Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (39): 6887-6895.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.39.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty
Zhu Xing-yang1, Su Hai-tao2, Huang Yong-ming2
- 1 Second Clinical Medical College, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
2 Department of Orthopedics, Traditional Chinese Medicinal Hospital of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2013-09-24Published:2013-09-24 -
Contact:Su Hai-tao, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Traditional Chinese Medicinal Hospital of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China suhaitao1234@yahoo.com.cn -
About author:Zhu Xing-yang★, Studying for master’s degree, Second Clinical Medical College, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China 250040974@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Xing-yang, Su Hai-tao, Huang Yong-ming. Periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(39): 6887-6895.
share this article
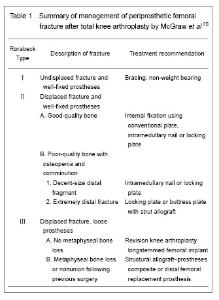
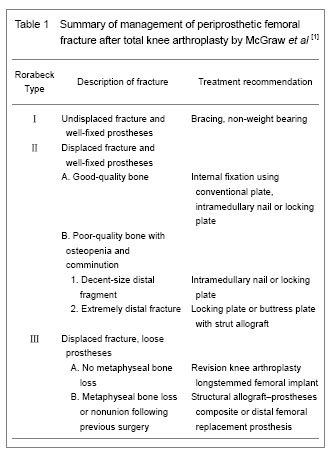
Basic information of inclusion date Among the 40 included articles on periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty[1-40] , 5 articles were about risk factors of periprosthetic femoral fracture[7-11] , 2 articles were about classification[13-14] , 6 articles were about treatment by plates[15-16, 21, 24-26] , 3 articles were about supplemental bone grafting[17-19] , 4 articles were about intramedullary fixation[4, 27-29] , 3 articles were about extramedullary fixation[31-33] , 5 articles were about revision[34-38] , and 12 articles were about others[1-6, 12, 20, 22-23, 30, 39-40] . Research results of inclusion data Risk factor for periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty The independent correlation of weight and body mass index with the risk of periprosthetic femoral fracture following total knee arthroplasty has not been clearly demonstrated in the literature. Several other important patient-related and surgical risk factors in this fracture, however, have been identified. Trauma was the major cause of this fracture, and even minor trauma may be sufficient to cause it[2-3] . Documented risk factors of the patient were osteopenia, osteoporosis, female sex, local osteolysis, chronic application of corticosteroids, rheumatoid arthritis and previous revision arthroplasty[1-5] . Female sex, rheumatoid arthritis and chronic steroid application have been associated with an increased risk of periprosthetic femoral fracture because all of them could increase the likelihood of osteoporosis. It was unclear whether steroid application an independent risk factor or an indicator of the severity of rheumatoid arthritis[1] . Merkel et al [3] reported that patients with a revision total knee arthroplasty had a 1.6% incidence (10/637) of periprosthetic femoral fracture compared with 0.6% (26/4 596) for patients with primary total knee arthroplasty. Additionally, patients with neuromuscular disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, cerebellar ataxia, cerebral palsy, myasthenia gravis, poliomyelitis, or undefined neuropathic joints have also been consistently demonstrated to be the higher risk factors for periprosthetic femoral fracture[1-2, 6] . Although, no clear relationship between postoperative component malalignment and subsequent periprosthetic femoral fracture has been identified[3] , iatrogenic intraoperative factors were also considered to be the separate risk factors for this fracture. Evidenced that anterior femoral notching was an independent risk factor for periprosthetic femoral fractures, and there was still controversial. Most literatures asserted that femoral anterior cortical notching could weaken the cortex of the femur and could predispose to periprosthetic fractures in the early postoperative period. The incidence of supracondylar fracture in a notched femur above total knee arthroplasty was reported from 0.5% to 44.3%[7] . Lesh et al [8] investigated the biomechanical effects of notching of distal anterior femoral cortex in total knee arthroplasty using human cadaveric femurs and found a mean decrease of 18% in bending strength as well as a 42% mean reduction in torsional strength for full-thickness notching of the femur. Moreover, the author emphasized that fractures were originated at the notch edge and advocated that patients who sustain inadvertent notching should be consider to use a femoral stem extension as a mean to bypass the stress-riser of the anterior notch. However, Completo et al [7] used synthetic femurs to demonstrate that the application of a prophylactic stem was unnecessary for notches depths below 5 mm, because the strain raised at the notch edge seems to be low. And for depths greater or equal to 5 mm, it did not decrease considerably the stress-riser at the notch edge and could not be enough to reduce the risk of fracture. Shawen et al [9] also used cadaveric femurs to demonstrate that a 3-mm anterior cortical notch could reduce torsional load to failure. In a purely finite element study by Zalzal et al [10] manifested an increasing of the risk of supracondylar fracture for notch depths greater than 3 mm. Nevertheless, Ritter et al [11] , in a retrospective clinical study, did not find any relation between anterior notching of the distal femur cortex and the occurrence of periprosthetic fractures. They reviewed 1 089 cases at an average follow-up time of 5 years and noted anterior notching in 29.8% of the cases. During this period, there were only two cases of periprosthetic fractures, but both were in femur treated without notching. Other conditions including stiff knee[2] , stress shielding[1] , component loosening[12] , and instable knee[12] all were considered to be the likely causative factors. Classification for periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty Numerous classification systems have been described for periprosthetic femoral fractures. The comparatively primitive and mature classification of distal femoral fracture was Neer classification, which was based on the displacement and stability and created for fractures in knees without prostheses, so it failed to account for the relationship between the fracture and the implant[1] . The Rorabeck classification is commonly applied[13] , because it takes the displacement of the fracture and prosthesis condition (well fixed or instability) into account. However, it was not a perfect guideline for the selection of appropriate treatment option. A new classification schemes based on the status of the prosthesis, the quality of distal bone stock, and the reducibility of the fracture, proposed by Kim et al [14] , will be better able to guide clinicians. The Orthopaedic Trauma Association classification of femur fractures may additionally be applied in order to design surgical plan. Diagnosis for periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty Most of the periprosthetic femoral fractures following total knee arthroplasty were associated with only slight trauma, so there always, rather than any other fractures, do not have severe edema of the soft tissue. Standard anteroposterior and lateral views are basic for diagnosis. However, before identifying the differential fractural classification, a CT-scan was crucial to define whether any instability of the prosthesis had occurred. In fact, it was not always possible to make a definitive diagnosis of a loose prosthesis especially in a fracture situation since the loosening may be just partial or shielded by the implant. In addition, whether there was a septic loosening before periprosthetic fracture should be identified through assessing patients’ medical history and conventional X-ray. If the patient with a medical history of pain, fever or swelling around the prosthesis before the trauma, it might indicate that there was a previous instability. Therefore, joint aspiration and the analysis for leukocyte count, neutrophil differential, culture, and sometimes frozen section of the synovial fluid, should be recommended to patients with clinical signs of infection. Treatment for periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty (Table 1) A variety of procedures have been described to treat periprosthetic femoral fracture following total knee arthroplasty, and the choice of treatment programs mainly depended on the type of fracture and the bone stock of the host. McGraw et al [2] proposed a normalized treatment way by Rorabeck classification. The goals of treatment, no matter surgical or nonsurgical, were fracture healing, restoration and maintenance of knee range of motion, and pain-free function. A good result was a minimum of 90° of knee motion, fracture shortening for 2 cm, varus/valgus malalignment of 5°, and flexion/extension malalignment of 10°[1] . Sometimes, it was not easy to guarantee whether any loosening of the prosthesis has been occurred preoperatively. Therefore, the orthopedics surgeon should prepare a revision arthroplasty when an osteosynthesis was initially planned. Nonoperative treatment for periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty: Conservative methods, which included skeletal traction, plaster of paris and non-weight bearing of the knee for several weeks, were generally recommended for undisplaced fractures with a stable fixed prosthesis (Rorabeck Ⅰ or Kim IA). The advantages of nonoperative management were that it could eliminate surgical risks such as bleeding, infection and anesthetic complications. Nevertheless, immobilization in non-operative treatment always causes loss of motion and reduces walking capacity. Several studies have reported satisfactory results of fracture consolidation following nonoperative treatment. However, most of authors were not willing to reveal any data concerning knee function or systemic complications after the nonoperative treatment. Culp et al [6] reported the result in thirty patients treated nonoperatively. Fifteen patients (50%) had increased pain or decreased ambulatory status following nonoperative care, whereas this was only 13% of patients treated operatively. Harlow and Hoffman reviewed 142 periprosthetic femoral fractures treated conservatively and found that 29% of these fractures eventually required reoperation[12] . Therefore, nonoperative treatment may not be favorable in this fracture unless patients are too debilitated to undergo the operative procedure as there is a relatively high prevalence of secondary displacement, nonunion, functional loss and needing for early mobilization[12] . Operative treatment for periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty: Management of periprosthetic femoral fractures depended on bone quality, displacement of the fracture, size of distal fragment and condition of implants[2] . If the fractures with adequate bone stock and stable prosthesis (Rorabeck Ⅱ or kim IB), attempts should be made to fix the fracture as the high rate of progressive displacement, malunion, and joint misalignment[12] . Nevertheless, a revision surgery should be considered if the fracture was very low or the prosthesis was loose (Rorabeck Ⅲ or Kim Ⅱ or Ⅲ). Open reduction internal fixation with conventional plates for periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty: The aim of open reduction and internal fixation was to provide anatomical reconstruction and early rehabilitation for the patients. Conventional plates mainly include buttress plates, angle blade plates, and dynamic condylar screws which are initially internal fixation devices. However, it is difficult to achieve rigid internal fixation especially for those with significant osteopenia, osteoporosis or comminuted bones. A literature suggested that the lateral condylar buttress plate, which is not a fixed-angle device, had lead to secondary collapse up to 42% of the comminuted distal femur fractures[15]. The blade plate and the dynamic condylar screws which can offer fixed angular stability distally make some progresses. Yet, it is a pity that they cannot be utilized in total knee arthroplasty with intramedullary stems and are not well suited to minimally invasive techniques. Supplemental bone grafting for periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty: Severe osteoporosis or osteopenia always accompanied with such fracture, supplemental bone grafting benefits enhancing the stability of the internal fixation. However, studies to date are inconclusive as to the type, amount of grafting and the situations where it is needed[1] . Healy et al [16] performed bone grafting (either allograft or autograft) in 15 of 20 fractures, with good outcomes. Their results also suggested that patients with autogenous bone graft heal more quickly than those with allograft. Besides, the authors recommended reinforcing the fixation of the implant with methylmethacrylate and augmenting it with bone graft if necessary. Virolainen et al [17] had handled 71 periprosthetic fractures, 18 of which were around the knee implant with cortical allograft struts from 1/1999 until 12/2008. Although the authors did not separately report the knee group, they got an overall union rate of 91% during the average follow-up time of 943 days. Wang et al [18] described satisfactory results of using cortical allograft struts combined with compression plate for these fractures with severe osteopenia or failure of initial internal fixation. Authors deemed that although the placement of cortical allograft struts required more extensive soft-tissue stripping, it might provide additional support in cases of severe comminution or for management of nonunions. Moreover, Kumar et al [19] reported good results that intramedullary fibular strut allograft and lateral buttress plate had been used in three patients who had grossly osteopenic and comminuted periprosthetic fractures of the distal femur, and they concluded that this technique could offer both mechanical and biological advantage as well as enhanced implant fixation. Locking plate for periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty: New locked plate devices, which can provide a fixed angle construct and improve fixation in osteoporotic bone, are effective in the treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures without component loosening after total knee arthroplasty. These devices also can be inserted by using minimally invasive approach to preserve the blood supply and reduce the loss of intraoperative blood and the risk of infection. The stability of locked plates has been shown superior to non-locking plates in biomechanical studies using cadavers[5] . Clinical studies have also reported satisfactory results of locked plates. Althausen et al [20] reported less invasive stabilization system plates were superior to flexible intramedullary nails, plate fixation and retrograde intramedullary nails in terms of early return to preoperative function, low infection rates, maintenance of alignment and no requirement for acute bone grafting. A literature finished by Raab and Davis reported eleven periprosthetic fractures of the femur around the knee treated by using locked condylar plates. All nine acute fractures and one of two periprosthetic nonunions achieved union and with satisfactory alignment, the average range of motion was 4 degrees to 92 degrees[21] . Ehlinger et al [22] reported their results of 16 periprosthetic supracondylar fractures treated by locking plates and immediate mobilization. They obtained a consolidation rate of 93.8% within 10 weeks and had no mechanical or infectious complications. In addition, the authors hypothesized that minimally invasive surgery with a locking plate and immediate postoperative weight-bearing were essential for the functional recovery. Moreover, with the development of polyaxial locking plate, it can be used to avoid existing implant or to capture specific fracture fragments, as well as to improve stability, and then it will provide more advantages in improving fixation of this fracture[23-24] . The locking condylar plate (Synthes, Paoli, PA) is one of this type. This implant is a further development of the less invasive stabilization system plate and permits a choice between conventional and/or fixed-angle locking screws. Ricci et al [25] reported their results of treating 22 periprosthetic fractures with this locking condylar plates by closed indirect reduction methods without bone graft. Nineteen of 22 fractures (86%) healed after the index procedure, the other three patients who failed to heal were insulin-dependent diabetes, two of them developed infected nonunions and one an aseptic nonunion. Authors concluded that fixation of periprosthetic supracondylar femur fractures with a locking plate got satisfactory results in nondiabetic patients. Recently, a paper published by Erhardt et al [26] demonstrated another kind of locking plate: NCB DF plate (Zimmer inc., Warsaw, IN, USA), which allows all the screws to be positioned in the conventional technique initially. Angular stability can be achieved by fixing the head of the screw with an additional cap. This can improve plate and screw positioning and enable the use of the NCB for prostheses with intramedullary stems. The author treated 12 periprosthetic fractures of femur after total knee arthroplasty by this system and got satisfactory results. Certainly, these minimally invasive plats also have disadvantages, such as an increased risk of neurovascular injury as a blind approach, lack of visualization of the fracture for reduction. Intramedullary fixation for periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty: The devices of intramedullary fixation mainly contain flexible intramedullary rod and retrograde intramedullary locking nailing. Ritter et al [27] reported 22 displaced supracondylar periprothestic femur fractures treated with rush rod fixation, all patients healed within 3 to 4 months after surgery and had good functional recoveries. However, this technique is rarely used now because of reduced axial and rotational stability. Currently, retrograde intramedullary locking nailing, due to relatively minimally invasive and generally providing sufficient axial, angular and rotational stability, is widely propagated and adopted. Gliatis et al [28] reported their midterm results of treatment with a retrograde nail for supracondylar periprosthetic femoral fractures with a mean follow-up period of 34.5 months. Ten fractures all united within 3 months, only one of which united in extreme valgus (35 degrees) and was revised to a stemmed total knee replacement. It also turned out that the function of joints had no statistically significant difference in these series cases before the fracture and after the operation. In a retrospective study belong to Chettiar et al [4] , 15 patients with 16 fractures were treated by retrograde intramedullary nail, 14 fractures of them united without any further intervention, such as bone grafting or secondary surgery except two deaths during follow-up time, and 11 out of 13 patients achieved to return to pre-injury level of function. Han et al [29] treated nine patients (10 knees) with periprosthetic supracondylar fractures by retrograde intramedullary nailing. Three of them treated with a closed reduction were not successful and required an open reduction and additional fixation by using a shape memory alloy ring; seven patients (8 knees) achieved good function recovery and alignment excluding two deaths during an average follow-up period of 39 months. According to a retrospective analysis, from 29 case series with a total of 415 fractures, by Herrera DA, retrograde nailing was associated with relative risk reduction of 87% for developing a nonunion and 70% for requiring revision surgery compared to traditional (non-locking) plating methods[30] . However, rigid retrograde femoral nails are not without any problems, it is unsuitable for very distal or severe comminuted fractures. Additionally, it should not be used in patients with a pre-existing ipsilateral total hip replacement as it can lead to a stress riser below the femoral stem. Therefore, it has to be proven that the distal femoral prosthesis is open, before planning this implant osteosynthesis. External fixation for periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty: This method was not commonly used for this fracture. However, because of the minimal blood supply destruction, high fracture combination and low infection rate, it will be an option for those who accompanied with significant comorbidities, those who were too weakness to undergo the internal fixation. There were some isolated reports in literature about this procedure. Simon et al [31] reported a case in which they managed this fracture by using an Ilizarov external fixator. The fixator was removed at 10 weeks, during that time the fracture was solidly healed, patients could fully weight bearing without walking aids and had a knee range of motion of 0° to 110° at a follow-up period of 19 months. Hurson et al [32] reported a similar case that a patient who had multiple risk factors and did not accept conventional treatment was treated by a two-ring above-knee Ilizarov external fixator, which allowed full mobilization of the affected limb during fracture healing. Finally, the fracture achieved solid union with a good functional recovery of the joint. Pleva et al [33] also reported three periprosthetic femoral fractures after total knee arthroplasty treated by two different external fixations, but the author did not demonstrate the detail results about the healing time and the function. Revision for the treatment of periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty: Revision of prosthesis is a challenge and more so existing in a periprosthetic fracture. It is mainly used for a comminuted or extremely distal fracture where secure fixation cannot be achieved. A long-stemmed prosthesis, which can provide stable fixation and allows patients with early start mobilization and weight-bearing, is generally recommended to use. Srinivasan et al [34] treated six periprosthetic femoral fractures with cemented long stem revision arthroplasty prosthesis to address the issues of stability, alignment and early mobilization with good results. Authors highlighted the role of long stem prosthesis in periprosthetic fractures for offering stability and early mobilization. If patients can endure an instable prosthesis accompanied with a poor metaphyseal bone stock, rendering a conventional revision arthroplasty impossible, distal femoral replacement or a structural allograft should be considered[14] . In this situation, a custom implant may be generally required[2, 12, 23] , and the whole implant including the tibial components may have to be exchanged. Berend[35] reported the results of using rotating-hinged distal femoral replacement devices in 39 knees which included 13 periprosthetic fractures. This group contained some complications, however, patients got excellent pain relief and function with a low short-term reoperation rate and an implant survivorship rate of 87% in 46 months. Additionally, the author indicated that the immediate stability provided by distal femoral replacement might justify its application in the cases of periprosthetic fracture, especially for elderly, lower-demand patients. Study also reported the high complication rate and low survival period by this prosthesis[36] , nevertheless, it seemed a reasonable choice for elderly and sedentary patients as a limb-salvage option when other surgical procedures were not feasible. Modern hinged knee prosthesis can decrease the prosthesis-bone stresses through increasing the freedom of rotation, but it still cannot match the function and longevity of the femoral components. Therefore, rotating-hinge prosthesis may be a second choice behind allograft-prosthetic composite in younger or more active patients. Structural allograft can provide additional support for femoral components in patients with marked insufficient bone stock, and the success of which has been reported in several researches. Kassab et al [37] reported their satisfied results that 12 patients associated with poor bone quality were revised with a distal femoral allograft for periprosthetic femoral fractures of the femur. Radiographs showed no migration, no loosening, and good interface union in nine of the 10 patients available at an average follow-up of 6 years. Backstein et al [38] reviewed the results of using 68 structural allografts around the knee for different indications including 17 periprosthetic femoral fractures with mean follow-up period of 5.4 years. They did not separately report the results in periprosthetic fracture group, and totally had 13 failed knees (13/61) due to graft related complications including one nonunion, three aseptic loosening, three periprosthetic fractures, four deep infections, and two for instability. Toward these difficult cases, however, the authors thought that the overall results were inspiring. Rehabilitation and prophylaxis for periprosthetic femoral fracture after total knee arthroplasty: Rehabilitation is considered to be an important step in the treatment of periprosthetic femoral fracture. It is convinced that early movement is beneficial for functional recovery and can prevent complications of immobilization postoperation[22] . In most of the cases, partial weight-bearing should be recommended by using the aid of frames during the first several weeks after surgery. In well-fixed cemented revision prostheses, immediate full weight-bearing might be allowed. In uncemented revision stems, must pay attentions to the early stage after the operation. All patients must be treated with continuous passive movement of the knee after consolidation of the soft tissue[22, 39 ] . Because the effects of periprosthetic femoral fractures are always devastating and the treatments are complicated, it worth to emphasize that prevention is more effective than treatment. This fracture is caused by multi-factors, rather than separation, so efforts should be made to reduce the risk of periprosthetic knee fracture. It is important to control patient factors such as osteoporosis which plays a significant role in increasing the risk of these fractures. A recent study made a clear that bisphosphonate used in primary prevention could reduce post-operative risk of fracture after total knee arthroplasty by 50% and by 55% in secondary prevention[40] . As a general rule, anterior cortical notching should be avoided to minimize the increased risk of periprosthetic fracture at a weakened biomechanical interface between the distal femur and the femoral component. "
| [1]Su ET, DeWal H, Di Cesare PE. Periprosthetic femoral fractures above total knee replacements. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2004;12(1):12-20. [2]McGraw P, Kumar A. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur after total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Traumatol. 2010; 11(3):135-141. [3]Merkel KD, Johnson EW. Supracondylar fracture of the femur after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 1986;68(1):29-43. [4]Chettiar K, Jackson MP, Brewin J, et al. Supracondylar periprosthetic femoral fractures following total knee arthroplasty: treatment with a retrograde intramedullary nail. Int Orthop. 2009;33(4):981-985. [5]Bong MR, Egol KA, Koval KJ, et al. Comparison of the LISS and a retrograde-inserted supracondylar intramedullary nail for fixation of a periprosthetic distal femur fracture proximal to a total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17(7): 876-881. [6]Culp RW, Schmidt RG, Hanks G, et al. Supracondylar fracture of the femur following prosthetic knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;(222):212-222. [7]Completo A, Fonseca F, Relvas C, et al. Improved stability with intramedullary stem after anterior femoral notching in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(3):487-494. [8]Lesh M, Schneider D, Deol G, et al. The consequences of anterior femoral notching in total knee arthroplasty: a biomechanical study. J Bone Joint Surg. 2000;82(8): 1096-1010. [9]Shawen SB, Belmont PJ Jr, Klemme WR, et al. Osteoporosis and anterior femoral notching in periprosthetic supracondylar femoral fractures: a biomechanical analysis. J Bone Joint Surg. 2003;85(1):115-121. [10]Zalzal P, Backstein D, Gross A, et al. Notching of the anterior femoral cortex during total knee arthroplasty characteristics-that increase local stresses. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(5):737-743. [11]Ritter MA, Thong AE, Keating M, et al. The effect of femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty on the prevalence of postoperative femoral fractures and on clinical outcome. J Bone Joint Surg. 2005;87(11):2411-2414. [12]Dennis DA. Periprosthetic fractures following total knee arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2001;50:379-389. [13]Rorabeck CH, Taylor JW. Classification of periprosthetic fractures complicating total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North. 1999;30(2):209-214. [14]Kim KI, Egol KA, Hozack WJ, et al. Periprosthetic fractures after total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; 446:167-175. [15]Davison BL. Varus collapse of comminuted distal femur fractures after open reduction and internal fixation with a lateral condylar buttress plate. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2003;32(1):27-30. [16]Healy WL, Siliski JM, Incavo SJ. Operative treatment of distal femoral fractures proximal to total knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg. 1993;75(1):27-34. [17]Virolainen P, Mokka J, Seppänen M, et al. Up to 10 years follow up of the use of 71 cortical allografts (strut-grafts) for the treatment of periprosthetic fractures. Scand J Surg. 2010;99(4):240-243. [18]Wang JW, Wang CJ. Supracondylar fractures of the femur above total knee arthroplasties with cortical allograft struts. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17(3):365-372. [19]Kumar A, Chambers I, Maistrelli G, et al. Management of periprosthethic fracture above total knee arthroplasty using intramedullary fibular allograft and plate fixation. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(4):554-558. [20]Althausen PL, Lee MA, Finkemeier CG, et al. Operative stabilization of supracondylar femur fractures above total knee arthroplasty: a comparison of four treatment methods. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(7):834-839. [21]Raab GE, Davis CM. Early healing with locked condylar plating of periprosthetic fractures around the knee. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(8):984-989. [22]Ehlinger M, Adam P, Abane L, et al. Treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(9):1473-1478. [23]Parvizi J, Jain N, Schmidt AH. Periprosthetic knee fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(9):663-671. [24]Kregor PJ, Hughes JL, Cole PA. Fixation of distal femoral fractures above total knee arthroplasty utilizing the Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS). Injury. 2001;32 Suppl 3:64-75. [25]Ricci WM, Loftus T, Cox C, et al. Locked plates combined with minimally invasive insertion technique for the treatment of periprosthetic supracondylar femur fractures above a total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(3):190-196. [26]Erhardt JB, Grob K, Roderer G, et al. Treatment of periprosthetic femur fractures with the non-contact bridging plate: a new angular stable implant. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008;128(4):409-416. [27]Ritter MA, Keating EM, Faris PM, et al. Rush rod fixation of supracondylar fractures above total knee arthroplasties. J Arthroplasty. 1995;10(2):213-216. [28]Gliatis J, Megas P, Panagiotopoulos E, et al. Midterm results of treatment with a retrograde nail for supracondylar periprosthetic fractures of the femur following total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19(3):164-170. [29]Han HS, Oh KW, Kang SB. Retrograde intramedullary nailing for periprosthetic supracondylar fractures of the femur after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg. 2009;1(4):201-206. [30]Herrera DA, Kregor PJ, Cole PA, et al. Treatment of acute distal femur fractures above a total knee arthroplasty—systematic review of 415 cases (1981–2006). Acta Orthop. 2008;79(1):22-27. [31]Simon RG, Brinker MR. Use of Ilizarov external fixation for a periprosthetic supracondylar femur fracture. J Arthroplasty. 1999;14(1):118-121. [32]Hurson C, Synnott K, McCormack D. Above-knee Ilizarov external fixation for early periprosthetic supracondylar femoral fracture-a case report. Knee. 2005;12(2):145-147. [33]Pleva L, Sír M, Madeja R. Our experiences with the treatment of periprosthetic fractures of femur. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2004; 148(1): 75-79. [34]Srinivasan K, Macdonald DA, Tzioupis CC, et al. Role of long stem revision knee prosthesis in periprosthetic and complex distal femoral fractures: a review of eight patients. Injury. 2005;36(9):1094-1102. [35]Berend KR, Lombardi AV Jr. Distal femoral replacement in nontumor cases with severe bone loss and instability. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(2):485-492. [36]Pour AE, Parvizi J, Slenker N, et al. Rotating hinged total knee replacement: use with caution. J Bone Joint Surg. 2007;89(8):1735-1741. [37]Kassab M, Zalzal P, Azores GMS, et al. Management of periprosthetic femoral fractures after total knee arthroplasty using a distal femoral allograft. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19(3): 361-368. [38]Backstein D, Safir O, Gross A. Management of bone loss: structural grafts in revision total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop. 2006;446:104-112. [39]Ehlinger M, Adam P, Moser T, et al. Type C periprosthetic fracture treated with locking plate fixation with a mean follow up of 2.5 years. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2010; 96(1):42-47. [40]Prieto-Alhambra D, Javaid MK, Judge A, et al. Bisphosphonate use and risk of post-operative fracture among patients undergoing a total knee replacement for knee osteoarthritis: a propensity score analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(5):1555-1571. |
| [1] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [2] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [3] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [5] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [6] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [7] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| [8] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [9] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | Liu Xin, Yan Feihua, Hong Kunhao. Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [11] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [12] | Liu Jiangfeng. Nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 composite filling combined with locking plate in the treatment of fibrous dysplasia of femoral bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 542-547. |
| [13] | Nie Shaobo, Li Jiantao, Sun Jien, Zhao Zhe, Zhao Yanpeng, Zhang Licheng, Tang Peifu. Mechanical stability of medial support nail in treatment of severe osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 329-333. |
| [14] | Cheng Shigao, , Wang Wanchun, Jiang Dong, Li Tengfei, Li Xun, Ren Lian. Comparison of the standard and long-stem bone cement prosthesis replacement in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 362-367. |
| [15] | Wang Weigang, Yang Zhidong, Feng Zongquan, Wang Ding. A mid-term clinical follow-up of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with fixed bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 368-373. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||