Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (13): 2675-2682.doi: 10.12307/2025.042
Previous Articles Next Articles
Acellular cartilage extracellular matrix homogenate combined with oxymatrine on treatment of osteoarthritis in rats
Wu Fuzhang1, Zhang Pengli1, Zhang Zhenhua1, He Yongbing1, Sun Heyan2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Anhui Provincial Corps Hospital of Chinese Peoples Armed Police Force, Hefei 230041, Anhui Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230001, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2023-12-05Accepted:2024-03-08Online:2025-05-08Published:2024-09-11 -
About author:Wu Fuzhang, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Anhui Provincial Corps Hospital of Chinese Peoples Armed Police Force, Hefei 230041, Anhui Province, China -
Supported by:Anhui Province Key Medical and Health Specialty Construction Project during the “13th Five-Year” Plan Period, No. [2021]230 (to WFZ); Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province, No. 2008085MH291 (to SHY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Fuzhang, Zhang Pengli, Zhang Zhenhua, He Yongbing, Sun Heyan. Acellular cartilage extracellular matrix homogenate combined with oxymatrine on treatment of osteoarthritis in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2675-2682.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
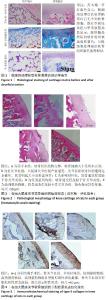
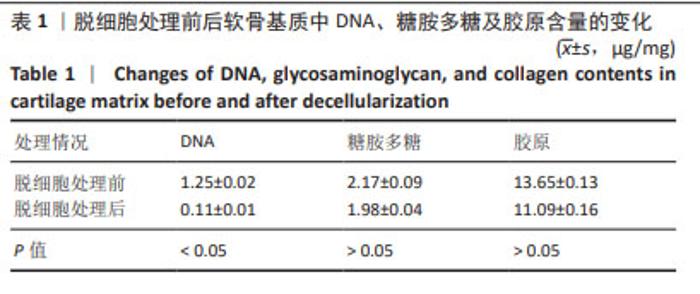
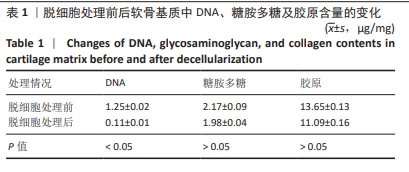
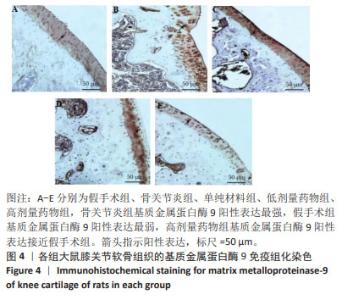
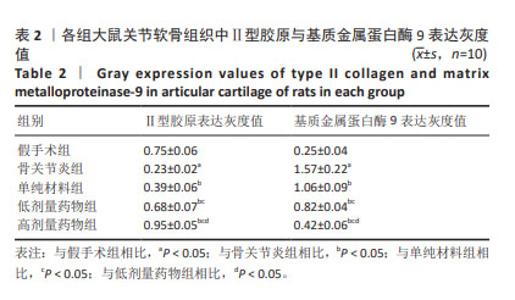
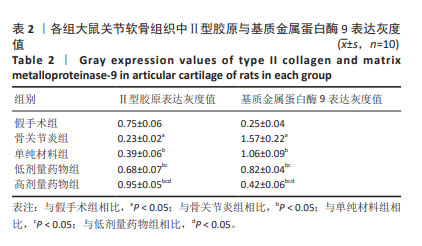
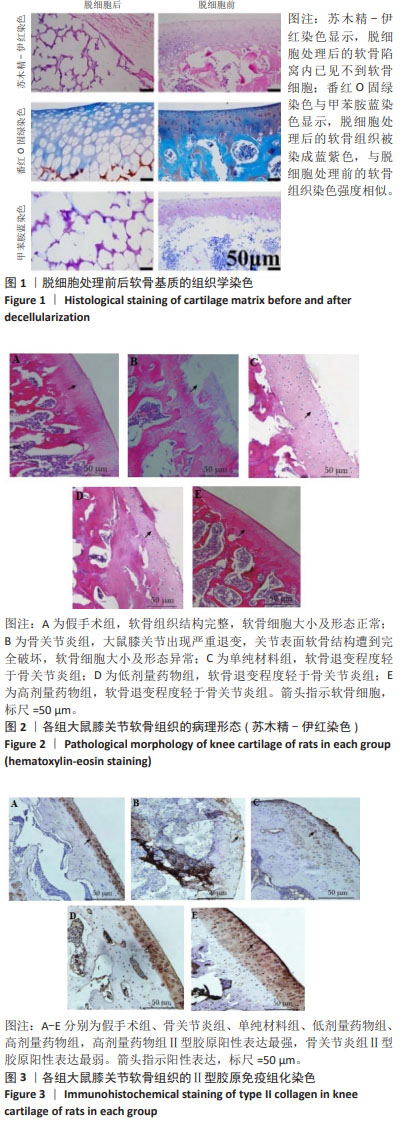
2.2 实验动物数量分析 术后无大鼠死亡,未出现膝关节感染、伤口感染与皮肤坏死等情况。骨关节炎造模大鼠造模后膝关节肿胀、活动受限与跛行等。50只大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.3 各组大鼠关节软骨病理形态变化 苏木精-伊红染色显示,假手术组大鼠膝关节表面软骨组织结构完整,软骨细胞大小及形态正常,各层次排列整齐且分布均匀;骨关节炎组大鼠膝关节出现严重退变,关节表面软骨结构遭到完全破坏,出现裂隙且深达软骨下骨,软骨细胞大小及形态异常,细胞萎缩、排列紊乱且无层次,软骨细胞数量显著减少;单纯材料组大鼠膝关节软骨存在退变表现,但病变未累及软骨下骨,软骨细胞形态较正常,软骨细胞数量较骨关节炎组增多;低剂量药物组、高剂量药物组大鼠膝关节软骨退变程度较轻,软骨细胞形态正常,软骨细胞数量较单纯材料组增多,其中高剂量药物组改善效果更明显,见图2。 免疫组化染色显示,假手术组大鼠关节软骨组织中Ⅱ型胶原呈强阳性表达,基质金属蛋白酶9呈弱阳性表达;与假手术组相比,骨关节炎组大鼠关节软骨组织中Ⅱ型胶原阳性表达显著减弱,基质金属蛋白酶9阳性表达显著增强;与骨关节炎组相比,单纯材料组大鼠关节软骨组织中Ⅱ型胶原阳性表达增强,基质金属蛋白酶9阳性表达减弱;与单纯材料组相比,低剂量药物组、高剂量药物组大鼠关节软骨组织中Ⅱ型胶原阳性表达进一步增强,基质金属蛋白酶9阳性表达进一步减弱;相较于低剂量药物组,高剂量药物组大鼠关节软骨组织中Ⅱ型胶原阳性表达增强,基质金属蛋白酶9阳性表达减弱,见图3,4。5组大鼠关节软骨组织中Ⅱ型胶原与基质金属蛋白酶9表达灰度值,见表2。"
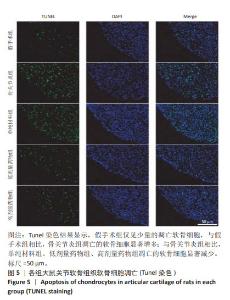
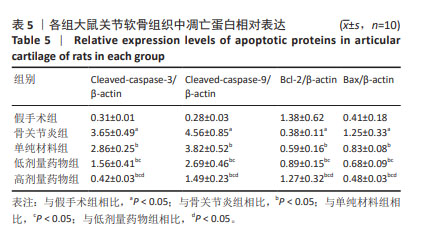
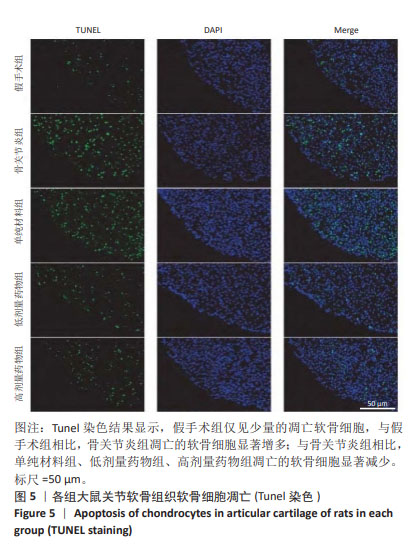
2.4 各组大鼠关节软骨组织病理评分 假手术组大鼠关节软骨组织OARSI评分为0,骨关节炎组、单纯材料组、低剂量药物组、高剂量药物组大鼠关节软骨组织OARSI评分分别为17.94±1.23,12.09±1.18,9.32±0.17,5.67±0.15,5组OARSI评分比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),组间两两比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.5 各组大鼠关节软骨细胞凋亡 Tunel染色结果显示,假手术组仅见少量的凋亡软骨细胞,与假手术组相比,骨关节炎组凋亡的软骨细胞显著增加多;与骨关节炎组相比,单纯材料组、低剂量药物组、高剂量药物组凋亡的软骨细胞显著减少,见图5。 Image J软件定量分析结果显示,假手术组、骨关节炎组、单纯材料组、低剂量药物组、高剂量药物组软骨细胞凋亡率依次为(6.23±0.38)%,(38.06±3.28)%,(28.17±3.07)%,(18.78±2.69)%,(11.74±1.87)%,骨关节炎组与假手术组、骨关节炎组与单纯材料组、单纯材料组与低剂量药物组、低剂量药物组与高剂量药物组软骨细胞凋亡率比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。"
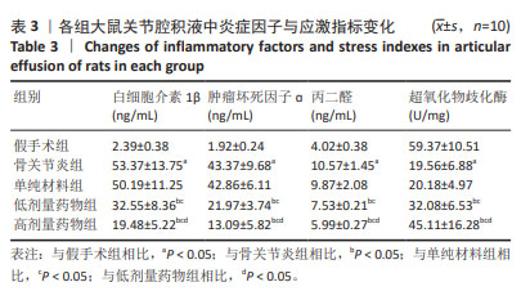
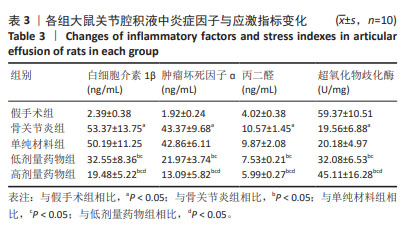
2.6 各组大鼠关节腔积液中炎症因子与应激指标变化 与假手术组比较,骨关节炎组大鼠关节腔积液中白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子ɑ、丙二醛水平升高(P < 0.05),超氧化物歧化酶水平显著降低(P < 0.05);与骨关节炎组比较,单纯材料组大鼠关节腔积液中白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子ɑ、丙二醛、超氧化物歧化酶水平均无明显变化(P > 0.05);与骨关节炎组比较,低剂量药物组、高剂量药物组大鼠关节腔积液中白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子ɑ、丙二醛的质量浓度降低(P < 0.05),超氧化物歧化酶含量升高(P < 0.05);与低剂量药物组比较,高剂量药物组大鼠关节腔积液中白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、丙二醛的质量浓度降低,超氧化物歧化酶含量升高(P < 0.05),见表3。"
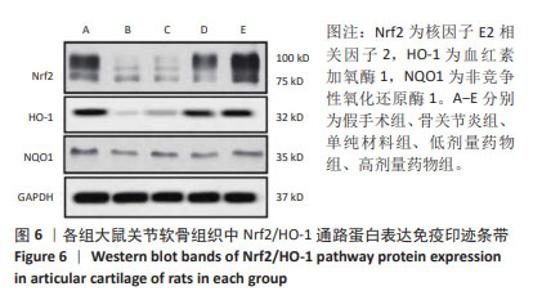
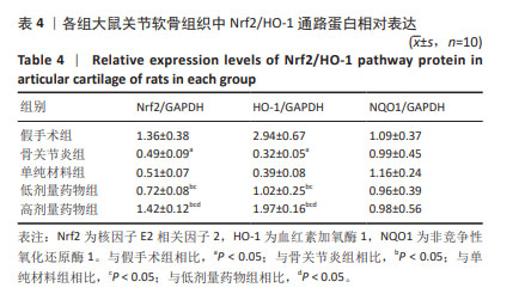
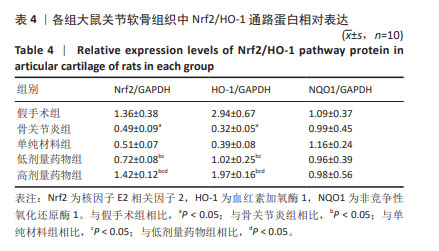
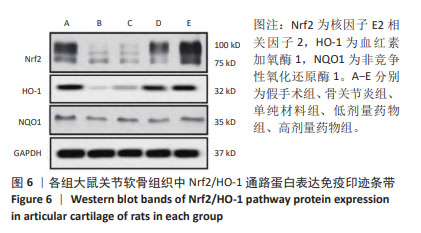
2.7 各组大鼠关节软骨组织中Nrf2/HO-1通路蛋白与凋亡蛋白表达 Western blot检测显示,与假手术组比较,骨关节炎组大鼠关节软骨组织中Nrf2、HO-1蛋白表达下降(P < 0.05);与骨关节炎组比较,单纯材料组大鼠关节软骨组织中Nrf2、HO-1蛋白表达无明显变(P > 0.05);与骨关节炎组比较,低剂量药物组、高剂量药物组大鼠关节软骨组织中Nrf2、HO-1蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);与低剂量药物组比较,高剂量药物组大鼠关节软骨组织中Nrf2、HO-1蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);5组大鼠关节软骨组织中NQO1蛋白表达比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图6,表4。"
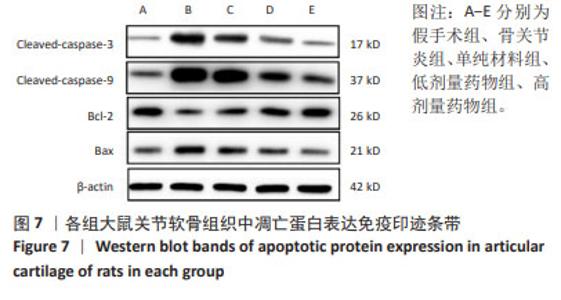
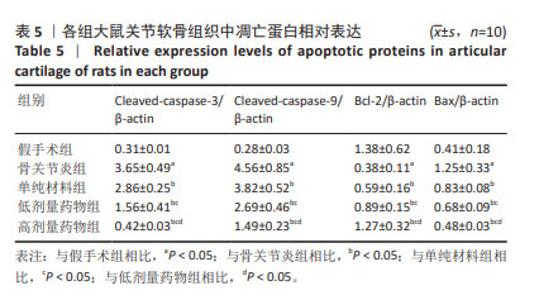
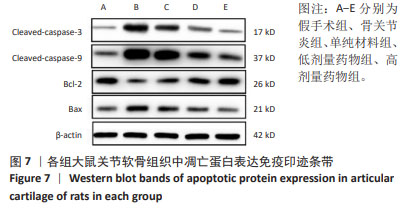
与假手术组比较,骨关节炎组大鼠关节软骨组织中Cleaved-caspase-3、Cleaved-caspase-9、Bax蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05),Bcl-2的蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05);与骨关节炎组比较,单纯材料组大鼠关节软骨组织中Cleaved-caspase-3、Cleaved-caspase-9、Bax蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);与单纯材料组比较,低剂量药物组、高剂量药物组大鼠关节软骨组织中Cleaved-caspase-3、Cleaved-caspase-9、Bax蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);与低剂量药物组比较,高剂量药物组大鼠关节软骨组织中Cleaved-caspase-3、Cleaved-caspase-9、Bax蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05),见图7,表5。"
| [1] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311. [2] HALL M, VAN DER ESCH M, HINMAN RS, et al. How does hip osteoarthritis differ from knee osteoarthritis? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(1):32-41. [3] KUMAR A, PALIT P, THOMAS S, et al. Osteoarthritis: Prognosis and emerging therapeutic approach for disease management. Drug Dev Res. 2021;82(1): 49-58. [4] BHATTACHARJEE M, ESCOBAR IVIRICO JL, KAN HM, et al. Injectable amnion hydrogel-mediated delivery of adipose-derived stem cells for osteoarthritis treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(4):e2120968119. [5] LI G, LIU S, CHEN Y, et al. An injectable liposome-anchored teriparatide incorporated gallic acid-grafted gelatin hydrogel for osteoarthritis treatment. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):3159. [6] ZHU W, CAO L, SONG C, et al. Cell-derived decellularized extracellular matrix scaffolds for articular cartilage repair. Int J Artif Organs. 2021;44(4):269-281. [7] CHEN D, ZHANG Y, LIN Q, et al. The effect of cartilage decellularized extracellular matrix-chitosan compound on treating knee osteoarthritis in rats. PeerJ. 2021;9:e12188. [8] TIAN G, JIANG S, LI J, et al. Cell-free decellularized cartilage extracellular matrix scaffolds combined with interleukin 4 promote osteochondral repair through immunomodulatory macrophages: In vitro and in vivo preclinical study. Acta Biomater. 2021;127:131-145. [9] KIM M, AHN J, LEE J, et al. Combined Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Cartilage Acellular Matrix Injection Therapy for Osteoarthritis in Goats. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022;19(1):177-187. [10] JEON HJ, YOON KA, AN ES, et al. Therapeutic Effects of Human Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Combined with Cartilage Acellular Matrix Mediated Via Bone Morphogenic Protein 6 in a Rabbit Model of Articular Cruciate Ligament Transection. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020; 16(3):596-611. [11] JIN X, FU W, ZHOU J, et al. Oxymatrine attenuates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced HUVEC injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis via the activation of the SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2021;48(4):187. [12] WANG XL, CHEN F, SHI H, et al. Oxymatrine inhibits neuroinflammation byRegulating M1/M2 polarization in N9 microglia through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;100:108139. [13] 高歌,方官琴,付凌云,等.氧化苦参碱通过抑制心肌细胞焦亡改善脂多糖诱导的心肌损伤[J].中药材,2022,45(12):2962-2968 [14] MOHETAER D, CAO L, WANG Y. Oxymatrine Protects Chondrocytes against IL-1β-triggered Apoptosis in Vitro and Inhibits Osteoarthritis in Mice Model. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:2745946. [15] 刘茜,李雪健,王忠山.猪软骨脱细胞基质对人脂肪干细胞增殖及分化的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2020,38(2):122-127 [16] ZHANG Y, DAI J, YAN L, et al. Intra-articular injection of decellularized extracellular matrices in the treatment of osteoarthritis in rabbits. PeerJ. 2020;8:e8972. [17] 李明静,张健强,郭靖,等.艾灸不同腧穴对KOA大鼠不同组织TNF-α、MMP-13表达的影响[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2023, 25(4):1390-1397. [18] JIN Z, CHANG B, WEI Y, et al. Curcumin exerts chondroprotective effects against osteoarthritis by promoting AMPK/PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;151:113092. [19] KARAMANOS NK, THEOCHARIS AD, PIPERIGKOU Z, et al. A guide to the composition and functions of the extracellular matrix. FEBS J. 2021;288(24): 6850-6912. [20] LIU C, PEI M, LI Q, et al. Decellularized extracellular matrix mediates tissue construction and regeneration. Front Med. 2022;16(1):56-82. [21] KARAMANOS NK, THEOCHARIS AD, PIPERIGKOU Z, et al. A guide to the composition and functions of the extracellular matrix. FEBS J. 2021;288(24): 6850-6912. [22] GUVATOVA ZG, BORISOV PV, ALEKSEEV AA, et al. Age-Related Changes in Extracellular Matrix.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2022;87(12):1535-1551. [23] LI SH, WU QF. MicroRNAs target on cartilage extracellular matrix degradation of knee osteoarthritis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(3):1185-1197. [24] ZOU ZL, SUN MH, YIN WF, et al. Avicularin suppresses cartilage extracellular matrix degradation and inflammation via TRAF6/MAPK activation. Phytomedicine. 2021;91:153657. [25] YANG Y, LIN H, SHEN H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular matrix enhances chondrogenic phenotype of and cartilage formation by encapsulated chondrocytes in vitro and in vivo. Acta Biomater. 2018;69: 71-82. [26] LU L, SHANG X, LIU B, et al. Repair of articular cartilage defect using adipose-derived stem cell-loaded scaffold derived from native cartilage extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(6):4244-4257. [27] LIU J, LU Y, XING F, et al. Cell-free scaffolds functionalized with bionic cartilage acellular matrix microspheres to enhance the microfracture treatment of articular cartilage defects. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(6):1686-1697. [28] MA P, YUE L, YANG H, et al. Chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of amurensin H by regulating TLR4/Syk/NF-κB signals. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(2):1958-1968. [29] YAO M, ZHANG J, LI Z, et al. Marein protects human nucleus pulposus cells against high glucose-induced injury and extracellular matrix degradation at least partly by inhibition of ROS/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;80:106126. [30] JIN Q, LI Z, XU Q, et al. Matrine From Sophora Flavescens Attenuates on Collagen-Induced Osteoarthritis by Modulating the Activity of miR-29B-3P/PGRN Axis. Physiol Res. 2023;72(4):475-483. [31] WEI K, DAI J, WANG Z, et al. Oxymatrine suppresses IL-1β-induced degradation of the nucleus pulposus cell and extracellular matrix through the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020;245(6): 532-541. [32] WU J, LI H, HU F, et al. Stevioside attenuates osteoarthritis via regulating Nrf2/HO-1/NF-κB pathway. J Orthop Translat. 2022;38:190-202. [33] CHEN Z, ZHONG H, WEI J, et al. Inhibition of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling leads to increased activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in osteoarthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):300. [34] ZHANG Q, LIU J, DUAN H, et al. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress.J Adv Res. 2021;34:43-63. [35] LIU X, ZHU Q, ZHANG M, et al. Isoliquiritigenin Ameliorates Acute Pancreatitis in Mice via Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and Modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:7161592. [36] FENG Y, CUI R, LI Z, et al. Methane Alleviates Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury by Inhibiting Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Apoptosis through the Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:7067619. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Ma Chi, Wang Ning, Chen Yong, Wei Zhihan, Liu Fengji, Piao Chengzhe. Application of 3D-printing patient-specific instruments combined with customized locking plate in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
| [3] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [4] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [5] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [6] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [7] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [8] | Chen Yueping, Chen Feng, Peng Qinglin, Chen Huiyi, Dong Panfeng . Based on UHPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular dynamics simulation to explore the mechanism of Panax notoginseng in treating osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [9] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [10] | Wang Peiguang, Zhang Xiaowen, Mai Meisi, Li Luqian, Huang Hao. Generalized equation estimation of the therapeutic effect of floating needle therapy combined with acupoint embedding on different stages of human knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [11] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [12] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [13] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [14] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [15] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||