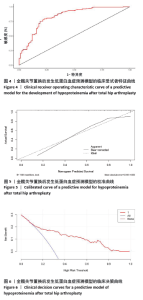
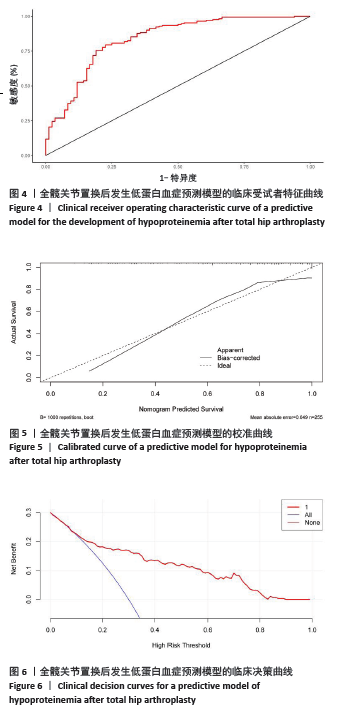
[1] CONSTANTINESCU DS, COSTELLO JP 2ND, YAKKANTI RR, et al. Varying Complication Rates and Increased Costs in Technology-Assisted Total Hip Arthroplasty Versus Conventional Instrumentation in 1,372,300 Primary Total Hips. J Arthroplasty. 2023;S0883-5403(23)01211-1.
[2] VENISHETTY N, BEALE J, MARTINEZ J, et al. Understanding factors that impact the length of stay after total hip arthroplasty - A national in-patient sample-based study. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2023;46:102284.
[3] LUO S, QIN WP, YU LZ, et al. Total hip arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty in the treatment of active elderly patients over 75 years with displaced femoral neck fractures: a retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):745.
[4] KAMATH AF, MCAULIFFE CL, KOSSEIM LM, et al. Malnutrition in Joint Arthroplasty: Prospective Study Indicates Risk of Unplanned ICU Admission. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2016;4(2):128-131.
[5] PASS B, MALEK F, ROMMELMANN M, et al. The Influence of Malnutrition Measured by Hypalbuminemia and Body Mass Index on the Outcome of Geriatric Patients with a Fracture of the Proximal Femur. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58(11):1610.
[6] WU XD, CHENG J, LI YJ, et al. The necessity of routine postoperative laboratory tests after total hip arthroplasty for hip fracture in a semi-urgent clinical setting. J Orthop Traumatol. 2020;21(1):19.
[7] Yao W, TANG WY, WANG W, et al. Correlation between admission hypoalbuminemia and postoperative urinary tract infections in elderly hip fracture patients. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):774.
[8] NAM NH,MINH ND, HAI TX, et al. Pre-operative Factors Predicting Mortality in Six Months and Functional Recovery in Elderly Patients with Hip Fractures. Malays Orthop J. 2023;17(1):10-17.
[9] HUANG JB, GE HA, ZHU XP, et al. Risk factors analysis and nomogram construction for postoperative pulmonary infection in elderly patients with hip fractures. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2023;35(9):1891-1899.
[10] ARQUES S. Serum albumin and cardiovascular disease: State-of-the-art review. Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2020;69(4):192-200.
[11] ABATZIS-PAPADOPOULOS M, TIGKIROPOULOS K, NIKAS S, et al. The effectiveness and safety of direct oral anticoagulants compared to conventional pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis in hip fracture patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2023;109(2):103364.
[12] 原炜, 冯杰. 严重创伤患者低白蛋白血症的发生机制及治疗研究[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2022,24(11):867-872.
[13] SOETERS PB, WOLFE RR, SHENKIN A, et al. Hypoalbuminemia: Pathogenesis and Clinical Significance. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2019;43(2):181-193.
[14] HE YQ, XIAO J, SHI ZJ, et al. Supplementation of enteral nutritional powder decreases surgical site infection, prosthetic joint infection, and readmission after hip arthroplasty in geriatric femoral neck fracture with hypoalbuminemia. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):292.
[15] CONNER BJ. Treating Hypoalbuminemia. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2017;47(2):451-459.
[16] GOUNDEN V, VASHISHT R , JIALAL I. Hypoalbuminemia. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2024.
[17] WIEDERMANN CJ. Hypoalbuminemia as Surrogate and Culprit of Infections. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9):4496.
[18] 石利涛,赵景新.老年髋部骨折患者术前低蛋白血症发生情况分析[J]. 东南大学学报(医学版),2020,39(6):821-825.
[19] 周洁,章静,吕亚,等.老年髋关节置换术后患者发生低蛋白血症的影响因素研究[J]. 当代护士(下旬刊),2023,30(10):96-99.
[20] ALI KM, ALI AM, TAWFEEQ HM, et al. Hypoalbuminemia in patients following their recovery from severe coronavirus disease 2019. J Med Virol. 2021;93(7):4532-4536.
[21] SHEINENZON A, SHEHADEH M, MICHELIS R, et al. Serum albumin levels and inflammation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;184:857-862.
[22] OSTALSKA-NOWICKA D, MALINSKA A, ZABEL M, et al. Nephrotic syndrome unfavorable course correlates with downregulation of podocyte vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)-2. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2011;49(3):472-478.
[23] CHEN J, TIAN Z, ZHANG HX, et al. Risks of postoperative respiratory failure in elderly patients after hip surgery: a retrospective study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):140.
[24] 桂珊珊,曹亚琴,闵继康,等.全膝/髋关节置换患者短期内非计划性再入院危险因素的Meta分析[J]. 护士进修杂志,2020,35(18): 1690-1696.
[25] 张婷,赵轶男,牛志霞,等.高龄髋部骨折行人工髋关节置换术后患者再入院危险因素分析[J]. 中国骨伤,2022,35(5):460-463.
[26] DING YJ, FENG DH, LIU Y, et al. The prevalence and risk factors of dislocation after primary total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Belg. 2022;88(3):467-474.
[27] DEMOPOULOS C, ANTONOPOULOU S, THEOHARIDES TC. COVID-19, microthromboses, inflammation, and platelet activating factor. Biofactors. 2020;46(6):927-933.
[28] COULDWELL G, MACHLUS KR. Modulation of megakaryopoiesis and platelet production during inflammation. Thromb Res. 2019;179: 114-120.
[29] GUO M, SUN T, ZHAO Z, et al. Preoperative Platelet to Albumin Ratio Predicts Outcome of Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;27(2):84-90.
[30] 张玉萍,王瑜. 老年髋部骨折患者接受术后个体化营养支持预防术后低蛋白的效果[J]. 山西医药杂志,2019,48(15):1931-1933.
[31] ECKART A, STRUJA T, KUTA A, et al. Relationship of Nutritional Status, Inflammation, and Serum Albumin Levels During Acute Illness: A Prospective Study. Am J Med. 2020;133(6):713-722.e7. |