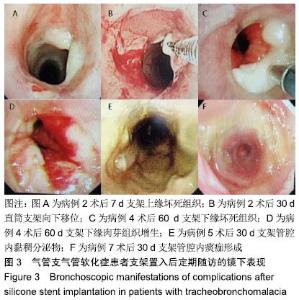
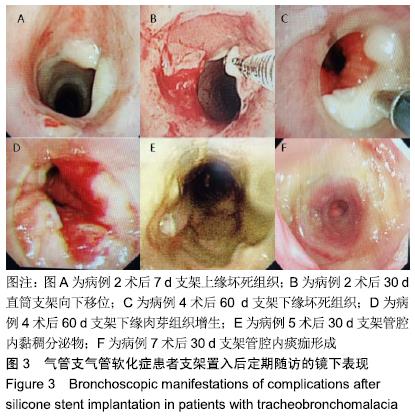
[1] CARDEN KA, BOISELLE PM, WALTZ DA, et al. Tracheomalacia and tracheobronchomalacia in children and adults: an in-depth review. Chest. 2005;127(3):984-1005.
[2] SEPTIMIU M, HENRI C. Tracheobronchomalacia and excessive dynamic airway collapse. Clin Chest Med. 2013; 34(3):527.
[3] MENON B, AGGARWAL B, IQBAL A. Mounier-Kuhn syndrome: report of 8 cases of tracheobronchomegaly with associated complications. South Med J. 2008;101(1):83-87.
[4] 蒋胜华,胡依粉,山凤莲,等.成人气管软化症和过度动态气道塌陷2例并文献复习[J].山东大学学报(医学版),2017,55(4): 111-113+116
[5] 贾丽萍,陈慧冬,黄汉平,等.35例结核分枝杆菌感染致气管支气管软化症的临床分析[J].临床肺科杂志,2017,22(11):2037-2041.
[6] BASTOS HN, TEIXEIRA N, REDONDO M, et al. Mechanical ventilation for the treatment of severe excessive dynamic airway collapse. Respir Care.2015; 60(4):90-91.
[7] DEWBERRY L, WINE T, PRAGER J, et al. Thoracoscopic Posterior Tracheopexy Is a Feasible and Effective Treatment for Tracheomalacia. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2019.
[8] DE TREY LA , DUDLEY J , ISMAIL-KOCH H , et al. Treatment of severe tracheobronchomalacia: Ten-year experience. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;83(4):57-62.
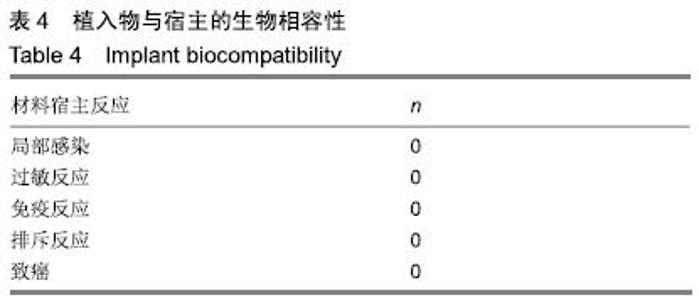
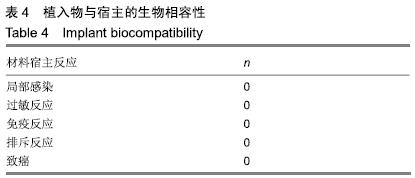
[9] 高雪萍,胡晓媛.气道支架置入治疗气道狭窄的生物相容性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2008,12(30):5942-5944.
[10] 李晓,马芸,张晓菊,等.气管镜引导下经硬质气管镜鞘管放置硅酮支架及T型管治疗良性气管狭窄疗效观察[J].新乡医学院学报, 2019,36(2):143-146.
[11] 何海艳,马航,朱杰,等.喉罩通气全身麻醉下经纤维支气管镜辅助置入Montgomery T型硅酮支架治疗气管狭窄的临床研究[J].中国内镜杂志,2018,24(9):54-58.
[12] 林珑,高宝安.Y型硅酮支架治疗复发性多软骨炎1例并文献复习[J].临床肺科杂志,2018,23(9):1744-1746.
[13] DALAR L, TURAL ÖNÜR S, ÖZDEMIR C, et al. Is silicone stent insertion a clinically useful option for tracheobronchomalacia? Turk J Med Sci. 2016;46(2): 437-442.
[14] 王继旺,蒋胜华.气管支气管软化症与过度动态气道塌陷[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志,2017,40(6):469-472.
[15] CHOO E, LEDFORD D. Tracheobronchomalacia and hyperdynamic airway collapse.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015;3(4):644-645;quiz 646.
[16] KUGLER C, STANZEL F. Tracheomalacia. Thoracic Surg Clin. 2014; 24(1):51-58.
[17] HYSINGER EB. Laryngomalacia, tracheomalacia and bronchomalacia. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2018;48(4):113-118.
[18] REPRESAS-REPRESAS C, LEIRO-FERNÁNDEZ V, MALLO-ALONSO R, et al. Excessive dynamic airway collapse in a small cohort of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. Ann Thor Med. 2015;10(2):118-122.
[19] BUITRAGO DH, WILSON JL, PARIKH M, et al. Current concepts in severe adult tracheobronchomalacia: evaluation and treatment. J Thor Dis.2017; 9(1):E57-E66.
[20] RYU Y, KIM H, CHANG YU, et al. Comparison of Natural and Dumon airway stents for the management of benign tracheobronchial stenoses. Respirology.2006; 11(6):748-754.
[21] 邹珩,张楠,王洪武,等.气管硅酮支架治疗创伤性气管狭窄的临床应用体会[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志,2015,38(9):704-706.
[22] ERNST A, MAJID A, FELLER-KOPMAN D, et al. Airway Stabilization With Silicone Stents for Treating Adult Tracheobronchomalacia. Chest. 2007;132(2):609-616.
[23] HOHENFORST-SCHMIDT W, LINSMEIER B, ZAROGOULIDIS P, et al. Transtracheal single-point stent fixation in posttracheotomy tracheomalacia under cone-beam computer tomography guidance by transmural suturing with the Berci needle–a perspective on a new tool to avoid stent migration of Dumon stents. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015;11: 837-850.
[24] WAN IY, LEE TW, LAM HC, et al. Tracheobronchial stenting for tuberculous airway stenosis. Chest. 2002;122(1):370-374.
[25] SCHMIDT B, OLZE H, BORGES AC, et al. Endotracheal balloon dilatation and stent implantation in benign stenoses. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;71(5):1630-1634.
[26] KENNEDY AS , SONETT JR , ORENS JB , et al. High dose rate brachytherapy to prevent recurrent benign hyperplasia in lung transplant bronchi: theoretical and clinical considerations. J Heart Lung Trans. 2000; 19(2):155-159.
[27] TENDULKAR RD, FLEMING PA, REDDY CA, et al. High-dose-rate endobronchial brachytherapy for recurrent airway obstruction from hyperplastic granulation tissue. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70(3):701-706.
[28] CHOONG CK, HADDAD FJ, GEE EY, et al. Feasibility and safety of airway bypass stent placement and influence of topical mitomycin C on stent patency. J Thoracic Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;129(3):632-638.
[29] 王婷,张杰,王娟,等.紫杉醇对人胚肺成纤维细胞增殖的影响[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志,2010,33(1):17-20.
|