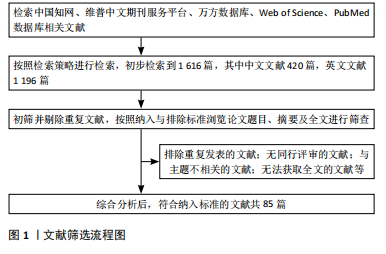
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (17): 3657-3667.doi: 10.12307/2025.623
Previous Articles Next Articles
Exercise intervention for sarcopenic obesity in older adults
Zhao Yanan1, Lu Donglei2, Tan Sijie1, 3
- 1School of Sports and Health, 2School of Sports Training, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China; 3Tianjin College of Media and Arts, Tianjin 301901, China
-
Received:2024-06-04Accepted:2024-07-15Online:2025-06-18Published:2024-11-06 -
Contact:Tan Sijie, Professor, School of Sports and Health, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China; Tianjin College of Media and Arts, Tianjin 301901, China -
About author:Zhao Yanan, Master candidate, School of Sports and Health, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Yanan, Lu Donglei, Tan Sijie, . Exercise intervention for sarcopenic obesity in older adults[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3657-3667.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
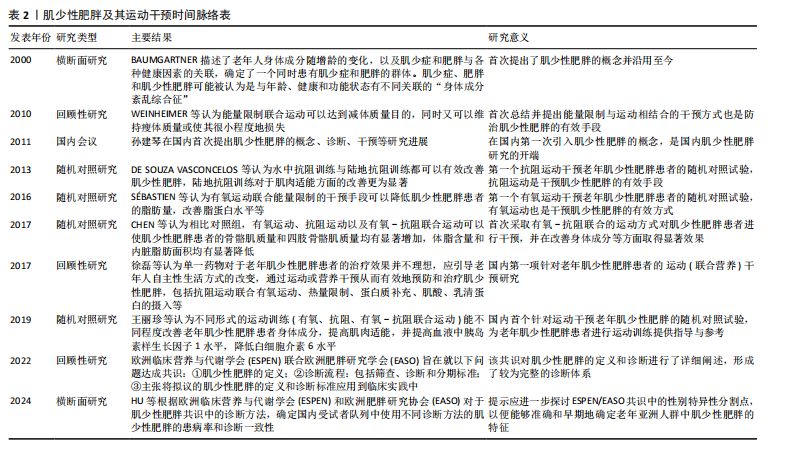
临床结局等逐步趋于完善[15],共识中也给予肌少性肥胖以新的定义,即表现为人体脂肪量升高、骨骼肌质量下降以及骨骼肌功能降低的一种肌少症与肥胖共同存在的临床功能性疾病。中国对于肌少性肥胖的研究起步较晚,对于该方面的探索较少,2011年的中国疾病预防控制中心达能营养中心第十四届学术年会中孙建琴学者较早地提及了肌少性肥胖,自此之后,中国学者对于肌少性肥胖的研究便开始涌现。 目前,尚无明确的治愈肌少性肥胖的方法,主要的防治手段有运动干预、营养干预以及药物干预,其中运动是预防和治疗老年人肌少性肥胖十分有效的非药物干预手段[16-17]。运动干预可以抵消和/或逆转肌少性肥胖所带来的一系列临床症状[18],如调节骨骼肌蛋白质的代谢、改善炎症反应以及调控线粒体功能等来改善和延缓肌少性肥胖的发病及进展[19]。近年来,对于老年人肌少性肥胖运动干预领域的研究层出不穷,主要的干预方式包括抗阻运动、有氧运动、有氧-抗阻联合运动等,其中抗阻运动干预肌少性肥胖的研究较为丰富。总之,运动干预已经成为老年人肌少性肥胖防治策略中的重要组成部分,见表2。 2.2 肥胖与肌少症的串联机制 肥胖与肌少症串联的前提是脂肪酸在骨骼肌中的异位沉积,过量的脂肪酸不仅储存在脂肪组织中,还会在骨骼肌中沉积并在骨骼肌中转化为肌肉内脂肪组织、肌细胞内三磷酸甘油脂以及脂肪酸衍生物等[20],骨骼肌被脂肪组织浸润,产生脂毒性环境,诱导和加重线粒体功能障碍、氧化应激、胰岛素抵抗和全身性炎症等,导致骨骼肌质量、力量降低。一项研究将骨骼肌细胞和脂肪细胞进行共培养,发现两者之间出现竞争性抑制现象,且骨骼肌细胞中肌萎缩相关的基因与蛋白表达增加,而与肌细胞增殖与分化相关的蛋白水平下调[21],如肌源性胰岛素样生长因子Ⅱ及其结合蛋白IGFBP-5的表达显著降低(胰岛素样生长因子Ⅱ与IGFBP-5为生肌因子,可以诱导骨骼肌肥大)[22]。 肥胖使机体处于一种低程度的慢性炎症状态,脂肪组织过量生成并依次经历肥大、增生、激活等过程,造成促炎巨噬细胞等免疫细胞积累以及脂肪因子失调[23]。人体脂肪组织中巨噬细胞主要分为M1型(促炎效应)与M2型(抗炎效应)[24],在肥胖者脂肪组织中以M1型为主,在脂肪酸过度堆积的环境中,M2型巨噬细胞还可以向M1型巨噬细胞进行转变[25],脂肪组织M1型巨噬细胞比例升高、M2型巨噬细胞比例降低,是导致老年人脂肪组织慢性炎症状态与骨骼肌萎缩的重要基础与前提。脂肪组织M1型巨噬细胞可以被γ干扰素、T细胞等激活,分泌肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6等促炎细胞因子[26]。另外,就脂肪因子失调而言,肥胖者脂肪组织分泌的脂"

肪因子中瘦素水平升高、脂联素水平降低[27],其中脂联素是一种抗炎因子,而瘦素水平升高会刺激促炎因子的生成,如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6等,两者可以使肌环指蛋白1(MuRF-1)、肌萎缩Fbox-1蛋白(MAFbx, 即Atrogin-1)等肌萎缩因子表达增加[28],同时会激活核因子κB通路等[29],最终诱导骨骼肌降解。研究表明,较高水平的肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6等促炎因子与较低水平的骨骼肌力和肌肉质量显著相关(白细胞介素6:r=-0.13,P < 0.001,肿瘤坏死因子α:r=-0.08,P < 0.001)[30]。 上述一系列的变化会导致脂肪细胞表现出更高的促炎状态,进而造成全身性慢性低程度炎症状态,进一步促发胰岛素抵抗与骨骼肌功能障碍等[31]。 肥胖会诱导胰岛素抵抗的发生,胰岛素抵抗是许多代谢性疾病的基础。正常情况下,胰岛素与胰岛素受体酪氨酸激酶结合,使胰岛素受体底物等结合蛋白活化,进而发生一系列的级联反应并引发生物效应,如骨骼肌、脂肪组织等能量代谢主要由上述过程介导[32]。而肥胖状态下葡萄糖、游离脂肪酸等代谢紊乱,会诱导和/或加重胰岛素抵抗,如脂肪酸代谢紊乱产生的脂质代谢物参与蛋白激酶Cθ和Jun激酶的活化,促进胰岛素受体底物1的苏氨酸/丝氨酸磷酸化,这就阻碍了胰岛素受体底物1正常的酪氨酸磷酸化,导致胰岛素信号通路受损而诱导胰岛素抵抗[33]。而胰岛素抵抗会使FoxO转录因子家族的表达上调从而直接或间接加速骨骼肌蛋白质降解等过程[34],FoxO转录因子家族最重要的功能是调节骨骼肌蛋白质分解代谢水平,如FoxO3通过激活骨骼肌自噬和泛素蛋白酶体系统使骨骼肌蛋白发生降解[35]。 衰老、肥胖过程中线粒体功能障碍、氧化应激以及活性氧的产生等同样会导致肌少性肥胖的发生。如前所述,肥胖导致脂肪酸在骨骼肌异位沉积会损伤线粒体的功能,阻碍脂肪酸的β氧化,使活性氧产生增多进而诱发骨骼肌细胞凋亡,这一系列过程会降低骨骼肌功能[31],同时脂肪因子产生增加,也会诱导活性氧产生与氧化应激[36];活性氧生成增多还会影响肌卫星细胞的功能从而导致骨骼肌质量减少、力量下降,原因是肌卫星细胞是修复受损骨骼肌的主要细胞,随着衰老的进程,肌卫星细胞会逐渐减少,再生能力受到活性氧靶向控制,再生环节受氧化还原调节[37],见图2。 2.3 运动与老年人肌少性肥胖 运动干预对于老年人肌少性肥胖的改善作用得到了广泛的研究与证实。骨骼肌不仅是运动器官,更是全身最大的内分泌器官,近年来有大量研究表明,骨骼肌能表达、合成和分泌多种生物信号分子,即肌肉因子,包括调节肽、细胞因子和生长因子等,以旁分泌和/或自分泌方式调节骨骼肌的生长、代谢和运动功能,同时还可以以血液循环内分泌的方式调节机体远隔器官组织的功能[38]。运动可以诱导肌肉因子的释放,肌肉因子在预防与缓解肌少性肥胖中起到关键作用[39],如鸢尾素可以促进骨骼肌肥大和改善肌肉萎缩[40],还具有减少脂质堆积、促进脂联素分泌以及促使白色脂肪转变为褐色脂肪等作用[39];胰岛素样生长因子可以促进生长与调节代谢,其中胰岛素样生长因子1是调节肌肉生长和再生以及糖脂代谢的关键因子,胰岛素样生长因子1可以通过丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)信号传导途径和磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase/protein kinase B,PI3K/Akt)途径来增加骨骼肌中蛋白质合成、抑制蛋白质分解,从而促进骨骼肌肥大、抑制与改善骨骼肌萎缩[41]。虽然运动干预对于老年人肌少性肥胖的积极作用已得到证实,但缺乏相关的运动干预方案,不同的运动会产生不同的效果,对于肌少性肥胖的运动干预主要包括有氧运动、抗阻运动以及有氧-抗阻联合运动等,而运动处方主要包括FITT-VP原则,即运动频率(Frequency)、运动强度(Intensity)、运动时间(Time)与运动方式(Type)等,下面将从以上几个方面来探讨不同运动方式对于肌少性肥胖的干预效果,并结合纳入的文献给出适合老年肌少性肥胖患者的运动处方建议。"
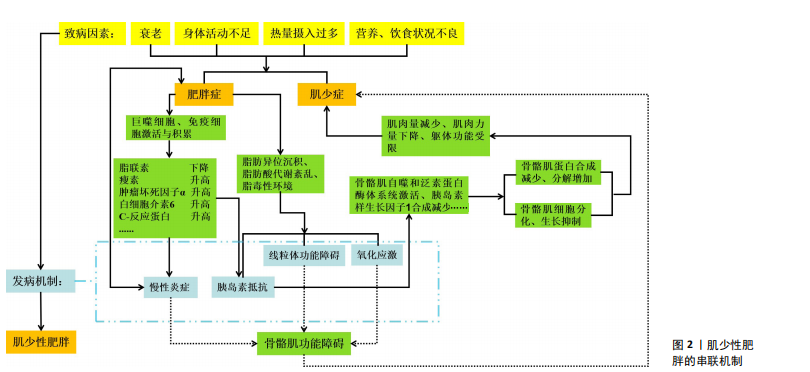
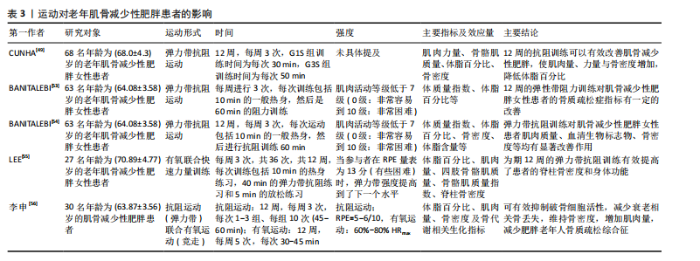
2.3.1 抗阻运动与老年人肌少性肥胖 (1)抗阻运动对老年肌少性肥胖患者的影响:抗阻运动又称阻力运动,肌肉通过对抗阻力从而提高肌肉适能。许多研究表明,相比于其他运动形式,抗阻训练对预防和缓解肌少性肥胖更加有效。根据KANZLEITER等[42]的研究,抗阻运动可以促使血浆中核心蛋白聚糖(Decorin)水平升高,且与运动强度呈正相关,Decorin作为肌肉生长抑制素的拮抗剂,负责调节骨骼肌中卵泡抑制素、肌分化因子、Mighty以及Atrogin-1与肌肉环状指基因1等表达来促进肌肉生长、诱导骨骼肌肥大。许多研究也证实抗阻训练会影响血液中的胰岛素样生长因子1水平,如前文所述,胰岛素样生长因子1可以通过PI3K/Akt/(雷帕霉素靶蛋白mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)信号通路促进蛋白质合成,抑制蛋白质分解。同时,抗阻训练可以使骨骼肌中卫星细胞的含量增加[43],卫星细胞在骨骼肌纤维的生长、修复和再生过程中起着至关重要的作用,长期的抗阻训练可以逆转与年龄相关的Ⅱ型肌纤维萎缩和卫星细胞含量的减少[44]。对于老年肌少性肥胖患者的抗阻训练主要包括渐进式抗阻训练、弹力带抗阻训练、低负荷抗阻运动结合血流限制、抗阻训练联合营养膳食等方式。 对于渐进式抗阻训练,VASCONCELOS等[45]对28名65-80岁的肌少性肥胖女性患者进行了随机对照试验,试验组进行共10周、2次/周、1 h/次的渐进式抗阻训练,结果显示,与对照组相比,试验组下肢肌肉的力量、耐力有所提高。DE OLIVEIRA SILVA等[46]探讨抗阻训练对肌少性肥胖患者的身体成分、肌肉力量以及身体功能能力等方面的影响,以49名年龄在66-70岁之间的患有以及未患有肌少性肥胖的老年女性为研究对象,进行为期16周、每周2次、每次3组的抗阻训练干预,结果表明16周的运动干预使患有肌少性肥胖的受试者肥胖指数得到改善,肌肉力量与身体功能得到增加。STOEVER等[47]旨在研究抗阻训练对28名(年龄≥65岁)老年肥胖且伴随肌肉减少症患者的身体功能的影响,进行了为期16周、每周2次、每次60 min的抗阻训练干预,结果显示肥胖且伴随肌肉减少症组握力(9%)、步行速度(5%)、简易体能状况量表(SPPB)(13%)与改良体能测试(11%)等方面得到显著提升。同样的,在GADELHA等[48]的研究中,(67.0±5.2)岁的肌少性肥胖女性患者进行为期24周、每周3次、每次3组的渐进式抗阻训练,结果显示渐进式抗阻训练组去脂体质量显著增加(P < 0.01),表明抗阻训练可以有效改善老年肌少性肥胖患者的身体成分。总之,渐进式抗阻运动从较低的运动负荷逐渐增加至较高的负荷,对于老年人来说具有较高的安全性,增加了患者在运动干预过程中的依从性;同时,渐进式抗阻运动对老年人肌少性肥胖的改善作用主要体现在肌肉适能、身体成分与身体功能等方面。此外,还有研究对老年肌骨减少性肥胖患者采取抗阻运动干预[49],结果显示抗阻运动可有效改善患者的身体成分,减少体脂百分比并增加骨骼肌质量指数,说明运动干预肌骨减少性肥胖研究的必要性,但在干预过程中的风险尚不明确,在未来需要进行更广泛的研究(如更大的样本数量和更长的干预时间)。 弹力带抗阻训练是一种新型的干预老年人肌少性肥胖的抗阻训练方式,与传统的抗阻训练相比,弹力带抗阻训练对于老年人来说更加简便、安全且有效[50]。HUANG等[51]选取渐进式弹力带抗阻运动对老年女性肌少性肥胖患者进行了12周的干预,结果显示干预后患者的总脂肪量、四肢脂肪量减少,体脂百分比降低,骨密度增加。此外,LIAO等[52]为探究弹力带抗阻训练对老年女性肌少性肥胖患者肌肉质量和身体功能的影响,进行了一项为期12周的随机对照试验,结果显示与对照组相比,弹力带抗阻训练干预组的身体成分(骨骼肌质量指数、四肢骨骼肌质量等)与身体功能(单腿站立、步速、起立行走测试、椅子测试等)得到了显著改善。在为老年肌少性肥胖患者制定抗阻训练干预处方时,可以采用弹力带抗阻训练的方式,从而更好地改善患者的身体成分与身体功能等。对于老年肌骨减少性肥胖患者,弹力带抗阻运动亦能产生有益的影响,尤其是在改善骨密度和身体成分等方面效果显著[53-56],见表3。 低负荷抗阻运动结合血流限制是一种新的运动干预手段,血流限制训练是指在低强度运动过程中通过限制肌肉的血流量,从而刺激肌肉产生对低强度运动的适应性反应,进而提高骨骼肌质量与力量[57],主要通过压缩装置,"
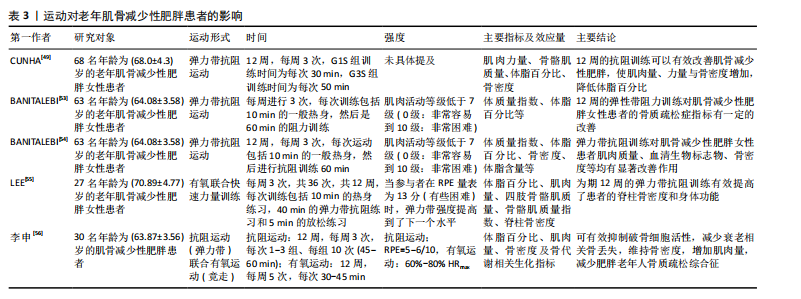
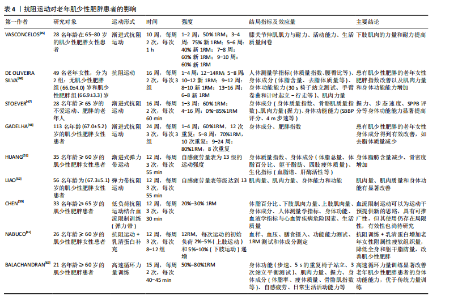
如充气袖带,对近心端肢体施加外部压力,在抗阻训练期间限制静脉血流[58]。CHEN等[59]对33名年龄在65岁以上的老年肌少性肥胖患者进行了12周的随机对照试验,对肌肉力量、身体成分、生活质量、心血管疾病危险因素等方面的有效性、安全性与传统高负荷阻力训练比较。以往的一些研究证明低负荷抗阻运动结合血流限制对肌肉质量、力量产生的增益效果与传统高负荷阻力训练是相似的,但低负荷抗阻运动结合血流限制对老年肌少性肥胖患者干预效果的文献较少,同时也鲜有研究对该训练方式的安全性及其可能存在的不良后果进行深入探讨。低负荷抗阻运动结合血流限制可能是代替传统高负荷抗阻运动的有效训练方法,在将来应增加低负荷抗阻运动结合血流限制对于老年肌少性肥胖患者进行干预的研究,更加系统地评述该训练方法的有效性与安全性。 抗阻训练联合营养膳食对于防治肌少性肥胖同样十分关键。一项关于蛋白质补充结合抗阻运动对老年肌少性肥胖患者影响的系统综述与荟萃分析表明,与单纯的抗阻训练相比,蛋白质补充结合抗阻运动预防老年人衰老相关的肌肉质量衰减以及腿部力量损失更加有效[60]。NABUCO等[61]研究发现,进行抗阻训练的同时增加乳清蛋白摄入,可以更好地增加老年女性肌少性肥胖患者的四肢骨骼肌质量、减少总脂肪量,这提示在为老年肌少性肥胖患者制定抗阻运动方案时可以考虑与营养膳食补充相结合,可以在改善与提高老年人肌少性肥胖的肌肉量、力量与身体功能等方面取得更大的益处。 高速循环训练也是一种新颖的干预老年人肌少性肥胖的方式,BALACHANDRAN等[62]将高速循环力量训练应用于老年肌少性肥胖患者(高速循环力量训练指利用重复运动序列进行的力量训练,其组间间歇时间比传统的抗阻训练更短[63]),发现该方法可以有效降低患者体脂百分比、增加肌肉质量与力量等,高速循环力量训练在改善老年肌少性肥胖患者的身体功能方面显著优于传统力量训练[95%CI (-0.1-2.4),P=0.08]。但针对老年肌少性肥胖患者的高速循环力量训练相关研究仅有1篇,所以建议未来扩大样本量、进一步研究高速循环力量训练干预老年人肌少性肥胖的机制与效果。 抗阻运动对老年肌少性肥胖患者的影响,见表4。 (2)老年肌少性肥胖患者抗阻运动处方建议:根据已有的研究与证据,针对运动频率、运动强度、运动量与运动方式给出老年肌少性肥胖患者抗阻运动处方的建议。 运动频率:纳入的多数研究中建议每周进行两三次抗阻训练,且每次不低于30 min,在干预过程中也未发生运动损伤与心血管事件。根据美国运动医学会的一项研究[64],每周进行两三次的抗阻训练可以更好地改善体脂率与瘦体质量。同时,一项针对骨骼肌功能受限老年人抗阻训练的系统评价以及美国体能协会给出的推荐量[65],都提到老年人每周应进行两三次、每次30-60 min的大肌群抗阻运动。 运动强度:对于抗阻训练的运动强度设置,常用1RM的不同百分比或绝对值来表示。1RM指以正确的动"
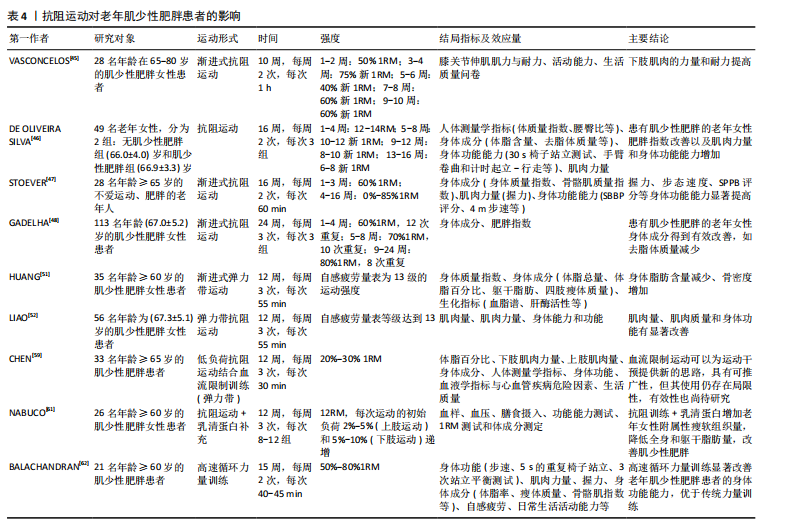
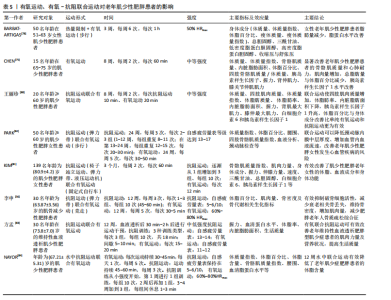
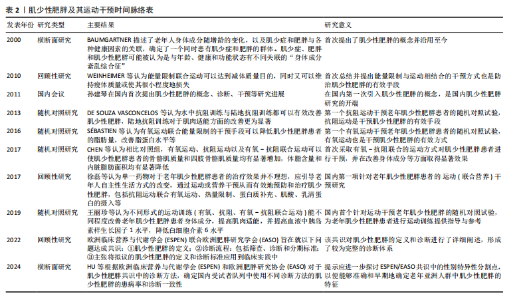
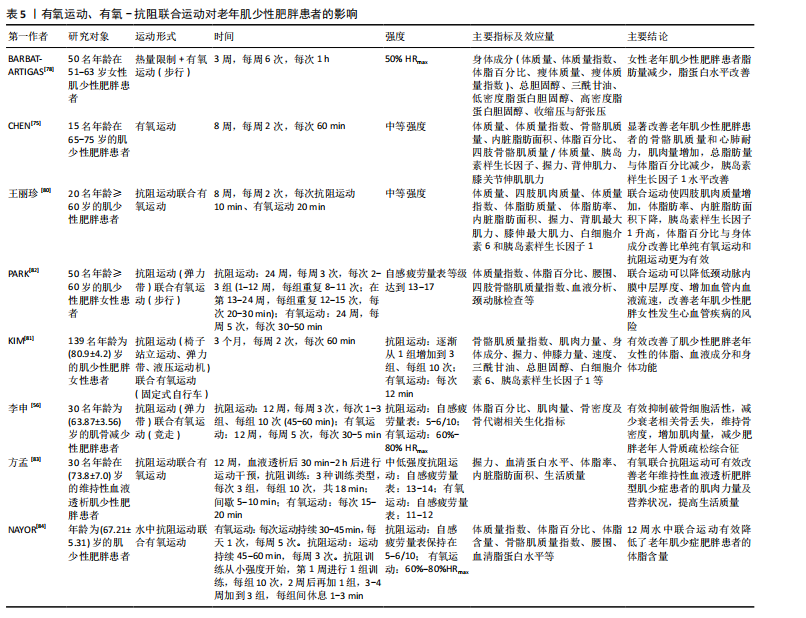
作能够举起且仅能举起一次的质量,被视为动力性最大力量测试的“金标准”[66]。美国体能协会于2019年发表的立场声明中提到,中高强度的抗阻训练(70%-85%1RM)对于老年人来说可以产生更好的神经肌肉适应[67]。但纳入的多项研究考虑到老年肌少性肥胖患者肌肉力量与运动能力下降,采取较高强度的负荷可能会使运动中的风险增加,因此多采用渐进式抗阻训练模式,即从较低强度逐渐增加到中高强度。除用1RM来制定运动强度外,纳入的有些研究中还采用主观感觉疲劳等级量表来制定与评价运动强度[51-52],主观感觉疲劳等级量表考虑到不同个体的差异且体现个性化原则。 运动量:运动量由强度、组数、重复次数、组间间隔等要素共同决定。强度在上文中已经提及,所以此处主要以重复次数与组间间隔进行讨论。重复次数是指每组动作所要完成的次数;组间间隔是指每组之间的间歇,即组间的休息时间。肌肉衰减综合征营养与运动干预中国专家共识中提到抗阻训练组间休息时间应该不少于2 min,才可以更好地改善肌肉质量[68]。对于老年肌少性肥胖患者来说,还应考虑患者的体力活动水平与心血管危险因素等来制定合理的组间间隔与重复次数。 运动方式:抗阻训练的方式主要包括自重训练、徒手力量练习与使用健身器械等方式。自重抗阻训练与徒手力量练习是指不借助健身器械,仅依靠自身质量来完成各种抗阻训练,包括标准俯卧撑、卷腹、站姿提踵及自重深蹲等;使用健身器械进行抗阻训练可以通过肩臂提升训练器、伸髋屈膝肌肉训练器、用于血流限制训练的充气袖带等压缩装置以及新颖的带有负荷数值的弹力带等。在运动医学与康复领域,还会采用等速力量训练的方式,即借助等速训练仪器让受试者在各个关节活动度下进行抗阻训练,从而达到最佳的效果。 综上所述,对于老年肌少性肥胖患者的抗阻运动处方建议为渐进式抗阻训练,具体来说,运动频率在每周两三次,每次训练时间为30-60 min,组间间隔为60-180 s,运动强度采用由较低负荷渐进式增加至中高强度,运动方式可以选用自重与徒手力量练习、健身器械、弹力带训练、低负荷抗阻运动结合血流限制以及抗阻训练联合营养膳食等。同时,有研究将抗阻训练与平衡训练以及姿势控制训练相结合,可以有效改善老年肌少性肥胖患者的步态与神经肌肉控制能力,为运动干预肌少性肥胖提供了新思路[69]。 2.3.2 有氧运动与老年人肌少性肥胖 (1)有氧运动对老年肌少性肥胖患者的影响:有氧运动是指在运动过程中主要以有氧代谢提供能量的运动方式,是全身大肌群参与的持续时间较长的运动,运动过程中所需的能量由能源物质氧化来供给[70]。尽管已经有较为充分的证据表明,抗阻运动在提高骨骼肌的质量和力量方面发挥着主要的作用,但是有氧运动在维持衰老骨骼肌的最大摄取氧气的能力和细胞稳态(尤其是维持线粒体功能)方面起着至关重要的作用[71]。长期、科学的有氧运动可以增加骨骼肌毛细血管密度、促进骨骼肌中营养物质的运输与利用,从而有利于肌原纤维蛋白合成和提高肌肉质量[72-73];同时可以改善线粒体功能与线粒体适应,提高骨骼肌的有氧工作能力[74]。有氧运动对体脂含量、心肺适能等也会产生有益的影响,尤其是与膳食补充相联合,因此有氧运动也被视为延缓肥胖发展的有效策略。CHEN等[75]研究了不同运动方式对肌少性肥胖患者的身体成分、肌肉力量与体内胰岛素样生长因子1水平的影响,其中有氧运动组采用共8周、每周2次、每次60 min的中等强度的训练方案,之后停训随访4周,12周结束后,测试结果显示有氧运动方案不仅显著改善了老年肌少性肥胖患者的总骨骼肌质量,而且使心肺耐力显著提高,同时,内脏脂肪面积、体脂百分比水平等也显著降低(上述指标P < 0.05)。郭宇枢等[76]通过分析老年肌少性肥胖患者的影响因素,发现内脏脂肪面积增大是其独立危险因素之一,因此有氧运动在减少肌少性肥胖患者体质量方面起到有效的作用。此外,有氧运动与膳食干预相结合可以有效控制肥胖的发展[77],BARBAT-ARTIGAS等[78]研究了有氧运动与热量限制相结合对女性老年肌少性肥胖患者的影响,膳食处方由20%-25%的蛋白质、25%-30%的脂类与50%-55%的碳水化合物组成,有氧训练计划为持续3周、每周6 d、每天步行1 h且运动强度为50%最大心率,在运动结合饮食干预后,肌少性肥胖患者的脂肪量、脂蛋白水平得到改善(P < 0.05),但并不会对瘦体质量产生有害影响。虽然有氧运动干预与防治老年人肌少性肥胖的研究有限,但对于改善老年肌少性肥胖患者脂肪含量与肌肉适能方面(尤其是提高最大摄氧量与减少内脏脂肪面积),有氧运动是有效的干预方式。 (2)老年肌少性肥胖患者有氧运动处方建议:由于有氧运动干预老年肌少性肥胖患者的研究较少,所以结合纳入的文献,建议老年肌少性肥胖患者进行频率为每周3-5次、时间每次1 h、运动强度为50%最大心率的中等强度有氧运动,运动方式选择步行为宜,此外,还可以采用多种形式简单的有氧运动进行组合,如将原地踏步、高膝跑、菱形步、点步跳等运动进行组合,从而增加运动干预过程中依从性。 2.3.3 联合运动与老年肌少性肥胖 (1)联合运动对老年肌少性肥胖患者的影响:联合运动是有氧运动与抗阻运动的结合,联合运动一方面有利于增加骨骼肌质量、改善身体成分并减少脂肪含量;另一方面有利于增加骨骼肌力量、提高身体功能能力。有氧-抗阻联合运动在提高骨骼肌力量方面优于单一的运动模式[79],同时联合运动的方式多样,可以增加老年肌少性肥胖患者运动干预过程中的依从性。王丽珍等[80]探究了不同运动方式对于老年肌少性肥胖患者的影响,发现抗阻运动联合有氧运动(8周,每周2次,每次抗阻运动10 min、有氧运动20 min,且为中等强度)干预后,受试者四肢肌肉质量增加、体脂肪率与内脏脂肪面积下降、胰岛素样生长因子1水平升高,而在改善体脂百分比与身体成分方面比单纯有氧运动和抗阻运动更为有效(P < 0.05);KIM等[81]针对日本老年女性肌少性肥胖患者所做的有氧-抗阻联合运动干预也得到了与之相似的结果。PARK等[82]还发现有氧-抗阻联合运动可以减少老年肌少性肥胖患者发生心血管疾病的风险,选取50名年龄为(74.1±6.1)岁的老年人肌少性肥胖女性患者作为受试者,研究有氧(步行)-抗阻(弹力带运动)联合运动对颈动脉参数的影响,干预24周后的结果表明,联合运动可以使肌少性肥胖患者的颈动脉内膜中层厚度显著降低(P < 0.01),同时使颈动脉收缩期(P < 0.01)、舒张期血流速度(P < 0.001)和血管壁剪切速率(P < 0.05)显著增加。李申等[56]指出,共12周的抗阻运动(弹力带)联合有氧运动(竞走)可有效抑制老年骨质疏松型肌少性肥胖患者破骨细胞活性,减少衰老相关的骨丢失,维持骨密度,并增加肌肉量,减少肌少性肥胖老年人骨质疏松综合征。此外,2023年方孟团队[83]研究了有氧联合抗阻运动对老年维持性血液透析肥胖型肌少症患者的影响,研究结果显示,在干预进行至第6周时,干预组内脏脂肪面积显著低于对照组,在12周运动干预结束时,干预组的握力、体脂率、内脏脂肪面积以及生活质量等方面均得到显著改善,改善效果明显优于对照组(均P < 0.05)。水中运动可以有效提高老年人下肢肌力[84],QI等[85]采用新形式的水中有氧-抗阻联合运动干预肌少性肥胖患者,同样取得了明显的效果。未来仍需要进一步研究、细化联合运动中有氧和抗阻运动的具体干预方式。 (2)老年肌少性肥胖患者有氧-抗阻联合运动处方建议:由于针对有氧-抗阻联合运动干预老年肌少性肥胖患者的研究较少,结合纳入的文献,建议老年肌少性肥胖患者进行频率为每周两三次、时间为每次30-50 min、运动强度为中等强度(可用自我感觉疲劳量表等级来制定运动强度)的有氧-抗阻联合运动。 有氧运动、有氧-抗阻联合运动对老年肌少性肥胖患者的影响,见表5。 2.4 老年肌少性肥胖患者运动处方建议 通过总结归纳相关文献,制定老年人肌少性肥胖防治的运动处方建议,见表6。"
| [1] JI T, LI Y, MA L. Sarcopenic Obesity: An Emerging Public Health Problem. Aging Dis. 2022;13(2):379-388. [2] XU J, HU Q, DING J, et al. Construction of an Exercise Intervention Program for Patients with Sarcopenic Obesity: A Delphi Method Study. Clin Interv Aging. 2024;19:727-736. [3] 龙宜,杨佳明,叶花,等.细胞外囊泡在少肌性肥胖中的作用及机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(2):315-320. [4] ROUBENOFF R. Sarcopenic obesity: the confluence of two epidemics. Obes Res. 2004;12(6):887-888. [5] CANCELLO R, BRENNA E, SORANNA D, et al. Sarcopenia Prevalence among Hospitalized Patients with Severe Obesity: An Observational Study. J Clin Med. 2024;13(10):2880. [6] 刘海明,张娜,张俊仕.肌肉减少性肥胖与老年患者冠心病发病率及死亡风险的相关性研究[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2023, 25(7):680-683. [7] PETERMANN-ROCHA F, DIAZ-TORO F, VALERA-GRAN D, et al. Bibliometric analysis of research on sarcopenic obesity: a review of scientific literature. Obes Rev. 2024:e13784. doi: 10.1111/obr.13784. [8] BINU AJ, KAPOOR N, BHATTACHARYA S, et al. Sarcopenic Obesity as a Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease: An Underrecognized Clinical Entity. Heart Int. 2023;17(2):6-11. [9] JANANI S, SEDHUNIVAS R. Effectiveness of exercise interventions on muscle mass among older adults with sarcopenic obesity: A scoping review. Aging Med (Milton). 2024;7(1):115-120. [10] PHILLIPS BE, ATHERTON PJ, VARADHAN K, et al. The effects of resistance exercise training on macro- and micro-circulatory responses to feeding and skeletal muscle protein anabolism in older men. J Physiol. 2015;593(12):2721-2734. [11] DEBES WA, SADAQA M, NÉMETH Z, et al. Effect of Resistance Exercise on Body Composition and Functional Capacity in Older Women with Sarcopenic Obesity-A Systematic Review with Narrative Synthesis. J Clin Med. 2024;13(2):441. [12] WAGENAAR CA, DEKKER LH, NAVIS GJ. Prevalence of sarcopenic obesity and sarcopenic overweight in the general population: The lifelines cohort study. Clin Nutr. 2021;40(6):4422-4429. [13] VILLAREAL DT, AGUIRRE L, GURNEY AB, et al. Aerobic or Resistance Exercise, or Both, in Dieting Obese Older Adults. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376(20):1943-1955. [14] BAUMGARTNER RN. Body composition in healthy aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;904:437-448. [15] 刘妍慧,陈树春.2022年欧洲临床营养与代谢学会和欧洲肥胖研究学会《肌肉减少性肥胖的定义和诊断标准共识》解读及启示[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(12):1422-1428. [16] QIN JWM, SUN L, ET AL. Current status of non-pharmacologic interventions for sarcopenic obesity in the elderly. Evid Based Nurs. 2023;9(11):1966-1969. [17] KIM YC, KI SW, KIM H, et al. Recent Advances in Nutraceuticals for the Treatment of Sarcopenic Obesity. Nutrients. 2023;15(17):3854. [18] DA SILVA GONÇALVES L, SANTOS LOPES DA SILVA L, RODRIGUES BENJAMIM CJ, et al. The Effects of Different Exercise Training Types on Body Composition and Physical Performance in Older Adults with Sarcopenic Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Nutr Health Aging. 2023;27(11):1076-1090. [19] GHIOTTO L, MUOLLO V, TATANGELO T, et al. Exercise and physical performance in older adults with sarcopenic obesity: A systematic review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:913953. [20] STINKENS R, GOOSSENS GH, JOCKEN JW, et al. Targeting fatty acid metabolism to improve glucose metabolism. Obes Rev. 2015;16(9):715-757. [21] PELLEGRINELLI V, ROUAULT C, RODRIGUEZ-CUENCA S, et al. Human Adipocytes Induce Inflammation and Atrophy in Muscle Cells During Obesity. Diabetes. 2015;64(9):3121-3134. [22] DESHMUKH AS, COX J, JENSEN LJ, et al. Secretome Analysis of Lipid-Induced Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle Cells by a Combined Experimental and Bioinformatics Workflow. J Proteome Res. 2015; 14(11):4885-4895. [23] KALINKOVICH A, LIVSHITS G. Sarcopenic obesity or obese sarcopenia: A cross talk between age-associated adipose tissue and skeletal muscle inflammation as a main mechanism of the pathogenesis. Ageing Res Rev. 2017;35:200-221. [24] CASTOLDI A, NAFFAH DE SOUZA C, CÂMARA NO, et al. The Macrophage Switch in Obesity Development. Front Immunol. 2016;6:637. [25] KRATZ M, COATS BR, HISERT KB, et al. Metabolic dysfunction drives a mechanistically distinct proinflammatory phenotype in adipose tissue macrophages. Cell Metab. 2014;20(4):614-625. [26] 刘源,杨风英.脂肪组织炎症反应在运动缓解肥胖性肌少症中的作用[J].山东体育学院学报,2022,38(1):81-87. [27] ZHAO S, KUSMINSKI CM, SCHERER PE. Adiponectin, Leptin and Cardiovascular Disorders. Circ Res. 2021;128(1):136-149. [28] LI Y, ZHANG F, MODRAK S, et al. Chronic Alcohol Consumption Enhances Skeletal Muscle Wasting in Mice Bearing Cachectic Cancers: The Role of TNFα/Myostatin Axis. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020;44(1):66-77. [29] ALIZADEH PAHLAVANI H. Exercise Therapy for People With Sarcopenic Obesity: Myokines and Adipokines as Effective Actors. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:811751. [30] TUTTLE CSL, THANG LAN, MAIER AB. Markers of inflammation and their association with muscle strength and mass: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;64:101185. [31] LI CW, YU K, SHYH-CHANG N, et al. Pathogenesis of sarcopenia and the relationship with fat mass: descriptive review. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(2):781-794. [32] SHEN J, WANG X, WANG M, et al. Potential molecular mechanism of exercise reversing insulin resistance and improving neurodegenerative diseases. Front Physiol. 2024;15:1337442. [33] TONG Y, XU S, HUANG L, et al. Obesity and insulin resistance: Pathophysiology and treatment. Drug Discov Today. 2022;27(3): 822-830. [34] LIU ZJ, ZHU CF. Causal relationship between insulin resistance and sarcopenia. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023;15(1):46. [35] MAMMUCARI C, MILAN G, ROMANELLO V, et al. FoxO3 controls autophagy in skeletal muscle in vivo. Cell Metab. 2007;6(6):458-471. [36] FERNÁNDEZ-SÁNCHEZ A, MADRIGAL-SANTILLÁN E, BAUTISTA M, et al. Inflammation, oxidative stress, and obesity. Int J Mol Sci. 2011; 12(5):3117-3132. [37] 郭怡洵,关晓印,王博,等.肌少性肥胖的发病机制及潜在治疗靶点研究进展[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2023,28(3): 341-346. [38] 陈演,邱俊强,于涛,等.肌肉-器官交互作用:运动诱导的肌肉因子研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2022,41(11):887-895. [39] ZHANG L, LV J, WANG C, et al. Myokine, a key cytokine for physical exercise to alleviate sarcopenic obesity. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(3): 2723-2734. [40] 田峰,涂来勇,张恩丰,等.鸢尾素抑制炎症因子表达促成骨分化改善糖尿病小鼠骨代谢的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2024,30(4): 511-516. [41] TIMMER LT, HOOGAARS WMH, JASPERS RT. The Role of IGF-1 Signaling in Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1088:109-137. [42] KANZLEITER T, RATH M, GÖRGENS SW, et al. The myokine decorin is regulated by contraction and involved in muscle hypertrophy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;450(2):1089-1094. [43] RAHMATI M, SHARIATZADEH JONEYDI M, KOYANAGI A, et al. Resistance training restores skeletal muscle atrophy and satellite cell content in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):2535. [44] VERDIJK LB, SNIJDERS T, DROST M, et al. Satellite cells in human skeletal muscle; from birth to old age. Age (Dordr). 2014;36(2):545-547. [45] VASCONCELOS KS, DIAS JM, ARAÚJO MC, et al. Effects of a progressive resistance exercise program with high-speed component on the physical function of older women with sarcopenic obesity: a randomized controlled trial. Braz J Phys Ther. 2016;20(5):432-440. [46] DE OLIVEIRA SILVA A, DUTRA MT, DE MORAES WMAM, et al. Resistance training-induced gains in muscle strength, body composition, and functional capacity are attenuated in elderly women with sarcopenic obesity. Clin Interv Aging. 2018;13:411-417. [47] STOEVER K, HEBER A, EICHBERG S, et al. Influences of Resistance Training on Physical Function in Older, Obese Men and Women With Sarcopenia. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2018;41(1):20-27. [48] GADELHA AB, PAIVA FM, GAUCHE R, et al. Effects of resistance training on sarcopenic obesity index in older women: A randomized controlled trial. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2016;65:168-173. [49] CUNHA PM, RIBEIRO AS, TOMELERI CM, et al. The effects of resistance training volume on osteosarcopenic obesity in older women. J Sports Sci. 2018;36(14):1564-1571. [50] MARTINS WR, DE OLIVEIRA RJ, CARVALHO RS, et al. Elastic resistance training to increase muscle strength in elderly: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2013;57(1):8-15. [51] HUANG SW, KU JW, LIN LF, et al. Body composition influenced by progressive elastic band resistance exercise of sarcopenic obesity elderly women: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2017;53(4):556-563. [52] LIAO CD, TSAUO JY, HUANG SW, et al. Effects of elastic band exercise on lean mass and physical capacity in older women with sarcopenic obesity: A randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2317. [53] BANITALEBI E, FARAMARZI M, GHAHFAROKHI MM, et al. Osteosarcopenic obesity markers following elastic band resistance training: A randomized controlled trial. Exp Gerontol. 2020;135:110884. [54] BANITALEBI E, GHAHFARROKHI MM, DEHGHAN M. Effect of 12-weeks elastic band resistance training on MyomiRs and osteoporosis markers in elderly women with Osteosarcopenic obesity: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):433. [55] LEE YH, LEE PH, LIN LF, et al. Effects of progressive elastic band resistance exercise for aged osteosarcopenic adiposity women. Exp Gerontol. 2021;147:111272. [56] 李申,黄力平,王磊,等.12周有氧步行联合快速力量训练对肌骨减少性肥胖老年人干预效果研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2020, 35(4):420-426. [57] SATO Y. The history and future of KAATSU Training. Int J Kaatsu Train Res. 2005; 1(1):1-5. [58] LOENNEKE JP, WILSON JM, MARÍN PJ, et al. Low intensity blood flow restriction training: a meta-analysis. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(5): 1849-1859. [59] CHEN N, HE X, ZHAO G, et al. Efficacy of low-load resistance training combined with blood flow restriction vs. high-load resistance training on sarcopenia among community-dwelling older Chinese people: study protocol for a 3-arm randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2021;22(1):518. [60] LIAO CD, TSAUO JY, WU YT, et al. Effects of protein supplementation combined with resistance exercise on body composition and physical function in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2017;106(4):1078-1091. [61] NABUCO HCG, TOMELERI CM, FERNANDES RR, et al. Effect of whey protein supplementation combined with resistance training on body composition, muscular strength, functional capacity, and plasma-metabolism biomarkers in older women with sarcopenic obesity: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2019;32:88-95. [62] BALACHANDRAN A, KRAWCZYK SN, POTIAUMPAI M, et al. High-speed circuit training vs hypertrophy training to improve physical function in sarcopenic obese adults: a randomized controlled trial. Exp Gerontol. 2014;60:64-71. [63] PASHAEI Z, MALANDISH A, ALIPOUR S, et al. Effects of HIIT training and HIIT combined with circuit resistance training on measures of physical fitness, miRNA expression, and metabolic risk factors in overweight/obese middle-aged women. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2024;16(1):123. [64] WESTCOTT WL, WINETT RA, ANNESI JJ, et al. Prescribing physical activity: applying the ACSM protocols for exercise type, intensity, and duration across 3 training frequencies. Phys Sportsmed. 2009;37(2):51-58. [65] PAPA EV, DONG X, HASSAN M. Resistance training for activity limitations in older adults with skeletal muscle function deficits: a systematic review. Clin Interv Aging. 2017;12:955-961. [66] GRGIC J, LAZINICA B, SCHOENFELD BJ, et al. Test-Retest Reliability of the One-Repetition Maximum (1RM) Strength Assessment: a Systematic Review. Sports Med Open. 2020;6(1):31. [67] FRAGALA MS, CADORE EL, DORGO S,et al. Resistance Training for Older Adults: Position Statement From the National Strength and Conditioning Association. J Strength Cond Res. 2019;33(8):2019-2052. [68] 孙建琴,张坚,常翠青,等.肌肉衰减综合征营养与运动干预中国专家共识(节录)[J].营养学报,2015,37(4):320-324. [69] FERHI H, GAIED CHORTANE S, DURAND S, et al. Effects of Physical Activity Program on Body Composition, Physical Performance, and Neuromuscular Strategies during Walking in Older Adults with Sarcopenic Obesity: Randomized Controlled Trial. Healthcare (Basel). 2023;11(16):2294. [70] 王晨,张培珍.不同类型的运动对高血压患者认知功能影响的研究进展[J].中华高血压杂志(中英文),2024,32(8):714-721+700. [71] LIANG J, ZHANG H, ZENG Z, et al. Lifelong Aerobic Exercise Alleviates Sarcopenia by Activating Autophagy and Inhibiting Protein Degradation via the AMPK/PGC-1α Signaling Pathway. Metabolites. 2021;11(5):323. [72] YOO SZ, NO MH, HEO JW, et al. Role of exercise in age-related sarcopenia. J Exerc Rehabil. 2018;14(4):551-558. [73] LAUGHLIN MH, ROSEGUINI B. Mechanisms for exercise training-induced increases in skeletal muscle blood flow capacity: differences with interval sprint training versus aerobic endurance training. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008;59 Suppl 7(Suppl 7):71-88. [74] LUNDBY C, JACOBS RA. Adaptations of skeletal muscle mitochondria to exercise training. Exp Physiol. 2016;101(1):17-22. [75] CHEN HT, CHUNG YC, CHEN YJ, et al. Effects of Different Types of Exercise on Body Composition, Muscle Strength, and IGF-1 in the Elderly with Sarcopenic Obesity. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(4):827-832. [76] 郭宇枢,薛倩,魏雅楠,等.老年肥胖患者肌少症发生情况及其危险因素研究[J].中国全科医学,2021,24(24):3048-3053. [77] BOUAZIZ W, SCHMITT E, KALTENBACH G, et al. Health benefits of endurance training alone or combined with diet for obese patients over 60: a review. Int J Clin Pract. 2015;69(10):1032-1049. [78] BARBAT-ARTIGAS S, GARNIER S, JOFFROY S, et al. Caloric restriction and aerobic exercise in sarcopenic and non-sarcopenic obese women: an observational and retrospective study. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2016;7(3):284-289. [79] YIN YH, LIU JYW, VÄLIMÄKI M. Effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions on the management of sarcopenic obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Exp Gerontol. 2020;135:110937. [80] 王丽珍,郭颖彬,骆俊宏.居家运动训练对老年肥胖型肌少症的效果[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(1):90-96. [81] KIM H, KIM M, KOJIMA N, et al. Exercise and Nutritional Supplementation on Community-Dwelling Elderly Japanese Women With Sarcopenic Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2016;17(11):1011-1019. [82] PARK J, KWON Y, PARK H. Effects of 24-Week Aerobic and Resistance Training on Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness and Flow Velocity in Elderly Women with Sarcopenic Obesity. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2017;24(11):1117-1124. [83] 方孟,戴敏,杨文娟,等.有氧联合抗阻运动对老年维持性血液透析肥胖型肌少症患者的影响[J].护理学杂志,2023,38(5): 95-100. [84] NAYLOR LH, MASLEN BA, COX KL, et al. Land- versus water-walking interventions in older adults: Effects on body composition. J Sci Med Sport. 2020;23(2):164-170. [85] QI S, HORII N, KISHIGAMI K, et al. Effects of water exercise on body composition and components of metabolic syndrome in older females with sarcopenic obesity. J Phys Ther Sci. 2023;35(1):24-30. |
| [1] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [2] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [3] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [4] | Zheng Huakun, Yin Mingyue, Liu Qian. Effects of interval and continuous training on the quality of life in physically inactive adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1727-1740. |
| [5] | Lou Guo, Zhang Min, Fu Changxi. Exercise preconditioning for eight weeks enhances therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells in rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [6] | Zheng Rongfa, Mo Weibin, Huang Peng, Chen Junji, Liang Ting, Zi Fangyu, Li Guofeng. Effects of electroacupuncture on the expression of metabolic enzymes and autophagy genes in gastrocnemius muscle tissues of exercising rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1127-1136. |
| [7] | Zhao Xiaoxuan, Liu Shuaiyi, Li Qi, Xing Zheng, Li Qingwen, Chu Xiaolei. Different exercise modalities promote functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1248-1256. |
| [8] | Zhang Wenhua, Li Xun, Zhang Weichao, Li Xinying, Ma Guoao, Wang Xiaoqiang . Promoting myogenesis based on the SphK1/S1P/S1PR2 signaling pathway: a new perspective on improving skeletal muscle health through exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1265-1275. |
| [9] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [10] | Wang Dongyang, Yang Qiaohui, Lin Xinchao. Relationship between vitamin D levels and reproductive characteristics and exercise dietary situation in postmenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1021-1025. |
| [11] | Zhu Chuanxi, Qiu Long, Li Lingxu, Ji Guangcheng. Chinese herbal prescription combined with head acupuncture exercise therapy improves limb spasticity in rats with ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7571-7577. |
| [12] | Liu Xuan, Ding Yuqing, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang, Hu Shujuan. Exercise prevention and treatment of insulin resistance: role and molecular mechanism of Keap1/nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| [13] |
Li Zhipeng, Xing Rongxin, Hu Lianghong.
Roles of SOX5 in bone metabolism and prevention of bone diseases and the relationship with exercise#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7589-7600.
|
| [14] | Ji Long, Chen Ziyang, , Jin Pan, Kong Xiangkui, Pu Rui, . Lipophagy, exercise intervention and prevention and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7611-7619. |
| [15] | Yang Yu, Li Yinghao, Duo Zhuangzhi, Zhou Dingrong. Effect of overall functional physical exercise on lumbar biomechanics in patients with lumbar disc herniation after surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7096-7101. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||