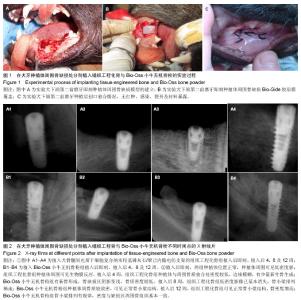
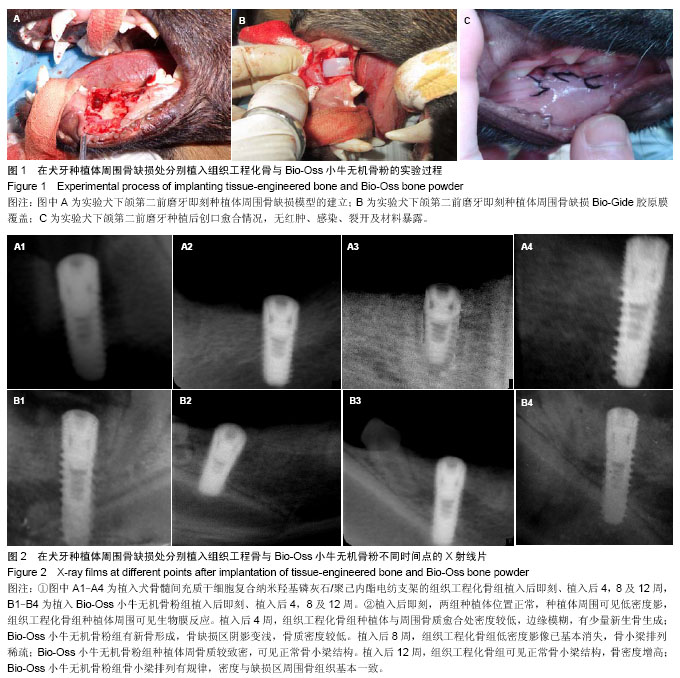
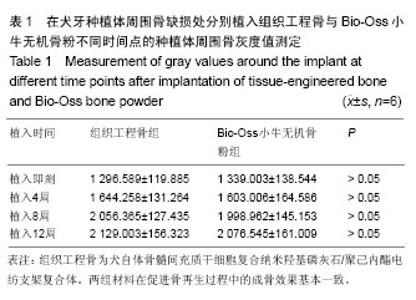
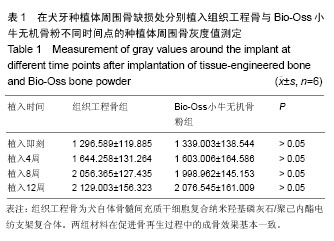
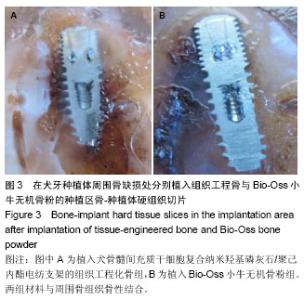
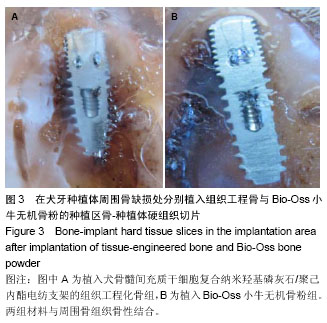
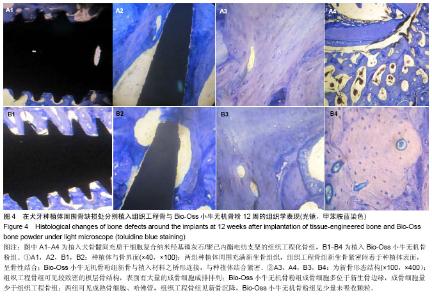
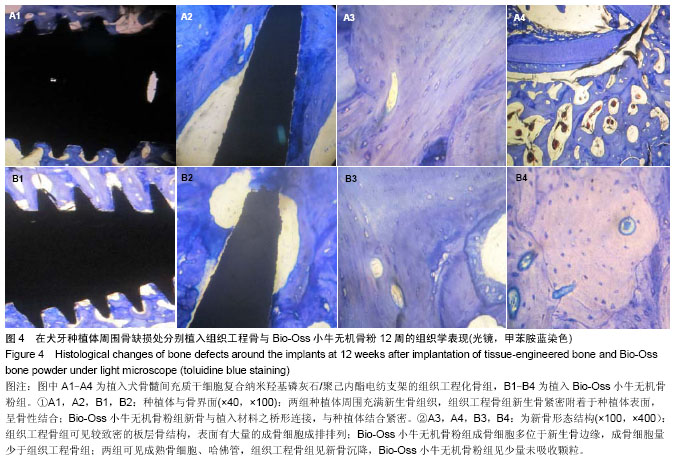
| [1] 何家才,郑先雨,张志愿.BMSCs复合PRP修复牙种植体周围骨缺损的实验研究[J].口腔颌面外科杂志2009,19(5):313-318.
[2] Healy KE,Guldberg RE.Bone tissue engineering.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact.2007;7(4):328-330.
[3] Nair MB,Suresh Babu S,Varma HK,et al.A trip hasic ceramic-coated porous hyd- roxyl apatite for tissue engineering application.Acta Biomater.2008;4(1):173-181.
[4] Okuda T,Uysal AC,Tobita M,et al.Prefabrication of tissue engineered bone grafts: an experimental study.Ann Plast Surg.2010;64(1):98-104.
[5] 刘顺振,侯玉东.骨组织工程支架材料的研究进展及临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(42):7911-7914.
[6] 李扬,李钊.组织工程骨在口腔种植中的应用与思考[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(33):6190-6193.
[7] 李吉鹏,邓国英.种子细胞-支架复合体在骨组织修复中的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(20):1857-1860.
[8] Wang G,Yang H,Li M,et al.The use of silk fibroin/ hydroxyapatite composite co-cultured with rabbit bone-marrow stromal cells in the healing of a segmental bone defect.Bone Joint Surg Br.2010;92(2):320-325.
[9] Liu ZJ,Zhuge Y,Velazquez OC.Trafficking and differentiation of mesenchymal s- tem cells.J Cell Biochem. 2009;106(6): 984-991.
[10] El Tamer MK,Reis RL.Progenitor and stem cells for bone and cartilage regeneration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2009;3(5): 327-337.
[11] Neuhuber B,Swanger SA,Howard L,et al.Effects of plating density and culture time on bone marrow stromal cell characteristics. Exp Hematol.2008;36(9):1176-1185.
[12] 徐西强,吴华.骨髓间充质干细胞及其在骨组织工程中的研究进展[J].临床外科杂志,2009, 17(1):53-55.
[13] Jones E,McGonagle D.Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vivo. Rheumatology (Oxford).2008;47(2): 126-131.
[14] 张森林,毛天球.生物可降解的骨组织工程支架材料的研究进展[J].医学研究生学报,2008,21(10):1098-1100.
[15] Ma PX.Biomimetic Materials for Tissue Engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2008;60(2):184-198.
[16] 李家锋,徐金霞,管海虹,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚己内酯复合大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(38):7042-7046.
[17] 许勇,朱立新,田京,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖复合材料与兔骨髓间充质干细胞的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(8):1423-1426.
[18] 陈红亮,孙勇.引导骨再生技术在口腔颌骨缺损中的应用回顾及展望[J].西南国防医药, 2009,19(7):752-753.
[19] 解芳,滕利,蔡磊,等.犬骨髓间充质干细胞分离纯化和成骨诱导分化:Ficoll液密度梯度离心法体外分离的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(6):951-956.
[20] 刘尧,林晓萍,谭丽思,等.成骨诱导的犬骨髓间充质干细胞复合Bio-Oss构建组织工程化骨的体外研究[J].上海口腔医学,2006, 15(6):627-631.
[21] 武登诫,李盛林.软硬组织切磨技术在口腔医学研究中的应用[J].北京大学学报:医学版, 2007,39(1):94-95.
[22] Carmagnola D,Berglundh T,Araujo M,et al.Bone healing around implants placed in a jaw defect augmented with Bio-Oss: An experimental study in dogs.J Clin Periodontol. 2000;27(11):799-805.
[23] Araujo MG,Carmagnola D,Berglundh T,et al.Orthodontic movement in bone def -ects augmented with Bio-Oss. An experimental study in dogs.J Clin Periodontol.2001;28(1): 73-80.
[24] 耿威,宿玉成,徐刚,等. Bio-Oss 结合Bio-Gide 修复牙种植体周围骨缺损的组织学研究[J].口腔医学研究,2005,21(1):4-7.
[25] 邓霞,夏熹,陈治清.电纺纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酯酰胺复合支架材料的制备及其细胞相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(51):9565-9569.
[26] 邱立新,林野,王兴.骨劈开技术在上颌前牙种植外科中的应用[J].中国口腔种植学杂志, 2000, 5(2):67-69.
[27] 王磊,黄远亮,潘可风.实验性种植体周围骨缺损动物模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(33):6561-6564.
[28] Filho Cerruti H,Kerkis I,Kerkis A,et al.Allogenous bone grafts improved by bone marrw stem cells and platelet growth factors: clinical case reports.Artif Organs.2007; 31(4):268-273.
[29] 康博,刘成军,刘国华,等.牙种植体周围骨缺损引导骨组织再生后骨结合的生物力学研究[J].中国口腔种植学杂志, 2009,14(1): 1-4.
[30] 蒋斯,韩泽民.引导骨组织再生技术在牙槽骨植骨中的应用现状[J].武警医学院学报,2011,20(8):686-688. |