Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (31): 4986-4991.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.31.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
Spinal external fixator distraction reduction combined with vertebroplasty in the repair of osteoporotic vertebral fractures
Li Zhu1, Wang Wen-jun2, Yao Nv-zhao2, Song Xi-zheng2
- 1Department of Surgery, 8730 Armed Forces Hospital, Guangzhou 510800, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Spine Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital, University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2014-06-10Online:2014-07-23Published:2014-07-23 -
Contact:Wang Wen-jun, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital, University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Li Zhu, Attending physician, Department of Surgery, 8730 Armed Forces Hospital, Guangzhou 510800, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zhu, Wang Wen-jun, Yao Nv-zhao, Song Xi-zheng. Spinal external fixator distraction reduction combined with vertebroplasty in the repair of osteoporotic vertebral fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(31): 4986-4991.
share this article
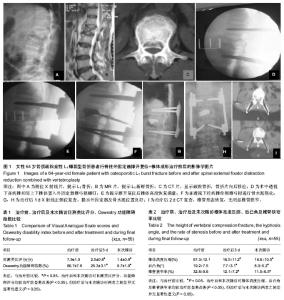
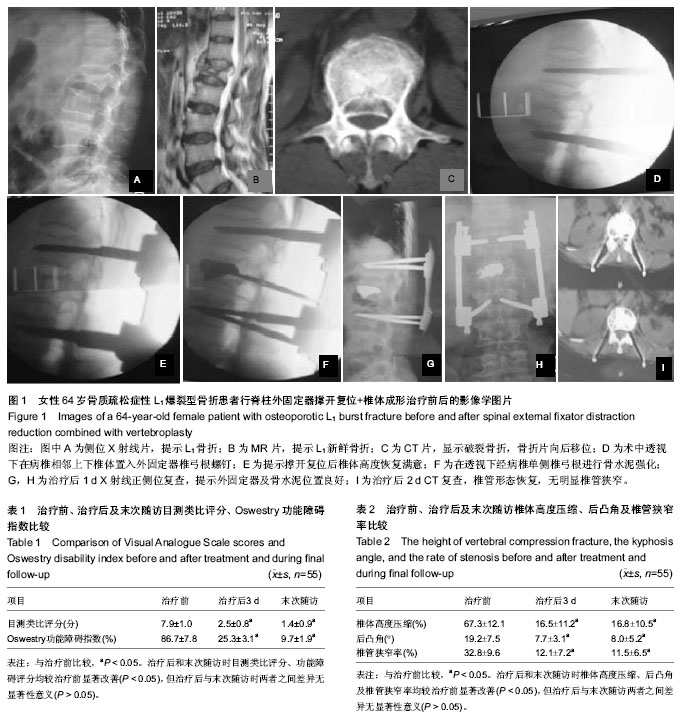
2.1 参与者数量分析 按意向性处理,纳入骨质疏松性椎体严重骨折患者55例,全部进入结果分析,无脱落。 2.2 围手术期结果 本组55例患者均顺利完成手术,手术时间为60-80 min,平均69 min;失血量为15-80 mL,平均30 mL。 2.3 治疗结果 患者治疗后第1天胸腰部疼痛明显缓解,治疗后1-3 d即可带腰围下床活动。腰背部疼痛目测类比评分和Oswestry功能障碍指数见表1。 治疗后及末次随访时患者目测类比评分及Oswestry功能障碍指数明显改善,与治疗前比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 治疗后椎体高度均有不同程度恢复,治疗后椎体前缘、中部、后缘高度均较治疗前显著性增大(P < 0.05),最终随访时较治疗后无明显高度丢失(P > 0.05)。 治疗后后凸角明显矫正、椎管狭窄基本解除。治疗后椎管内狭窄率、后凸角均较治疗前显著改善(P < 0.05),治疗后与最终随访比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。具体数据见表2,3。 2.4 典型病例 女性患者,64岁。因“外伤致腰痛、活动明显受限1 d”入院,骨密度检查示:骨质疏松症,诊断为L1爆裂型骨折。经南华大学附属第一医院脊柱外科科内讨论后,认为患者有行脊柱外固定器撑开复位+椎体成形治疗的指征,治疗后患者腰痛症状明显缓解,复查腰椎X射线片及CT后,带腰围下地活动,无明显特殊不适,术后4 d出院,见图1。 2.5 不良事件 骨水泥渗漏4例,其中侧方和后方渗漏各1例,前方渗漏2例,未见并发神经损伤病例。随访6-18个月未见相邻椎体再骨折发生。"
| [1] Afzal S, Dhar S, Vasavada NB, et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic fractures. Pain Physician. 2007;10(4):559-563. [2] 刘杰,王建.椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松胸椎椎体重度压缩性骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(4):399-403. [3] Genant HK,Wu CY,Van Kui JK,et al.Vertebral fracture assessment using a semi-quantitative technique. Bone Miner Res. 1993;8(9):1137-1148. [4] Buchbinder R, Osborne RH, Ebeling PR, et al. A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(6): 557-568. [5] 岳文峰,夏虹,王建华.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定对骨质疏松患者有利无弊[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(17):3081-3088. [6] Lee ST,Chen JF. Closed reduction vertebroplastry for the treatment of osteoporosis vertebral compression fracture. Technique note. J Neurosurg. 2004;100(4Sppl):392-396. [7] Kallmes DF, Comstock BA, Heagerty PJ, et al. A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic spinal fractures. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(6): 569-579. [8] Lotz JC. Trials of vertebroplasty for vertebral fractures. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(21): 2098-2100. [9] Aebi M. Vertebroplasty: about sense and nonsense of uncontrolled “controlled randomized prospective trials”. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(9):1247-1248. [10] Klazen CA, Lohle PN, de Vries J, et al. Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9746):1085-1092. [11] 葛建忠,张慧东,靳文剑,等.CT引导单侧椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折[J].中国骨伤, 2011, 24(10): 824-827. [12] 练辉,陈德基,何明基,等.侧卧位行经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的临床研究[J].中国介入影像与治疗学, 2007, 4(6):466-469. [13] Zou J, Mei X, Zhu X, et al. The long-term incidence of subsequent vertebral body fracture after vertebral augmentation therapy: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Pain Physician. 2012;15(4): E515-522. [14] Shi MM, Cai XZ, Lin T, et al. Is there really no benefit of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral fractures? A meta-analysis. Cl in Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470(10): 2785-2799. [15] Papanastassiou ID, Phillips FM, Van Meirhaeghe J, et al. Comparing effects of kyphoplasty, vertebroplasty, and non-surgical management in a systematic review of randomized and non-randomized controlled studies. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(9): 1826-1843. [16] Chosa K, Naito A, Awai K. Newly developed compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty: comparison with conservative treatment.Jpn J Radiol. 2011;29(5):335-341. [17] Xing D, Ma JX, Ma XL, et al. A meta-analysis of balloon kyphoplasty compared to percutaneous vertebroplasty for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Clin Neurosci. 2013;20(6): 795-803. [18] 郑召民,邝冠明,董智勇,等.新型Vessel-X骨材料填充器经皮椎体成形术(Vesselplasty) ——球囊扩张椎体后凸成形术的替代选择[J].中国微创外科杂志,2007, 7(2):143-145. [19] 陈富强,沈珊安,王方,等.微创球囊扩张椎体后凸成形术治疗中老年胸腰椎压缩性骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2007,22(6): 485-486. [20] Garnier L, Tonetti J, Bodin A, et al. Kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty in osteoporotic thoracolumbar spine fractures. Short-term retrospective review of a multicentre cohort of 127 consecutive patients. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(6 Suppl): S112-119. [21] Han S, Wan S, Ning L, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus balloon kyphoplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a meta-analysis of randomised and non-randomised controlled trials. Int Orthop. 2011;35(9): 1349-1358. [22] Inamasu J, Guiot BH, Uribe JS. Flexion-distraction injury of the L1 vertebra treated with short-segment posterior fixation and Optimesh. J Clin Neurosci. 2008;15(2): 214-218. [23] Belkoff SM, Molloy S. Temperature measurement during polymerization of polymethylmethacrylate cement used for vertebroplasty. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(14): 1555-1559. [24] Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Erbe EM, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of a new bone cement for use in vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000 ;25(9): 1061-1064. [25] Bae H, Hatten HP Jr, Linovitz R, et al. A prospective randomized FDAIDE trial comparing Cortoss with PMMA for vertebroplasty: a comparative effectiveness research study with 24-month follow-up. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(7): 544-550. [26] 郑召民,李佛保.经皮椎体成形术和经皮椎体后凸成形术--问题与对策[J]. 中华医学杂志,2006,(27):1878-1880. [27] Mckiernan FE. The broadening spectrum of osteoporotic vertebral fracture. Skeletal Radiol. 2009;38(4): 303-308. [28] Varga PP, Bors IB, Lazáry Á. Orthopedic treatment of vertebral compression fractures in osteoporosis. Orv Hetil. 2011;152(33): 1328-1336. [29] 徐耀宁,郑秋坚,昌耘冰,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的进展[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志, 2012, 4(4):300-307. [30] 胡继军,田全良,王松,等.PKP与过伸复位加PVP治疗新鲜骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的比较[J].内蒙古中医药, 2013,32(5): 93. [31] 尹立刚,唐炳魁.手法复位配合经皮穿刺椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的近期疗效观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2011,19(16): 1344-1345. [32] Chen LH, Lai PL, Chen WJ. Current status of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fracture. Chang Gung Med J. 2011;34(4): 352-359. [33] 纪昌宾,郑修军,柳翔云,等. PKP治疗陈旧性骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的效果[J].青岛大学医学院学报, 2013, 49(5): 451-452. [34] Sigaux J, Guignard S, Tuilier T, et al. Efficacity and feasibil ity of vertebroplasty for severe vertebral fracture: A retrospective study of 12 vertebroplasties. Joint Bone Spine. 2013;80(3): 328-331. [35] Zhang HT, Sun ZY, Zhu XY, et al. Kyphoplasty for the treatment of very severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. J Int Med Res. 2012;40(6): 2394-2400. [36] 王建,张年春,刘杰,等.单侧入路经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗重度骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2009,23(1): 68- 71. [37] Radcliff KE, Reitman CA, Delasotta LA, et al. Pulmonary cement embolization after kyphoplasty: a case report and review of the literature.Spine J. 2010;10(10): e1-e5. [38] Kim KH, Kuh SU, Chin DK, et al. Kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty: restoration of vertebral body height and correction of kyphotic deformity with special attention to the shape of the fractured vertebrae. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012; 25(6): 338-344. [39] Zhang JD, Poffyn B, Sys G, et al. Comparison of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for complications. Orthop Surg. 2011;3(3):158-160. [40] Gu Y, Zhang F, Jiang X, et al. Minimally invasive pedicle screw fixation combined with percutaneous vertebroplasty in the surgical treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporosis fracture. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;18(6): 634-640. [41] 杜心如,赵玲秀,石继川,等.经伤椎椎弓根螺钉复位治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折的临床解剖学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2007,25(3): 239-242. [42] 杨长远,王文军,罗光平,等.新型脊柱外固定器联合椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].医学临床研究,2007, 24(8):1333-1335. [43] 王程,王文军,姚女兆,等.新型脊柱外固定器在胸腰椎爆裂性骨折临床应用中的适应证探讨[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(14): 1114-1115. [44] 宋西正,易国良,王文军,等.外固定器整复下经皮椎体成形术治疗伤椎后壁破损的骨质疏松性压缩骨折[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2011,21(8): 659-662. [45] 胡安文,罗光平,肖业生,等.脊柱外固定器下MED技术联合椎体成形治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(12): 982-986. |
| [1] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [2] | Feng Guancheng, Fang Jianming, Lü Haoran, Zhang Dongsheng, Wei Jiadong, Yu Bingbing. How does bone cement dispersion affect the early outcome of percutaneous vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3450-3457. |
| [3] | Sun Yiqiang, Xing Jianqiang, Li Xuecheng, Wang Xin, Tian Shenglan, Zhao Zihao, Geng Xiaopeng. Kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture in the elderly: a comparison of vertebral height recovery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2851-2855. |
| [4] | Li Qiang, Li Jun, Luan Jian, Jin Canghai, Hao Meng, Lin Yong. Bone cement distribution of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2466-2471. |
| [5] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of bone filling bag vertebroplasty and percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1930-1935. |
| [6] | Jing Wanli, Zhang Tao, Teng Donghui, Shi Tao, Zhou Qiang. Poor outcomes of bone filling mesh container vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with vertebral body wall incompetence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1522-1527. |
| [7] | Zhang Zhiwei, Li Li, Huang Ziyu, Wu Duoyi, Gan Farong, Ye Baofei, Zhang Yan, Zhang Taibiao, Hu Wanjun. Percutaneous vertebroplasty through unilateral and bilateral pedicle approaches and unilateral pedicle extrapedicle approach for the treatment of thoracolumbar vertebral compression fractures: bone cement perfusion volume and cement leakage rate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1353-1358. |
| [8] | Wang Yiya, Zhang Han, Lan Hai. Digital evaluation of finite element model for percutaneous kyphoplasty with bone cement injection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1378-1383. |
| [9] | Fang Yi, Zhao Wenzhi, Pan Deyue, Han Xin, Zhang Lu, He Hongtao, Shi Feng, Tian Tingxiao. Acromioclavicular joint dislocation: how to achieve anatomical reduction, sustained stability and micro-motion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 796-802. |
| [10] | Li Kaiming, Wang Shangquan, Li Linghui, Zhu Liguo, Zhang Qing, Xie Rui. Bone filling bag vertebroplasty and percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fractures: a meta-analysis of improving Cobb angle and reducing bone cement leakage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 650-656. |
| [11] | Wang Xiuting, Li Sisheng, Sun Jian, Zhang Genyuan, Liu Fayin, Zhang Jintao. Effectiveness of artificial intelligent laser location system in reducing the location time and radiation dose of vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5295-5299. |
| [12] | Zhan Fangbiao, Xie Lizhong, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Cheng Jun, Zhang Xianwei. Efficacy and safety of percutaneous kyphoplasty versus posterior short-segment fixation with vertebra augmentation for Kummell’s disease: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5397-5404. |
| [13] | Liu Ruizhen, Wang Wangren, Hao Chen, Liang Dongmu, Guan Haishan. Effect of bone cement distribution on adjacent vertebral body fracture after unilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty for single segment osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4498-4504. |
| [14] | Pang Jutao, Chen Hong, Liu Bin, Zhang Wei, Sun Jianhua, Zhou Lianjun, Zhang Xinhu. Lateral versus anterior open injectors in the percutaneous vertebroplasty treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(16): 2461-2466. |
| [15] | Wu Haibo, Yu Zhijun, Bai Manmo. Correlation of percutaneous vertebroplasty effect on osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture with injection amount and dispersion degree of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(16): 2473-2477. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||