Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (14): 3051-3060.doi: 10.12307/2025.399
Previous Articles Next Articles
The gut microbiota characteristics of athletes
Zhang Qiuping1, 2, Xu Qian1, 2, Tian Huajun1, 2, Chu Yudan1, 2, He Junliang1, 2, Ma Guoqiang1, 2, Qiu Jun1, 2
- 1Shanghai Research Institute of Sports Science (Shanghai Anti-Doping Agency), Shanghai 200030, China; 2Key Laboratory of General Administration of Sport for Exercise Performance Evaluation, Shanghai 200030, China
-
Received:2024-05-08Accepted:2024-07-06Online:2025-05-18Published:2024-09-29 -
Contact:Ma Guoqiang, PhD, Researcher, Master’s supervisor, Shanghai Research Institute of Sports Science (Shanghai Anti-Doping Agency), Shanghai 200030, China; Key Laboratory of General Administration of Sport for Exercise Performance Evaluation, Shanghai 200030, China -
About author:Zhang Qiuping, MS, Associate researcher, Shanghai Research Institute of Sports Science (Shanghai Anti-Doping Agency), Shanghai 200030, China; Key Laboratory of General Administration of Sport for Exercise Performance Evaluation, Shanghai 200030, China -
Supported by:Shanghai Social Development Science and Technology Research Project - “Science and Technology Innovation Action Plan,” No. 23DZ1204102 (to MGQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Qiuping, Xu Qian, Tian Huajun, Chu Yudan, He Junliang, Ma Guoqiang, Qiu Jun. The gut microbiota characteristics of athletes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(14): 3051-3060.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
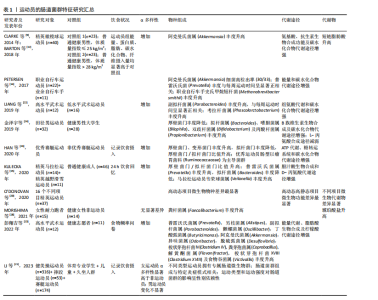
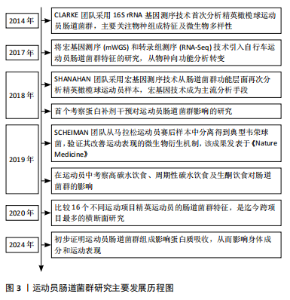
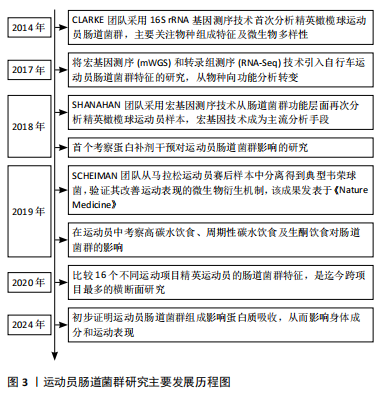
2.2 运动员的肠道菌群特征 阐述运动员肠道微生物特征的报道主要来自于横断面研究。尽管横断面研究受混杂因素的影响较大,无法有效确定运动和/或饮食与肠道微生物群变化之间的因果关系,但这些研究仍然提供了重要信息,为识别和提取运动员最佳肠道菌群特征及未来纵向研究方向提供依据。 2.2.1 精英运动员区别于普通人的肠道菌群特征 CLARKE等[9]将精英橄榄球运动员与体质量指数匹配的普通健康人进行对比分析,发现精英运动员炎症和代谢指标改善,并且肠道微生物拥有更高的多样性;在菌群组成中,运动员肠道中阿克曼氏菌属(Akkermansia)的丰度显著高于对照组。阿克曼氏菌属中的多数成员,如嗜黏蛋白阿克曼菌(Akkermansia muciniphilla)具有黏液蛋白降解功能,与代谢状况改善有关[11]。之后,该团队进行宏基因测序分析,结果显示:与对照组相比,运动员拥有更多具有潜在健康益处的微生物代谢途径,如氨基酸和抗生素的生物合成、碳水化合物的代谢等,并且代谢物分析显示短链脂肪酸含量显著增加[12]。短链脂肪酸通常与健康和瘦表型相关,这表明精英运动员肠道中具有健康益处的微生物代谢表达增强。进一步的分析发现,运动员微生物多样性与蛋白质摄入量和肌酸激酶水平呈显著正相关,表明饮食(蛋白质摄入量)和运动是肠道微生物多样性增加的有利驱动因素[9]。近期一项分析高水平武术运动员肠道菌群及代谢通路特征的国内研究也得到了相似结论[13],与普通健康对照组相比,武术运动员肠道菌群的多样性(包括α多样性和β多样性)显著提高;有趣的是,该研究也发现阿克曼氏菌属(Akkermansia)在运动员体内富集,肠道微生物在能量代谢、脂肪酸生物合成及柠檬酸代谢方面的能力显著高于健康对照组。阿克曼氏菌属(Akkermansia)在运动员体内的高检出率并非偶然,PETERSEN等[14]在职业和业余自行车手中也检测到了高丰度的阿克曼氏菌属(Akkermansia),进一步提示阿克曼氏菌属可能是运动员的特征菌群之一。 典型耐力运动员因更高的能量代谢需求及胃肠道反应为肠道菌群研究提供了特殊模型,对其进行研究能够揭示运动员肠道菌群的更多特征。KULECKA等[15]将马拉松运动员和越野滑雪运动员与健康久坐人群(对照组)进行对比分析,发现除了微生物多样性增加外,厚壁菌门/拟杆菌门比值(F/B)也显著高于对照组;物种分析显示精英耐力运动员普雷沃氏菌属(Prevotella)和韦荣球菌属(Veilonella)丰度显著升高,而拟杆菌属(Bacteroides)丰度降低;代谢途径分析显示,胆汁酸生物合成和D-丙氨酸代谢途径在耐力运动员中富集。基于普通健康人群的研究结果,较高的微生物多样性和厚壁菌门/拟杆菌门比值通常与较高的最大摄氧量(VO2max)水平相关[16-17],因此,推测其可能是精英耐力运动员肠道菌群的典型特征之一。 然而,MORISHIMA等[18]同样基于耐力运动员的研究却显示出不一样的结果:与健康对照组相比,精英耐力跑者的微生物多样性并无显著提升;细菌类群中粪杆菌属(Faecalibacterium)丰度显著增加(为对照组的2倍);粪便代谢物中琥珀酸盐浓度升高。尽管粪杆菌属在多数情况下被认为是一种健康有益菌,但当代谢物中琥珀酸盐累积时需要重新定义粪杆菌的作用。过度运动引发肠道环境的改变可能导致粪杆菌代谢途径的异常,无法将初级代谢物琥珀酸盐代谢为丁酸盐(短链脂肪酸的主要成分之一),而琥珀酸盐积聚在肠道内会进一步诱发炎症,引起肠道菌群生态失调[19]。由此可见,微生物物种与功能途径并非简单的一一对应关系,一个物种可能具备多种代谢潜能,而代谢功能的最终发挥与生理状态和肠道环境密切相关。因此,在运动员肠道菌群特征的描述中考虑运动强度和生理适应的关系是十分必要的。 2.2.2 不同项目/水平运动员肠道菌群特征比较 不同项目间运动员的肠道菌群比较对于明确运动项目与肠道菌群的关系,进而探索项目规律、指导运动实践具有重要意义。O’DONOVAN团队[20]对来自16个不同运动项目的爱尔兰精英运动员进行了肠道微生物及代谢物的分析,结果显示:无论是从微生物物种组成还是功能途径的角度分析,来自同一项群的样本通常能够聚类在一起,不同项群间存在显著的微生物类群、功能潜力和代谢物差异,表明不同的运动类型是促成肠道微生物差异的重要因素之一。其中,最大摄氧量水平通常与微生物多样性显著关联;而骨骼肌参与度对微生物特定功能的发挥具有潜在作用。近期国内团队开展的一项比较健美操、摔跤和赛艇运动员肠道菌群特征的研究也证实了不同类型运动员拥有专属肠道微生物群的研究假设[21],并且进一步提出不同的微生物类群组成可能与特定的炎症模式相关联,这对于个性化监测运动员炎症风险、实施以肠道菌群为导向的个性化炎症干预策略具有指导意义。 同一项目不同训练水平间运动员的肠道菌群差异也值得关注。LIANG 等[22]和HAN等[23]的研究均表明,与低水平/非优秀运动员相比,同项目的高水平/优秀运动员具有更高的肠道微生物多样性和厚壁菌门/拟杆菌门比值,可能与更高的最大摄氧量水平相关。PETERSEN等[14]的研究发现,在职业和业余自行车手中,普雷沃氏菌属(Prevotella)虽然与运动员属性没有显著相关性,但其丰度与每周运动时间显著相关。普雷沃氏菌丰度的增加与氨基酸尤其是支链氨基酸合成及碳水化合物代谢途径相关,这对于需要缓解肌肉疲劳且从高强度运动中快速恢复的运动员来说是非常有益的。LIANG等[22]的研究也涉及运动时间和菌群关系的探讨:与低水平武术运动员相比,高水平运动员肠道中副拟杆菌属(Parabacteroides)丰度显著升高,并且该有益菌属丰度与运动员一周训练时间呈显著正相关。由此可见,训练时间可能是影响肠道菌群的另一重要因素。综合以上,不同专业类型运动员具有独特的微生物类群特征,而运动时间强化了某些特征菌群的优势发展,从而适应更高水平的生理需求。 2.2.3 小结 有关运动员肠道菌群特征研究的汇总见表1。这些研究表明,运动员的肠道菌群特征与运动项目类型、训练时间及饮食摄入密切相关。与普通人群相比,精英"
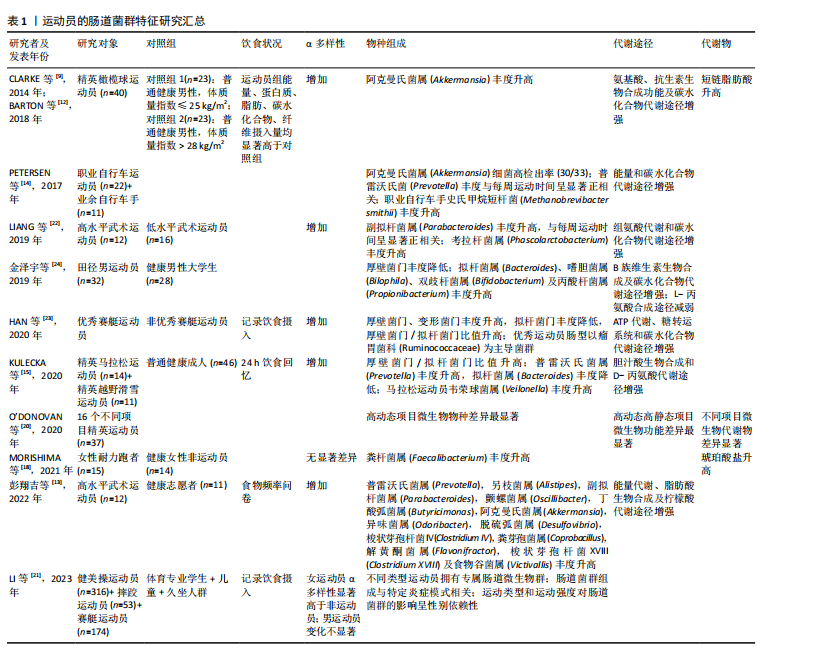
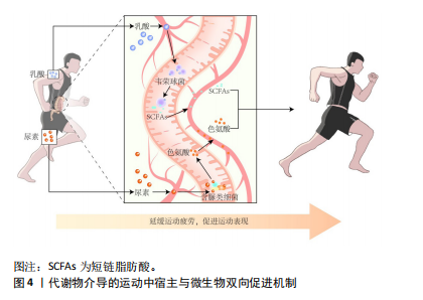
运动员的肠道菌群呈现出一些共性特征,如α多样性增加,厚壁菌门/拟杆菌门比值升高,某些健康有益菌(如阿克曼氏菌属、韦荣球菌属和粪杆菌属)丰度升高,有助于运动表现的功能途径富集,如氨基酸合成和碳水化合物代谢增强,显示出较强的组织修复和能量收集潜能,与运动员高能量需求和高细胞更新相适应。值得注意的是,当运动负荷超过生理适应限度可能会改变肠道菌群特征,尤其会改变微生物代谢途径,引起代谢表型的差异。肠道菌群对生理适应的敏感性也使得特征微生物群和相关功能有望成为筛选优秀运动员或潜力运动员的生物标志物,反映大强度训练背景下的生理适应能力。 2.3 运动训练对肠道菌群的影响 上述横断面研究描绘了运动员肠道菌群样貌的基本特征,但这些特征的形成通常是内外因共同作用的结果。为了进一步阐明运动训练的作用及可能机制,需要严格控制相关变量的纵向研究提供更多依据。运动训练对运动员肠道菌群影响的纵向研究汇总[25-32],见表2。 2.3.1 急性运动的影响 目前考察急性运动对运动员肠道菌群影响的研究主要集中于以马拉松为代表的长距离耐力型运动。ZHAO等[25]比较了业余马拉松运动员一次半程马拉松比赛前后的肠道菌群变化,结果显示运动员赛后红蝽菌科(Coriobacteriaceae)丰度显著增加,微生物代谢途径与粪便代谢物综合分析结果显示,红蝽菌科在调节马拉松运动员肠道环境中发挥重要作用,微生物衍生的戊糖磷酸途径显著增强,有利于运动中葡萄糖的氧化利用;此外,潜在病原体放线菌属(Actinomyces)丰度显著降低,表明运动具有一定的抗炎作用。这些发现强调了一种能够将运动和健康/表现改善作用联系起来的微生物衍生机制。 明确微生物衍生机制对未来发展以微生物介导的运动训练干预策略至关重要。GROSICKI等[26]和SCHEIMAN等[10]的研究为这一领域增添了重要证据。GROSICKI等[26]追踪1名世界级超级马拉松运动员参加极限山地竞走比赛后的肠道菌群变化,最显著的差异是韦荣球菌属(Veillonella)丰度提高了143倍,与SCHEIMAN团队[10]的结果不谋而合。SCHEIMAN等[10]进一步采用动物实验验证了典型韦荣球菌(Veillonella atypical)改善运动表现(延长小鼠跑步时间)的作用;之后,该团队在超级马拉松运动员和赛艇运动员急性运动后的粪便样本中重现了韦荣球菌属的变化,在粪便分离株中观察到大量乳酸透膜酶,结合宏基因分析结果显示甲基丙二酰辅酶A途径的过度表达,推测运动中肌肉产生的乳酸进入胃肠道管腔并被韦荣球菌代谢为短链脂肪酸,可能是运动中宿主与肠道菌群相互作用的机制。这一推测得到了动物实验的验证,从而确立了一个宿主与肠道微生物良性互动的模型:运动中产生的全身乳酸穿过肠上皮屏障进入肠腔,高乳酸环境选择性地优势发展乳酸代谢菌(韦荣球菌),韦荣球菌代谢乳酸生成短链脂肪酸,促进运动表现[10](图4)。"
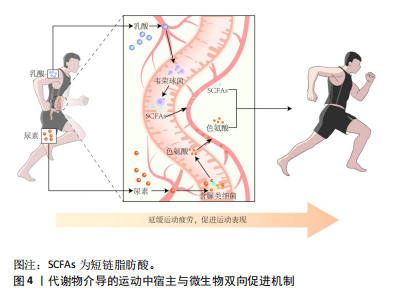

当然,运动中宿主和微生物双向促进的良性机制并非在所有研究中均可观察到。SATO等[28]报道了9名超级马拉松运动员赛后的肠道菌群变化,结果发现在近100 km的马拉松比赛后,运动员体内粪杆菌(Faecalibacterium prausnitzii)和其他3种产丁酸盐有益菌的丰度显著降低,影响了肠道中丁酸盐水平,进而影响宿主免疫和恢复。因此,未来研究应重点探讨有利于宿主运动表现的微生物衍生机制在何种生理状态下能够建立,是否与特定运动因素和基线微生物结构间存在明确的因果关系,以及如何培养或定植目标菌群,这将是运动干预研究的有趣命题。 2.3.2 阶段训练的影响 与一次急性运动造成的生理应激不同,阶段训练通常包含训练和恢复的交替过程,更能体现人体对运动训练的适应能力,也是考察菌群弹性和复原能力的良好模型。潘凤伟等[29]比较了2个不同强度训练阶段对游泳女运动员肠道菌群组成的影响,结果发现:在高强度训练阶段,运动员肠道中会富集更多的丁酸盐产生菌,如布劳特氏菌属(Blautia)、罗斯氏菌属(Roseburia)、厌氧丝菌属(Anaerostipes)及丁酸球菌属(Butyricicoccus),表明运动员的肠道菌群适应了高强度训练的刺激,通过富集有益菌保护机体免受高强度训练的损伤,从而快速响应运动强度的变化。AKAZAWA等[30]在有关阶段训练的纵向研究中也发现,训练阶段的分期能够显著改变运动员肠道中布劳特氏菌属(Blautia)和双歧杆菌(Bifidobacterium)等有益菌的丰度,并且微生物组的变化与有氧能力的变化显著相关,与无氧能力也存在潜在相关性。 值得关注的是,阶段训练所产生的菌群结构或功能的变化可能具有延续效应。KEOHANE等[31]追踪4名男性运动员参加33 d跨海赛艇比赛(5 000 km)前后肠道菌群的变化,该长时间极限运动可以视为阶段训练的极端模型;该研究发现长时间运动后肠道微生物呈现适应运动刺激的有益改变(α多样性增加,丁酸盐产生菌富集,参与S腺苷蛋氨酸、必需氨基酸和中长链脂肪酸生物合成的功能潜力增加),并且这种改变在赛后3个月依然维持,其中2名运动员的α多样性甚至在3个月的随访中呈持续增加态势。GRAVEN等[32]的研究也有类似发现:3周增量训练会在低分类水平上引发特定物种的丰度变化,并且这些变化在逐渐减量后1周并没有恢复至基线水平。这些研究表明,阶段训练引发微生物群的变化通常不会在训练结束后即刻消失,不同的训练模式可能会对微生物群恢复时间产生影响,对这一复原时间的探索或能为训练方法提供更多依据,如训练间隔时间及赛前调整期的确定。 2.3.3 小结 在控制饮食等相关变量后,这些纵向研究显示运动是改变肠道菌群结构和功能的重要因素,尤其韦荣球菌属代谢乳酸功能途径的确定为探究运动与肠道微生物关系提供了良好范本,表明运动中人体产生的应激代谢物从血液转移至胃肠道系统是影响肠道菌群发展的重要机制,而菌群利用人体代谢物发挥代谢潜能又会影响运动表现。因此,将血液代谢组学和肠道微生物研究相结合是未来探究运动与肠道微生物关系的可行方案。此外值得注意的是,一次急性运动与阶段训练不同,对肠道微生物产生的代谢刺激也不同,在研究或实践中应加以区分,加强对真实比赛或特殊训练阶段前后的纵向追踪研究有助于筛选和鉴定特色菌群、挖掘相关调控机制。 2.4 运动员特殊饮食对肠道菌群的影响 尽管上述研究表明运动作为独立因素影响运动员肠道菌群,但不可否认饮食摄入是另一个重要的外部影响因素。运动员的饮食摄入通常具有鲜明特点,如总能量摄入增加、蛋白质供能比升高、耐力运动员精制碳水摄入量增加等[33-34],这些特点最终会与运动训练一起,对运动员肠道微生物产生叠加或削弱效应。因此,了解饮食摄入对肠道菌群的影响对相关干预策略的形成具有重要意义。 2.4.1 低膳食纤维饮食 碳水化合物的范畴包含了膳食纤维,但众所周知,职业运动员尤其耐力运动员的饮食策略通常只纳入简单碳水化合物,避免纤维的大量摄入。这种策略的目的是支持营养吸收、胃的快速排空及内脏血管的充分灌注,降低胃肠道不适的风险[35],然而这种饮食策略没有充分考虑营养素对肠道微生物群的影响。事实上,与简单碳水化合物相比,膳食纤维对肠道菌群具有更深远的影响,因此可溶性膳食纤维又被称为“微生物可利用碳水化合物[36]”。 这些膳食纤维为肠道微生物发酵提供了重要底物。增加膳食纤维摄入有助于改善肠道中的营养生态环境,使得具有纤维发酵功能的微生物扩大其种群,这有利于微生物多样性的发展[37-38]。此外,微生物发酵膳食纤维会产生一类重要的代谢物——短链脂肪酸,这是微生物介导宿主健康效应的重要机制[5,38]。短链脂肪酸除了直接为人体多个组织器官提供能量底物外[39],还能影响葡萄糖和脂质代谢过程,改善骨骼肌胰岛素敏感性,减轻炎症反应,为健康组织的生长和周转提供支持[40-41];此外,短链脂肪酸能够调节饱腹感,有助于体质量控制和瘦型表达[42],这些作用都对运动表现具有积极意义。 尽管目前基于运动员开展的探讨膳食纤维摄入与肠道菌群关系的研究较少,但来自于普通健康人群的数据仍然具有重要参考价值。KOPONEN等[37]基于人群的大型横断面研究验证了富含植物纤维的饮食与更多样化的肠道微生物群相关,并且更有可能产生短链脂肪酸。WASTYK等[36]在一项随机对照研究中发现,6周植物纤维干预虽然没有改变微生物多样性,但增加了微生物编码的多糖降解酶活性,表明微生物隐藏的代谢潜力被食物(纤维)摄入所激发。这与BARBER等[43]的研究结论如出一辙,2周地中海饮食(富含膳食纤维)干预虽然不能对核心物种组成造成显著影响,但对其代谢功能影响重大,表明微生物能够迅速适应底物可用性的变化,恢复隐藏的代谢潜力。ZHU等[44]的研究甚至将这一功能潜力恢复时间缩短至4 d,仅4 d,地中海饮食就能改变微生物组成和代谢功能,使其转向有益于健康的特征。 膳食纤维对肠道微生物的显著作用,使其成为运动员肠道菌群特征研究中的重要考量因素。正如JANG等[45]在将健美运动员和优秀长跑运动员与久坐健康人群进行对照研究时发现,运动员的肠道微生物多样性并没有出现预期的增加,并且某些健康有益菌丰度在运动员中显著降低,与CLARKE等[9]报道的结果截然相反。这种差异可能与运动员的整体营养摄入状况,尤其是膳食纤维的摄入量密切相关,表明运动员低纤维摄入可能会抵消运动带来的肠道微生物益处。 综合以上,这些研究为运动员饮食策略提供了重要信息,使得通过膳食纤维干预激发肠道微生物代谢潜能,增加短链脂肪酸的产生,进而促进运动和饮食的叠加效应成为可能。但值得注意的是,膳食纤维的干预效果可能取决于个体基线微生物群的组成,尤其是普雷沃氏菌属的丰度。CHRISTENSEN等[46]的研究表明,基线普雷沃氏菌属丰度高的受试者对高纤饮食的减重应答最强;MA等[47]的研究也表明,基线普雷沃氏菌属丰度与纤维摄入对炎症反应的应答有关。这种基线肠型分型在运动员人群中是否与饮食干预应答有关值得进一步探究。 2.4.2 高蛋白饮食 高蛋白饮食在运动人群中盛行,运动员往往摄入普通人2倍以上的蛋白质,以此应对运动压力带来的额外肌肉蛋白分解,提高肌肉质量和功能[48]。此外,高蛋白饮食还有助于运动员体质量减轻和瘦体质量维持,改善离心运动中的肌肉酸痛[49-50]。 尽管较高比例的蛋白质摄入符合高强度运动人群的需求,但这种饮食策略较少考虑对肠道微生物的影响。在高蛋白饮食中,未消化的蛋白质最终会进入肠道引起微生物的氨基酸发酵,产生一系列代谢产物,这些代谢产物包括支链氨基酸、短链脂肪酸、氨、硫化物、吲哚酸和酚类化合物[51]。虽然其中一些代谢物(如短链脂肪酸)能够发挥健康效应,但较高浓度的其他代谢物(如氨、硫化物和酚类代谢物)会对肠道上皮细胞造成损害,尤其当蛋白质摄入过量时这些蛋白水解产物超过宿主的吸收、转化和解毒能力,可能会对肠道屏障和抗炎功能带来负面影响[52]。值得关注的是,运动员长期使用蛋白补充剂,即便在蛋白质摄入量轻微增加的情况下也可能对肠道微菌群造成不利影响。一项基于耐力运动员的随机对照研究显示,男性越野跑者每天补充蛋白质补剂(10 g乳清分离蛋白+10 g牛肉水解蛋白)连续10周就会显著降低包括长双歧杆菌在内的健康有益菌丰度,提示长期补充蛋白补剂可能对运动员肠道微生物产生负面影响[53]。 增加膳食纤维摄入量可能是改善这种负面影响的有效策略之一。正如2.4.1所述,膳食纤维作为肠道微生物的首选碳源,能够有效调节蛋白水解发酵菌的相对丰度,从而减弱高蛋白摄入的影响;此外,膳食纤维发酵产生的代谢物也有利于维持良好的肠道环境,平衡蛋白质水解产物[5]。因此,当蛋白质的摄入量增加时,用膳食纤维平衡蛋白质与碳水化合物的比例可能是缓解肠道菌群失调的有效途径。除了蛋白质的摄入量,蛋白质的来源、加工方式等也可能对肠道微生物产生影响。有研究显示,植物来源的蛋白质对微生物多样性的影响可能比动物来源的蛋白质更显著[54]。近期一项饮食干预研究对男子优秀水球运动员进行31 d的植物蛋白联合益生菌补充,发现能显著改善运动员身体成分,进而促进运动表现,而这种改善与肠道菌群组成的变化紧密相关[55]。当然,这些结论尚需要在运动员中进行进一步的探究和验证,以便形成通过调节肠道微生物结构和功能使其有助于蛋白质吸收和利用的有效策略,促进骨骼肌合成代谢与功能,最终发挥肠-肌轴介导的营养摄入促进运动表现的积极作用。 2.4.3 高脂饮食/生酮饮食 针对运动员的饮食策略通常不推荐高脂饮食,但运动员对采用高脂生酮饮食提高运动表现和控制体质量的兴趣却日益浓厚[56-57]。此外,受现代工业社会食品加工的影响,或出于高蛋白摄入的目的,运动员在日常饮食中不可避免地摄入了大量脂肪。 事实上,生酮饮食对运动表现的影响颇具争议。尽管高脂低碳饮食在一定程度上能够增加脂肪氧化,但目前没有足够证据支持其能提高运动表现[57-58]。相反,有证据表明,生酮饮食可能会降低高强度运动的表现,并从肠道微生物的角度探讨了两者之间的关系及可能机制。MURTAZA等[59]在精英竞走运动员中开展的随机对照研究显示,与高碳水和周期性碳水饮食相比,生酮饮食对肠道菌群有着更深远的影响,能够显著升高拟杆菌属(Bacteroides)和多雷菌(Dorea spp.)的丰度,降低粪杆菌属(Faecalibacterium)的丰度;肠道微生物的这些变化与运动表现相关,拟杆菌属丰度与脂肪氧化呈显著负相关,而多雷菌与运动经济性指标呈负相关,表明生酮饮食引起的肠道微生物变化可能降低运动表现。 WAN等[60]基于健康成年人的随机对照研究支持上述结论,在这项长达6个月的研究中,发现与低脂和中脂摄入相比,高脂饮食会显著升高拟杆菌属丰度并降低粪杆菌属丰度;此外,高脂饮食会显著降低粪便短链脂肪酸浓度,增加有害代谢物(对甲酚和吲哚)的产生并与血浆促炎因子升高有关;代谢途径分析结果显示,高脂饮食与花生四烯酸和脂多糖生物合成途径的富集有关。ZHU等[44]的研究发现4 d高脂快餐饮食就足以改变肠道微生物结构,使得有益于神经元细胞功能的代谢物(吲哚-3-乳酸和吲哚-3-丙酸)显著减少,影响“肠-脑轴”效应的发挥。这些结果均表明,长期高脂饮食可能对健康和运动表现结局产生不利影响。 然而,生酮饮食对肠道微生物的影响并不局限于上述负面效应,一些研究也显示出有益的趋势,如:生酮饮食能够促进微生物介导的胆汁酸途径,增加线粒体氧化磷酸化和脂肪酸β氧化,促进骨骼肌功能[61];生酮饮食能够提高乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus)和阿克曼氏菌属(Akkermansia muciniphila)的丰度,有助于提高胰岛素敏感性,促进短链脂肪酸的产生,进而有利于体质量减轻和血糖下降[62]。生酮饮食对肠道菌群作用的两极分化实际上可能与脂肪摄入的类型密切相关,研究显示饱和脂肪摄入与微生物多样性和丰富度降低有关,增加脂多糖生成和转运,导致促炎因子Toll样受体激活[5,63];而不饱和脂肪酸,尤其ω-3多不饱和脂肪酸则不会影响肠道多样性和丰富度,还能增加双歧杆菌、乳酸杆菌和阿克曼氏菌的丰度,促进短链脂肪酸产生,发挥了类似于运动训练的有益效应[62,64]。近期一项针对男子足球运动员的饮食干预研究为此提供了相关证据[65],这项研究考察了以不饱和脂肪酸为主的生酮地中海饮食对运动员肠道菌群的影响,结果显示生酮地中海饮食并没有改变运动员肠道微生物的组成,有别于上述传统生酮饮食对肠道菌群带来的负面影响,被认为是维持/调节运动员肠道菌群的安全饮食模式。因此,在探讨有关运动员高脂饮食与肠道微生物关系的研究中考虑脂肪的来源和类型至关重要。 2.4.4 小结 饮食摄入对肠道菌群结构和功能的影响不容忽视,在解释运动相关的研究结论时必须慎重,尤其是考虑宏量营养素摄入的影响。需要注意的是,这些营养素的摄入不是单一发生的,而是以组合的形式共同摄入,因此,在营养策略的制定上应当考虑营养素之间的交互作用,以及不同的食物来源、类型和组合对微生物选择性发展的促进作用,最终通过营养处方调节菌群结构及代谢能力,与运动训练发挥协同叠加效应,实现运动表现收益的最大化。"

| [1] O’BRIEN MT, O’SULLIVAN O, CLAESSON MJ, et al. The Athlete Gut Microbiome and its Relevance to Health and Performance: A Review. Sports Med. 2022;52(Suppl 1):119-128. [2] CLAUSS M, GERARD P, MOSCA A, et al. Interplay Between Exercise and Gut Microbiome in the Context of Human Health and Performance. Front Nutr. 2021;8:637010. [3] WEGIERSKA AE, CHARITOS IA, TOPI S, et al. The Connection Between Physical Exercise and Gut Microbiota: Implications for Competitive Sports Athletes. Sports Med. 2022;52(10):2355-2369. [4] BONOMINI-GNUTZMANN R, PLAZA-DIAZ J, JORQUERA-AGUILERA C, et al. Effect of Intensity and Duration of Exercise on Gut Microbiota in Humans: A Systematic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022; 19(15):9518. [5] CHEN Y, ZHOU J, WANG L. Role and Mechanism of Gut Microbiota in Human Disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:625913. [6] HUGHES RL, HOLSCHER HD. Fueling Gut Microbes: A Review of the Interaction between Diet, Exercise, and the Gut Microbiota in Athletes. Adv Nutr. 2021;12(6):2190-2215. [7] BONOMINI-GNUTZMANN R, PLAZA-DIAZ J, JORQUERA-AGUILERA C, et al. Effect of Intensity and Duration of Exercise on Gut Microbiota in Humans: A Systematic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022; 19(15):9518. [8] MANKOWSKA K, MARCHELEK-MYSLIWIEC M, KOCHAN P, et al. Microbiota in sports. Arch Microbiol. 2022;204(8):485. [9] CLARKE SF, MURPHY EF, O’SULLIVAN O, et al. Exercise and associated dietary extremes impact on gut microbial diversity. Gut. 2014;63(12): 1912-1920. [10] SCHEIMAN J, LUBER JM, CHAVKIN TA, et al. Meta-omics analysis of elite athletes identifies a performance-enhancing microbe that functions via lactate metabolism. Nat Med. 2019;25(7):1104-1109. [11] EVERARD A, BELZER C, GEURTS L, et al. Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(22):9066-9071. [12] BARTON W, PENNEY NC, CRONIN O, et al. The microbiome of professional athletes differs from that of more sedentary subjects in composition and particularly at the functional metabolic level. Gut. 2018;67(4):625-633. [13] 彭翔吉,梁茹,谭振林,等.基于高通量测序分析高水平武术运动员肠道菌群及其代谢通路特征[J].北京体育大学学报,2022,45(3): 84-93. [14] PETERSEN LM, BAUTISTA EJ, NGUYEN H, et al. Community characteristics of the gut microbiomes of competitive cyclists. Microbiome. 2017;5(1):98. [15] KULECKA M, FRACZEK B, MIKULA M, et al. The composition and richness of the gut microbiota differentiate the top Polish endurance athletes from sedentary controls. Gut Microbes. 2020;11(5):1374-1384. [16] DURK RP, CASTILLO E, MARQUEZ-MAGANA L, et al. Gut Microbiota Composition Is Related to Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Healthy Young Adults. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2019;29(3):249-253. [17] KASPEREK MC, MAILING L, PICCOLO BD, et al. Exercise training modifies xenometabolites in gut and circulation of lean and obese adults. Physiol Rep. 2023;11(6):e15638. [18] MORISHIMA S, AOI W, KAWAMURA A, et al. Intensive, prolonged exercise seemingly causes gut dysbiosis in female endurance runners. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2021;68(3):253-258. [19] FERNANDEZ-VELEDO S, VENDRELL J. Gut microbiota-derived succinate: Friend or foe in human metabolic diseases. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2019;20(4):439-447. [20] O’DONOVAN CM, MADIGAN SM, GARCIA-PEREZ I, et al. Distinct microbiome composition and metabolome exists across subgroups of elite Irish athletes. J Sci Med Sport. 2020;23(1):63-68. [21] LI Y, CHENG M, ZHA Y, et al. Gut microbiota and inflammation patterns for specialized athletes: a multi-cohort study across different types of sports. mSystems. 2023;8(4):e0025923. [22] LIANG R, ZHANG S, PENG X, et al. Characteristics of the gut microbiota in professional martial arts athletes: A comparison between different competition levels. PLoS One. 2019;14(12):e0226240.
[23] HAN M, YANG K, YANG P, et al. Stratification of athletes’ gut microbiota: the multifaceted hubs associated with dietary factors, physical characteristics and performance. Gut Microbes. 2020;12(1):1-18. [24] 金泽宇,李威,孙宝林.宏基因组测序分析男性运动员肠道菌群物种组成及代谢通路特点[J].生物学杂志,2019,36(4):7-13. [25] ZHAO X, ZHANG Z, HU B, et al. Response of Gut Microbiota to Metabolite Changes Induced by Endurance Exercise. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:765. [26] GROSICKI G, DURK RP, BAGLEY JR. Rapid gut microbiome changes in a world-class ultramarathon runner. Physiol Rep. 2019;7(24):e14313. [27] TABONE M, BRESSA C, GARCIA-MERINO JA, et al. The effect of acute moderate-intensity exercise on the serum and fecal metabolomes and the gut microbiota of cross-country endurance athletes. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):3558. [28] SATO M, SUZUKI Y. Alterations in intestinal microbiota in ultramarathon runners. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):6984. [29] 潘凤伟,张磊,张晨虹,等.不同运动强度对女游泳运动员肠道菌群的影响[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2019,38(5):1837-1846. [30] AKAZAWA N, NAKAMURA M, EDA N, et al. Gut microbiota alternation with training periodization and physical fitness in Japanese elite athletes. Front Sports Act Living. 2023;5:1219345. [31] KEOHANE DM, WOODS T, O’CONNOR P, et al. Four men in a boat: Ultra-endurance exercise alters the gut microbiome. J Sci Med Sport. 2019;22(9):1059-1064. [32] CRAVEN J, COX AJ, BELLINGER P, et al. The influence of exercise training volume alterations on the gut microbiome in highly-trained middle-distance runners. Eur J Sport Sci. 2022;22(8):1222-1230. [33] NEGLIA A. Nutrition, Eating Disorders, and Behavior in Athletes. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2021;44(3):431-441. [34] MOORE DR, SYGO J, MORTON JP. Fuelling the female athlete: Carbohydrate and protein recommendations. Eur J Sport Sci. 2022; 22(5):684-696. [35] PODLOGAR T, WALLIS GA. New Horizons in Carbohydrate Research and Application for Endurance Athletes. Sports Med. 2022;52(Suppl 1):5-23. [36] WASTYK HC, FRAGIADAKIS GK, PERELMAN D, et al. Gut-microbiota-targeted diets modulate human immune status. Cell. 2021;184(16): 4137-4153. [37] KOPONEN KK, SALOSENSAARI A, RUUSKANEN MO, et al. Associations of healthy food choices with gut microbiota profiles. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021;114(2):605-616. [38] GUAN Z, YU EZ, FENG Q. Soluble Dietary Fiber, One of the Most Important Nutrients for the Gut Microbiota. Molecules. 2021;26(22): 6802. [39] HEE B, WELLS JM. Microbial Regulation of Host Physiology by Short-chain Fatty Acids. Trends Microbiol. 2021;29(8):700-712. [40] CAREY RA, MONTAG D. Exploring the relationship between gut microbiota and exercise: short-chain fatty acids and their role in metabolism. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2021;7(2):e000930. [41] PORTINCASA P, BONFRATE L, VACCA M, et al. Gut Microbiota and Short Chain Fatty Acids: Implications in Glucose Homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1105. [42] IGUDESMAN D, Crandell J, CORBIN KD. The Intestinal Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Association with Advanced Metrics of Glycemia and Adiposity Among Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes and Overweight or Obesity. Curr Dev Nutr. 2022;6(10):nzac107. [43] BARBE C, MEGO M, SABATER C, et al. Differential Effects of Western and Mediterranean-Type Diets on Gut Microbiota: A Metagenomics and Metabolomics Approach. Nutrients. 2021;13(8):2638. [44] ZHU C, SAWREY-KUBICEK L, BEALS E, et al. Human gut microbiome composition and tryptophan metabolites were changed differently by fast food and Mediterranean diet in 4 days: a pilot study. Nutr Res. 2020;77:62-72. [45] JANG LG, CHOI G, KIM SW, et al. The combination of sport and sport-specific diet is associated with characteristics of gut microbiota: an observational study. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2019;16(1):21. [46] CHRISTENSEN L, VUHOLM S, ROAGER HM, et al. Prevotella Abundance Predicts Weight Loss Success in Healthy, Overweight Adults Consuming a Whole-Grain Diet Ad Libitum: A Post Hoc Analysis of a 6-Wk Randomized Controlled Trial. J Nutr. 2019;149(12):2174-2181. [47] MA W, NGUYEN LH, SONG M, et al. Dietary fiber intake, the gut microbiome, and chronic systemic inflammation in a cohort of adult men. Genome Med. 2021;13(1):102. [48] HECTOR AJ, PHILLIPS SM. Protein Recommendations for Weight Loss in Elite Athletes: A Focus on Body Composition and Performance. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2018;28(2):170-177. [49] HSU KJ, CHIEN KY, TSAI SC, et al. Effects of Exercise Alone or in Combination with High-Protein Diet on Muscle Function, Aerobic Capacity, and Physical Function in Middle-Aged Obese Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Nutr Health Aging. 2021;25(6):727-734. [50] BAGHERI R, KARGARFARD M, SADEGHI R, et al. Effects of 16 weeks of two different high-protein diets with either resistance or concurrent training on body composition, muscular strength and performance, and markers of liver and kidney function in resistance-trained males. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2023;20(1):2236053. [51] CAI J, CHEN Z, WU W, et al. High animal protein diet and gut microbiota in human health. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(22):6225-6237. [52] OLIPHANT K, ALLEN-VERCOE E. Macronutrient metabolism by the human gut microbiome: major fermentation by-products and their impact on host health. Microbiome. 2019;7(1):91. [53] MORENO-PEREZ D, BRESSA C, BAILEN M, et al. Effect of a Protein Supplement on the Gut Microbiota of Endurance Athletes: A Randomized, Controlled, Double-Blind Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2018;10(3):337. [54] BUTTEIGER DN, HIBBERD AA, MCGRAW NJ, et al. Soy Protein Compared with Milk Protein in a Western Diet Increases Gut Microbial Diversity and Reduces Serum Lipids in Golden Syrian Hamsters. J Nutr. 2016;146(4):697-705. [55] FRITZ P, FRITZ R, BODAY P, et al. Gut microbiome composition: link between sports performance and protein absorption. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2024;21(1):2297992. [56] ASHTARY-LARKY D, BAGHERI R, BAVI H, et al. Ketogenic diets, physical activity and body composition: a review. Br J Nutr. 2022;127(12):1898-1920. [57] VARGAS-MOLINA S, GOMEZ-URQUIZA JL, GARCIA-ROMERO J, et al. Effects of the Ketogenic Diet on Muscle Hypertrophy in Resistance-Trained Men and Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(19):12629. [58] MURPHY NE, CARRIGAN CT, MARGOLIS LM. High-Fat Ketogenic Diets and Physical Performance: A Systematic Review. Adv Nutr. 2021;12(1): 223-233. [59] MURTAZA N, BURKE LM, VLAHOVICH N, et al. The Effects of Dietary Pattern during Intensified Training on Stool Microbiota of Elite Race Walkers. Nutrients. 2019;11(2):261. [60] WAN Y, WANG F, YUAN J, et al. Effects of dietary fat on gut microbiota and faecal metabolites, and their relationship with cardiometabolic risk factors: a 6-month randomised controlled-feeding trial. Gut. 2019; 68(8):1417-1429. [61] COLLINS SL, STINE JG, BISANZ JE, et al. Bile acids and the gut microbiota: metabolic interactions and impacts on disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2023;21(4):236-247. [62] PAOLI A, MANCIN L, BIANCO A, et al. Ketogenic Diet and Microbiota: Friends or Enemies. Genes (Basel). 2019;10(7):534. [63] WOLTERS M, AHRENS J, ROMANI-PEREZ M, et al. Dietary fat, the gut microbiota, and metabolic health - A systematic review conducted within the MyNewGut project. Clin Nutr. 2019;38(6):2504-2520. [64] FU Y, WANG Y, GAO H, et al. Associations among Dietary Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, the Gut Microbiota, and Intestinal Immunity. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:8879227. [65] MANCIN L, AMATORI S, CAPRIO M, et al. Effect of 30 days of ketogenic Mediterranean diet with phytoextracts on athletes’ gut microbiome composition. Front Nutr. 2022;9:979651. |
| [1] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [2] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [3] | Yuan Weibo, Liu Chan, Yu Limei. Potential application of liver organoids in liver disease models and transplantation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [4] | Zhang Zixian, Xu Youliang, Wu Shaokui, Wang Xiangying. Effects of blood flow restriction training combined with resistance training on muscle indicators in college athletes: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1705-1713. |
| [5] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [6] | Zheng Huakun, Yin Mingyue, Liu Qian. Effects of interval and continuous training on the quality of life in physically inactive adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1727-1740. |
| [7] | Lou Guo, Zhang Min, Fu Changxi. Exercise preconditioning for eight weeks enhances therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells in rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [8] | Zheng Rongfa, Mo Weibin, Huang Peng, Chen Junji, Liang Ting, Zi Fangyu, Li Guofeng. Effects of electroacupuncture on the expression of metabolic enzymes and autophagy genes in gastrocnemius muscle tissues of exercising rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1127-1136. |
| [9] | Zhao Xiaoxuan, Liu Shuaiyi, Li Qi, Xing Zheng, Li Qingwen, Chu Xiaolei. Different exercise modalities promote functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1248-1256. |
| [10] | Zhang Wenhua, Li Xun, Zhang Weichao, Li Xinying, Ma Guoao, Wang Xiaoqiang . Promoting myogenesis based on the SphK1/S1P/S1PR2 signaling pathway: a new perspective on improving skeletal muscle health through exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1265-1275. |
| [11] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [12] | Wu Yihan, Liu Zhongqiang, Wei Qiaoye, Liu Mingdong, Chen Keyi, Li Zhigang. Effect of balance training with different visual conditions on proprioception in patients with chronic ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1050-1057. |
| [13] | Wang Dongyang, Yang Qiaohui, Lin Xinchao. Relationship between vitamin D levels and reproductive characteristics and exercise dietary situation in postmenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1021-1025. |
| [14] | Zhu Chuanxi, Qiu Long, Li Lingxu, Ji Guangcheng. Chinese herbal prescription combined with head acupuncture exercise therapy improves limb spasticity in rats with ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7571-7577. |
| [15] | Liu Xuan, Ding Yuqing, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang, Hu Shujuan. Exercise prevention and treatment of insulin resistance: role and molecular mechanism of Keap1/nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||