Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (22): 3559-3565.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2258
Previous Articles Next Articles
Polyisobutylene and its thermoplastic elastomers: how to transform from industry to medical treatment
Jiang Li, Fang Xiaojuan, Pan Banglun, Lin Hanchao, Li Wei
- Laboratory Medical School and School of Life Science, Wenzhou Medical University, Key Laboratory of Laboratory Medicine of Ministry of Education, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Medical Genetics, Wenzhou 325035, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Received:2019-08-13Revised:2019-09-06Accepted:2019-10-31Online:2020-08-08Published:2020-04-26 -
Contact:Li Wei, MD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Laboratory Medical School and School of Life Science, Wenzhou Medical University, Key Laboratory of Laboratory Medicine of Ministry of Education, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Medical Genetics, Wenzhou 325035, Zhejiang Province, China -
About author:Jiang Li, MD, Researcher assistant, Laboratory Medical School and School of Life Science, Wenzhou Medical University, Key Laboratory of Laboratory Medicine of Ministry of Education, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Medical Genetics, Wenzhou 325035, Zhejiang Province, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research and Development Program of China, No. 2017YFC1104502
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Li, Fang Xiaojuan, Pan Banglun, Lin Hanchao, Li Wei. Polyisobutylene and its thermoplastic elastomers: how to transform from industry to medical treatment[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(22): 3559-3565.
share this article
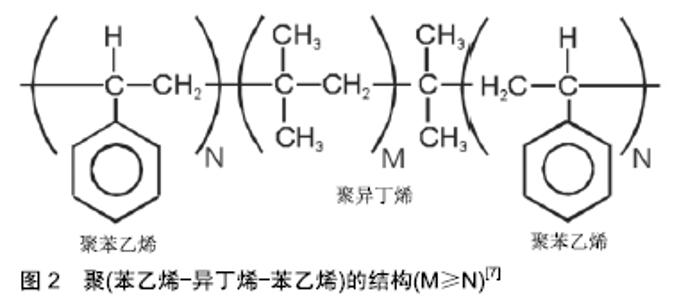
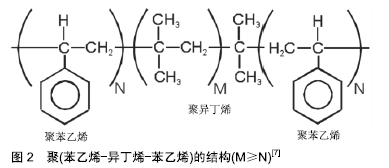
2.1 聚异丁烯的工业应用 聚异丁烯是由单体异丁烯经聚合反应合成的一种完全饱和的烃类高分子材料。与大多数聚合物不同的是,聚异丁烯的重复单元具有对称结构[3],该结构赋予了聚异丁烯优异的耐化学性,阻气性和机械阻尼特性,使其在工业中被广泛应用,如作为黏合剂、密封剂、增稠剂及口香糖添加剂等[4]。根据分子质量的大小,聚异丁烯可分为低分子质量、中分子质量和高分子质量3类。低分子质量聚异丁烯(相对分子质量350-3 500)由异丁烯通过阳离子聚合得到[5],杂质少且透明度高[6],通常为液态。随着分子质量的增加,聚异丁烯会逐渐向发黏的半固态转变,并进一步转变为橡胶状弹性体。 液态聚异丁烯在工业中常作为润滑油和化妆品中的油相成分;而固态聚异丁烯的热稳定性好,韧性和回弹性高,具有优良的耐腐蚀、耐紫外线等性能,常用作橡胶原料、密封剂和电绝缘材料等需求量巨大的领域。此外,异丁烯与异戊二烯(1%-3%)的共聚物称为丁基橡胶,其应用与聚异丁烯类似。 2.2 聚异丁烯嵌段共聚物及热塑性弹性体 聚异丁烯分子链主链为饱和碳链,末端带有一个C=C不饱和双键。作为主单体的异丁烯与作为第二单体的苯乙烯通过活性碳阳离子聚合反应,共聚形成两端封闭的聚异丁烯碳链,见图2[7],聚苯乙烯硬链段和聚异丁烯软链段发生共价键合与微相分离,聚苯乙烯相在聚异丁烯相中通过物理交联形成热塑性弹性体。这种介于橡胶和树脂间的新型高分子材料,被称为第三代橡胶[8]。自从1991年Kennedy等用活性正离子聚合的方法合成线型聚(苯乙烯-异丁烯-苯乙烯)(Poly(Styrene-b-Isobutylene-b- Styrene),PS-b-PIB-b-PS,SIBS)三嵌段共聚物后[9],人们发现聚异丁烯还可与其他常见的生物相容性聚合物材料(如聚丙烯酸酯、甲基丙烯酸酯、聚硅氧烷、聚内酯、聚氨酯、聚环氧乙烷和聚乙烯醇等)相互结合[10-13],合成不同特性的嵌段共聚物。 "
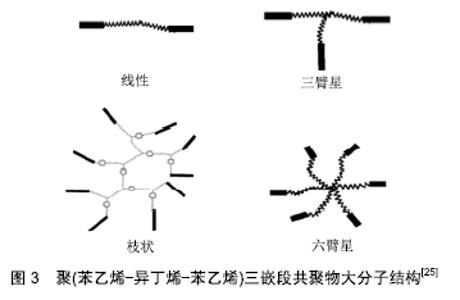
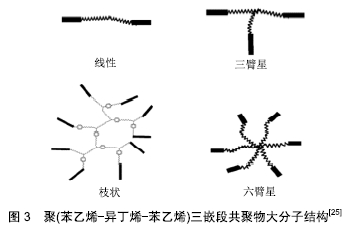
SIBS的性质取决于分子质量及其分布和组成。根据聚异丁烯-聚苯乙烯等嵌段共聚物大分子构造[14-22],Akron大学高分子科学与工程学院(原美国橡胶研究中心[23])的Puskas等将其结构分为3种,第一种是线型和三臂星结构,第3种是多臂星结构,第3种是枝状结构[24],见图3[25]。SIBS是一种物理性能与医用级硅橡胶类似的透明材料,由于其具有微相分离和物理交联的能力,因此不需要增强填料或化学交联剂[26]。例如,聚异丁烯-聚苯乙烯共聚物的体外测试结果显示,该材料具有良好的生物相容性和生物稳定性,用煮沸的浓硝酸处理后,物理性质不受影响;对照组的聚氨酯结构则被破坏,硅橡胶变脆,抗拉强度减至原先的10%[11]。 "
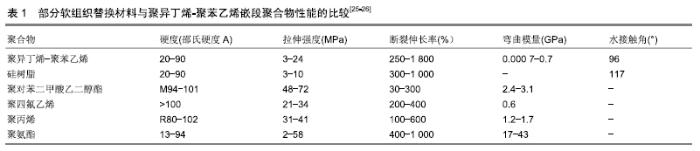
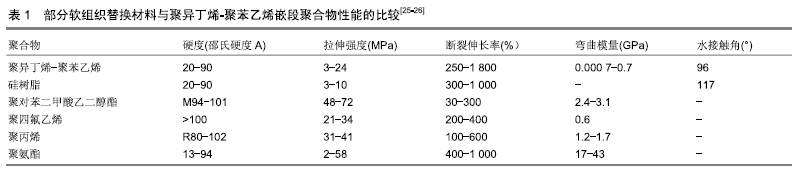
另一种通过纳米碳增强后的聚异丁烯弹性体,抗拉强度达到原先的2倍以上,不仅具有优异的机械性能,并且亲水性得到增强,也更加柔软;植入兔软组织180 d后形成的组织囊厚度较薄,表现出较好的组织相容性[27]。 交联后的聚异丁烯嵌段共聚物具有优异的抗氧化能力、生物相容性和光学性能,在一些性能指标上优于常用的橡胶和聚氨酯材料。由于这些特性,基于聚异丁烯的新型嵌段共聚物有进一步应用于生物医学工程的潜力。与硅橡胶相比,各种聚异丁烯基热塑性弹性体的另一个优点是可以通过改变硬/软相组成、分子质量和整体结构来调整材料的性能,如SIBS可通过改变苯乙烯/异丁烯比例和分子质量获得不同的机械性能。苯乙烯比例较低的SIBS与橡胶的机械性能相似,而比例较高的SIBS则类似增韧塑料[28]。这种三嵌段聚合物的性质要优于异丁烯和苯乙烯的简单无规聚合,可显著改进其拉伸强度和撕裂强度等物理性质。其中,枝状聚异丁烯类热塑性弹性体将是线性SIBS材料在生物医学应用中的极佳替代品[29]。 表1是常用软组织材料性能的比较,其中聚异丁烯-聚苯乙烯的弯曲模量最小,为0.000 7-0.7 GPa,相比于其他热塑性材料(聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯2.4-3.1 GPa,聚四氟乙烯0.6 GPa,聚丙烯1.2-1.7 GPa,聚氨酯 17-43 GPa)更加富有弹性。此外,其最大伸长率可达 1 800%,远高于其他材料。SIBS聚合物具有比相同硬度范围的硅橡胶更高的拉伸强度和断裂伸长率。从接触角数据可以看出,SIBS还具有更高的表面亲水性[25-26]。 "
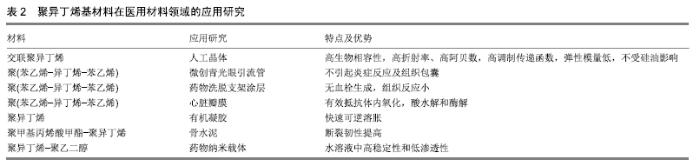
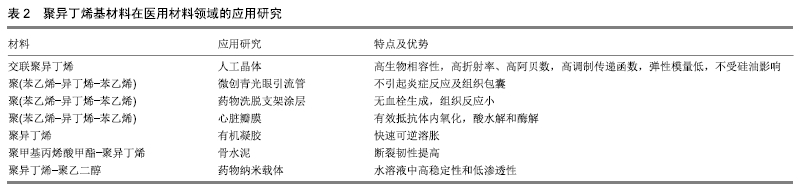
以上数据显示作为新型的软生物材料,聚异丁烯嵌段共聚物力学性能的调控范围更大,这使其可更好地与天然组织匹配。随着活性聚合技术的不断进步,利用阴/阳离子、自由基等活性聚合体系对链段结构和分子质量分布进行精确调控,通过亲水和疏水片段所产生的两亲性网络,具有独特结构和性质的聚异丁烯嵌段共聚物还将不断被合成出来。聚异丁烯分子质量和交联程度差异所带来的性能变化,可制备成不同力学性能的材料来满足不同植入部位的要求。 2.3 聚异丁烯在传统医疗及可植入器材领域的应用 聚异丁烯早期曾应用于与皮肤接触的压敏黏合剂[30]。交联丁基橡胶则由于其优良的阻隔性能(比其他交联弹性体低一个数量级)用于瓶塞和血袋的制作[25]。 在医用材料领域聚异丁烯有着优良的生物稳定性和体外抗钙化能力[31],可被研究用作药物控释、体外导管、植入支架等的制备原料,见表2,目前在血管金属支架涂层和眼科植入物等领域已取得了成功的临床应用。与普通医用硅胶相比,基于聚异丁烯的热塑性弹性体拥有极低的渗透性和较强的氧化稳定性,可通过改变软/硬相组成、分子质量和整体结构来调整材料的性能,如聚氨酯热塑性弹性体的弹性模量范围可跨越塑料和橡胶[32]。此外,热塑性弹性体具有易于加工成型,制备方法较为简单等优点。 "
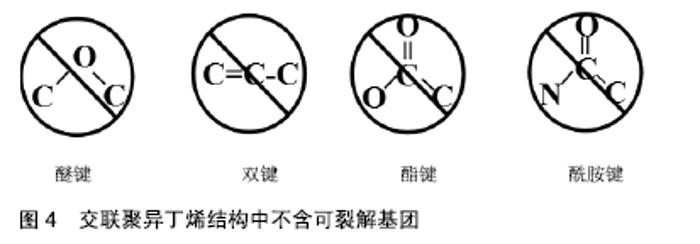
2.3.1 眼科植入材料 人工晶状体植入是目前治疗白内障最为有效的方法之一。交联聚异丁烯是由异丁烯、4-乙烯基苯并环丁烯及苯乙烯单体组成的混合物在高于180 ℃的温度下加热固化得到的。相比传统的聚异丁烯交联方式(如硫化交联),交联聚异丁烯仅涉及热交联,即苯并环丁烯基团与亲二烯体发生的反应,其在稳定的交联温度下无残留的有毒化合物[33]。目前采用具有优异光学性能的交联聚异丁烯材料制成的人工晶状体,是该行业中的最新一代产品。该三维热固性材料是透明的,不含有任何可裂解的基团,见图4,可防止长期植入后材料游离基团在周围组织中引起的炎症反应,或由于材料裂解、微光、闪光对造成的视力损害。进一步的研究还发现,交联聚异丁烯制成的透镜具有高折射率、高阿贝数、高调制传递函数、弹性模量低(200%)等特性,此外不受硅油影响[34]。其制成的人工晶状体在通过直径小于1.5 mm的插入器孔径时能够伸长,随后可恢复原来形状而不受损坏,是一种理想的微切口材料。课题组参照GB/T 16886和ISO10993国际标准对交联聚异丁烯浸提液的细胞相容性及免疫毒性进行了一系列评价,结果证明了该材料浸提液不影响小鼠成纤维细胞L929的增殖能力,对小鼠单核巨噬细胞RAW264.7的增殖和炎症相关蛋白和基因的表达也无显著影响。此外,交联聚异丁烯可通过模制、挤出或浇铸等方法制成所需要的形状,不需要后处理、溶剂萃取等二次加工就可成型。作为新一代的人工晶状体材料,交联聚异丁烯在当今充满挑战的医疗经济环境中将处于有利地位[34-35]。 "
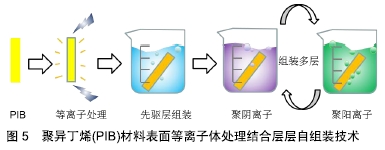
SIBS良好的生物相容性、低廉的制造成本、先进的性能和可微创植入,使其可应用于青光眼和心脏疾病的植入治疗。如SIBS微创青光眼引流管(InnFocus MicroShunt?)在体内植入实验中展现出了优异的生物相容性[7,36-38]。研究表明SIBS 具有优越的稳定性,在兔体内几乎没有任何的异物反应,兔眼植入6个月后的组织学染色结果显示,材料没有引起炎症反应和组织包囊的形成[38]。 经过十几年的不断改进和临床试验,青光眼引流管(InnFocus MicroShuntVR)的1年植入成功率已从43%提高到目前的100%[39]。 2.3.2 血管支架涂层及心脏瓣膜 聚异丁烯基材料还被广泛用作心血管植入物的药物载体[40]。如通过SIBS聚合物体系中苯乙烯的化学改性(羟基苯乙烯或其乙酰化形式),实现紫杉醇的释放调节[41]。著名的商品化紫杉醇洗脱支架TAXUSTM(Boston Scientific Corp.)[36],是将SIBS用作涂层的药物洗脱支架用于抑制血管壁平滑肌细胞增殖,该支架于2004年获得美国食品药品监督管理局批准。作为其最重要的生物医学应用,TAXUSTM支架已植入600多万患者体内用于血管疾病的治疗。此外,还可通过与药物的共价结合或苯乙烯基团衍生物类型的变化调控药物的释放行为[42-43]。 作为新型三叶瓣心脏瓣膜的备选材料,SIBS (QuatromerTM)成功通过了机械和血液相容性测试[44],其可以有效防止体内氧化、酸水解和酶解等生化反应造成的材料降解和裂缝出现。 为避免SIBS在长期负载下变形,内含增强聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯织物的SIBS复合材料也被尝试作为心脏瓣膜替换材料。当增强聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯织物表面覆有SIBS的光滑涂层(25 μm厚度)时,与暴露在血液和组织中的对照组相比,材料的组织反应(细胞浸润和包裹程度)是最小的[45]。此外,SIBS还被用于制备人工主动脉瓣[46]。交联后的SIBS也具有类似的体内稳定性[47]。 2.3.3 其他组织及纳米材料领域的应用探索 人造血管、隆胸等软生物材料可分为聚酯类、氟代聚合物、聚丙烯、有机硅及聚氨酯等种类。与以上常用材料相比,聚异丁烯-聚苯乙烯嵌段聚合物在软组织替代材料领域发展已取得了长足进步,例如作为乳房重建中用到的填充物以及半渗透性的免疫隔离膜[48-49]。 在凝胶制备方面,CEYLAN等[50]采用以氯化硫(S2Cl2)为交联剂、线型聚异丁烯为溶液的交联法成功地制备出了具有大孔径的有机凝胶。DOGU等[51]则利用低温环境制备出均一多孔结构的聚异丁烯有机凝胶,该凝胶具有100 μm×50 μm的空隙结构,实现了快速可逆溶胀。 聚异丁烯基免疫隔离膜主要用于隔离抗体和免疫球蛋白等“攻击分子”,防止产生对外来血小板的免疫反应,在具有橡胶的可塑性和弹性的基础上还具有透明和空隙大小稳定(允许葡萄糖、氨基酸、代谢废物和胰岛素等小分子通过)等诸多优点。实验中包被猪胰岛素源性β细胞的隔离膜可维持长达数月的通透性,使严重高血糖得到了有效控制[49]。 在骨修复材料上,Akron大学肯尼迪学院的研究小组还曾开发过一种聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯-聚异丁烯分子,用以改性加固聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥,以提高材料的断裂韧性。研究结果发现与普通骨水泥相比,含9.2%聚异丁烯(Mn=18 000 g/mol)的骨水泥具有更好的整体性能[10]。 聚异丁烯具有高度疏水性的特点,还被用作纳米聚合物囊泡的疏水段。如聚异丁烯-聚乙二醇两亲性聚合物囊泡是一种极富潜力的纳米封装/传递系统[52]。相比脂质体,该自组装膜厚度可达21 nm,在水溶液中具有更长时间的稳定性和更低的渗透性[53]。 2.4 聚异丁烯未来用于生物医学工程的改进策略 组织工程旨在利用工程化的微环境,通过体外制备或体内再生手段,寻求并重现天然组织中的关键因素[54],是生物材料进入临床实验前的热门研究领域。通过改进材料自身结构和利用组织工程中常用的表面改性等手段,可加快推进聚异丁烯类新型材料从工业向医疗应用的转变。 2.4.1 结构改进 缺少可氧化部分及水解或酶解基团,这是聚异丁烯材料的优势,也是其不足。通过马来酸酐化、胺化、硫醇基化和环氧化等方法可以活化异丁烯的末端双键,提高反应活性[55]。此外,组织工程常用到的可降解吸收材料也可作为聚异丁烯基材料未来发展方向之一。 虽然聚异丁烯在生物体内不可降解,但其共聚物是可以降解的。已有研究人员在这个方向进行了有益的探索。例如,由二钾-聚异丁烯-醇化物遥爪聚合物引发的L-丙交酯阴离子开环聚合得到聚(L-丙交酯)-聚异丁烯-聚(L-丙交酯)三嵌段共聚物,是一种可部分生物降解的热塑性弹性体[56]。通过碳阳离子反应和酶促聚合反应还可与ε-己内酯聚合生成可降解共聚物聚异丁烯-聚己内酯和聚己内酯-聚异丁烯-聚己内酯[57]。这些研究结果都为聚异丁烯作为体内可降解支架材料提供了可能。 2.4.2 表面改性技术 聚合物材料的表面特性,如润湿性、亲-疏水性、表面电荷及分布、表面粗糙度、材料刚性、对血液蛋白吸附/解吸能力、对细胞的黏附等,对植入后包括炎症细胞在内的细胞行为具有深远影响。 聚异丁烯分子链中缺乏活性基团,无法向细胞传递增殖、迁移等相关生物信号,需要对其表面进一步的修饰,以提高其对体内复杂环境的适应性。磷酸胆碱(细胞膜成分)等磷脂可以将极性头部基团定向到局部组织水分子,提高磷脂双层涂层材料的表面亲水性,抑制蛋白吸附并使补体作用最小化。 文献报道即使是临床上广泛使用的SIBS涂层血管支架,也会引起一定程度的异物反应,使得血浆蛋白特别是纤维蛋白原吸附到支架表面并在周围形成纤维包膜[58]。要制备与血液长期接触的材料,进一步的抗凝修饰也是必不可少的。例如磷脂修饰SIBS心脏瓣膜后,通过体外荧光标记观察发现修饰后的血小板黏附数大量减少[59],材料的血液相容性得到极大改善。除磷脂外,还可使用生物抗凝血剂和化学修饰的方法进行材料改性。 肝素是临床上广泛使用的抗凝药物,可使促凝血酶失活并抑制血栓的发展,除了其抗凝血特性外,肝素还被证明可在体外和体内抑制动脉平滑肌细胞增殖和内膜增生。将肝素固定或吸附到血管支架材料上也是人工血管抗凝修饰的经典策略之一。例如,WU等[60]将肝素通过“点击化学”反应固定到带有枝状羟基的聚异丁烯基材料(arb-SIBS-OH)上,作为小口径血管的基质材料,修饰后的材料表面亲水性得到提高(水接触角从83°降至50°),血小板黏附减少,血液相容性得到改善。 通过引入极性基团和功能蛋白等修饰方法也可有效改善聚异丁烯原有的生物惰性[61-62],如将极性基团(胸腺嘧啶、聚乙二醇等)加入线状聚异丁烯中,并采用酶催化酯化反应将功能性聚合物接枝在热塑性弹性体表面,可以有效制备功能性聚合物。功能化的聚异丁烯具有足够的链长和链可动性,能够与热塑性弹性体中的聚异丁烯中间模块缠结,成为热塑性弹性体的有效组成部分。进行表面涂层后,以聚异丁烯基热塑性弹性体的接触角由95°降至79°-83°,亲水性得到改善;纤维蛋白原的吸附有显著差异,在原始的热塑性弹性体上测得其吸附量为256 ng/cm2,聚异丁烯-聚乙二醇-OH涂层表面降至22 ng/cm2,相比之下,硅橡胶的吸附量则高达590 ng/cm2[58]。另一项研究将环丙沙星(一种广谱抗生素)通过氢键和胸腺嘧啶的连接对聚苯乙烯进行了功能化修饰,使环丙沙星有效吸附在了材料表面,提高了枝状聚异丁烯-聚苯乙烯材料的生物相容性[10]。 等离子体处理技术为人们提供了一种改变材料表面特征的同时,不破坏其自身特性的方法[63],非常适合于惰性材料的表面改性。如DU等[64]利用该技术预处理成功在聚异丁烯材料表面接枝了聚合物抗污层。此外,结合聚阳离子和聚阴离子在材料表面层层自组装技术,可进一步调控负载量,见图5。 "
| [1] 魏利娜,甄珍,奚廷斐.生物医用材料及其产业现状[J].生物医学工程研究, 2018,37(1):1-5. [2] 奚廷斐.我国生物医用材料现状和发展趋势[J].中国医疗器械信息, 2013, 19(8):1-5. [3] KUNAL K, PALUCH M, ROLAND CM, et al.Polyisobutylene: a most unusual polymer. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys.2008;46:1390-1399. [4] 韩秀山.我国聚异丁烯的生产及应用概况[J].橡胶科技市场, 2009,7(8): 4-8. [5] WU YX, ZHOU Q, DU J, et al.Controlled/Living Cationic Polymerization of Olefins: System, Process and Application.Acta Polym Sin. 2017;(7):1047-1057. [6] 刘杰.低分子量聚异丁烯环氧化研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2013. [7] PINCHUK L, RISS I, BATLLE JF, et al.The use of poly (styrene-block-isobutylene-block-styrene) as a microshunt to treat glaucoma.Regen Biomate.2016;3(2):1-6. [8] “第三代橡胶”热塑性弹性体特性及应用分析[J].橡塑技术与装备(橡胶),2018,44(5):57-58. [9] 马育红,程斌,杨万泰,等.异丁烯正离子聚合的进展及应用[J].合成橡胶工业,2003,26(1):53-58. [10] COZZENS D, OJHA U, KULKARNI P, et al. Long term in vitro biostability of segmented polyisobutylene-based thermoplastic polyurethanes.J Biomed Mater Res A.2010;95A(3):774-782. [11] PUSKAS JE, CHEN Y, DAHMAN Y, et al. Polyisobutylene-based biomaterials.J Polym Sci A Pol Chem.2004;42:3091-3109. [12] TUROWEC BA, GILLIES ER. Sythesis, properties and degradation of polyisobutylene-polyester graft copolymers.Polym Int.2017;66(1):42-51. [13] TOTH K, NUGAY N, KENNEDY JP. Polyisobutylene-based polyurethanes:VII.structure/property investigations for medical applications.J Polym Sci A Pol Chem.2016;54(4):532-543. [14] LAWRENCE SS, SHINOZAKI DM, PUSKAS JE, et al. Micro-mechanical testing of polyisobutylene-polystyrene block-type thermoplastic elastomers.Rubber Chem Technol.2001;74:601-613. [15] CADIEUX P, WATTERSON JD, HARBOTTLE R, et al. A new biomaterial for application to the urinary tract, and potential for lactobacillus proteins to reduce the risk of device-associated infections.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2002;28(2-3):95-105. [16] PUSKAS JE, CHEN Y, ANTONY P, et al. Atomic force microscopic and encrustation studies of novel prospective polyisobutylene-based thermoplastic elastomeric biomaterials.Polym Adv Technol. 2003; 14(11-12):763-770. [17] ANTONY P, KWON Y, PUSKAS JE, et al.Atomic force microscopic studies of polystyrenepolyisobutylene block copolymers.Eur Polym J. 2003;40:149-157. [18] PUSKAS JE, ANTONY P, FRAY ME, et al.Effect of hard and soft segment composition on the mechanical properties of polyisobutylene- polystyrene thermoplastic elastomeric block copolymers.Eur Polym J. 2003;39:2041-2049. [19] PUSKAS JE, KWON Y, PRINCE A, et al.Synthesis and characterization of novel dendritic(arborescent, hyperbranched) polyisobutylene-polystyrene block copolymers.J Polym Sci Pol Chem. 2005;43:1811-1826. [20] PUSKAS JE, DOS SANTOS L, KASZAS G. Innovation in material science: the chameleon block copolymer.J Polym Sci Pol Chem. 2006;44:6494-6497. [21] PUSKAS JE, KWON Y. Biomacromolecular engineering: desing, synthesis and characterization one-post synthesis of block copolymers of arborescent polyisobutylene and polystyrene.Polym Adv Technol. 2006;17:615-620. [22] FOREMAN EA, PUSKAS JE, KASZAS G. Synthesis and characterization of arborescent (hyperbranched) polyisobutylenes from the 4-(1,2-oxirane-isopropyl) styrene inimer.J Polym Sci Pol Chem.2007;45:5847-5856. [23] 滕雅娣,黄鑫龙.Akron大学橡胶合成研究进展[J].合成橡胶工业, 2015, 38(4):258-262. [24] GÖTZ C, LIM GT, PUSKAS JE, et al.Investigation of structure-property relationships of polyisobutylene based biomaterials: Morphology, thermal, quasi-static tensile and long-term dynamic fatigue behavior.J Mech Behav Biomed Meter.2012;10(6):206-215. [25] PUSKAS JE, SANTOS LMD, ORLOWSKI E. Polyisobutylene-based thermoplastic biorubbers.Rubber Chem Technol.2009;(83):235-246. [26] PUSKAS JE, CHEN Y. Biomedical application of commercial polymers and novel polyisobutylene based thermoplastic elastomers for soft tissue replacement.Biomacromolecules.2004;5(4):1141-1154. [27] PUSKAS JE, FOREMAN-ORLOWSKI EA, LIM GT, et al.A nanostructured carbon-reinforced polyisobutylene-based thermoplastic elastomer.Biomaterials.2010;31(9):2477-2488. [28] FITTIPALDI M, GRACE LR. Lipid-induced degradation in biocompatible poly(Styrene-IsobutyleneStyrene) (SIBS) thermoplastic elastomer.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2017;68:80-87. [29] FRAY ME, PROWANS P, PUSKAS JE, et al. Biocompatibility and Fatigue Properties of Polystyrene-Polyisobutylene-Polystyrene, an Emerging Thermoplastic Elastomeric Biomaterial. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7:844-850. [30] VENKATRAMAN S, GALE R. Skin adhesives and skin adhesion. Biomaterials.1998;19:1119-1136. [31] KEKEC NC, AKOLPOGLU MB, BOZUYUK U, et al.Calcification resistance of polyisobutylene and polyisobutylene-based materials.Polym Advan Technol.2019:1-11. [32] 杨舒逸,金怀洋,高山俊,等.热塑性聚氨酯弹性体改性研究进展[J].工程塑料应用,2018,46(6):138-142. [33] Y•周, L•平楚克.用于生物医学用途的交联聚烯烃及其制造方法: CN 101918461 B[P]. 2015-09-16. [34] PINCHUK L, BATLLE JF, RISS I, et al.The use of polyisobutylene polymers for glaucoma drainage tubes and intraocular lenses.4th International Conference on Clinical & Experimental Ophthalmology,2014. [35] 杨愔,谢继红.有晶状体眼后房人工晶体:CN 205831963 U[P].2016-12-28. [36] PINCHUK L, WILSON GJ, BARRY JJ, et al. Medical applications of poly(styrene-block- isobutylene -block-styrene) ("SIBS"). Biomaterials. 2008;(29):448-460. [37] ARRIETA EA, ALY M, PARRISH R, et al.Clinicopathologic Correlations of Poly-(styrene-b-isobutylene-b-styrene) Glaucoma Drainage Devices of Different Internal Diameters in Rabbits.Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging.2011;42(4):338-345. [38] ACOSTA AC, ESPANA EM, YAMAMOTO H, et al.A newly designed glaucoma drainage implant made of poly (styrene-b-isobutylene-b- styrene): biocompatibility and function in normal rabbit eyes. Arch Ophthalmol.2006;124(12):1742-1749. [39] PINCHUK L, RISS I, BATLLE JF, et al.The development of a micro-shunt made from poly(styrene-block-isobutylene-block-styrene) to treat glaucoma.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2017;105(1):211-221. [40] REN K, ZHANG M, HE J, et al.Preparation of polymeric prodrug paclitaxel-poly(lactic acid)-b-polyisobutylene and its application in coatings of drug eluting stent. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(21): 11263-11271. [41] SIPOS L, SOM A, FAUST R.Controlled delivery of paclitaxel from stent coatings using poly(hydroxystyrene-b-isobutylene-b-hydroxystyrene) and its acetylated derivative.Biomacromolecules.2005;6:2570-2582. [42] CHO JC, CHENG G, FENG D, et al Synthesis, characterization, properties, and drug release of poly(alkyl methacrylate-b-isobutylene- b-alkyl methacrylate).Biomacromolecules. 2006;7:2997-3007. [43] TRANT JF, MCEACHRAN M, SRAN I, et al.Covalent polyisobutylene- paclitaxel conjugates for controlled release from potential vascular stent coatings.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(26):14506-14517. [44] GALLOCHER SL, AGUIRRE AF, KASYANOV V, et al.A novel polymer for potential use in a trileaflet heart valve.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2006;79(2):325-334. [45] WANG Q, MCGORON AJ, PINCHUK L, et al.A novel small animal model for biocompatibility assessment of polymeric materials for use in prosthetic heart valves.J Biomed Mater Res A.2009;(2):442-453. [46] CLAIBORNE TE, GIRDHAR G, GALLOCHER-LOWE S, et al. Thrombogenic potential of innovia polymer valves versus Carpentier-Edwards Perimount Magna aortic bioprosthetic valves. ASAIO J.2011:26-31. [47] SHERIFF J, CLAIBORNE TE, TRAN PL, et al.Physical characterization and platelet interactions under shear flows of a novel thermoset polyisobutylene-based co-polymer.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(39):22058-22066. [48] LIM GT, VALENTE SA, HART-SPICER CR, et al.New biomaterial as a promising alternative to silicone breast implants.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2013;21:47-56. [49] KENNEDY JP.Designed rubbery biomaterials.Macromol Symp. 2001; 175:127-131. [50] CEYLAN D, OKAY O.Macroporous polyisobutylene gels: a novel tough organogel with superfast responsivity.Macromolecules.2007;40: 8742-8749. [51] DOGU S, OKAY O.Tough organogels based on polyisobutylene with aligned porous structures[J]. Polymer.2008;49:4626-4634. [52] BURKHARDT M, RUPPEL M, TEA S, et al. Water-soluble interpolyelectrolyte complexes of polyisobutylene-block-poly (methacrylic acid) micelles formation and properties.Langmuir.2008;24: 1769-1777. [53] ASKES SHC, BOSSERT N, BUSSMANN J, et al.Dynamics of dual-fluorescent polymersomes with durable integrity in living cancer cells and zebrafish embryos.Biomaterials.2018;168:54-63. [54] BAKER BM, HANDORF AM, IONESCU LC, et al.New direcion in nanofibrous scaffolds for soft tissue engineering and regeneration. Expert Rev Med Devices.2009;6(5):515-532. [55] PUSKAS JE, SEN S.Synthesis of Biodegradable Polyisobutylene Disulfides by Living Reversible Recombination Radical Polymerization.Macromolecules.2017;50(7):2615-2624. [56] SIPOS L, ZSUGA M, DEAK G.Synthesis of poly (L-lactide)-block- polyisobutylene-block- poly(L-lactide), a new biodegradable thermoplastic elastomer.Macromol Rapid Comm. 1995;16:935-940. [57] CASTANO M, ALVAREZ A, BECKER ML, et al.Synthesis of polyisobutylene-polycaprolactone block copolymers using enzyme catalysis.Express Polym Lett.2016;10(8):693-700. [58] ALBARRAN AA, ROSENTHAL-KIM EQ, KANTOR J, et al. Stimuli- responsive antifouling polyisobutylene-based biomaterials via modular surface functionalization.J Polym Sci A Polym Chem. 2017;55(10): 1742-1749. [59] DURAISWAMY N, CHOKSI TD, PINCHUK L, et al. A Phospholipid- modified Polystyrene-Polyisobutylene- Polystyrene (SIBS) Triblock Polymer for Enhanced Hemocompatibility and Potential Use in Artificial Heart Valves.J Biomater Appl. 2008;23(4):367-379. [60] WU Y, LI K, XIANG D, et al.Surface immobilization of heparin on functional polyisobutylene-based thermoplastic elastomer as a potential artificial vascular graft.Appl Surf Sci.2018;445:8-15. [61] NOOR M, DWORECK T, SCHENK A, et al.Polymersome surface decoration by an EGFP fusion protein employing Cecropin A as peptide “anchor”.J Biotechnol.2012;(157):31-37. [62] CADIEUX P, WATTERSON JD, DENSTEDT J, et al.Potential application of polyisobutylene-polystyrene and a Lactobacillus protein to reduce the risk of device-associated urinary tract infections.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2003;28(2-3):95-105. [63] TSENG DY, EDELMAN E.Effects of amide and amine plasma-treated ePTFE vascular grafts on endothelial cell lining in an artificial circulatory system.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 1998;42(2):188-198. [64] DU Y, LI C, JIN J, et al. Surface modification of polyisobutylene via grafting amino acid-based poly (acryloyl-6-aminocaproic acid) as multifunctional material.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2018;(161):73-82. [65] LIM GT, PUSKAS JE, RENEKER DH, et al.Highly hydrophobic electrospun fiber mats from polyisobutylene-based thermoplastic elastomers.Biomacromolecules.2011;12:1795-1799. |
| [1] | Yang Feng, Zhao Qian, Zhang Shixuan, Zhao Tienan, Feng Bo. Effectiveness and safety of rapamycin combined with CD133 antibody stent in preventing vascular restenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 579-584. |
| [2] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [3] | Yun Xiao, Ding Tong, Yang Weiqiang, Guo Xinjun. Nano hydroxyapatite/chitosan scaffold loaded with Akebia saponin D in bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(27): 4293-4299. |
| [4] | Hu Qiuyu, Yang Long, Yang Yong, Song Shenchao. Aligned poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/type I collagen fibers promote tendon-bone healing after anterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(27): 4314-4319. |
| [5] | Liu Liang, Hu Gaoquan, Wei Zhao, Chen Lin, Hong Feng. Potential of bacterial nanocellulose/polydopamine composite tubes as small-diameter artificial blood vessel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3535-3542. |
| [6] | Guo Yangyan, Yu Zhengwen, Zhang Jian. Research hotspots of magnesium alloy biomaterials in an in vivo animal [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3556-3565. |
| [7] | Jin Herong, Cui Jingbin, Shao Cang. Materials of interbody fusion cage: advantages and focus of clinical application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3592-3597. |
| [8] | Li Duchenhui, Tian Ai, Tang Zhenglong. Angiogenesis induced by bone bioscaffold materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3602-3608. |
| [9] | Yan Kaiquan, Liu Huishan, Wang Xiaowei, Wu Xiaoqin, Zhang Weibo, Li Xiangyang, Wang Yinlong, Chen Jialong. Epigallocatechin gallate/hexanediamine coating grafted chlorhexidine improves the antibacterial properties of implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3332-3337. |
| [10] | Feng Le, Qiu Peng, Liu Min, Zhou Hui. Characterization of chitosan-modified polyetheretherketone and its effect on MC3T3-E1 cell adhesion and proliferation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3351-3356. |
| [11] | Zhou Shicheng, Han Hongguang, Ji Fang, Xu Liying, Zhang Xiaohui, Sun Chang. Effect and histocompatibility of expended polytetrafluoroethylene in modified Blalock-Taussig shunt [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3394-3400. |
| [12] | Gao Feifei, Du Bin, Liu Xin, Chen Hao, Chen Yang, Hou Wei. Advantage of mesoporous materials in bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3401-3409. |
| [13] | Yuan Long, Li Sen, Bian Jichao, Li Wanxiang, Wang Guodong. Reasonable choice and application of bio-ink sterilization technology for 3D bioprinting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2914-2921. |
| [14] | Ma Ziyu, Zhang Yuntao, Ma Xiangrui, Qiao Luhui, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Surface treatment of iron oxide nanoparticles in bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2570-2575. |
| [15] | Che Zhenjia, Zhu Zhengqing, Zhu Liwei, Li Youbin, Zhu Chenyi, Huang Lanfeng. Effects of biochemical modification of titanium implant surface on the osseointegration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2576-2583. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

