Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (17): 3650-3656.doi: 10.12307/2025.639
Previous Articles Next Articles
Evaluating the compensatory function of intelligent assistive devices for the blind in China based on the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health
Bu Nan1, Yang Yicheng1, 2, Song Beibei1, Bai Kaixiang1, Du Yunyun1, 2
- 1Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China; 2Engineering Research Center of Sports Health Intelligent Equipment of Hubei Province, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2024-06-12Accepted:2024-08-05Online:2025-06-18Published:2024-11-06 -
Contact:Du Yunyun, PhD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China; Engineering Research Center of Sports Health Intelligent Equipment of Hubei Province,Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Bu Nan, MS, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the “14th Five-Year Plan” for Hubei Higher Education Advantageous Characteristic Disciplines (Groups), No. [2021]5 (to DYY [project participant])
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Bu Nan, Yang Yicheng, , Song Beibei, Bai Kaixiang, Du Yunyun, . Evaluating the compensatory function of intelligent assistive devices for the blind in China based on the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3650-3656.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
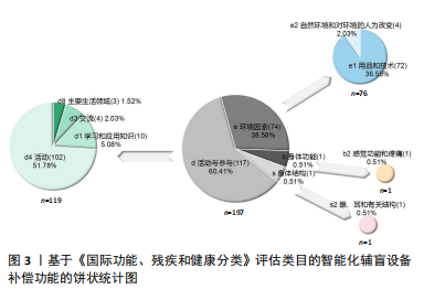
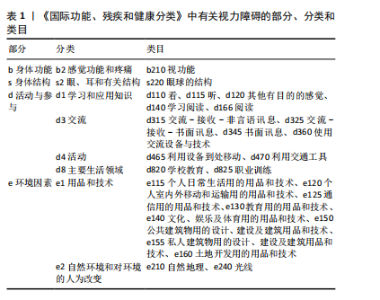
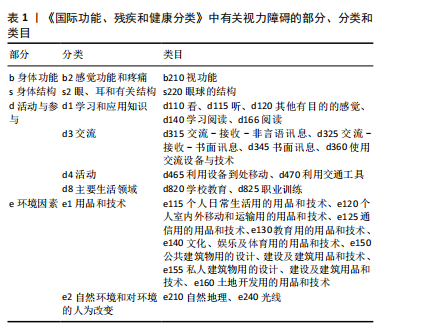
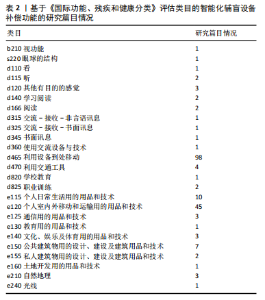
通过数据库检索的文献与《国际功能、残疾和健康分类》框架进行结合梳理,包含4个部分、8个分类、25个类目,各部分、分类和类目的篇目统计如下:身体功能1篇,包含b2,涉及b210;身体结构1篇,包含s2,涉及s220;活动与参与共119篇,包含d1(10篇)涉及d110、d115、d120、d140、d166,d3(4篇)涉及d315、d325、d345、d360,d4(102篇)涉及d465、d470,d8 (3篇)涉及d820、d825;环境因素共76篇,包含e1(72篇)涉及e115、e120、e125、e130、e140、e150、e155、e160,e2(4篇)涉及e210、e240。总体统计情况见图3。"
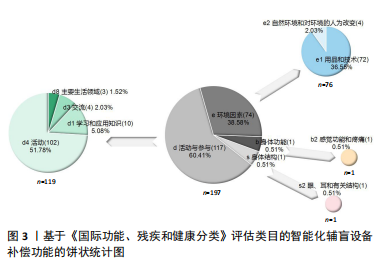

2.3 国内智能化辅盲设备补偿功能的分类 《国际功能、残疾和健康分类》各成分相互联系、相互影响。通过平行归纳类目中的内容,可得国内有关视力障碍人士智能化辅盲设备补偿功能研究主要涉及以下领域。 2.3.1 身体补偿类 就视力障碍人群身体功能结构而言,是指对其视感觉功能和视器官结构等进行直接改造和间接补偿的智能化介入的用品和技术,包含功能补偿、结构补偿、活动补偿等内容,涉及类目b210、s220、d110、d115、d120。 其中,功能补偿主要是指视力障碍人群视感觉功能的智能化干预。b210中,利用头戴式系统对低视力人群进行视功能的增强。结构补偿主要是指视力障碍人群眼球相关结构的智能化干预。s220中针对眼球的视网膜结构,应用互联网延续护理技术在视网膜脱落术后帮助视力改善。活动补偿主要是指视力障碍人群活动中调动视觉及其他感知觉补偿的智能化干预。d110中,利用多传感器融合同时定位与地图构建技术进行视觉辅助,使机器极大可能地代替人眼。d115中,陈冰萸[29]的研究涉及运用在线视频描述通过视觉转语音的听觉补偿方式。d120中主要是利用其他有目的的感觉,例如朱文霖等[30]的研究涉及到基于视-触跨模态感知的触觉进行感知觉的补偿。 2.3.2 生活用品类 就视力障碍人群日常生活而言,是指供其个人生活环境内使用的各类智能化辅助用品及技术,包含生活辅具、信息通讯、文娱活动、居住环境等内容,涉及类目e115、e125、e140、e155。 其中,生活辅具主要是视力障碍人群在家中可利用到的智能化物品。e115中主要针对视力障碍人群日常活动中使用的辅助设备、用品和技术,例如介入盲文设计和智能语音的用品包装设计[28]、识别行为特征的智能织物手镯、实现听觉和触觉智能提醒的饮水杯、可检测室外温度与天气的辅盲衣架、视力障碍人群的阅读书桌、物联网磁吸插座、视力障碍老人家用医疗产品等。信息通讯主要是满足视力障碍人群现代化互联网社交而进行的相关智能化设计。e125中,赵娜[31]的研究涉及到视力障碍者智能手机作为媒介的使用。文娱活动主要是满足视力障碍人群精神层面的文化、娱乐和体育等活动的设计与干预。e140中,刘彪等[32]的研究涉及利用卷积神经网络识别模型在盲文音乐图片上的应用、蔡豪源[33]的研究涉及利用虚拟模拟、增强现实和人工智能技术所构想设计的智能图书馆等。居家环境主要是对视力障碍人群居住空间和居住产品的无障碍智能化设计。e155的辅盲设备补偿功能突出对个人建筑物的智能化设计,包括智能家居产品和居住空间环境、室内定位导航和远程监控系统的设计等。 2.3.3 教育学习类 就视力障碍人群教育层面而言,是指对信息和知识的学习、应用和交流以及在校或在职等教育领域的智能化技术与设计,包含基本学习与应用、信息交流与接收、教育用品与技术、特殊教育与培训等内容,涉及类目d140、d166、d315、d325、d345、d360、d820、d825、e130。 其中,基本学习与应用主要是利用智能化设备使得视力障碍人群有效完成对文字(主要是盲文)和符号等书面材料的阅读与理解,再延伸到阅读信息的应用。d140中,国家亮等[34]的研究涉及通过设计开发的拼音和汉字标注软件进行盲文的计算机标注;张名章等[35]的研究涉及利用智能技术重塑有声读物的出版方式及版权保护机制。d166中,朱莉[36]的研究主要针对“盲人数字阅读推广工程”实践与服务探索。信息交流与接收主要是满足视力障碍人群对姿势、符号、盲文等讯息输入和理解的智能化介入,以及各类方便其交流的智能化设备与技术。d315中,刘静等[37]的研究有利用先进信息技术和智能阅读辅助设备帮助视力障碍人群获取多元化的精神文化信息。d325中,张居晓[38]的研究用不确定有穷自动机描述盲文与汉字点位编码的转换过程,再运用逆序拆分子集法对其确定化进而实现盲人使用计算机更方便。d345中涉及盲文智能化打字机的设计与应用。d360中涉及一类屏幕智能协助系统。教育用品与技术主要指针对视力障碍人群教育与培训过程中可应用到的智能化设备与产品。e130中为教育领域方法和技术,如李志鹏等[39]的研究涉及基于马尔科夫模型的盲文点显示器所制作的智能汉字盲文转换系统,适用于盲人和盲校的阅读与教学应用。特殊教育与培训主要是对于视力障碍人群等特殊群体完成在校教育和(或)职业培训中涉及到的智能化指导与训练。d820中主要针对个别化的特殊教育与人工智能的结合,使人工智能技术更有效地为特殊儿童个别化教育提供支持。d825中主要涉及职业教育中的各项活动指导,例如公共图书馆为视力障碍人群开展新媒体技术培训服务等。 2.3.4 出行导盲类 就视力障碍人群出行导盲而言,是指辅助其完成各类表面或空间内外移动活动的智能化设备和技术,以及对公共交通的特殊化设计,包含出行设备技术、公共交通设计,涉及类目d465、d470、e120。 其中,出行设备技术上,导盲器、导盲仪或导盲装置等在名称上尚未完全统一,但其本质上都归属于供视力障碍人群使用的各类应用导盲设备。d465中主要是利用各类智能化技术或功能的导盲杖[40-41]、导盲仪、导盲车、导盲机械狗、导盲机器人等设备帮助视力障碍人群出行。e120中主要是可穿戴的导盲用品以及各种帮助视力障碍人群于室内外活动的导盲设备和技术,例如基于机器视觉的导盲眼镜[42]、基于超声波测距传感的智能语音导盲服[43]、结合视听技术或可视图法设计的导盲机器人[44-45]、基于深度相机的导盲系统等[46]。公共交通设计上,d470中聚焦于视力障碍人群对公交、地铁等公共交通工具的使用或乘坐层面的设计。 此外,就导盲设备分类,主要可分为智能导盲杖、穿戴式导盲产品、移动式导盲机器产品,其中,国内穿戴式导盲产品涉及导盲帽、导盲头盔、导盲手套、导盲服、导盲腰带、导盲鞋等;移动式导盲机器产品涉及智能导盲犬、导盲机器人、导盲无人机等;此外,还有导盲车、导盲轮椅等设备。就导盲技术分类,主要可分为雷达、红外、超声波、蓝牙、激光、GPS、物联网、可穿戴式、图像识别等技术。就导盲功能分类,主要可完成避障、测距、定位、屏幕显示、导向导航、语音播报、人机对话、触觉提醒、安全监测与报警等功能。 2.3.5 布局规划类 就视力障碍人群场所规划而言,是指社会场所中的公共建筑和土地的设计与开发,以及对自然环境的真实或虚拟化的改造,包含公共建筑规划、土地开发布局、自然环境改造等内容,涉及类目e150、e160、e210、e240。 其中,公共建筑规划主要是视力障碍人群在社会交际活动中涉及到的公共场所建筑的用品、设备、技术和设计上的智能化。e150的设备补偿功能突出对公共建筑物的智能化设计,例如路口和马路[47]、城市盲道、交通系统、公共图书馆等公开场所及建筑物的规划[48]。土地开发布局主要是视力障碍人群在室外活动中政策影响所确定的地域内适应性或特殊化的智能设计。e160中主要指土地开发使用的技术和设计,如为视力障碍者提供的包含盲道、智能辅助、导向等功能的无障碍景观设计。自然环境改造主要是满足视力障碍人群无障碍活动,进而对自然地理特征进行真实改造或虚拟模拟的智能性规划。e210中针对自然地理环境或形态进行改变,主要体现在科技化的无障碍环境体系构建和虚拟环境的技术运用,如陈铭等[49]的探究涉及高校内部进行智能化交通空间、休闲空间和建筑空间的无障碍规划和管理,以及利用虚拟现实技术完成空间构建,并让视力障碍学生在虚拟环境中锻炼定向行走能力等[50]。e240中主要针对光线进行改变与设计,包括自然光或人造光的光线品质、强度、色彩等内容。 2.4 智能化辅盲设备补偿功能研究的评价 基于《国际功能、残疾和健康分类》整理出的研究分类及内容存在因类目不同而产生的篇目数量差距,其篇数在各不同部分、分类、类目下的差距也可显示出国内视力障碍智能化设备补偿功能研究的优势所在和不足之处。 2.4.1 基于《国际功能、残疾和健康分类》理论框架的研究篇目数量的对比 基于《国际功能、残疾和健康分类》各部分篇数对比,d最多(119),e其次(76),b和s最少(1),未介入个人因素。基于《国际功能、残疾和健康分类》各分类篇数对比,d中由多到少排序为d4(102)、d1(10)、d3(4)、d8(3),e中由多到少排序为e1(72)、e2(4)。基于《国际功能、残疾和健康分类》各类目篇数对比,d中的d1分类下,d120最多(3),d115、d140、d166其次(2),d110最少(1);d3分类下,d315、d325、d345、d360相同(1);d4分类下,d465(98)远大于d470(4);d8分类下,d825(2)较d820(1)多1篇。e中的e1分类下,由多到少排序为e120(45)、e115(10)、e150(7)、e125和e140(3)、e155(2)、e130和e160(1);e2分类下,e210(3)较e240(1)多2篇。 2.4.2 国内智能化辅盲设备研究的讨论与评价 基于《国际功能、残疾和健康分类》各部分篇数对比,可见国内在d和e的智能化设备补偿功能研究上明显优于b和s。多数研究体现在对视力障碍人士个体的活动参与,和对社会联系与周围环境的介入,而缺少对具体身体局部器官结构和功能,特别是对于眼球和视功能直接的智能化介入,即存在个人水平和社会水平的研究较多、器官水平的研究较少。 基于《国际功能、残疾和健康分类》各分类篇数对比,可见国内对于辅盲设备的智能化研究中,对视力障碍人士的身体移动的活动干预最多,尤其是外出参与社会活动。因为出行是视力障碍人士所面临的最大难题,这可能是造成研究有所偏重的最大原因之一。同时,因为听觉、触觉等感知觉能够最大限度地补偿部分视觉缺陷,实现以手代目、以耳代目,并且视力障碍人士和普通人一样具有健全的大脑和基本的认知、理解、分析、推理和判断能力[51],因此学习知识、接受教育、交流等活动受到视觉影响相对较少,故此上述部分的研究涉及相较出行活动的研究少。国内对于e的智能化研究侧重于对视力障碍人士的生活环境中各领域可能接触到的用品和技术的智能化介入。特殊群体需要从日常生活以及社会参与中可能使用到的产品上获取帮助,用品和技术的特殊化设计关系到视力障碍人群的各方面,对于提高视力障碍人群的生活质量起着举足轻重的作用[52]。而自然环境的真实改造需要大量时间、人力和财力支出,改造能力、规模和成果有限;虚拟现实技术的应用和推广存在难点的同时,也未能体现直接针对各类视力障碍人群生活环境的干预,所以该部分研究多为策略类探索或设计类展望。故此,对于生活环境中用品和技术的研究多于对环境的真实或虚拟化改造的研究。 基于《国际功能、残疾和健康分类》各类目篇数对比,可见个人利用设备进行室内外活动、运输的用品和技术的智能化介入研究明显多于其他类目,其主要原因也在于这两个类目的内容涉及了与视力障碍人群最直接、最重要的出行问题的处理。"

| [1] HOU C, PU C. Association Between Visual Impairment and Health Care Use. Am J Ophthalmol. 2022;234:166-173. [2] World Health Organization. Blindness and vision impairment.https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/blindness-and-visual-impairment,2023-12-31. [3] 范韫仪,郑晓瑛.我国视力残疾人社会参与状况及其影响因素[J].医学与社会,2023,36(10):46-52. [4] STEINMETZ JD, BOURNE RRA, BRIANT PS, et al. Causes of blindness and vision impairment in 2020 and trends over 30 years, and prevalence of avoidable blindness in relation to VISION 2020: the Right to Sight: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet Glob Health. 2021;9(2):e144-e160. [5] COLLABORATORS BVI. Vision Loss Expert Group of the Global Burden of Disease Study.Trends in prevalence of blindness and distance and near vision impairment over 30 years: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet Glob Health. 2021;9(2):e130-e143. [6] 江飞涛.技术革命浪潮下创新组织演变的历史脉络与未来展望:数字经济时代下的新思考[J].学术月刊,2022,54(4):50-62. [7] HAN Y , LEI Y , BAO Z ,et al. Research and Implementation of Mobile Internet Management Optimization and Intelligent Information System Based on Smart Decision. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2021:2021:5144568. [8] 辞海.智能化[OL]. [2024-01-21] https://www.cihai.com.cn/detail? q=%E6%99%BA%E8%83%BD%E5%8C%96&docId= 5639581&docLibId=72,2023-12-31. [9] SHENG B, CHEN X, LI T, et al. An overview of artificial intelligence in diabetic retinopathy and other ocular diseases. Front Public Health. 2022;10: 971943. [10] 隋勇,张立国,李采丰,等.人工智能赋能青少年体质健康精准治理:现实困境、治理向度和实践路径[J].中国教育学刊,2023(7):72-77. [11] 任相阁,任相颖,李绪辉,等.医疗领域人工智能应用的研究进展[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2022,24(2):762-770. [12] 张杭,贺强,刘青,等.人工智能与二维数字模板辅助规划全髋置换预测假体型号的对比分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(29): 4620-4627. [13] 朱培坤,白金柱.青少年特发性脊柱侧弯矫形器分类比较与数字智能技术的应用进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(21):3418-3423. [14] 李路,唐文.下颈椎后路椎弓根钉置钉:人工智能发展将如何提高治疗效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(3):474-479. [15] MADDEN RH, BUNDY A. The ICF has made a difference to functioning and disability measurement and statistics. Disabil Rehabil. 2019;41(12): 1450-1462. [16] SYKES CR, MARIBO T, STALLINGA HA, et al. Remodeling of the ICF: A commentary. Disabil Health J. 2021;14(1):100978. [17] LI B, YU Y, HU J. Applying the ICF-CY in visually impaired rehabilitation: a case report in China. Ann Palliat Med. 2021;10(3):3459-3468. [18] NEGRI L, SPOLADORE D, FOSSATI M, et al. Proposal for an ICF-based methodology to foster the return to work of persons with disability. Work. 2023;74(2):649-662. [19] 邱卓英,陈迪.基于ICF的残疾和康复信息标准体系及其应用研究[J].中国康复理论与实践,2014,20(6):501-507. [20] 邱卓英,张爱民.《国际功能、残疾和健康分类》应用指导(一)[J].中国康复理论与实践,2003,9(1):25-39. [21] DELLA MV, ALMBORG AH, MARTINUZZI M, et al. Harmonization of ICF Body Structures and ICD-11 Anatomic Detail: One foundation for multiple classifications. PLoS One. 2023;18(7):e0280106. [22] 蒋小艳,胡作进.ICF框架下的视力障碍儿童功能性视力评估分类要素分析[J].中国康复理论与实践,2015,21(11):1344-1347. [23] 燕铁斌.借力网络与人工智能,进一步推动《国际功能、残疾和健康分类(ICF)》的临床应用与研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2019, 34(2):121-124. [24] 尹梓名,王洁,郭珅,等.全体系康复辅助器具智能评估配置云平台研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2023,38(12):1707-1714+1718. [25] 盛小平,曾翠.知识管理的理论基础[J].中国图书馆学报,2010, 36(5):14-22. [26] 梁继文,杨建林,王伟.知识单元重组视角下的科学主题预测研究[J].情报学报,2023,42(5):511-524. [27] CIEZA A, GEYH S, CHATTERJI S, et al. ICF linking rules: an update based on lessons learned. J Rehabil Med. 2005;37(4):212-218. [28] 周作好,王刚,宋雨婷.盲人用品包装的智能设计[J].包装工程, 2017,38(22):258-260. [29] 陈冰萸.基于在线视频描述的视障人士辅助系统[J].计算机时代, 2022(9):23-27. [30] 朱文霖,刘华平,王博文,等.基于视-触跨模态感知的智能导盲系统[J].智能系统学报,2020,15(1):33-40. [31] 赵娜.互促相融:技术赋权与视障者的媒介生活:以视障者智能手机使用为例[J].传媒,2022(6):71-73+75. [32] 刘彪,黄蓉蓉,林和,等.基于卷积神经网络的盲文音乐识别研究[J].智能系统学报,2019,14(1):186-193. [33] 蔡豪源.智慧图书馆驱动下的视障读者服务创新探究[J].国家图书馆学刊,2018,27(4):64-69. [34] 国家亮,高雪珍,吕明,等.现行盲文拼音汉字标注研究[J].中国特殊教育,2019(1):54-58. [35] 张名章,宋俊锋.公共图书馆在视障群体服务中的智能化有声出版路径探索[J].新世纪图书馆,2022(6):11-17. [36] 朱莉.山东省“盲人数字阅读推广工程”实践探索[J].山东图书馆学刊,2021(1):67-74. [37] 刘静,孙通,刘宝瑞.智能技术赋能视障读者的智慧阅读研究[J].河南图书馆学刊,2023,43(7):81-82+85. [38] 张居晓.非确定有穷自动机在盲文转码中的应用[J].计算机科学, 2017,44(1):271-276. [39] 李志鹏,王锐,张天驰,等.基于马尔科夫模型的智能汉字盲文转换系统设计[J].单片机与嵌入式系统应用,2019,19(10):33-36. [40] 吴煜霞,吴宇辉,杜海英,等.基于STM32单片机控制的智能导盲手杖设计[J].扬州大学学报(自然科学版),2021,24(4):33-37+63. [41] 夏伦腾,张莉.基于K近邻和动态时间规整算法的盲人物联网手杖系统[J].计算机应用,2020,40(8):2441-2448. [42] 何腾鹏,张荣芬,刘超,等.基于机器视觉的智能导盲眼镜设计[J].电子技术应用,2017,43(4):58-61. [43] 王静,孙倩倩,茹冬全,等.基于超声波测距传感模块的智能语音播报导盲服[J].北京服装学院学报(自然科学版),2020,40(2):76-81. [44] 李子康,徐桂芝,郭苗苗.视听融合导盲机器人的设计与研究[J].激光与光电子学进展,2017,54(12):346-356. [45] 陈超,唐坚,靳祖光,等.一种基于可视图法导盲机器人路径规划的研究[J].机械科学与技术,2014,33(4):490-495. [46] 谌海云,袁杰敏.基于RGB-D深度相机的智能导盲系统[J].传感器与微系统,2021,40(1):85-87+90. [47] 王勇强,黄晓辉,沈晓峰,等.路口导盲及马路障碍物检测提醒系统的设计[J].测控技术,2018,37(10):114-118+123. [48] 刘富军,赵梦凡.人工智能环境下的公共图书馆信息无障碍服务[J].河北大学学报(哲学社会科学版),2020,45(5):154-160. [49] 陈铭,章梦圆.智能视角下高校无障碍环境体系构建及提升策略研究:以武汉理工大学马房山校区为例[J].建筑与文化,2022(9):29-31. [50] 谌小猛,林运福,李志云,等.盲生在虚拟环境中的定向行走探索及策略运用[J].中国特殊教育,2023(7):34-43+70. [51] 朱征.基于缺陷补偿理论激活多感官参与的盲校化学课堂:以“一包干燥剂引发的探究”教学为例[J].化学教育(中英文), 2017,38(23):39-42. [52] 黄凌玉.视觉障碍者日常用品创新设计研究[J].包装工程,2018, 39(14):114-117. |
| [1] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [2] | Liu Yan, Wang Kai, Wu Min. Relationship between coronal angle fluctuation of ankle point and recovery of joint function after ankle fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1820-1826. |
| [3] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [4] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [5] |
Liang Xiaoxiao, Zheng Jiejiao, Duan Linru, Chen Xi, Zhang Tingyu.
Characterization of postural stability in elderly patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1208-1213.
|
| [6] | Li Jiatong, Jin Yue, Liu Runjia, Song Bowen, Zhu Xiaoqian, Li Nianhu . Association between thyroid function levels and phenotypes associated with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1312-1320. |
| [7] | Wang Rongrong, Huang Yushan, Li Xiangmiao, Bai Jinzhu. Prostaglandin E1 regulates vascular-related factors and protects microcirculatory function during the acute phase of traumatic spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 958-967. |
| [8] | Li Shuai, Liu Hua, Shang Yonghui, Liu Yicong, Zhao Qihang, Liu Wen. Stress distribution on the maxilla when wearing the Twin-block appliance for Class II malocclusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 881-887. |
| [9] | Liu Zan, An Ran, Li Baocheng. Effect of pravastatin on functional recovery from sciatic nerve crush injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 942-950. |
| [10] | Yang Bin, Tao Guangyi, Yang Shun, Xu Junjie, Huang Junqing . Visualization analysis of research hotspots of artificial intelligence in field of spinal cord nerve injury and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 761-770. |
| [11] | Jiang Qiyu, Zeng Huiyan. A novel analysis and prediction method for potential mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine based on artificial intelligence and omics data-driven approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7552-7561. |
| [12] | Zhang Xiaoyu, Wei Shanwen, Fang Jiawei, Ni Li. Prussian blue nanoparticles restore mitochondrial function in nucleus pulposus cells through antioxidation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7318-7325. |
| [13] | Yang Yu, Li Yinghao, Duo Zhuangzhi, Zhou Dingrong. Effect of overall functional physical exercise on lumbar biomechanics in patients with lumbar disc herniation after surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7096-7101. |
| [14] | Jiang Tao, Zhang Chuankai, Hao Liang, Liu Yong. MAKO robot- and navigation-assisted knee replacement: comparison of lower limb force alignment and prosthesis position accuracy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7150-7157. |
| [15] | Yan Jinlian, Xu Zhengquan, Wei Renjie, Wang Yehua. Hip joint function recovery and prediction model construction after proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7189-7195. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||