Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (11): 2277-2284.doi: 10.12307/2025.375
Previous Articles Next Articles
Metabolomics analysis of the lumbar spine after alendronate sodium intervention in ovariectomized rats with osteoporosis
Chen Xinfei1, Dai Yahui1, Xie Bingying2, 3, Huang Xiaobin2, 3, Huang Huimin2, 3, Huang Jingwen2, 3, Li Shengqiang2, 3, Ge Jirong2, 3
- 1Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China; 2Institute of Basic Research, Fujian Academy of Chinese Medical Science, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China; 3Fujian Key Laboratory of Combined Traditional Chinese and Western Medicines for Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis (Rehabilitation Hospital Affiliated to Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fujian Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences), Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-17Accepted:2024-06-12Online:2025-04-18Published:2024-08-10 -
Contact:Li Shengqiang, MD, Researcher, Institute of Basic Research, Fujian Academy of Chinese Medical Science, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China; Fujian Key Laboratory of Combined Traditional Chinese and Western Medicines for Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis (Rehabilitation Hospital Affiliated to Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fujian Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences), Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China -
About author:Chen Xinfei, Master candidate, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81774350 (to LSQ); Basic Research Project of Fujian Provincial Public Research Institute, Science and Technology Department, No. 2019R1003-1 (to LSQ); Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, No. 2023J01856 (to XBY); Fujian Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Project, No. 2021zylc42 (to LSQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Xinfei, Dai Yahui, Xie Bingying, Huang Xiaobin, Huang Huimin, Huang Jingwen, Li Shengqiang, Ge Jirong. Metabolomics analysis of the lumbar spine after alendronate sodium intervention in ovariectomized rats with osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2277-2284.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
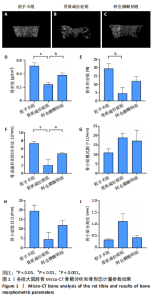
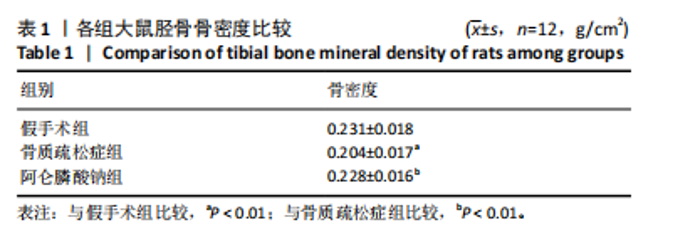
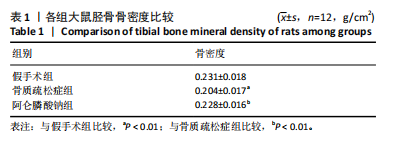
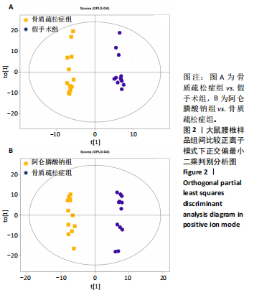
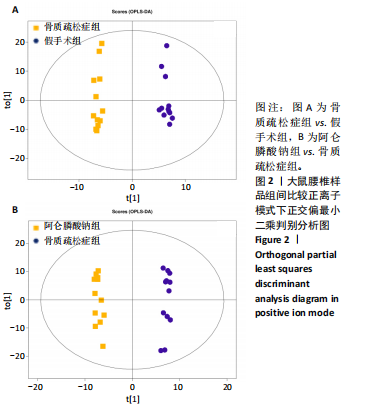
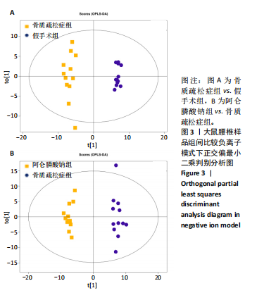
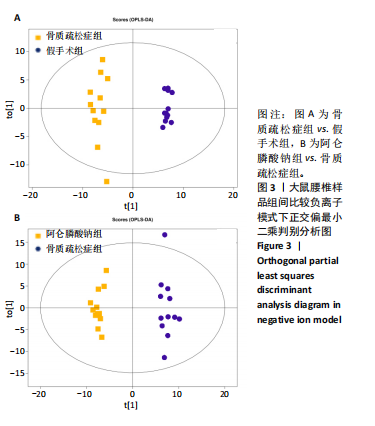
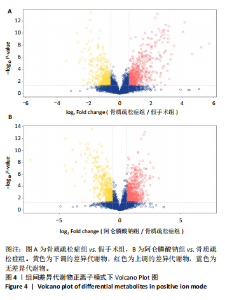
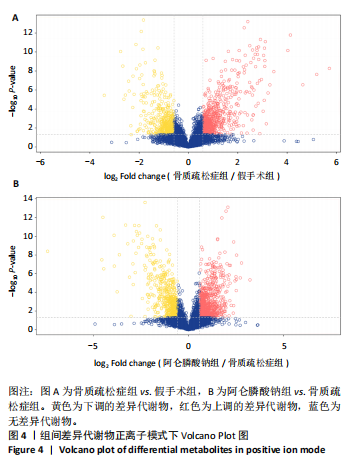
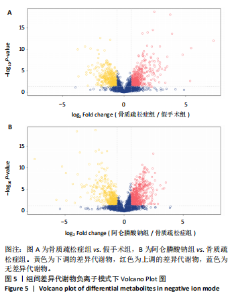
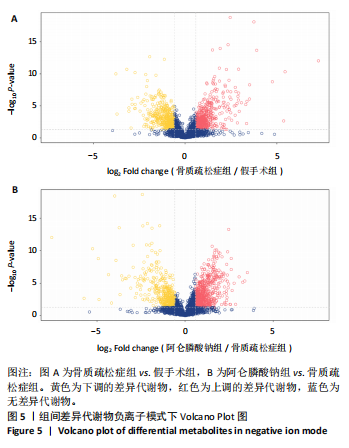
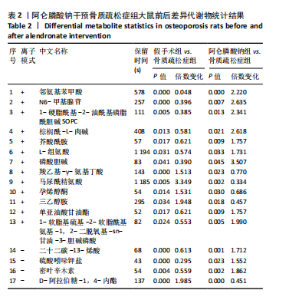
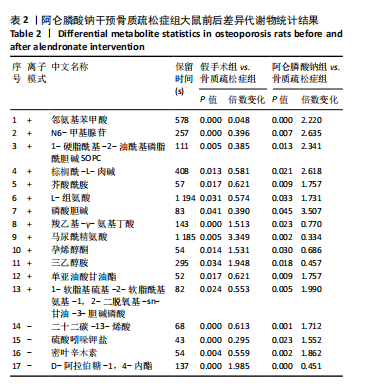
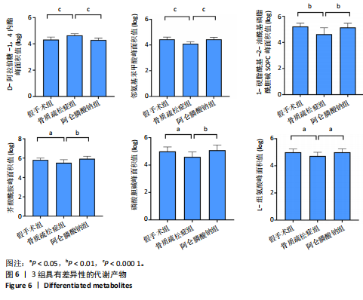
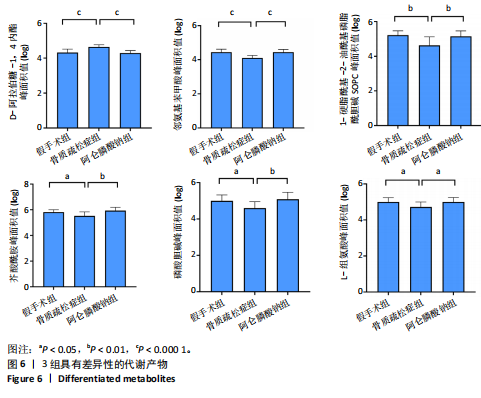
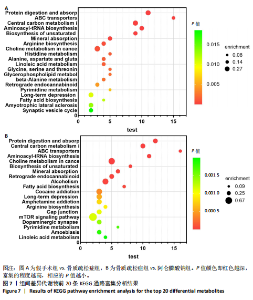
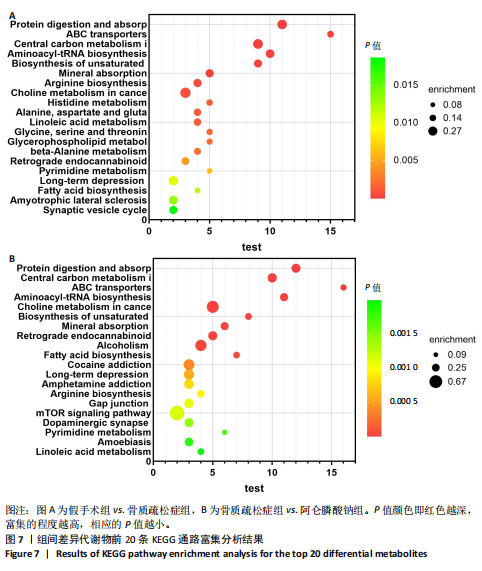
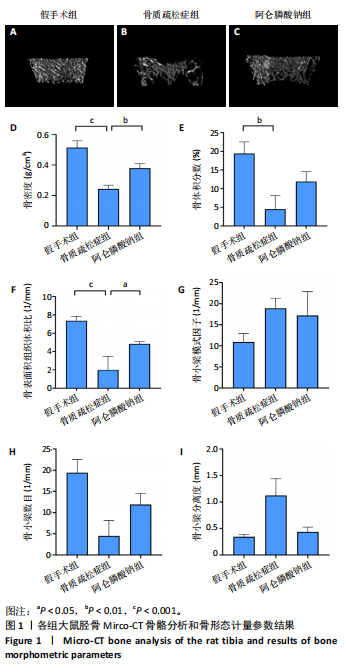
2.3 大鼠胫骨Mirco-Ct分析 利用Mirco-Ct观察3组大鼠胫骨骨小梁情况发现,与假手术组比较,骨质疏松症组大鼠骨小梁数目少、间隙大、排列稀疏;阿仑膦酸钠组大鼠骨小梁数目增多、间隙减小,排列整齐,见图1A-C。骨微观参数分析显示,与假手术组比较,骨质疏松症组大鼠骨密度、骨体积分数、骨表面积组织体积比均显著降低(P < 0.05);与骨质疏松症组相比,阿仑膦酸钠组大鼠骨密度、骨体积分数、骨表面积组织体积比升高(P < 0.05);与假手术组比较,骨质疏松症组和阿仑膦酸钠组大鼠的骨小梁模式因子增加,骨小梁分离度变宽,骨质疏松症组大鼠骨小梁数目减少;与骨质疏松症组比较,阿仑膦酸钠组大鼠骨小梁数目增加,但差异均无显著性意义,见图1D-I。"
| [1] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2022,15(6):573-611. [2] HARRIS K, ZAGAR CA, LAWRENCE KV. Osteoporosis: Common Questions and Answers. Am Fam Physician. 2023;107(3):238-246. [3] No authors listed. Management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: the 2021 position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2021;28(9):973-997. [4] ARCEO-MENDOZA RM, CAMACHO PM. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: Latest Guidelines. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2021;50(2):167-178. [5] AYERS C, KANSAGARA D, LAZUR B, et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Treatments to Prevent Fractures in People With Low Bone Mass or Primary Osteoporosis: A Living Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis for the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2023; 176(2):182-195.
[6] NGUYEN PV, BOUIN M, STE-MARIE LG. Upper gastrointestinal safety of oral bisphosphonate in hospitalized patients. Osteoporos Int. 2021; 32(1):193-197.
[7] NICHOLSON JK, LINDON JC, HOLMES E. ‘Metabonomics’: understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica. 1999;29(11):1181-1189.[8] 魏丽英,李景欣. HPLC法对阿仑膦酸钠成分的测定[J].北方药学, 2021,18(12):1-3. [9] WANG Q, YU Q, ZENG P, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Annual Infusion of Zoledronic Acid and Weekly Oral Alendronate in the Treatment of Primary Osteoporosis: A Meta-Analysis. J Clin Pharmacol. 2023; 63(4):455-465. [10] GEHRKE B, ALVES COELHO MC, BRASIL D’ALVA C, et al. Long-term consequences of osteoporosis therapy with bisphosphonates. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2023;68:e220334. [11] 陈赛楠,吴华嵩,程佑民,等.续苓健骨方对去卵巢骨质疏松模型大鼠血液钙磷代谢的影响 [J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(4): 528-532. [12] 张海永,黄景文,谢冰颖,等.骨疏康治疗去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松的腰椎代谢组学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(32):5185-5190. [13] Cummings SR, Santora AC, Black DM, et al. History of alendronate. Bone. 2020;137:115411. [14] Wilkins Parker LR, Preuss CV. Alendronate. 2023 // StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. [15] CHANDRAN M. The why and how of sequential and combination therapy in osteoporosis. A review of the current evidence. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2022;66(5):724-738. [16] SHEN J, KE Z, DONG S, et al. Pharmacological Therapies for Osteoporosis: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2022;28:e935491. [17] PIRIYAKHUNTORN P, TANTIWORAWIT A, PHIMPHILAI M, et al. The efficacy of alendronate for the treatment of thalassemia-associated osteoporosis: a randomized controlled trial.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1178761. [18] 朱忠华,唐丽琴,张世能.阿仑膦酸钠联合辛伐他汀通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(5):704-708. [19] 马广丽,臧巧源,杨青,等.阿仑膦酸钠治疗骨质疏松对骨密度与血清Klotho蛋白水平的影响[J].中国医药,2023,18(5):709-713. [20] TSUJI A, IKEDA Y, YOSHIKAWA S, et al. The Tryptophan and Kynurenine Pathway Involved in the Development of Immune-Related Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5742. [21] BALLESTEROS J, RIVAS D, DUQUE G. The Role of the Kynurenine Pathway in the Pathophysiology of Frailty, Sarcopenia, and Osteoporosis. Nutrients. 2023;15(14):3132. [22] HUANG M, XU S, LIU L, et al. m6A Methylation Regulates Osteoblastic Differentiation and Bone Remodeling. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 783322. [23] HAN J, KONG H, WANG X, et al. Novel insights into the interaction between N6-methyladenosine methylation and noncoding RNAs in musculoskeletal disorders. Cell Prolif. 2022;55(10):e13294. [24] CHEN J, TIAN Y, ZHANG Q, et al. Novel Insights Into the Role of N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification in Bone Pathophysiology. Stem Cells Dev. 2021;30(1):17-28. [25] WU Y, XIE L, WANG M, et al. “Mettl3-mediated m6A RNA methylation regulates the fate of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and osteoporosis. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4772. [26] TIAN C, HUANG Y, LI Q, et al. Mettl3 Regulates Osteogenic Differentiation and Alternative Splicing of Vegfa in Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):551. [27] LIN G, WANG H, DAI J, et al. Conjugated linoleic acid prevents age-induced bone loss in mice by regulating both osteoblastogenesis and adipogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;490(3):813-820. [28] RAHMAN MM, FERNANDES G, WILLIAMS P. Conjugated linoleic Acid prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss in mice by modulating both osteoclastogenesis and osteoblastogenesis. Lipids. 2014;49(3):211-224. [29] FENG W, WANG X, HUANG D, et al. Role of diet in osteoporosis incidence: Umbrella review of meta-analyses of prospective observational studies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(19):3420-3429. [30] JIANG H, WANG L, WANG D, et al. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid biomarkers and risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and mortality. Clin Nutr. 2022;41(8):1798-1807. [31] ENGELEN M, JONKER R, SULAIMAN H, et al. ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation improves postabsorptive and prandial protein metabolism in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomized clinical trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2022;116(3):686-698. [32] GHAMARZAD SHISHAVAN N, MASOUDI S, MOHAMADKHANI A, et al. The association of dietary intake and plasma fatty acid panel in pancreatic cancer patients: results from golestan cohort study.Nutr Health. 2024;30(2):319-330. [33] TAO SS, WANG P, WANG XY, et al. Causal effect of polyunsaturated fatty acids on bone mineral density and fracture. Front Nutr. 2022; 9:1014847. [34] GAO J, XIE C, YANG J, et al. The Effects of n-3 PUFA Supplementation on Bone Metabolism Markers and Body Bone Mineral Density in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of RCTs. Nutrients. 2023;15(12):2806. [35] DOU Y, WANG Y, CHEN Z, et al. Effect of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid on bone health: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food Sci Nutr. 2021;10(1):145-154. [36] MARTÍNEZ-RAMÍREZ MJ, PALMA S, MARTÍNEZ-GONZÁLEZ MA, et al. Dietary fat intake and the risk of osteoporotic fractures in the elderly. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2007;61(9):1114-1120. [37] COETZEE M, HAAG M, KRUGER MC. Effects of arachidonic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, prostaglandin E(2) and parathyroid hormone on osteoprotegerin and RANKL secretion by MC3T3-E1 osteoblast-like cells. J Nutr Biochem. 2007;18(1):54-63. [38] JÄRVINEN R, TUPPURAINEN M, ERKKILÄ AT, et al. Associations of dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids with bone mineral density in elderly women. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2012;66(4):496-503. [39] PHOEMSAPTHAWEE J, RUANGTHAI R, TUMNAK P, et al. Synergistic Effects of Combined Concurrent Training and Eri-Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation on Bone Mineral Density, Muscle Strength, and Inflammation. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2023;28(1):10-20. [40] LAU BY, COHEN DJ, WARD WE, et al. Investigating the role of polyunsaturated fatty acids in bone development using animal models. Molecules. Molecules. 2013;18(11):14203-14227. [41] BENOVA A, FERENCAKOVA M, BARDOVA K, et al. Omega-3 PUFAs prevent bone impairment and bone marrow adiposity in mouse model of obesity. Commun Biol. 2023;6(1):1043. [42] ORCHARD TS, CAULEY JA, FRANK GC, et al. Fatty acid consumption and risk of fracture in the Women’s Health Initiative. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;92(6):1452-1460. |
| [1] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [2] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [3] | Yang Lei, Liu Sanmao, Sun Huanwei, Che Chao, Tang Lin. Comparison of six machine learning models suitable for use in medicine: support for osteoporosis screening and initial diagnosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7499-7510. |
| [4] | Zhang Yixuan, Li Dongna, Liu Chunyan. Pathological processes, inflammatory responses, and related biomarkers of periodontitis: a multi-omics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7601-7610. |
| [5] | Chai Jinlian, Sun Tiefeng, Li Wei, Zhang Bochun, Li Guangzheng, Zhou Zhongqi, Liang Xuezhen, Wang Ping. Therapeutic effect of Cornus Cervi Colla on steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rat models: fecal metabolomics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6187-6197. |
| [6] | Liu Haowei, Tian Haodong, Huang Li, Yu Hanglin, Peng Li. Acute effects of blood flow restriction resistance exercise on serum metabolites in obese young men [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6249-6259. |
| [7] | Wu Wangxiang, Ran Dongcheng, Xu Jiamu, Xu Jiafu, Chen Jingjing, Wang Chunqing. Long noncoding RNAs related to osteoporosis: current research status and developmental trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6360-6368. |
| [8] | Wang Zhifeng, Yang Jiao, Xi Yujiang, Xu Shuangfeng, Shi Ting, Lan Junfeng, Hao Zhihui, He Pengfen, Yang Aiming, Pan Pan, Wang Jian. Biomarkers affecting the progression of mild to moderate cognitive impairment after stroke: #br# a non-targeted metabolomics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5116-5126. |
| [9] | Liang Zhou, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Yang Bo, Pu Zhanglin, Liu Hua, Peng Jinhui, Wen Lichun, Ling Guanhan, Chen Feng. Anti-osteoporotic mechanisms of kaempferol based on gut microbiota and comprehensive targeted metabolomics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4190-4204. |
| [10] | Lyu Hao, Zhang Ge, Hu Zhimu, Wang Yan, Chu Qingsong, Zhou Yao, Jiang Ting, Wang Jiuxiang. Inflammation, metabolites and osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3697-3704. |
| [11] | Lai Yue, Lin Xuan, Xu Miao, Liu Huan, Shen Jianlin, Huang Wenhua. Medication pattern and mechanism of marine traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3713-3723. |
| [12] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Li Kunjian, Mo Jian, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong . Current status and trends of research on animal models of postmenopausal osteoporosis: a bibliometric visualization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(14): 3070-3080. |
| [13] | Pei Yunxiang, Wu Hao. Hyperbaric oxygen intervention eliminates exercise-induced fatigue in a high-intensity interval training shock microcycle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(14): 2979-2988. |
| [14] | Zhang Wensheng, Guo Haiwei, Weng Rui, Mo Ling, Song Zhenjie, Tian Han, Zhong Yelin, Wang Yuancheng, Tang Hanwu, Liu Caijun, Yuan Chao, Li Ying. Liquiritin inhibits osteoclast differentiation and alleviates bone loss [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2429-2437. |
| [15] | Song Jiating, Chen Jianmin, Wang Kewen, Huang Lanying, Xu Senming, Gui Yuchang, Xu Jianwen. Metabolomics analysis of serum and urine in patients with traumatic spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(在线): 1-6. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||