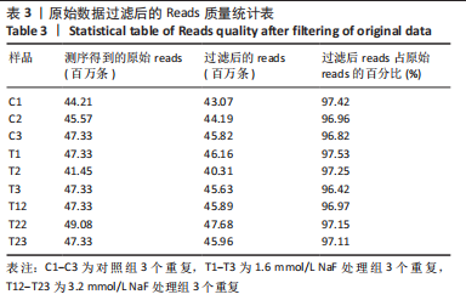
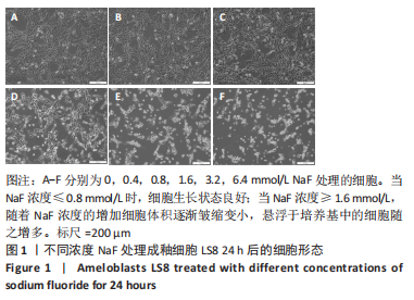
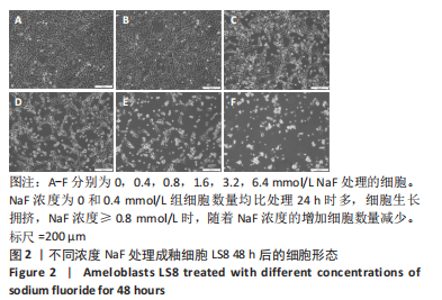
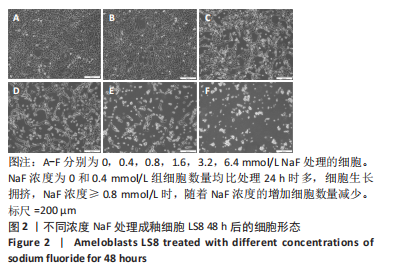
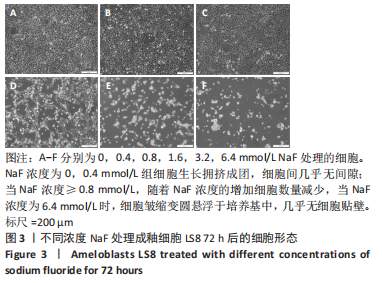
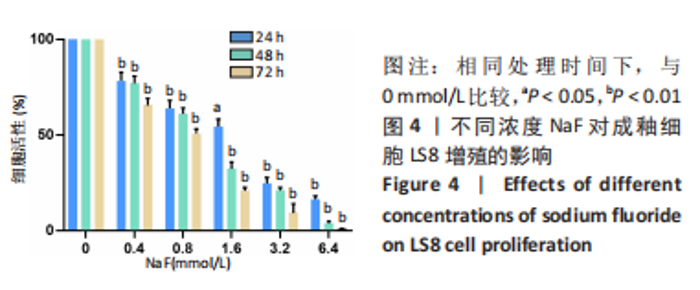
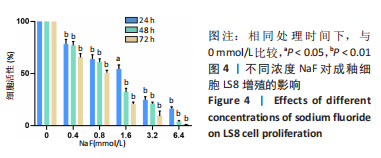
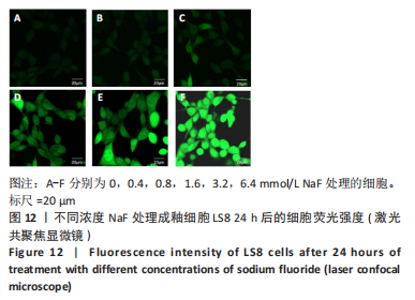
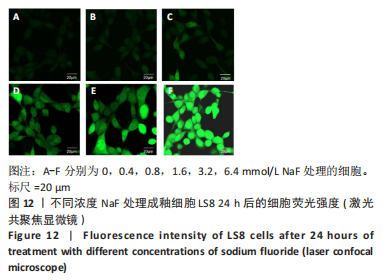
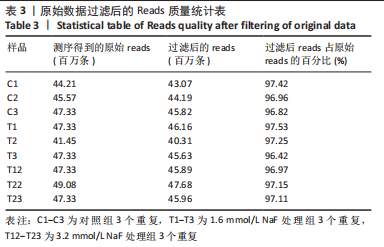
2.3 转录组测序分析结果 根据CCK-8实验得出NaF 处理LS8细胞 24 h 的半抑制浓度为1.640 mmol/L,因此实验选择NaF 浓度为1.6 mmol/L处理LS8细胞24 h作为中间浓度组(T1)、NaF 浓度为3.2 mmol/L处理LS8细胞24 h作为高浓度组(T2),选择NaF浓度为0 mmol/L(不加NaF)作为对照组,分为3 个组,每组3 个生物学重复,一共9 个样本,进行转录组测序,每个样品平均产出6.74 G数据,一共检测到16 517个基因。测序的原始数据去除低质量、接头污染以及未知碱基N含量过高的reads,过滤后reads质量统计见表3,整体测序数据质量达到分析要求。"
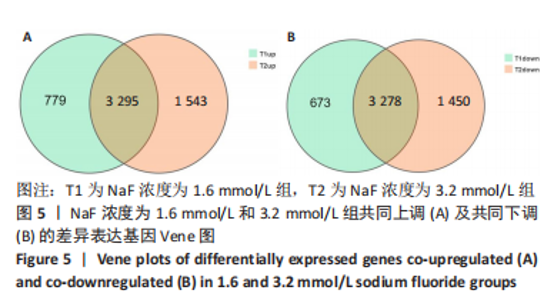
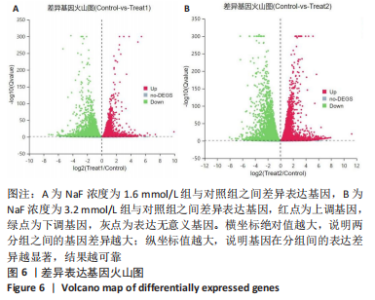
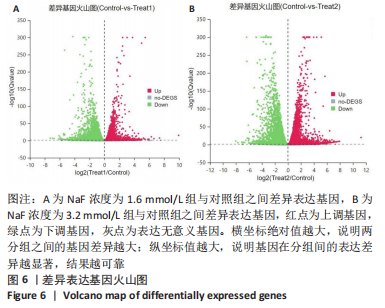
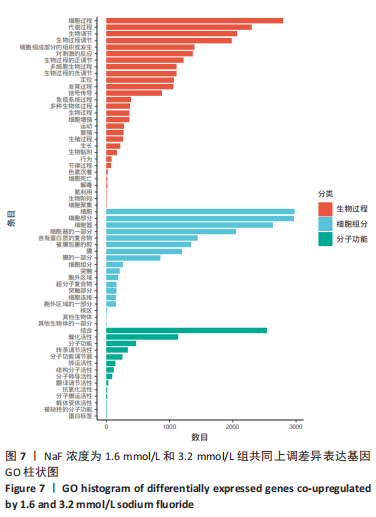
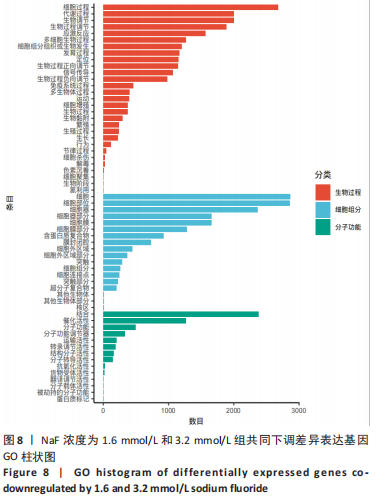
2.3.1 差异表达基因分析结果 基因差异表达分析显示,NaF浓度为1.6 mmol/L组上调的基因有4 074 个、下调的有3 951 个,NaF浓度为3.2 mmol/L组上调的基因有4 838 个、下调的有4 728 个,由于NaF浓度为1.6 mmol/L和3.2 mmol/L两组差异表达基因数目过多不利于分析,为了更好地说明NaF对成釉细胞的影响,筛选NaF浓度为1.6 mmol/L和3.2 mmol/L两组共同差异表达基因进行分析,Venn分析表明,如图5A绿色部分(T1 up)是NaF浓度为1.6 mmol/L处理LS8细胞24 h 的转录组测序分析,结果得出上调的差异表达基因有779 个;粉色部分(T2 up)是NaF浓度为3.2 mmol/L处理LS8细胞24 h的转录组测序分析,结果得出上调的差异表达基因有1 543 个,两组共同上调的基因有3 295 个。如图5B绿色部分(T1 down)是NaF浓度为1.6 mmol/L处理LS8细胞24 h的转录组测序分析,结果得出下调调的差异表达基因有673 个;粉色部分(T2 down)是NaF浓度为3.2 mmol/L处理LS8细胞24 h的转录组测序分析,结果得出下调的差异表达基因有1 450 个,共同下调基因有3 278 个。"
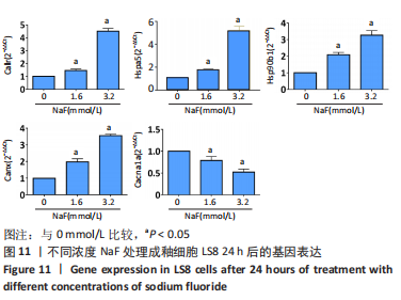
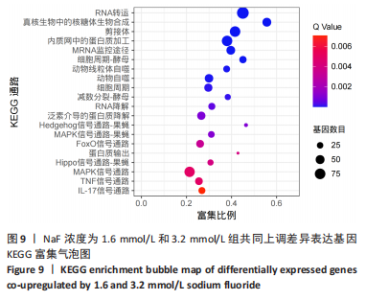
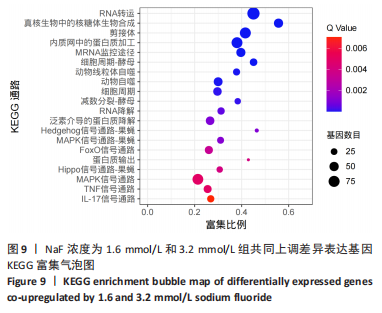
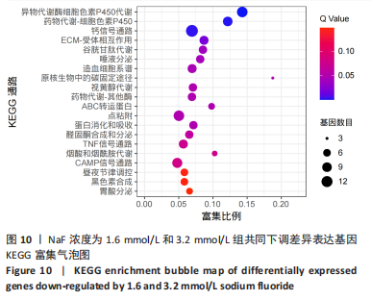
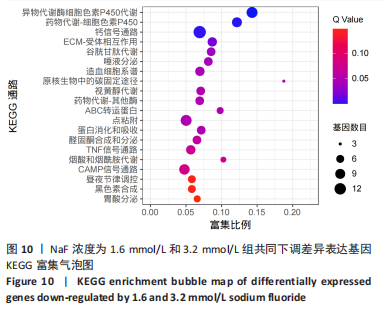
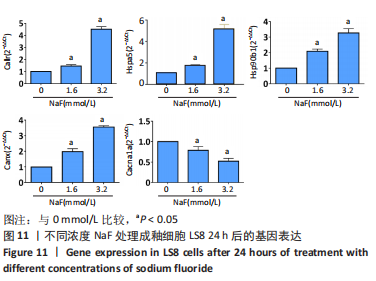
通过KEGG对差异表达基因进行信号通路富集分析,显著富集的通路主要有蛋白质在内质网中的加工、钙信号通路及代谢通路等,并具有统计学意义。通过对富集的信号通路进一步分析发现,蛋白质在内质网中加工信号通路显著富集的基因(如:Hsp90b1、Canx、Calr、Hspa5、Bax、Xbp1、Atf6、upd1、Sec61a1、Sec61a1)和钙信号通路中显著富集的基因(如:Cacna1a、Itpka、Ptk2b、Ptgf、Calml4、Plcd1、Camk2b、Adra1d、Gna14、Nos1)参与调控细胞的Ca2+浓度。 2.4 RT-qPCR 验证测序结果 为进一步验证RNA-seq筛选出的基因的表达水平,实验选择了5 个显著差异基因采用RT-qPCR进行验证,选择差异倍数较高的基因Cacna1a、Hsp90b1、Canx、Calr、Hspa5。RT-qPCR检测结果显示,Hsp90b1、Canx、Calr、Hspa5的表达显著上调,Cacna1a的表达显著下调(P < 0.05),见图11。通过上述结果进一步验证 RNA-seq测序结果可靠,同时证明了NaF影响LS8细胞基因的表达水平。"
| [1] 高秀秀,王富珍.氟斑牙危险因素的研究进展[J].系统医学,2017,2(15): 152-153. [2] 永娜,张岱尊,肖文林,等.不同浓度氟化物对氟牙症釉质的影响[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2015,25(6):375-377. [3] 官志忠,吴昌学,齐晓岚.综合治理后贵州省燃煤型地氟病区人群健康状况评价[J].贵州医科大学学报,2018,43(10):1124-1128. [4] WEI W, PANG S, SUN D. The pathogenesis of endemic fluorosis: Research progress in the last 5 years. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(4):2333-2342. [5] 敬珮.细胞自噬在氟诱导成釉细胞凋亡中的作用[D].遵义:遵义医学院,2018. [6] 曾蔼霖,李惠如,胡小艳,等.氟斑牙大鼠发生纤维瘤:内质网应激和线粒体的激活途径(英文)[J].遵义医科大学学报,2021,44(4):433-439. [7] 迟戈夫.染氟对成纤维细胞和成骨细胞c-fos和c-jun基因表达的影响[J].内蒙古民族大学学报(自然科学版),2008,23(2):184-188. [8] 李玉波.高氟地区学龄儿童氟斑牙发生情况及其影响因素分析[J].现代医学与健康研究电子杂志,2021,5(22):89-92. [9] 王俊东,孙子龙.氟的毒理学研究[J].山西农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018,38(6):1-7. [10] LI YB, LI F, GUO S, et al. Microscopic observation of the enamel microstructures of SD rats with different degrees of fluorosis. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021;56(12): 1261-1266. [11] 房程龙,陆玉成,付庆喜,等.热休克蛋白90与肿瘤相关性研究进展[J].海南医学,2019,30(13):1744-1747. [12] 陈明帅,徐超,宋兴超,等.热休克蛋白的研究进展[J].经济动物学报, 2016,20(1):44-53. [13] 梁永红,冯超,周忠信.热休克蛋白90α通过增强钙库操作性钙离子内流活性促进肝癌细胞转移[J].实用医学杂志,2018,34(23):3859-3864. [14] 张乐,王军强,高江红,等.培养基加氟导致的渗透压变化对成釉细胞生物学特性的影响[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2020,41(5):718-723. [15] RODRIGUES BL, DOTTI I, PASCOAL LB, et al. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Colonic Mucosa of Ulcerative Colitis Patients Is Mediated by PERK and IRE1 Pathway Activation. Mediators Inflamm. 2022;2022:6049500. [16] 戴琳玉,闫宇,王路广,等.下调钙网蛋白基因表达可促进肝星状细胞凋亡[J].第三军医大学学报,2021,43(10):908-914. [17] 张超,白剑英,王东新,等.甲醛对人肝癌细胞株HepG2内质网应激相关Bip和CANX mRNA及蛋白表达水平的影响[J].癌变•畸变•突变, 2017,29(5):340-345+351. [18] ELFIKY A. Natural products may interfere with SARS-CoV-2 attachment to the host cell. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021;39:3194-3203. [19] COSTINITI V, BOMFIM GH, MITAISHVILI E, et al. Calcium Transport in Specialized Dental Epithelia and Its Modulation by Fluoride. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:730913. [20] 冯竞仰,陆冰,朱鸿,等.热休克蛋白5调控内质网应激在视网膜色素上皮细胞保护中的作用[J].眼科新进展,2019,39(12):1111-1115. [21] 范雪新,杨磊,项斌,等.钙离子通道蛋白的研究进展[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2016,43(12):1129-1138. [22] 张颖,马林,李健,等.过量氟诱导成釉细胞钙超载及细胞凋亡的实验研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2014,32(6):542-546. [23] 刘颖,于海波,孔庆飞.癫痫的治疗和药物发现现状[J].药学学报,2021, 56(4):924-938. [24] VINCENZ DL, HIPP MS. The endoplasmic reticulum: A hub of protein quality control in health and disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017;108:383-393. [25] MONTEVERDE T, TAIT-MULDER J, HEDLEY A, et al. Calcium signalling links MYC to NUAK1. Oncogene. 2018;37:982-992. [26] COSTINITI V, BOMFIM GH, MITAISHVILI E, et al. Calcium Transport in Specialized Dental Epithelia and Its Modulation by Fluoride. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:730913. [27] 李健,张颖,马林,等.氟对大鼠成釉细胞GRP-78和caspase-12表达的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2015,24(1):1-5. [28] EMRICH SM, YOAST RE, XIN P, et al. Omnitemporal choreographies of all five STIM/Orai and IPRs underlie the complexity of mammalian Ca signaling. Cell Rep. 2021;34(9):108760. [29] JOHNSON J, BLACKMAN R, GROSS S, et al. Control of STIM and Orai function by post-translational modifications. Cell Calcium. 2022;103:102544. [30] CHU F, WAN H, XIAO WD, et al. Ca-Permeable Channels/Ca Signaling in the Regulation of Ileal Na/Gln Co-Transport in Mice. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13: 816133. [31] CALI T, BRINI M, CARAFOLI E. Regulation of Cell Calcium and Role of Plasma Membrane Calcium ATP ases. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2017;332:259-296. |
| [1] | Yang Chun, Wen Jianxia, Feng Jianglong, Guan Zhizhong, Wei Na. Expression of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor and endoplasmic reticulum stress related pathway proteins in brain tissue of fluorosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1070-1075. |
| [2] | Deng Longfei, Zhang Yeting, Fu Yan. Aerobic exercise inhibits neuroinflammation and alleviates cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2209-2214. |
| [3] | Zhang Li, Yang Wenjun, Sang Xiaohong, Han Yuanyuan, Mao Zhijie, Wang Shun, Lu Chen. Effect of overexpression of protein phosphatase 2Cm on transcriptome of human renal tubular epithelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 68-73. |
| [4] | Li Yangjie, Qi Rong, Zhang Xinyu, Cheng Jiaji, Zhou Ning, Cui Xue, Cheng Shuang, Wang Zhengdong, Yan Nan. Neuroprotective effects of sodium butyrate and acetylation proteomics analysis in fluorosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3151-3157. |
| [5] | Liang Weiye, Duan Qinghong. Correlation between femur bone morphogenetic protein 2 expression and bone fluoride content in fluorosis rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2675-2680. |
| [6] | Tang Yujing, Lan Fengjun, Li Guangdi, Wang Jian, Liu Riguang. Role of calcium ions in the pathogenesis of chronic fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2745-2753. |
| [7] | Wen Hongjie, Chen Zhong, Yang Huagang, Xu Yongqing. Transcriptome sequencing analysis of osteogenic rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2333-2338. |
| [8] | Cai Bo, Li Xiaoxiao, Zhang Linghan, Liu Yanxing, Mao Genhong. Editing immune-related gene HLA-DRA for the first time by CRISPR/Cas9 technology combined with liposome transfection of endometrial cancer cells with single-plasmid gene knockout method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2356-2362. |
| [9] | Sun Honglei, Qi Fengna, Cheng Ruiqing. ICON penetrating resin for treatment of dental fluorosis: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5419-5424. |
| [10] | Ding Xue, Jia Ying, Liu Chun, Yang Shirong, Lai Lingyan, Yang Hua, Ding Qi. Displacement and rate changes of orthodontic tooth movement in Sprague-Dawley rats with chronic fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4687-4692. |
| [11] | Chen Xia, Shang Yuwei, Wang Linxiao, Shi Yichao, Liu Huijun, Sun Huiting. Transcriptome sequencing of the uterine in a mouse model of vitamin D deficiency [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4101-4106. |
| [12] | Gu Xiaodong, Li Fei, Che Xianda, Li Pengcui. Relationship between apoptosis of osteoarthritis chondrocytes and reduction of histone deacetylase 4 content [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(20): 3147-3151. |
| [13] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [14] | Zhao Qianzeng, Zhao Zhenqun, Liu Wanlin. Endoplasmic reticulum stress regulates autophagy and apoptosis in steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4685-4690. |
| [15] | Zhang Xujian, Zhao Zhenqun, Liu Wanlin. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the pathogenesis of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1759-1765. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||