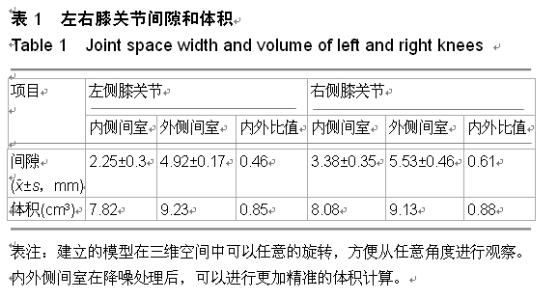
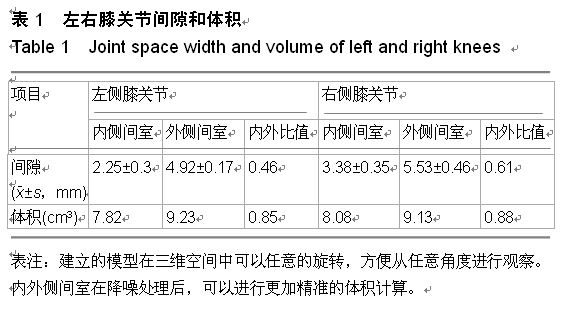
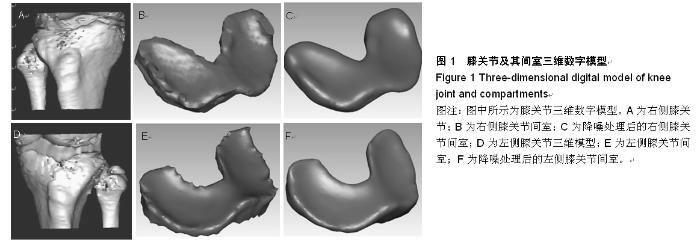
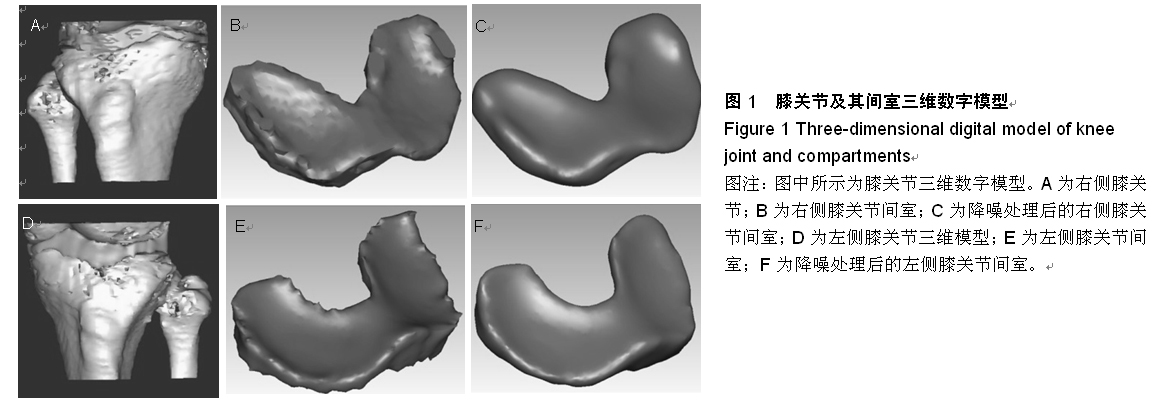
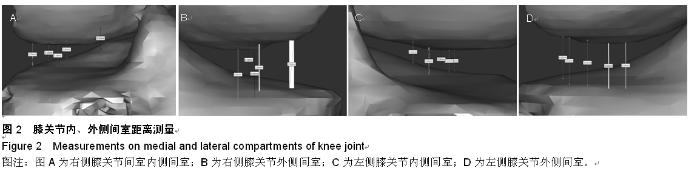
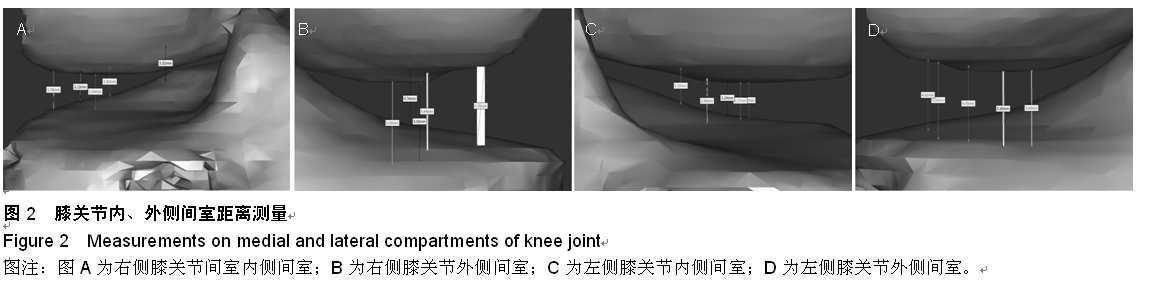
| [1] 邝适存,郭霞.肌肉骨骼系统基础生物力学(译本)[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2008:117.
[2] McAlindon TE, Bannuru RR. Osteoarthritis: is viscosupplementation really so unsafe for knee OA? Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012; 8:635-636.
[3] Berenbaum F, Grifka J, Cazzaniga S, et al. A randomised, double-blind, controlled trial comparing two intra-articular hyaluronic acid preparations differing by their molecular weight in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012; 71:1454-1460.
[4] Maheu E, Zaim M, Appelboom T, et al. Comparative eff icacy and safety of two different molecular weight (MW) hyaluronans F60027 and Hylan G-F20 in symptomatic osteoarthritis of the knee (KOA): results of a non inferiority, prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011; 29:527-535.
[5] Mazzuca SA, Brandt KD. Is knee radiography useful for studying the efficacy of a disease-modifying osteoarthritis drug in humans? Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2003;29(4): 819-830.
[6] Mazzuca SA, Brandt KD, Buckwalter KA, et al. Pitfalls in the accurate measurement of joint space narrowing in semiflexed, anteroposterior radiographic imaging of the knee. Arthritis Rheum.2004;50(8):2508-2515.
[7] Emrani PS, Katz JN, Kessler CL, et al. Joint space narrowing and Kellgren-Lawrence progression in knee osteoarthritis: an analytic literature synthesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16(8):873-882.
[8] Rutjes AW, Jüni P, da Costa BR, et al. Viscosupplementation for osteoarthritis of the knee: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157:180-191.
[9] Strand V, Baraf HS, Lavin PT, et al. A multicenter, randomized controlled trial comparing a single intraarticular injection of Gel-200, a new cross-linked formulation of hyaluronic acid, to phosphate buffered saline for treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2012; 20:350-356.
[10] McAlindon TE, Bannuru RR, Sullivan MC, et al. OARSI guidelines for the nonsurgical management of knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014; 22:363-388.
[11] Kijowski R, Blankenbaker DG, Stanton PT, et al. Radiographic findings of osteoarthritis versus arthroscopic findings of articular cartilage degeneration in the tibiofemoral joint. Radiology. 2006; 239(3):818-824.
[12] Beattie KA, Duryea J, Pui M, et al. Minimum joint space width and tibial cartilage morphology in the knees of healthy individuals: a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2008;9:119.
[13] Schiphof D, Boers M, Bierma-Zeinstra SM. Differences in descriptions of Kellgren and Lawrence grades of knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(7):1034-1036.
[14] Guermazi A, Hunter DJ, Roemer FW. Plain radiography and magnetic resonance imaging diagnostics in osteoarthritis: validated staging and scoring. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91 Suppl:154-162.
[15] Roemer FW, Crema MD, Trattnig S, et al. Advances in imaging of osteoarthritis and cartilage. Radiology. 2011; 260(2): 332-354.
[16] 吴涛,王卉. Mimics三维重建模型在人体解剖学学习中的应用[J]. 中国医学教育技术,2012,26(6):664-667.
[17] 张美超,赵卫东,原林,等.建立数字化虚拟中国男性一号膝关节的有限元模型[J].第一军医大学学报,2003,23(6):527-529.
[18] 李鉴轶,赵卫东,余正红,等. 膝关节关节软骨的三维构建[J].解剖学杂志, 2007, 30(6):695-697.
[19] 向湘松,李峰,蒲丹,等. Mimics软件在测量股骨远端旋转力线的应用[J].临床医学工程, 2010,17(2):48-50.
[20] 肖建林,刘潼,秦彦国,等. 基于CT图像三维重建测量股骨外翻角[J].中国实验诊断学,2011,15(12):2041-2043.
[21] 邱锋,马向阳,杨进城.应用Mimics测量脊髓容积[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2013,23(11):1043-1045.
[22] 王亦进,郭新全,陈敬武,等.健康成人与老年性骨关节炎病人卧、立位膝关节内、外侧间隙宽度的测量研究[J].中国临床医学影像杂志,2000,11(5):329.
[23] Kalinosky B, Sabol JM, Piacsek K, et al. Quantifying the tibiofemoral joint space using x-ray tomosynthesis. Med Phys. 2011;38(12):6672-6682.
[24] Hochberg MC, Altman RD, April KT, et al. American College of Rheumatology 2012 recommendations for the use of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapies in osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012; 64:465-674.
[25] Jevsevar DS. Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: evidence-based guideline, 2nd edition. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2013;21:571-576.
[26] 杨立伟,张礼荣,王冬青,等.3.0 T MRI与X线平片上分别测量膝关节间隙宽度的对比研究[J].临床放射学杂志,2013,32(7): 1003-1007.
[27] Crema MD, Roemer FW, Marra MD, et al. Articular cartilage in the knee: current MR imaging techniques and applications in clinical practice and research. Radiographics. 2011;31:37-61.
[28] Wang Y, Hall S, Hanna F, et al. Effects of Hylan G-F 20 supplementation on cartilage preservation detected by magnetic resonance imaging in osteoarthritis of the knee: a two-year single-blind clinical trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:195.
[29] 陈利军,刘文刚,叶振中,等.下肢力线变化与胫股关节退行性变的相关性[J].中医正骨, 2003,15(10):9-10.
[30] Hellio Le Graverand MP, Mazzuca S, Duryea J, et al. Radiographic-based grading methods and radiographic measurement of joint space width in osteoarthritis. Radiol Clin N Am. 2009;47:567-579.
[31] Duryea J, Neumann G, Niu J, et al. Comparison of radiographic joint space width with magnetic resonance imaging cartilage morphometry: analysis of longitudinal data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010;62:932-937.
[32] Guermazi A, Hunter DJ, Roemer FW. Plain radiography and magnetic resonance imaging diagnostics in osteoarthritis: validated staging and scoring. Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:54-62.
[33] Conaghan PG, Hunter DJ, Maillefert JF, et al. Summary and recommendations of the OARSI FDA osteoarthritis Assessment of Structural Change Working Group. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19:606-610.
[34] Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012; 380:2197-2223.
[35] Hunter DJ.Viscosupplementation for osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(11):1040-1047.
[36] Runhaar J, van Middelkoop M, Reijman M, et al. Malalignment: a possible target for prevention of incident knee osteoarthritis in overweight and obese women. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53(9):1618-1624.
[37] Hinman RS, Bennell KL.Advances in insoles and shoes for knee osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2009;21(2): 164-170.
|