Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (17): 3668-3674.doi: 10.12307/2025.626
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of alpha-synuclein in mitochondrial damage induced by Parkinson’s disease
Wang Jingying1, 2, Ren Binbin2, Ma Suna1, Yang Yueyue1, 2, Wu Song1, 2, Guan Mengya1, 2
- 1School of Rehabilitation, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2024-05-11Accepted:2024-07-15Online:2025-06-18Published:2024-11-06 -
Contact:Ren Binbin, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Wang Jingying, Master candidate, School of Rehabilitation, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance and Innovation Talent Project (Zhongjing Project) (to RBB); 2022 Henan Province Chinese Medicine Top Talent Cultivation Program Special Project, No. 2022ZYBJ09 (to RBB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Jingying, , Ren Binbin, Ma Suna, Yang Yueyue, , Wu Song, , Guan Mengya, . Mechanism of alpha-synuclein in mitochondrial damage induced by Parkinson’s disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3668-3674.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
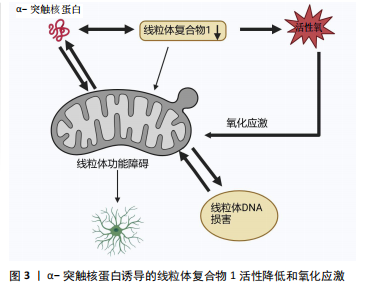
2.1 α-突触核蛋白概述 α-突触核蛋白是小型高电荷蛋白质家族中的一员并在神经元中高度表达[1]。在过往的20余年研究中,人们对α-突触核蛋白的结构、功能以及在退行性神经疾病中的作用有了更深刻的了解。最初的体外实验表明,α-突触核蛋白的自发性聚集现象随其浓度的递增而增加[2]。在细胞及体内模型研究中发现α-突触核蛋白积聚成毒性低聚物与帕金森病多巴胺能神经变性有关[3]。正常情况下,α-突触核蛋白以可溶性未折叠状态存在[4],但在某些病理因素作用下,会发生错误折叠,聚集为有毒的聚集体,引发神经元的损伤变性,继而导致帕金森病的发生,见表1。 2.1.1 α-突触核蛋白的结构及功能 α-突触核蛋白由SNCA基因编码,包含140个氨基酸,分子质量为14.5 kD[5],由3个不同的区域组成:N端区域(氨基酸残基1-60)是具有7个氨基酸KTKEGV重复序列的六聚体基序,该序列易形成两性α螺旋,是介导α-突触核蛋白与脂质膜结合的区域。中心疏水区域(氨基酸残基61-95)为非淀粉样蛋白成分区域,介导α-突触核蛋白聚集。C端区域(氨基酸残基96-140)具有较高的氨基酸含量,由于其高净负电荷的存在,可通过降低pH值来诱导α-突触核蛋白的聚集来中和这些负电荷[6]。需要注意的是,α-突触核蛋白的C末端含有较多与帕金森病相关的翻译后修饰位点,如磷酸化、硝酸化、截断等加速其聚集速率[7]。 在生理状态下,α-突触核蛋白以无序单体状态在中枢神经系统内高度存在,也在外周神经元、骨髓的造血细胞以及循环血细胞中表达[8]。研究表明,神经元中α-突触核蛋白主要位于突触前末端并与膜相互作用进而调节突触囊泡、神经递质以及参与微管动力学等[9-10]。病理状态下α-突触核蛋白具有自组装倾向,形成低聚物、原纤维以及较大的聚集体,即毒性α-突触核蛋白[11]。这些有毒形式的α-突触核蛋白可以通过各种细胞过程,如参与氧化应激、细胞凋亡、线粒体功能等,产生负面影响导致帕金森病发生[12]。目前一个新兴的假设正受到广泛关注:是否由于α-突触核蛋白低聚物和原纤维直接引起线粒体损伤诱导的细胞毒性从而引起帕金森病。 2.1.2 α-突触核蛋白的聚集毒性及基因突变 α-突触核蛋白在人脑动态平衡中存在有不同的构象和聚合状态,包括天然构象(未折叠单体、螺旋折叠的四聚体)和有毒构象(低聚状态、原纤维),各种构象形状和低聚状态之间存在着动态平衡[13]。α-突触核蛋白低聚物主要通过细胞膜的透化来发挥细胞毒性作用,氧化应激、翻译后修饰、金属毒性、蛋白水解等可以调节α-突触核蛋白的结构和低聚化状态[14]。α-突触核蛋白亦受翻译后修饰的影响,主要包括磷酸化以及泛素化,这些修饰似乎都有利于寡聚化形成。有趣的是,硝化和磷酸化形式的α-突触核蛋白存在于帕金森病患者的大脑中[15],其中残基Ser129处的磷酸化在调节α-突触核蛋白聚集和神经毒性中起关键作用[16]。帕金森病动物模型中也观察到了磷酸化α-突触核蛋白在Ser129处的积累。此外,与表达野生型或磷酸化缺陷形式的小鼠相比,Ser-129的磷酸化加速了过表达α-突触核蛋白的转基因小鼠神经元丢失;而泛素化的失调可导致帕金森病期间错误折叠蛋白质的积累[17]。除此之外,天冬酰胺内肽酶亦可切割α-突触核蛋白,触发其聚集并加剧神经毒性,导致帕金森病小鼠多巴胺能神经元丢失和运动障碍。在帕金森病的 SNCA 转基因小鼠实验中缺失天冬酰胺内肽酶可减轻多巴胺能神经元损失并改善运动缺陷[18]。 α-突触核蛋白的错误折叠是帕金森病发病机制中的关键事件,SNCA基因的点突变、双重复制、三倍复制会加速α-突触核蛋白的错误折叠和家族性及散发性帕金森病出现[19]。最早在患有左旋多巴反应性帕金森病的意大利裔美国人家族(Contursi家族)和3个较小的希腊家族的尸检中发现SNCA基因点突变,该突变包括了丙胺酸残基53向苏氨酸(A53T)的转变,表现出更高的原纤维形成率[20]。A30P、E46K、H50Q、G51D、A53E也与家族性形式有关,其中E46K、H50Q和A53T突变增加了α-突触核蛋白的聚集倾向,而G51D和A53E则相反,A30P似乎更容易发生寡聚化[21-24]。 2.2 帕金森病中α-突触核蛋白诱导线粒体功能障碍的机制 随着生物化学研究技术的进步,α-突触核蛋白已被鉴定为路易体的主要蛋白质成分[25]。线粒体是细胞产生能量的关键细胞器,其功能决定细胞状态。线粒体功能障碍一直被认为是多巴胺能神经元损伤的核心启动因素[26]。越来越多的证据支持α-突触核蛋白的聚集体、蛋白质转换功能障碍和线粒体功能障碍是帕金森病发病的重要机制,引发黑质多巴胺能神经元死亡,促进了帕金森病的进展[27]。 2.2.1 α-突触核蛋白诱导的线粒体复合物1活性降低以及氧化应激 见图3。线粒体是细胞的动力源,通过4个蛋白复合物形成电子传递链Ⅰ-Ⅳ催化的氧化还原反应合成腺苷三磷酸(adenosine triphosphate,ATP)[28]。线粒体复合物1是参与氧化磷酸化的第一个也是最大的电子传递链复合物,在氧化磷酸化中起重要作用,其缺陷是生物能量功能急剧丧失,导致线粒体不稳定[29]。单体的α-突触核蛋白可以增强线粒体ATP合成酶的活性,过表达α-突触核蛋白会导致线粒体复合物1的损伤,引起线粒体复合物1活性降低,α-突触核蛋白的寡聚形式则影响线粒体复合物1的连接,导致特异性ATP合成酶氧化和细胞死亡率增加[30-31]。据报道大量的接触1-甲基-4-苯基-1,2,3,6-四氢吡啶(1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine,MPTP)、线粒体电子传递链的复合物Ⅰ抑制剂、鱼藤酮会导致出现帕金森病样综合征[32]。MPTP是一种亲脂性的分子,本身无毒性,能够轻松地穿过血脑屏障进入脑组织中,之后被星形胶质细胞中的单胺氧化酶B(monoamine oxidase type B ,MAO-B)氧化成多巴胺能神经毒素1-甲基-4-苯基吡啶离子(1-methyl-4-phenylpyridine ion,MPP+),MPP+通过多巴胺转运蛋白被多巴胺能细胞摄取从而诱导黑质中多巴胺能神经元丧失,并抑制呼吸链复合物Ⅰ以及促使活性氧产生[13]。同样,在啮齿动物中长期使用复合物Ⅰ抑制剂鱼藤酮会产生多系统变性,包括黑质多巴胺能神经元和路易体内含物的丧失[33]。总体来说,这些研究强烈支持以下观点,即复合物Ⅰ损伤可能是帕金森病中多巴胺能神经元死亡发病机制的核心。 尽管线粒体氧化磷酸化系统产生ATP,对许多基本细"
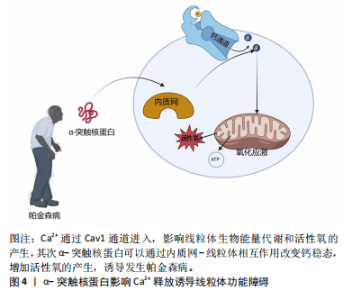
胞过程至关重要,但线粒体是活性氧的主要细胞来源,参与钙稳态以及细胞破坏性途径的调节和启动,是帕金森病中多巴胺能神经变性的基础。在生理状况下氧化磷酸化产生的活性氧如超氧自由基(O2?)和过氧化氢(H2O2)维持细胞稳态。当线粒体功能障碍时,活性氧产生增多,活性氧的积累与抗氧化剂(如超氧化岐物酶)防御之间存在不平衡时引起氧化应激,导致细胞和组织不可逆性损伤,最终导致细胞死亡[34]。活性氧的产生使氧化应激增加是多巴胺能神经元损伤的机制之一,其次活性氧升高有可能扰乱细胞的氧化还原平衡,损害蛋白质、DNA和RNA等生物大分子,从而导致氧化磷酸化异常,引起线粒体结构损伤,继而使ATP生成减少以及线粒体通透性改变,细胞发生凋亡[35]。 2.2.2 α-突触核蛋白影响Ca2+释放诱导线粒体功能障碍 见图4。钙是大脑中最普遍的信号之一,在维持神经元活性和功能中发挥重要作用。中脑黑质多巴胺能神经元是一种自主起搏器,在没有突触的情况下产生动作电位,并且这些动作电位宽广缓慢,使Ca2+最大化地进入细胞内[36-37]。 细胞内的Ca2+主要由钙结合蛋白和代谢性谷氨酸受体通过内质网储存调节继而通过钙单转运体以及线粒体相关膜孔进入线粒体基质,并通过这些孔直接与线粒体和内质网通信[38]。在帕金森病小鼠模型的胞质中Ca2+浓度增高促进α-突触核蛋白的聚集[39]。α-突触核蛋白聚集会导致线粒体功能障碍,抑制线粒体动力学,破坏钙稳态,导致线粒体促凋亡细胞色素C的释放等,以此形成恶性循环[40-42]。线粒体中Ca2+积累导致氧化磷酸化的激活和ATP的产生,这对于满足与神经元活动相关的代谢需求至关重要[43]。研究发现帕金森病患者中α-突触核蛋白可通过内质网-线粒体相互作用来改变钙稳态,当Ca2+失衡时,线粒体活性氧的产生增强了α-突触核蛋白的错误折叠,进一步诱导发生帕金森病[44]。另有研究表明,突变的α-突触核蛋白干扰Ca2+的稳态以及ATP的产生,导致线粒体膜上通透性过渡孔(membrane permeability transition pore,mPTP)的打开以及线粒体膜电位的震荡,影响线粒体功能[42]。mPTP有2种状态:一种为可逆的低电导状态参与钙处理,另一种为不可逆的高电导状态导致线粒体肿"
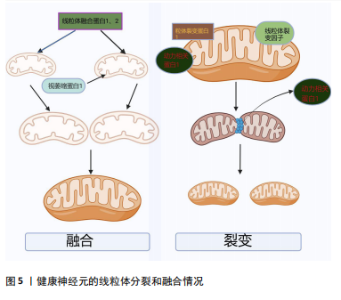
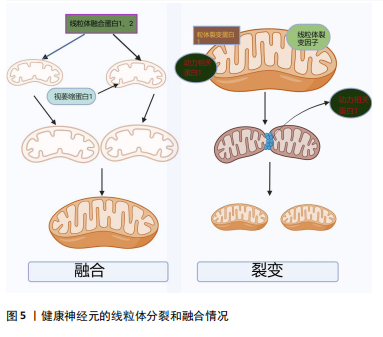
胀以及细胞色素C的释放,从而诱导细胞凋亡[28]。线粒体和内质网都与帕金森病的发病机制相关,除了Ca2+储存,内质网在细胞蛋白质平衡中至关重要。帕金森病发病机制中路易体形成恰巧反映了蛋白质平衡破坏并伴有内质网应激的现象[45]。内质网-线粒体接触在神经元中的表征很差,并且在神经元病理生理学中的确切作用也尚不清楚[46]。因此,内质网-线粒体关联的任何类型的改变都有望对神经元特别是中脑黑质多巴胺能神经元造成潜在的损害。 2.2.3 α-突触核蛋白诱导线粒体动力学的改变 见图5。线粒体是高度动态的细胞器,线粒体动力学是调节线粒体稳态的一组动态过程,主要包括线粒体的融合、裂变以及运输和清除[47]。研究表明在帕金森病模型中,α-突触核蛋白可以通过线粒体的融合、裂变来影响其大小、形态[48]。融合通过线粒体外膜上的线粒体融合蛋白(MFn1和MFn2)和线粒体内膜的视萎缩蛋白1(OPa1)相互作用协调发生[31]。体外研究显示膜融合与α-突触核蛋白的浓度增加呈负相关趋势,α-突触核蛋白与线粒体外膜结合通过影响膜曲率降低线粒体膜融合速率[49]。裂变指的是一个线粒体分裂为2个子细胞器的动态过程,主要由动力相关蛋白1引起的,将线粒体裂变分子、线粒体裂变蛋白1募集到线粒体,一旦连接到线粒体外膜,动力相关蛋白1就会形成一个环形结构,充当线粒体膜中的收缩隔膜[47]。线粒体的融合、裂变等动态过程受到α-突触核蛋白的影响,并直接或间接影响动力相关蛋白1活性[50]。在表达A53Tα-syn的转基因小鼠中以及SH-SY5Y神经母细胞瘤中过表达α-突触核蛋白会诱导线粒体破碎增加[51]。在动力相关蛋白1敲除小鼠的成纤维细胞中α-突触核蛋白诱导线粒体碎裂,在秀丽隐线虫中WTα-syn的过表达以年龄依赖的方式也可诱导线粒体碎裂[50]。过表达A53T的转基因小鼠中MFn1、MFn2和动力相关蛋白1表达的减少与线粒体减小相关[51]。线粒体动力学对维持线粒体功能至关重要,任何过程的减少或者过量均会导致帕金森病的发生[52]。以上研究均表明,α-突触核蛋白可能通过多种不同的机制损害线粒体动力学,继而诱导帕金森病。"
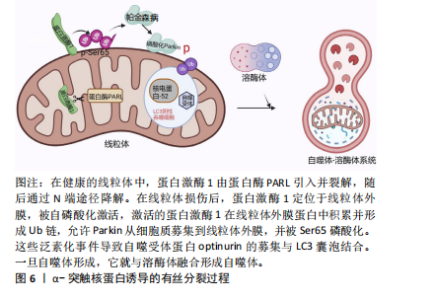
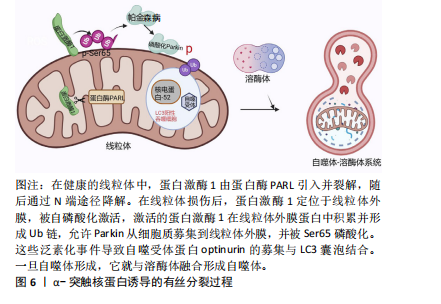
2.3 α-突触核蛋白诱导的线粒体自噬 见图6。线粒体自噬即线粒体选择性降解,可驱动功能失调的线粒体在自噬体中选择性降解,线粒体自噬缺陷和受损线粒体的积累是参与疾病病因的关键因素[53]。主要的线粒体自噬有2种:Parkin依赖性线粒体自噬以及独立性线粒体自噬。在Parkin依赖性线粒体自噬中,蛋白激酶1和Parkin起重要作用[54-55]。在帕金森病的神经元细胞模型中,α-突触核蛋白的过度积聚以及在细胞质中的寡聚化通过S-亚硝基化导致Parkin自泛素化和蛋白质的降解,促进Parkin的下调,失去了对α-突触核蛋白低聚物毒性的细胞保护作用从而触发线粒体功能障碍[56-57]。而过量的蛋白激酶1/Parkin可通过介导线粒体自噬来挽救α-突触核蛋白所介导的线粒体碎裂、膜去极化以及神经元损伤[58]。在散发性死后帕金森病患者脑组织中蛋白激酶1-Parkin通路活性升高,但很难知道这种积累是线粒体损伤增加还是清除率降低的结果[53]。此外,α-突触核蛋白也可以独立于Parkin依赖性线粒体自噬,α-突触核蛋白升高导致细胞质内Ca2+浓度增加以及Miro升高[59]。Miro是主管线粒体运动的膜蛋白,正常情况下受损的线粒体会启动清除Miro过程以促进线粒体自噬。在死后帕金森病患者的大脑中,Miro1蛋白水平与α-突触核蛋白水平显著相关。在果蝇帕金森病模型中降低Miro水平挽救了神经变性发生[60]。在过表达野生型SNCA细胞中,随着Miro1水平上调,线粒体融合蛋白MFn2、动力相关蛋白1以及线粒体相关蛋白LRRK2、蛋白激酶1和Parkin均未出现改变[61]。这些结果显示延迟线粒体自噬是α-突触核蛋白直接诱导Miro表达增加的结果。Miro可作为特定治疗的潜在分层标志物,也可作为近端线粒体自噬生物标志物,但尚未在患者中得到验证。 2.4 α-突触核蛋白作用与线粒体蛋白导入机制 线粒体含有1 500种蛋白质,核基因组编码约占99.9%,其中只有13种蛋白质被线粒体基因组编码并在线粒体中合成,而线粒体的功能取决于核编码蛋白是否成功导入[62-63]。线粒体蛋白导入机制是复杂且高度调节的,在α-突触核蛋白"
| [1] LURETTE O, MARTÍN-JIMÉNEZ R, KHAN M, et al. Aggregation of alpha-synuclein disrupts mitochondrial metabolism and induce mitophagy via cardiolipin externalization. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(11):729. [2] ANTONY PM, DIEDERICH NJ, KRÜGER R, et al. The hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease. FEBS J. 2013;280(23):5981-5993. [3] WÜLLNER U, BORGHAMMER P, CHOE CU, et al. The heterogeneity of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2023;130(6):827-838. [4] XU MM, RYAN P, RUDRAWAR S, et al. Advances in the development of imaging probes and aggregation inhibitors for alpha-synuclein. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41(4):483-498. [5] VILLAR-PIQUÉ A, LOPES DA FONSECA T, OUTEIRO TF. Structure, function and toxicity of alpha-synuclein: the Bermuda triangle in synucleinopathies. J Neurochem. 2016;139 Suppl 1:240-255. [6] CHEN R, GU X, WANG X. α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s disease and advances in detection. Clin Chim Acta. 2022;529:76-86. [7] VASQUEZ V, MITRA J, WANG H, et al. A multi-faceted genotoxic network of alpha-synuclein in the nucleus and mitochondria of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease: Emerging concepts and challenges. Prog Neurobiol. 2020;185:101729. [8] WAKABAYASHI K. Where and how alpha-synuclein pathology spreads in Parkinson’s disease. Neuropathology. 2020;40(5):415-425. [9] FUSCO G, PAPE T, STEPHENS AD, et al. Structural basis of synaptic vesicle assembly promoted by α-synuclein. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12563. [10] CARTELLI D, ALIVERTI A, BARBIROLI A, et al. α-Synuclein is a Novel Microtubule Dynamase. Sci Rep. 2016;6:33289. [11] TOFARIS GK. Initiation and progression of α-synuclein pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79(4):210. [12] ZHU M, QIN ZJ, HU D, et al. Alpha-synuclein can function as an antioxidant preventing oxidation of unsaturated lipid in vesicles. Biochemistry. 2006; 45(26):8135-8142. [13] NEGI S, KHURANA N, DUGGAL N. The misfolding mystery: α-synuclein and the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int. 2024;177:105760. [14] VAN ROOIJEN BD, CLAESSENS MM, SUBRAMANIAM V. Membrane interactions of oligomeric alpha-synuclein: potential role in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2010;11(5):334-342. [15] KAWAHATA I, FINKELSTEIN DI, FUKUNAGA K. Pathogenic Impact of α-Synuclein Phosphorylation and Its Kinases in α-Synucleinopathies. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6216. [16] CAVALLARIN N, VICARIO M, NEGRO A. The role of phosphorylation in synucleinopathies: focus on Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010;9(4):471-481. [17] JUNQUEIRA SC, CENTENO EGZ, WILKINSON KA, et al. Post-translational modifications of Parkinson’s disease-related proteins: Phosphorylation, SUMOylation and Ubiquitination. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865(8):2001-2007. [18] CHEN G, AHN EH, KANG SS, et al. UNC5C Receptor Proteolytic Cleavage by Active AEP Promotes Dopaminergic Neuronal Degeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(7):e2103396. [19] NWABUFO CK, AIGBOGUN OP. Diagnostic and therapeutic agents that target alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol. 2022;269(11):5762-5786. [20] KRÜGER R, KUHN W, MÜLLER T, et al. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet. 1998;18(2):106-108. [21] GHOSH D, SAHAY S, RANJAN P, et al. The newly discovered Parkinson’s disease associated Finnish mutation (A53E) attenuates α-synuclein aggregation and membrane binding. Biochemistry. 2014;53(41):6419-6421. [22] GHOSH D, MONDAL M, MOHITE GM, et al. The Parkinson’s disease-associated H50Q mutation accelerates α-Synuclein aggregation in vitro. Biochemistry. 2013;52(40):6925-6927. [23] SAHAY S, GHOSH D, SINGH PK, et al. Alteration of Structure and Aggregation of α-Synuclein by Familial Parkinson’s Disease Associated Mutations. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017;18(7):656-676. [24] POLYMEROPOULOS MH, LAVEDAN C, LEROY E, et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science. 1997;276(5321):2045-2047. [25] SIMON C, SOGA T, OKANO HJ, et al. α-Synuclein-mediated neurodegeneration in Dementia with Lewy bodies: the pathobiology of a paradox. Cell Biosci. 2021;11(1):196. [26] MALPARTIDA AB, WILLIAMSON M, NARENDRA DP, et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Mitophagy in Parkinson’s Disease: From Mechanism to Therapy. Trends Biochem Sci. 2021;46(4):329-343. [27] SOHRABI T, MIRZAEI-BEHBAHANI B, ZADALI R, et al. Common Mechanisms Underlying α-Synuclein-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. J Mol Biol. 2023;435(12):167992. [28] SCHAPIRA AH, COOPER JM, DEXTER D, et al. Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 1989;1(8649):1269. [29] PRZEDBORSKI S, KOSTIC V, JACKSON-LEWIS V, et al. Transgenic mice with increased Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase activity are resistant to N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neurotoxicity. J Neurosci. 1992;12(5):1658-1667. [30] SURMEIER DJ, GUZMAN JN, SANCHEZ-PADILLA J, et al. The role of calcium and mitochondrial oxidant stress in the loss of substantia nigra pars compacta dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience. 2011;198:221-231. [31] XIE W, CHUNG KK. Alpha-synuclein impairs normal dynamics of mitochondria in cell and animal models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. 2012;122(2): 404-414. [32] PESAH Y, PHAM T, BURGESS H, et al. Drosophila parkin mutants have decreased mass and cell size and increased sensitivity to oxygen radical stress. Development. 2004;131(9):2183-2194. [33] DI MAIO R, BARRETT PJ, HOFFMAN EK, et al. α-Synuclein binds to TOM20 and inhibits mitochondrial protein import in Parkinson’s disease. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(342):342ra78. [34] SUBRAMANIAM SR, CHESSELET MF. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2013;106-107:17-32. [35] SUBRAHMANIAN N, LAVOIE MJ. Is there a special relationship between complex I activity and nigral neuronal loss in Parkinson’s disease? A critical reappraisal. Brain Res. 2021;1767:147434. [36] BURTSCHER J, SYED MMK, KELLER MA, et al. Fatal attraction - The role of hypoxia when alpha-synuclein gets intimate with mitochondria. Neurobiol Aging. 2021;107:128-141. [37] THORNE NJ, TUMBARELLO DA. The relationship of alpha-synuclein to mitochondrial dynamics and quality control. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022;15: 947191. [38] YE H, ROBAK LA, YU M, et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Syndrome. Annu Rev Pathol. 2023;18:95-121. [39] LAPOINTE N, ST-HILAIRE M, MARTINOLI MG, et al. Rotenone induces non-specific central nervous system and systemic toxicity. FASEB J. 2004; 18(6):717-719. [40] IMBRIANI P, MARTELLA G, BONSI P, et al. Oxidative stress and synaptic dysfunction in rodent models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2022; 173:105851. [41] BORSCHE M, PEREIRA SL, KLEIN C, et al. Mitochondria and Parkinson’s Disease: Clinical, Molecular, and Translational Aspects. J Parkinsons Dis. 2021;11(1):45-60. [42] SURMEIER DJ, SCHUMACKER PT, GUZMAN JD, et al. Calcium and Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;483(4):1013-1019. [43] SURMEIER DJ, HALLIDAY GM, SIMUNI T. Calcium, mitochondrial dysfunction and slowing the progression of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol. 2017; 298(Pt B):202-209. [44] WILSON EL, METZAKOPIAN E. ER-mitochondria contact sites in neurodegeneration: genetic screening approaches to investigate novel disease mechanisms. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(6):1804-1821. [45] TSUNEMI T, PEREZ-ROSELLO T, ISHIGURO Y, et al. Increased Lysosomal Exocytosis Induced by Lysosomal Ca2+ Channel Agonists Protects Human Dopaminergic Neurons from α-Synuclein Toxicity. J Neurosci. 2019;39(29): 5760-5772. [46] LIN KJ, LIN KL, CHEN SD, et al. The Overcrowded Crossroads: Mitochondria, Alpha-Synuclein, and the Endo-Lysosomal System Interaction in Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(21):5312. [47] GANGULY G, CHAKRABARTI S, CHATTERJEE U, et al. Proteinopathy, oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction: cross talk in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017;11:797-810. [48] LUTH ES, STAVROVSKAYA IG, BARTELS T, et al. Soluble, prefibrillar α-synuclein oligomers promote complex I-dependent, Ca2+-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(31):21490-21507. [49] BARAZZUOL L, GIAMOGANTE F, BRINI M, et al. PINK1/Parkin Mediated Mitophagy, Ca2+ Signalling, and ER-Mitochondria Contacts in Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(5):1772. [50] GIORGI C, MARCHI S, PINTON P. The machineries, regulation and cellular functions of mitochondrial calcium. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(11):713-730. [51] BOHUSH A, LEŚNIAK W, WEIS S, et al. Calmodulin and Its Binding Proteins in Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(6):3016. [52] WU Y, WHITEUS C, XU CS, et al. Contacts between the endoplasmic reticulum and other membranes in neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017; 114(24):E4859-E4867. [53] MEYER JN, LEUTHNER TC, LUZ AL. Mitochondrial fusion, fission, and mitochondrial toxicity. Toxicology. 2017;391:42-53. [54] YAPA NMB, LISNYAK V, RELJIC B, et al. Mitochondrial dynamics in health and disease. FEBS Lett. 2021;595(8):1184-1204. [55] POZO DEVOTO VM, FALZONE TL. Mitochondrial dynamics in Parkinson’s disease: a role for α-synuclein? Dis Model Mech. 2017;10(9):1075-1087. [56] KAMP F, EXNER N, LUTZ AK, et al. Inhibition of mitochondrial fusion by α-synuclein is rescued by PINK1, Parkin and DJ-1. EMBO J. 2010;29(20): 3571-3589. [57] ADEBAYO M, SINGH S, SINGH AP, et al. Mitochondrial fusion and fission: The fine-tune balance for cellular homeostasis. FASEB J. 2021;35(6):e21620. [58] CLARK EH, VÁZQUEZ DE LA TORRE A, HOSHIKAWA T, et al. Targeting mitophagy in Parkinson’s disease. J Biol Chem. 2021;296:100209. [59] LIU J, LIU W, LI R, et al. Mitophagy in Parkinson’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Treatment. Cells. 2019;8(7):712. [60] GRÜNEWALD A, KUMAR KR, SUE CM. New insights into the complex role of mitochondria in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2019;177:73-93. [61] WILKANIEC A, LENKIEWICZ AM, CZAPSKI GA, et al. Extracellular Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers Induce Parkin S-Nitrosylation: Relevance to Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease Etiopathology. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(1):125-140. [62] WILKANIEC A, LENKIEWICZ AM, BABIEC L, et al. Exogenous Alpha-Synuclein Evoked Parkin Downregulation Promotes Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Neuronal Cells. Implications for Parkinson’s Disease Pathology. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:591475. [63] KRZYSTEK TJ, BANERJEE R, THURSTON L, et al. Differential mitochondrial roles for α-synuclein in DRP1-dependent fission and PINK1/Parkin-mediated oxidation. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(9):796. [64] RAY B, BHAT A, MAHALAKSHMI AM, et al. Mitochondrial and Organellar Crosstalk in Parkinson’s Disease. ASN Neuro. 2021;13:17590914211028364. [65] HSIEH CH, SHALTOUKI A, GONZALEZ AE, et al. Functional Impairment in Miro Degradation and Mitophagy Is a Shared Feature in Familial and Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Stem Cell. 2016;19(6):709-724. [66] SHALTOUKI A, HSIEH CH, KIM MJ, et al. Alpha-synuclein delays mitophagy and targeting Miro rescues neuron loss in Parkinson’s models. Acta Neuropathol. 2018;136(4):607-620. [67] DE MIRANDA BR, ROCHA EM, CASTRO SL, et al. Protection from α-Synuclein induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration by overexpression of the mitochondrial import receptor TOM20. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2020;6(1):38. [68] COPELAND WC, LONGLEY MJ. Mitochondrial genome maintenance in health and disease. DNA Repair (Amst). 2014;19:190-198. [69] PASCHEN SA, NEUPERT W. Protein import into mitochondria. IUBMB Life. 2001;52(3-5):101-112. [70] WIEDEMANN N, PFANNER N. Mitochondrial Machineries for Protein Import and Assembly. Annu Rev Biochem. 2017;86:685-714. |
| [1] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [2] | Sun Jiaqi, Bian Lu, Shi Wentao, Wu Xuechao, Lu Xiaojie. Mechanism of Piezo-type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 in rat pressure injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1578-1584. |
| [3] | Li Huayuan, Li Chun, Liu Junwei, Wang Ting, Li Long, Wu Yongli. Effect of warm acupuncture on PINK1/Parkin pathway in the skeletal muscle of rats with chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| [4] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [5] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [6] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [7] | Liu Lingyun, He Guixin, Qin Weibin, Song Hui, Zhang Liwen, Tang Weizhi, Yang Feifei, Zhu Ziyi, Ou Yangbin . Improvement of myocardial injury by traditional Chinese medicine: mitochondrial calcium homeostasis mediates macrophage autophagy and pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1276-1284. |
| [8] | Lu Ranran, Zhou Xu, Zhang Lijie, Yang Xinling. Dimethyl fumarate alleviates nerve damage in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 989-994. |
| [9] | Lin Xiaohui, Yang Mengyuan, Li Chunnian. Role and mechanism of biomimetic remineralization therapy for early enamel demineralization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 856-865. |
| [10] | Sima Xinli, Liu Danping, Qi Hui. Effect and mechanism of metformin-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes on regulating chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7728-7734. |
| [11] | Cai Zhixing, Xia Qiufang, Chen Lili, Zhu Danyang, Zhu Huiwen, Sun Yanan, Liang Wenyu, Zhao Heqian. Effect of Roujishuncuiyin on the improvement of skeletal muscle insulin resistance in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7537-7543. |
| [12] | Liu Xuan, Ding Yuqing, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang, Hu Shujuan. Exercise prevention and treatment of insulin resistance: role and molecular mechanism of Keap1/nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| [13] | Zhang Xiaoyu, Wei Shanwen, Fang Jiawei, Ni Li. Prussian blue nanoparticles restore mitochondrial function in nucleus pulposus cells through antioxidation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7318-7325. |
| [14] | Su Yongkun, Sun Hong, Liu Miao, Yang Hua, Li Qingsong. Development of novel antioxidants and antioxidant combination carried by nano-hydrogel systems in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7376-7384. |
| [15] | Wu Qingyun, Su Qiang. Antioxidant nanomedicine-mediated targeted therapy for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7431-7438. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||