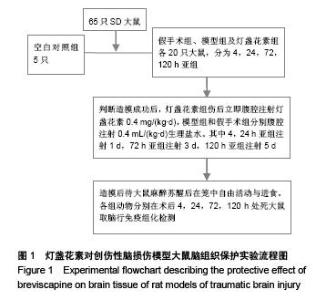
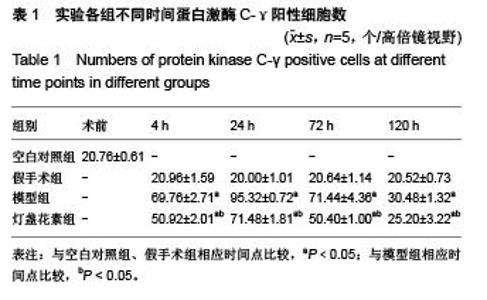
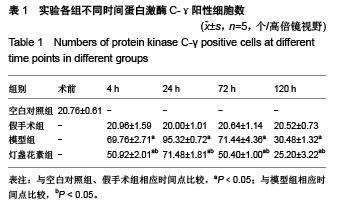
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (49): 7926-7931.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.49.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of breviscapine on protein kinase C-gamma expression in brain tissue of rat models of traumatic brain injury
Yin Yan-qing, Fang Qi, Liao Zhuang-bin, Lin Heng, Huang Zi-xiong, Liang Yuan-sheng, Xu Cheng-jie
- Department of Neurosurgery, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical College, Zhanjiang 524001, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2015-09-07Online:2015-11-30Published:2015-11-30 -
Contact:Xu Cheng-jie, Chief physician, Department of Neurosurgery, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical College, Zhanjiang 524001, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Yin Yan-qing, Master, Attending physician, Lecturer, Department of Neurosurgery, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical College, Zhanjiang 524001, Guangdong Province, China Fang Qi, Chief physician, Department of Neurosurgery, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical College, Zhanjiang 524001, Guangdong Province, China Liao Zhuang-bin, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Neurosurgery, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical College, Zhanjiang 524001, Guangdong Province, China Yin Yan-qing, Fang Qi and Liao Zhuang-bin contributed equally to this study. -
Supported by:a grant from Scientific and Technology Plan Project of Zhanjiang City of China, No. 2013B01297/2011C3106021
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yin Yan-qing, Fang Qi, Liao Zhuang-bin, Lin Heng, Huang Zi-xiong, Liang Yuan-sheng, Xu Cheng-jie. Effect of breviscapine on protein kinase C-gamma expression in brain tissue of rat models of traumatic brain injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(49): 7926-7931.
share this article
| [1] Steinberg SF. Structural basis of protein kinase C isoform function. Physiol Rev. 2008;88(4):1341-1378.[2] Selvatici R, Falzarano S, Franceschetti L, et al. Differential activation of protein kinase C isoforms following chemical ischemia in rat cerebral cortex slices. Neurochem Int. 2006; 49(8):729-736.[3] Leenders AG, Sheng ZH. Modulation of neurotransmitter release by the second messenger-activated protein kinases: implications for presynaptic plasticity. Pharmacol Ther. 2005; 105(1):69-84.[4] Mellor H, Parker PJ. The extended protein kinase C superfamily. Biochem J. 1998;332 ( Pt 2):281-292.[5] 徐光,张礼萍,沈慧芬,等. 野黄苓甙元及其类似物对蛋白激酶C的抑制作用[J].上海医科大学学报, 1993, 20(3):187-191.[6] Newton AC. Protein kinase C. IUBMB Life. 2008;60(11): 765-768.[7] Koponen S, Goldsteins G, Keinänen R, et al. Induction of protein kinase Cdelta subspecies in neurons and microglia after transient global brain ischemia. Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20(1):93-102.[8] Kurkinen K, Keinänen R, Li W, et al. Preconditioning with spreading depression activates specifically protein kinase Cdelta. Neuroreport. 2001;12(2):269-273.[9] Wang J, Bright R, Mochly-Rosen D, et al. Cell-specific role for epsilon- and betaI-protein kinase C isozymes in protecting cortical neurons and astrocytes from ischemia-like injury. Neuropharmacology. 2004;47(1):136-145.[10] Ni TS, Wu SX, Li YQ. Localization of protein kinase Cγ subunit in rat nervous system. Acta Anatomica Sinica. 2002; 33(2):113-117.[11] Hughes AS, Averill S, King VR, et al. Neurochemical characterization of neuronal populations expressing protein kinase C gamma isoform in the spinal cord and gracile nucleus of the rat. Neuroscience. 2008 2;153(2):507-517.[12] Chou WH, Messing RO. Protein kinase C isozymes in stroke. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2005;15(2):47-51.[13] Aronowski J, Labiche LA. Perspectives on reperfusion-induced damage in rodent models of experimental focal ischemia and role of gamma-protein kinase C. ILAR J. 2003;44(2):105-109.[14] Seki T, Takahashi H, Adachi N, et al. Aggregate formation of mutant protein kinase C gamma found in spinocerebellar ataxia type 14 impairs ubiquitin-proteasome system and induces endoplasmic reticulum stress. Eur J Neurosci. 2007; 26(11):3126-3140.[15] Suen PC, Wu K, Xu JL, et al. NMDA receptor subunits in the postsynaptic density of rat brain: expression and phosphorylation by endogenous protein kinases. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1998;59(2):215-228.[16] Hall KE, Browning MD, Dudek EM, et al. Enhancement of high threshold calcium currents in rat primary afferent neurons by constitutively active protein kinase C. J Neurosci. 1995;15(9):6069-6076.[17] 卢步峰, 鲁友明, 黄治森. 蛋白激酶C对大鼠缺血海马突触体谷氨酸摄取的调控作用[J].生物化学杂志,1994,10(3):371-374.[18] Lipton P. Ischemic cell death in brain neurons. Physiol Rev. 1999;79(4):1431-1568.[19] Joó F, Tósaki A, Oláh Z, et al. Inhibition by H-7 of the protein kinase C prevents formation of brain edema in Sprague-Dawley CFY rats. Brain Res. 1989;490(1):141-143.[20] 帅杰,董为伟. PKC抑制剂灯盏花素对缺血/再灌流脑损害的作用研究[J]. 中国药理学通报,1998,14(1):75-77.[21] Yang K, Taft WC, Dixon CE, et al. Endogenous phosphorylation of a 61,000 dalton hippocampal protein increases following traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 1994;11(5):523-532.[22] Sun FY, Faden AI. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors mediate post-traumatic increases of protein kinase C in rat brain. Brain Res. 1994;661(1-2):63-69.[23] 陈康宁,董为伟,张帆. 蛋白激酶C激动剂PMA对培养神经元胞体内游离钙的影响[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 1997, 19(8):408-410.[24] Arundine M, Tymianski M. Molecular mechanisms of glutamate-dependent neurodegeneration in ischemia and traumatic brain injury. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004;61(6):657-668.[25] Liu XW, Ma C, Xing RX, et al. The calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitor KN-93 protects rat cerebral cortical neurons from N-methyl-D-aspartic acid-induced injury.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8 (2): 111-120.[26] Manev H, Costa E, Wroblewski JT, et al. Abusive stimulation of excitatory amino acid receptors: a strategy to limit neurotoxicity. ASEB J. 1990;4(10):2789-2797.[27] Choi DW. Excitotoxic cell death. J Neurobiol. 1992;23(9): 1261-1276.[28] Schaphorst KL, Pavalko FM, Patterson CE, et al. Thrombin-mediated focal adhesion plaque reorganization in endothelium: role of protein phosphorylation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997;17(4):443-455.[29] Garcia JG, Verin AD, Schaphorst KL. Regulation of thrombin-mediated endothelial cell contraction and permeability. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1996;22(4):309-315.[30] 陈康宁,董为伟.灯盏花对脑缺血神经元凋亡的防治作用[J].中国临床神经科学,2000,8(1):5-7.[31] 余刚,罗勇,彭国光,等. 蛋白激酶C同工酶抑制剂对缺血/再灌注大鼠脑保护作用的实验研究[J].卒中与神经疾病, 2002, 9(6): 321-324.[32] 李俊彦,王东艳,杨金伟,等.灯盏花素干预体外培养大鼠脑皮质神经元的存活与生长[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(20): 3196-3201.[33] 胡嘉航,陈海军,刘海洋,等.灯盏花素对大鼠出血性脑损伤的保护作用[J].神经解剖学杂志,2013,29(2):209-213.[34] 霍永强,谭源福.一种改进的落体脑创伤模型[J].广西医科大学学报,2007,24(2):217-219.[35] Cernak I. Animal models of head trauma. NeuroRx. 2005;2(3): 410-422.[36] Arrieta-Cruz I, Pfaff DW, Shelley DN. Mouse model of diffuse brain damage following anoxia, evaluated by a new assay of generalized arousal. Exp Neurol. 2007;205(2):449-460.[37] Vakili A, Kataoka H, Plesnila N. Role of arginine vasopressin V1 and V2 receptors for brain damage after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005;25(8): 1012-1019.[38] 梁楠,王仙凤,张晓.颅脑损伤动物模型的制备及评价[J].创伤外科杂志,2008,10(4):376-378. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||