Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (29): 4715-4720.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.29.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
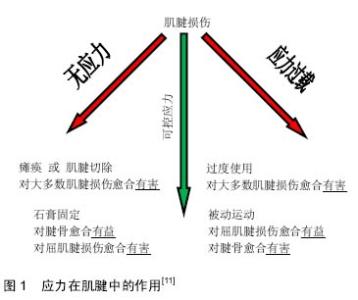
Stress in tendon healing
Guo Wen, Wang Ji-hong, Wen Shu-zheng, Xu Peng-cheng
- Department of Hand and Foot Microsurgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2015-07-09Published:2015-07-09 -
Contact:Wen Shu-zheng, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Hand and Foot Microsurgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Guo Wen, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Hand and Foot Microsurgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81441117
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Wen, Wang Ji-hong, Wen Shu-zheng, Xu Peng-cheng. Stress in tendon healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(29): 4715-4720.
share this article
| [1] Praemer A, Furner S, Rice D. Musculoskeletal Condition in the United States. Parke Ridge, IL: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 1999. [2] Katzel EB, Wolenski M, Loiselle AE, et al. Impact of Smad3 loss of function on scarring and adhesion formation during tendon healing. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(5):684-693. [3] Wong JK, Lui YH, Kapacee Z, et al. The cellular biology of flexor tendon adhesion formation: an old problem in a new paradigm. Am J Pathol. 2009;175(5):1938-1951. [4] Wang JH. Mechanobiology of tendon. J Biomech. 2006; 39(9):1563-1582. [5] James R, Kesturu G, Balian G, et al. Tendon: biology, biomechanics, repair, growth factors, and evolving treatment options. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33(1):102-112. [6] Lindsay WK, Birch JR. The fibroblast in flexor tendon healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1964;34:223-232. [7] Garner WL, McDonald JA, Koo M, et al. Identification of the collagen-producing cells in healing flexor tendons. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1989;83(5):875-879. [8] Fenwick SA, Hazleman BL, Riley GP. The vasculature and its role in the damaged and healing tendon. Arthritis Res. 2002; 4(4):252-260. [9] Liu SH, Yang RS, al-Shaikh R, et al. Collagen in tendon, ligament, and bone healing. A current review. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1995;(318):265-278. [10] Woon CY, Kraus A, Raghavan SS, et al. Three-dimensional- construct bioreactor conditioning in human tendon tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(19-20):2561-2572. [11] Killian ML, Cavinatto L, Galatz LM, et al. The role of mechanobiology in tendon healing. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(2):228-237. [12] Rui YF, Lui PP, Li G, et al. Isolation and characterization of multipotent rat tendon-derived stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(5):1549-1558. [13] Jelinsky SA, Lake SP, Archambault JM, et al. Gene expression in rat supraspinatus tendon recovers from overuse with rest. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(7): 1612-1617. [14] Wang JH, Li Z, Yang G, et al. Repetitively stretched tendon fibroblasts produce inflammatory mediators. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(422):243-250. [15] Eliasson P, Andersson T, Aspenberg P. Rat Achilles tendon healing: mechanical loading and gene expression. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009;107(2):399-407. [16] Rodeo SA, Arnoczky SP, Torzilli PA, et al. Tendon-healing in a bone tunnel. A biomechanical and histological study in the dog. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(12):1795-1803. [17] Arnoczky SP, Tian T, Lavagnino M, et al. Activation of stress-activated protein kinases (SAPK) in tendon cells following cyclic strain: the effects of strain frequency, strain magnitude, and cytosolic calcium. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(5): 947-952. [18] Docheva D, Müller SA, Majewski M, et al. Biologics for tendon repair. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;84:222-239. [19] Thornton GM, Hart DA. The interface of mechanical loading and biological variables as they pertain to the development of tendinosis. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2011;11(2): 94-105. [20] Evans CE, Trail IA. An in vitro comparison of human flexor and extensor tendon cells. J Hand Surg Br. 2001;26(4):307-313. [21] Li Z, Yang G, Khan M, et al. Inflammatory response of human tendon fibroblasts to cyclic mechanical stretching. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(2):435-440. [22] Miller BF, Olesen JL, Hansen M, et al. Coordinated collagen and muscle protein synthesis in human patella tendon and quadriceps muscle after exercise. J Physiol. 2005;567(Pt 3): 1021-1033. [23] Szczodry M, Zhang J, Lim C, et al. Treadmill running exercise results in the presence of numerous myofibroblasts in mouse patellar tendons. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(10):1373-1378. [24] Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, et al. Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3(5):349-363. [25] Cilli F, Khan M, Fu F, et al. Prostaglandin E2 affects proliferation and collagen synthesis by human patellar tendon fibroblasts. Clin J Sport Med. 2004;14(4):232-236. [26] Sun YL, Thoreson AR, Cha SS, et al. Temporal response of canine flexor tendon to limb suspension. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010;109(6):1762-1768. [27] Agarwal S, Long P, Seyedain A, et al. A central role for the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in anti-inflammatory and proinflammatory actions of mechanical strain. FASEB J. 2003; 17(8):899-901. [28] Barkhausen T, van Griensven M, Zeichen J, et al. Modulation of cell functions of human tendon fibroblasts by different repetitive cyclic mechanical stress patterns. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2003;55(2-3):153-158. [29] Waggett AD, Benjamin M, Ralphs JR. Connexin 32 and 43 gap junctions differentially modulate tenocyte response to cyclic mechanical load. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006;85(11):1145-1154. [30] Koshima H, Kondo S, Mishima S, et al. Expression of interleukin-1beta, cyclooxygenase-2, and prostaglandin E2 in a rotator cuff tear in rabbits. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(1):92-97. [31] Tsuzaki M, Guyton G, Garrett W, et al. IL-1 beta induces COX2, MMP-1, -3 and -13, ADAMTS-4, IL-1 beta and IL-6 in human tendon cells. J Orthop Res. 2003;21(2):256-264. [32] Griffin M, Hindocha S, Jordan D, et al. An overview of the management of flexor tendon injuries. Open Orthop J. 2012;6:28-35. [33] Thomopoulos S, Williams GR, Soslowsky LJ. Tendon to bone healing: differences in biomechanical, structural, and compositional properties due to a range of activity levels. J Biomech Eng. 2003;125(1):106-113. [34] Gimbel JA, Van Kleunen JP, Williams GR, et al. Long durations of immobilization in the rat result in enhanced mechanical properties of the healing supraspinatus tendon insertion site. J Biomech Eng. 2007;129(3):400-404. [35] Grangeon M, Guillot A, Sancho PO, et al. Rehabilitation of the elbow extension with motor imagery in a patient with quadriplegia after tendon transfer. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010;91(7):1143-1146. [36] Kawamura S, Ying L, Kim HJ, et al. Macrophages accumulate in the early phase of tendon-bone healing. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(6):1425-1432. [37] James R, Kesturu G, Balian G, et al. Tendon: biology, biomechanics, repair, growth factors, and evolving treatment options. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33(1):102-112. [38] Viidik A. The effect of training on the tensile strength of isolated rabbit tendons. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1967; 1(2):141-147. [39] Woo SL, Ritter MA, Amiel D, et al. The biomechanical and biochemical properties of swine tendons--long term effects of exercise on the digital extensors. Connect Tissue Res. 1980; 7(3):177-183. [40] Woo SL, Gomez MA, Amiel D, et al. The effects of exercise on the biomechanical and biochemical properties of swine digital flexor tendons. J Biomech Eng. 1981;103(1):51-56. [41] Zhang J, Wang JH. The effects of mechanical loading on tendons--an in vivo and in vitro model study. PLoS One. 2013; 8(8):e71740. [42] Gelberman RH, Menon J, Gonsalves M, et al. The effects of mobilization on the vascularization of healing flexor tendons in dogs. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980;(153):283-289. [43] Düzgün I, Baltac? G, Atay OA. Comparison of slow and accelerated rehabilitation protocol after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: pain and functional activity. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2011;45(1):23-33. [44] Khanna A, Gougoulias N, Maffulli N. Modalities in prevention of flexor tendon adhesion in the hand: what have we achieved so far? Acta Orthop Belg. 2009;75(4):433-444. [45] Forslund C. BMP treatment for improving tendon repair. Studies on rat and rabbit Achilles tendons. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 2003;74(308):I, 1-30. [46] Groth GN. Pyramid of progressive force exercises to the injured flexor tendon. J Hand Ther. 2004;17(1):31-42. [47] Peltz CD, Dourte LM, Kuntz AF, et al. The effect of postoperative passive motion on rotator cuff healing in a rat model. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(10):2421-2429. [48] Silva MJ, Brodt MD, Boyer MI, et al. Effects of increased in vivo excursion on digital range of motion and tendon strength following flexor tendon repair. J Orthop Res. 1999;17(5):777- 783. [49] Hettrich CM, Rodeo SA, Hannafin JA, et al. The effect of muscle paralysis using Botox on the healing of tendon to bone in a rat model. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(5): 688-697. [50] Lui PP, Maffulli N, Rolf C, et al. What are the validated animal models for tendinopathy? Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2011; 21(1):3-17. [51] Warden SJ. Development and use of animal models to advance tendinopathy research. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009;14:4588-4597. [52] Sereysky JB, Flatow EL, Andarawis-Puri N. Musculoskeletal regeneration and its implications for the treatment of tendinopathy. Int J Exp Pathol. 2013;94(4):293-303. [53] Alfredson H, Lorentzon R. Chronic tendon pain: no signs of chemical inflammation but high concentrations of the neurotransmitter glutamate. Implications for treatment? Curr Drug Targets. 2002;3(1):43-54. [54] Maganaris CN, Narici MV, Almekinders LC, et al. Biomechanics and pathophysiology of overuse tendon injuries: ideas on insertional tendinopathy. Sports Med. 2004; 34(14):1005-1017. [55] Cook JL, Purdam CR. Is tendon pathology a continuum? A pathology model to explain the clinical presentation of load-induced tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med. 2009;43(6): 409-416. [56] Tan SC, Chan O. Achilles and patellar tendinopathy: current understanding of pathophysiology and management. Disabil Rehabil. 2008;30(20-22):1608-1615. [57] EFSA GMO Panel Working Group on Animal Feeding Trials. Safety and nutritional assessment of GM plants and derived food and feed: the role of animal feeding trials. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008;46 Suppl 1:S2-70. [58] 杨建军,蒋佳.生物力学在肌腱愈合中作用的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(12):1158-1160. [59] Wang JH, Guo Q, Li B. Tendon biomechanics and mechanobiology--a minireview of basic concepts and recent advancements. J Hand Ther. 2012;25(2):133-140; quiz 141. |
| [1] | Li Shuwen, Yang Zhe, Yin Heping, Wu Yimin, Bai Ming, Du Zhicai, Wang Yupeng, Meng Gedong. Preserving ligamentum flavum for preventing dural adhesions after lumbar surgery in model rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 416-420. |
| [2] | Yang Lili, Bian Yaoyao, Zhao Min, Wang Yetong, Tang Shengjin, Li Wenlin, Zeng Li. Barrier materials for postoperative abdonimal adhesion: biological characteristics, merits and demerits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 272-277. |
| [3] | Gao Ping, Cheng Lin, Chen Bin, Li Ruizhi, Li Xin, Shi Mengrou, Li Guangyuan, Cheng Peng, Li Dongfeng, Yu Huan, Wang Xiaohui. Biosafety of medical injectable carboxymethyl glycosaminoglycan anti-adhesion gel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(10): 1570-1574. |
| [4] | Wang Wei. Exercise-induced Achilles tendon rupture: etiology, treatment, and evaluation of its mechanical properties and healing degree [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(8): 1300-1305. |
| [5] | Zhan Xin-lu, Zhou Meng-ni, Tan Bu-zhen. Stem cell repair of intrauterine adhesions: preliminary achievements and clinical translation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(5): 787-792. |
| [6] | Liu Ying-xuan, Chen Ling-feng, An Mei-wen. Finite element analysis of the human upper cervical vertebrae under high-speed post-impact condition [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(3): 398-403. |
| [7] | Lian Zi-yu, Yang Li-li, Bian Yao-yao, Wang Ya-jie, Ma Yan-ting, Wang Ye-tong, Tang Sheng-jin, Zeng Li, Li Wen-lin. Ligustrazine nano-spray against postoperative abdominal adhesion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(18): 2896-2902. |
| [8] |
Bai Jiang-bo, Zhao Hong-fang, Gao Rui-jiao, Zhang Bing, Yu Kun-lun, Yang Yan-tao, Ma Tao, Tian De-hu.
Fresh amniotic membrane versus acellular amniotic membrane for repair of the tendon sheath and prevention of tendon adhesion
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(30): 4842-4846.
|
| [9] |
Liu Hong-ze, Wei Jie.
Repair of abdominal wall defects by highly simulated chitosan scaffolds
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(26): 4205-4209.
|
| [10] | Chen Zao-mei, Li Ru-bing. Research progress of absorbable anti-adhesion membranes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(18): 2920-2926. |
| [11] | Kang Dong . Anti-adhesion effect of absorbable biomaterials during tendon reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(21): 3185-3192. |
| [12] | Liu Guo-li, Yu Kun-lun, Bai Jiang-bo, Ma Tao, Yang Yan-tao, Tian De-hu. Acellular amniotic membrane versus medical membrane to prevent tendon adhesion in tendon sheath repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(21): 3117-3123. |
| [13] | Wu Feng, Chen Xuan-huang, Huang Man-wei, Lin Hai-bin, Zheng Jin-qing. Construction of rat models of failed back surgery syndrome and the possible mechanisms of Shenshu magnetic stimulation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(40): 6413-6417. |
| [14] | Fan Yang-yang, Song Yu-long. Anti-adhesion effect of chitosan and sodium hyaluronate in obstetric patients: a biocompatibility comparison [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(30): 4855-4859. |
| [15] | Xu Peng-cheng, Wang Ji-hong, Wen Shu-zheng, Guo Wen. Prospect of tissue-engineered tendons in clinical applications: how to improve mechanical properties, tissue integration and late-stage degradation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(29): 4710-4714. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||