Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (13): 2683-2689.doi: 10.12307/2025.046
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparative proteomic analysis of rat adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes
Zhang Xinrui1, Han Yue1, Lei Lei1, Liu Jianyu1, Geng Chengkui2
- 1Second School of Clinical Medicine, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Chenggong Campus of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Yan’an Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2024-01-15Accepted:2024-03-26Online:2025-05-08Published:2024-09-11 -
Contact:Geng Chengkui, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Yan’an Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Zhang Xinrui, Master candidate, Second School of Clinical Medicine, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Chenggong Campus of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China; Han Yue, Master candidate, Second School of Clinical Medicine, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Chenggong Campus of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China Zhang Xinrui and Han Yue contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:Science and Technology Plan Project of Yunnan Provincial Department of Science and Technology, No. 202001AY070001-263 (to GCK)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Xinrui, Han Yue, Lei Lei, Liu Jianyu, Geng Chengkui. Comparative proteomic analysis of rat adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2683-2689.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
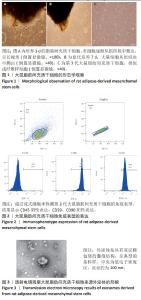
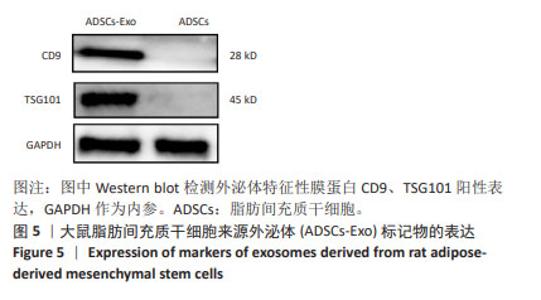
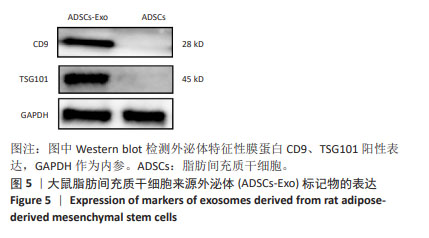
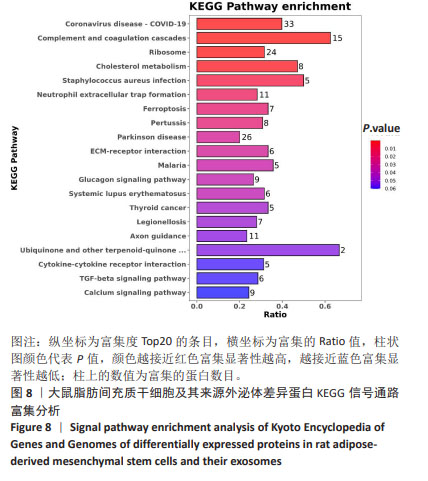
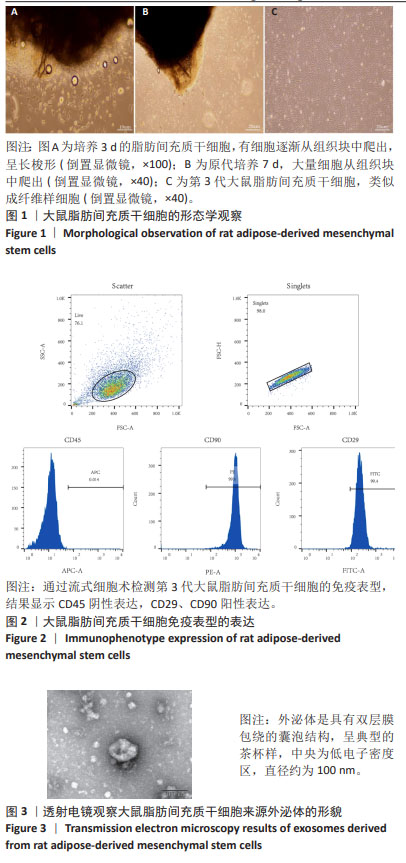
2.1 大鼠脂肪间充质干细胞形态学特征 采用组织块贴壁法培养2 d左右,可观察到从脂肪组织块周围陆续爬出贴壁的细胞,多为长梭形,还有多角形,培养10 d后待细胞达到80%-90%融合度时进行传代,可见脂肪间充质干细胞类似成纤维样细胞,群落生长,排列紧密,呈漩涡状,见图1。 2.2 大鼠脂肪间充质干细胞表面标记物的表达 第3代脂肪间充质干细胞免疫表型为CD29、CD90阳性表达,CD45阴性表达,见图2,鉴定所培养细胞为大鼠脂肪间充质干细胞。 2.3 外泌体在透射电镜下的形态学特征 在透射电镜下观察到呈茶杯型,可见清晰的双层膜性小囊泡结构,由磷脂双分子层包绕,中央为低电子密度区,边界清晰,囊泡直径约为100 nm,符合文献中外泌体的形态大小,见图3。"
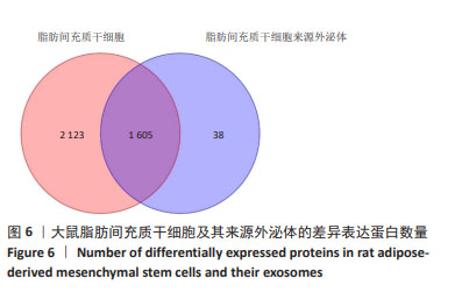
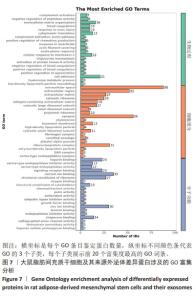
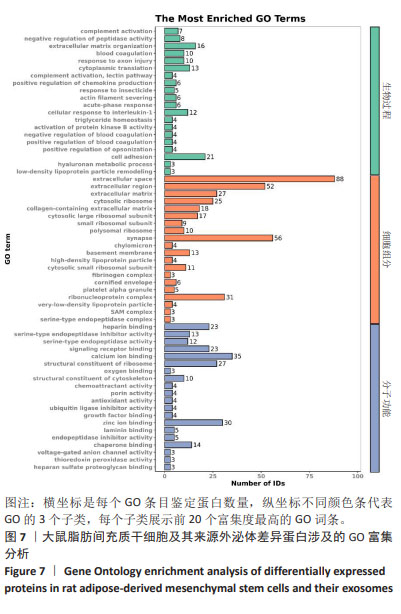
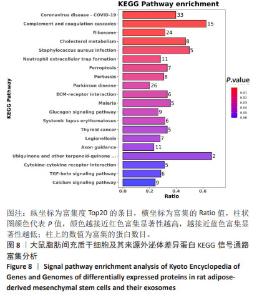
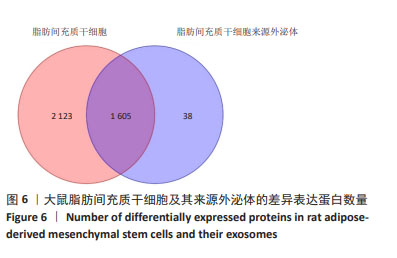
2.7 大鼠脂肪间充质干细胞及其来源外泌体的蛋白质组学分析 2.7.1 数据选择 使用Proteome Discoverer 2.4软件对原始数据进行检索。参数设置为酶切方式:胰蛋白酶,最大允许存在2个漏切位点。固定修饰为:氨基甲酰甲基(C)。可变修饰为:M氧化(15.995 Da);乙酰基(蛋白N-端)。一级质量偏差为:±15 ppm,二级质量偏差为:±0.02 Da。数据库为uniprot大鼠数据库(含有47 943个注释蛋白)。 2.7.2 蛋白组学分析结果 在蛋白定量和功能注释富集分析中,对原始搜库结果中样本的定量值不为空的蛋白进行统计,获取每个样本间蛋白数目,使用Perseus进行补值,填充缺失值数据,差异分析采用Maxquant Siginificance A检验法进行,差异表达蛋白质的选择标准为:表达差异倍数大于1.2倍,且P值 < 0.05。脂肪间充质干细胞及其来源外泌体样本中总蛋白数为3 766种,其中筛选出一致性表达蛋白(差异比< 1.2)为1 605种,细胞中表达的蛋白数为2 123种,外泌体中表达的蛋白数为38种,表明细胞及其来源外泌体在蛋白表达之间存在一定的差异性,见图6。"
| [1] MISHRA VK, SHIH HH, PARVEEN F, et al. Identifying the Therapeutic Significance of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cells. 2020;9(5):1145. [2] LIAU LL, LOOI QH, CHIA WC, et al. Treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Biosci. 2020;10:112. [3] RHODE SC, BEIER JP, RUHL T. Adipose tissue stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration-In vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci Res. 2021;99(2): 545-560. [4] ZHOU LN, WANG JC, ZILUNDU PLM, et al. A comparison of the use of adipose-derived and bone marrow-derived stem cells for peripheral nerve regeneration in vitro and in vivo. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1):153. [5] AL-GHADBAN S, BUNNELL BA. Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells: Immunomodulatory Effects and Therapeutic Potential. Physiology (Bethesda). 2020;35(2):125-133. [6] WANG Y, FANG J, LIU B, et al. Reciprocal regulation of mesenchymal stem cells and immune responses. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29(11): 1515-1530. [7] WANG LT, LIU KJ, SYTWU HK, et al. Advances in mesenchymal stem cell therapy for immune and inflammatory diseases: Use of cell-free products and human pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021;10(9):1288-1303. [8] WILLMS E, JOHANSSON HJ, MÄGER I, et al. Cells release subpopulations of exosomes with distinct molecular and biological properties. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22519. [9] SAILLIET N, ULLAH M, DUPUY A, et al. Extracellular Vesicles in Transplantation. Front Immunol. 2022;13:800018. [10] HADE MD, SUIRE CN, MOSSELL J, et al. Extracellular vesicles: Emerging frontiers in wound healing. Med Res Rev. 2022;42(6):2102-2125. [11] AN Y, LIN S, TAN X, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells and application to skin wound healing. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(3):e12993. [12] RECORD M, SILVENTE-POIROT S, POIROT M, et al. Extracellular vesicles: lipids as key components of their biogenesis and functions. J Lipid Res. 2018;59(8):1316-1324. [13] HE C, ZHENG S, LUO Y, et al. Exosome Theranostics: Biology and Translational Medicine. Theranostics. 2018;8(1):237-255. [14] HADE MD, SUIRE CN, SUO Z. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Applications in Regenerative Medicine. Cells. 2021;10(8): 1959. [15] BU H, HE D, HE X, et al. Exosomes: Isolation, Analysis, and Applications in Cancer Detection and Therapy. Chembiochem. 2019;20(4):451-461. [16] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977. [17] WORTZEL I, DROR S, KENIFIC CM, et al. Exosome-Mediated Metastasis: Communication from a Distance. Dev Cell. 2019;49(3):347-360. [18] WANG C, LI Z, LIU Y, et al. Exosomes in atherosclerosis: performers, bystanders, biomarkers, and therapeutic targets. Theranostics. 2021; 11(8):3996-4010. [19] WATANABE Y, TSUCHIYA A, TERAI S. The development of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in the present, and the perspective of cell-free therapy in the future. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2021;27(1):70-80. [20] FAMILTSEVA A, JEREMIC N, TYAGI SC. Exosomes: cell-created drug delivery systems. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019;459(1-2):1-6. [21] ZHANG Y, BI J, HUANG J, et al. Exosome: A Review of Its Classification, Isolation Techniques, Storage, Diagnostic and Targeted Therapy Applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:6917-6934. [22] MONDAL J, PILLARISETTI S, JUNNUTHULA V, et al. Hybrid exosomes, exosome-like nanovesicles and engineered exosomes for therapeutic applications. J Control Release. 2023;353:1127-1149. [23] 刘海琴,马华根,唐元瑜.原代大鼠脂肪间充质干细胞的体外培养扩增及鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(19):2953-2957. [24] DOYLE LM, WANG MZ. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells. 2019;8(7):727. [25] ZHAO R, ZHAO T, HE Z, et al. Composition, isolation, identification and function of adipose tissue-derived exosomes. Adipocyte. 2021;10(1): 587-604. [26] HAN Y, LI X, ZHANG Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine. Cells. 2019;8(8):886. [27] PIXLEY JS. Mesenchymal stem cells to treat type 1 diabetes. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(4):165315. [28] SONG Y, DU H, DAI C, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for osteoarthritis: a pilot study with long-term follow-up and repeated injections. Regen Med. 2018;13(3):295-307. [29] SHERMAN LS, ROMAGANO MP, WILLIAMS SF, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapies in brain disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019;95:111-119. [30] CHEN SY, YANG RL, WU XC, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation: Neuroprotection and Nerve Regeneration After Spinal Cord Injury. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:4763-4776. [31] FATHOLLAHI A, GABALOU NB, ASLANI S. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in systemic lupus erythematous, a mesenchymal stem cell disorder. Lupus. 2018;27(7):1053-1064. [32] REGMI S, PATHAK S, KIM JO, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for the treatment of inflammatory diseases: Challenges, opportunities, and future perspectives. Eur J Cell Biol. 2019;98(5-8):151041. [33] MAZINI L, ROCHETTE L, ADMOU B, et al. Hopes and Limits of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) and Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4):1306. [34] XUNIAN Z, KALLURI R. Biology and therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Cancer Sci. 2020;111(9): 3100-3110. [35] MELDOLESI J. Exosomes and Ectosomes in Intercellular Communication. Curr Biol. 2018;28(8):R435-R444. [36] TANG Y, ZHOU Y, LI HJ. Advances in mesenchymal stem cell exosomes: a review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):71. [37] AGUIAR KOGA BA, FERNANDES LA, FRATINI P, et al. Role of MSC-derived small extracellular vesicles in tissue repair and regeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;10:1047094. [38] SUN Y, LIU G, ZHANG K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):561. [39] HARRELL CR, VOLAREVIC V, DJONOV V, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Exosomes Derived from Adipose Tissue-Sourced Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Neural and Retinal Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(9):4487. [40] FANG Y, ZHANG Y, ZHOU J, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes: a novel pathway for tissues repair. Cell Tissue Bank. 2019;20(2):153-161. [41] GOODARZI P, ALAVI-MOGHADAM S, PAYAB M, et al. Metabolomics Analysis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2019; 8(Suppl1):30-40. [42] TOH WS, LAI RC, ZHANG B, et al. MSC exosome works through a protein-based mechanism of action. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018;46(4): 843-853. [43] KIMIZ-GEBOLOGLU I, ONCEL SS. Exosomes: Large-scale production, isolation, drug loading efficiency, and biodistribution and uptake. J Control Release. 2022;347:533-543. [44] PEGTEL DM, GOULD SJ. Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88: 487-514. [45] SALUNKHE S, DHEERAJ, BASAK M, et al. Surface functionalization of exosomes for target-specific delivery and in vivo imaging & tracking: Strategies and significance. J Control Release. 2020;326:599-614. [46] YAMASHITA T, TAKAHASHI Y, TAKAKURA Y. Possibility of Exosome-Based Therapeutics and Challenges in Production of Exosomes Eligible for Therapeutic Application. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(6):835-842. [47] ALONSO-ALONSO ML, GARCÍA-POSADAS L, DIEBOLD Y. Extracellular Vesicles from Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Review of Common Cargos. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022;18(3):854-901. [48] ZHU A, LIU N, SHANG Y, et al. Signaling pathways of adipose stem cell-derived exosomes promoting muscle regeneration. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022;135(21):2525-2534. [49] LEE M, BAN JJ, YANG S, et al. The exosome of adipose-derived stem cells reduces β-amyloid pathology and apoptosis of neuronal cells derived from the transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 2018;1691:87-93. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [3] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [4] | Lyu Liting, Yu Xia, Zhang Jinmei, Gao Qiaojing, Liu Renfan, Li Meng, Wang Lu. Bibliometric analysis of research process and current situation of brain aging and exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1457-1465. |
| [5] | Chang Jinxia, Liu Yufei, Niu Shaohui, Wang Chang, Cao Jianchun. Visualization analysis of macrophage polarization in tissue repair process [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1486-1496. |
| [6] | Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [7] | Cao Yue, Ye Xinjian, Li Biyao, Zhang Yining, Feng Jianying. Effect of extracellular vesicles for diagnosis and therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1523-1530. |
| [8] | Zhang Yu, Xu Ruian, Fang Lei, Li Longfei, Liu Shuyan, Ding Lingxue, Wang Yuexi, Guo Ziyan, Tian Feng, Xue Jiajia. Gradient artificial bone repair scaffold regulates skeletal system tissue repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 846-855. |
| [9] | Zhang Xiongjinfu, Chen Yida, Cheng Xinyi, Liu Daihui, Shi Qin . Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of young rats to reverse senescence in aged rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7709-7718. |
| [10] | Sima Xinli, Liu Danping, Qi Hui. Effect and mechanism of metformin-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes on regulating chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7728-7734. |
| [11] | Ma Weibang, Xu Zhe, Yu Qiao, Ouyang Dong, Zhang Ruguo, Luo Wei, Xie Yangjiang, Liu Chen. Screening and cytological validation of cartilage degeneration-related genes in exosomes from osteoarthritis synovial fluid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7783-7789. |
| [12] | Zhang Min, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Li Zhuangzhuang, Wang Xue, Wang Huike. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell exosomes repair radiation-induced submandibular gland damage in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7804-7815. |
| [13] | Guo Jia, Ren Yafeng, Li Bing, Huang Jing, Shang Wenya, Yang Yike, Liu Huiyao. Action mechanism of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying miRNAs in improving spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7827-7838. |
| [14] | Zhou Yang, Liu Kexin, Wang Deli, Sun Zhang. Regenerative effects of engineered extracellular vesicles on repairing bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7839-7847. |
| [15] | Zheng Yitong, Wang Yongxin, Liu Wen, Amujite, Qin Hu. Action mechanism of intrathecal transplantation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for repair of spinal cord injury under neuroendoscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7743-7751. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||