Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (39): 6896-6901.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.39.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Changes of biochemical indexes and joint function in the patients with rheumatoid arthritis after total knee arthroplasty
Wu Li-xin1, Zhang Hai-bin2, Li Xiao-hui3, Ren Kai-jing3, Yang Guo-yue4
- 1 Longhua County Hospital, Longhua 068450, Hebei Province, China; 2 Dongli District Hospital, Tianjin 300300, China; 3 Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China; 4 Tianjin Third Central Hospital, Tianjin 300170, China
-
Online:2013-09-24Published:2013-09-24 -
Contact:Li Xiao-hui, M.D., Associate chief physician, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China lxhchd@sina.com -
About author:Wu Li-xin, Associate chief physician, Longhua County Hospital, Longhua 068450, Hebei Province, China 13903145353@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Li-xin, Zhang Hai-bin, Li Xiao-hui, Ren Kai-jing, Yang Guo-yue. Changes of biochemical indexes and joint function in the patients with rheumatoid arthritis after total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(39): 6896-6901.
share this article
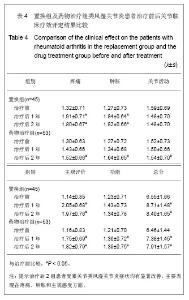
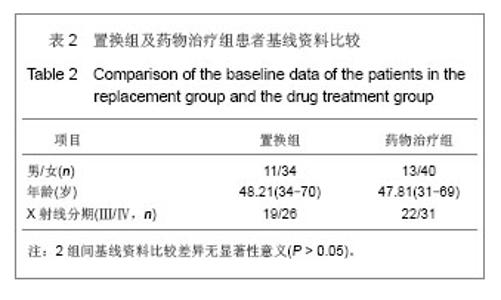
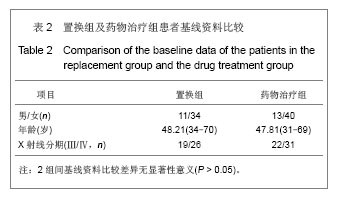
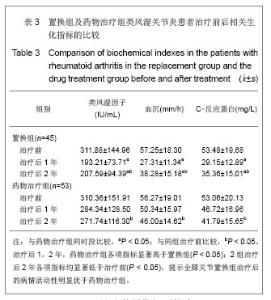
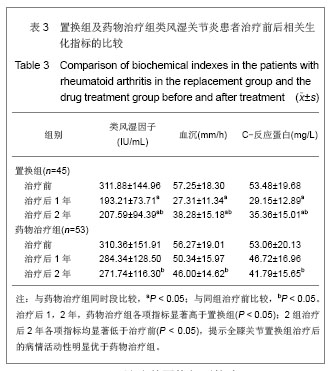
类风湿因子变化:治疗前置换组平均为311.88 IU/mL,药物治疗组平均为310.36 IU/mL,组间比较差异无显著性意义(t=0.053,P > 0.05)。治疗后2年置换组平均为207.59 IU/mL,药物治疗组平均为271.74 IU/mL,药物治疗组显著高于置换组(t = 3.101,P=0.02)。2组治疗后2年类风湿因子水平均显著低于治疗前(P < 0.05)。 血沉变化:治疗前置换组平均为57.25 mm/h;药物治疗组平均为56.27 mm/h,2组差异无显著性意义(t= 0.271,P > 0.05)。治疗后2年置换组平均为38.28 mm/h,药物治疗组平均为46.00 mm/h,药物治疗组显著高于置换组(t=-3.039,P=0.03)。2组治疗后2年血沉均显著低于治疗前(P < 0.05)。 C-反应蛋白变化:治疗前置换组平均为53.48 mg/L,药物治疗组平均为53.06 mg/L,2组差异无显著性意义(t= 0.112,P > 0.05)。治疗后2年置换组平均为35.36 mg/L,药物治疗组平均为41.79 mg/L,药物治疗组显著高于置换组(t=2.169,P=0.032)。2组治疗后2年C-反应蛋白水平均显著低于治疗前(P < 0.05)。 2.4 临床疗效 分别于治疗前和治疗后1,2年对全身受累关节进行评定,评定方法采用Ishikawa关节临床评分标准。随访结果显示,置换组治疗前平均6.55分,治疗后1年平均8.71分,治疗后2年平均8.4分,其中优8例(18%),良16例(36%),可18例(40%),差3例(7%)。药物治疗组治疗前平均6.46分,治疗后1年平均7.38分,治疗后2年平均7.91分,其中优8例(16%),良19例(36%),可22例(41%),差4例(7%)。治疗后受累关节类风湿关节炎症状的显著改善主要表现在疼痛、肿胀和主观感受方面,见表4。 2.5 不良事件 置换组1例患者置换后浅部感染,经过换药等处理治愈;另有1例患者出现下肢深静脉(腘静脉)血栓,经过固定、抗凝等处理,3周后血栓静止后开始功能锻炼,因屈膝功能恢复不满意,但经过锻炼,置换后6个月膝关节屈曲达到100°。 "

| [1]Satoh F, Seto Y, Hasegawa I, et al. Fatal Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in the Felty syndrome: a maltreatment- suspected case. Legal medicine (Tokyo, Japan). 2012;14(5): 246-248. [2]Perricone C, Ceccarelli F, Valesini G. An overview on the genetic of rheumatoid arthritis: a never-ending story. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10(10): 599-608. [3]Basisht GK, Singh RH, Chandola H. Management of rheumatoid arthritis (Aamavata) using symbiohealth healthcare system. Ayu. 2012; 33(4):466-474. [4]Desai SS, Myles JD, Kaplan MJ. Suboptimal cardiovascular risk factor identification and management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a cohort analysis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(6): R270. [5]Aalbers J. Rheumatoid arthritis management options for 2012. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2012; 23(6):355. [6]Liepe K. Efficacy of radiosynovectomy in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(10):3219-3224. [7]Schaumburger J, Trum S, Anders S, et al. Chemical synovectomy with sodium morrhuate in the treatment of symptomatic recurrent knee joint effusion. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(10): 3113-3117. [8]da Silva E, Doran MF, Crowson CS, et al. Declining use of orthopedic surgery in patients with rheumatoid arthritis? Results of a long-term, population-based assessment. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49(2): 216-220. [9]Trieb K, Schmid M, Stulnig T, et al. Long-term outcome of total knee replacement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2008;75(2): 163-166. [10]Momohara S, Inoue E, Ikari K, et al. Risk factors for total knee arthroplasty in rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2007; 17(6): 476-480. [11]March LM, Barcenilla AL, Cross MJ, et al. Costs and outcomes of total hip and knee joint replacement for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2008;27(10): 1235- 1242. [12]Mochizuki T, Saito S. Total knee arthroplasty for massive joint destruction in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis complicated with fibrous dysplasia. Mod Rheumatol. 2009;19(2): 204-208. [13]Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988; 31(3): 315-324. [14]Goodman SM. Rheumatoid arthritis: preoperative evaluation for total hip and total knee replacement surgery. J Clin Rheumatol. 2013;19(4):187-192. [15]Johnson BK, Goodman SM, Alexiades MM, et al. Patterns and associated risk of perioperative use of anti-tumor necrosis factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis undergoing total knee replacement. J Rheumatol. 2013;40(5): 617-623. [16]Pantos PG, Tzioufas AG, Panagiotakos DB, et al. Demographics, clinical characteristics and predictive factors for total knee or hip replacement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Greece. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013;31(2): 195-200. [17]Skytta ET, Honkanen PB, Eskelinen A, et al. Fewer and older patients with rheumatoid arthritis need total knee replacement. Scand J Rheumatol. 2012;41(5): 345-349. [18]Bongartz T, Halligan CS, Osmon DR, et al. Incidence and risk factors of prosthetic joint infection after total hip or knee replacement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59(12): 1713-1720. [19]Laskin RS. The classic: total condylar knee replacement in patients who have rheumatoid arthritis. A ten-year follow-up study. 1990. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(11): 2589-2596. [20]March LM, Barcenilla AL, Cross MJ, et al. Costs and outcomes of total hip and knee joint replacement for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2008;27(10): 1235-1242. [21]Trieb K, Schmid M, Stulnig T, et al. Long-term outcome of total knee replacement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2008;5(2): 163-166. [22]Sokka T, Kautiainen H, Hannonen P. Stable occurrence of knee and hip total joint replacement in Central Finland between 1986 and 2003: an indication of improved long-term outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66(3): 341-344. [23]Sharma S, Nicol F, Hullin MG, et al. Long-term results of the uncemented low contact stress total knee replacement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(8): 1077-1080. [24]de Hair MJ, Harty LC, Gerlag DM, et al. Synovial tissue analysis for the discovery of diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in patients with early arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2011; 38(9): 2068-2072. [25]Ganesan K, Balachandran C, Manohar BM, et al. Effects of testosterone, estrogen and progesterone on TNF-alpha mediated cellular damage in rat arthritic synovial fibroblasts. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(10): 3181-3188. [26]Schrama JC, Espehaug B, Hallan G, et al. Risk of revision for infection in primary total hip and knee arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with osteoarthritis: a prospective, population-based study on 108,786 hip and knee joint arthroplasties from the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010;62(4): 473-479. [27]Bongartz T, Halligan CS, Osmon DR, et al. Incidence and risk factors of prosthetic joint infection after total hip or knee replacement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59(12): 1713-1720. [28]Bartok B, Firestein GS. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2010; 233(1): 233-255. [29]Dessein PH, Joffe BI, Stanwix AE. High sensitivity C-reactive protein as a disease activity marker in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2004;31(6): 1095-1097. [30]Sokka T, Pincus T. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, or rheumatoid factor are normal at presentation in 35%-45% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis seen between 1980 and 2004: analyses from Finland and the United States. J Rheumatol. 2009;36(7): 1387-1390. [31]Nakamura H, Tanaka H, Yoshino S. Long-term results of multiple synovectomy for patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis. Effects on disease activity and radiological progression. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2004;22(2): 151-157. [32]Cope AP, Patel SD, Hall F, et al. T cell responses to a human cartilage autoantigen in the context of rheumatoid arthritis-associated and nonassociated HLA-DR4 alleles. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42(7): 1497-1507. [33]Murakami M, Hirano T. A four-step model for the IL-6 amplifier, a regulator of chronic inflammations in tissue-specific MHC class II-associated autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2011; 2: 22. [34]Blass S, Schumann F, Hain NA, et al. p205 is a major target of autoreactive T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42(5): 971-980. [35]Nakamura H, Nagashima M, Ishigami S, et al. The anti-rheumatic effect of multiple synovectomy in patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis. Int Orthop. 2000;24(5): 242-245. [36]Yano K, Ikari K, Inoue E, et al. Effect of total knee arthroplasty on disease activity in patients with established rheumatoid arthritis: 3-year follow-up results of combined medical therapy and surgical intervention. Mod Rheumatol. 2010; 20(5): 452-457. [37]Momohara S, Inoue E, Ikari K, et al. Efficacy of total joint arthroplasty in patients with established rheumatoid arthritis: improved longitudinal effects on disease activity but not on health-related quality of life. Mod Rheumatol. 2011;21(5): 476-481. |
| [1] | Ma Rui, Wang Jialin, Wu Mengjun, Ge Ying, Wang Wei, Wang Kunzheng. Relationship of pathogenic bacteria distribution with drug resistance and treatment cycle for periprosthetic joint infection after total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 380-385. |
| [2] | Chen Deng, Zhang Yaxin, Dai Jihang, Chen Duoyun, Sun Yu. Analysis on relative factors affecting pyrexia following total hip replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2846-2850. |
| [3] | Zhou Qi, Gao Yi, Wei Kang, Li Jun, Xu Jianda, Jiang Yang, Qu Yuxing. Total knee arthroplasty for rheumatoid arthritis: knee function and biochemical index changes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1337-1341. |
| [4] | Cao Houran, Deng Peng, Ye Pengcheng, Jie Ke, Zeng Jianchun, Feng Wenjun, Chen Jinlun, Qi Xinyu, Li Jie, Tan Xueqiu, Zhang Haitao, Zeng Yirong. Platelet count as a novel potential predictor of periprosthetic joint infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(30): 4795-4801. |
| [5] | Zhao Jianfeng, Geng Yu, Chen Qianbo, Yang Jinghui, Li Yan. Changes in insulin resistance and inflammatory factors in cataract patients with glaucoma after phacoemulsification and trabeculectomy: a self-controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(11): 1750-1755. |
| [6] | Zhao Hongshun, A Jiancuo, Gao Shunhong, Li Yonggang, Guo Liping. Intraoperative and postoperative blood loss and levels of C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 after local application of tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 493-498. |
| [7] | Wu Xingyuan, Zhang Guoru, Liu Tang, Zhou Caisheng. Intravenous and intraarticular tranexamic acid can reduce blood loss and inflammatory response during cemented posterior cruciate ligament-retaining unilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(36): 5753-5759. |
| [8] | Wang Changbing1, 2, Lu Mingfeng2, He Lilei2, Xing Jisi2, Xu Ting2, Zhao Lilian2, Liu Xiaofang1 . Diagnosis and treatment of early joint infection after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5592-5599. |
| [9] | Yin Cong, Chen Xin, Sun Hui, Yu Axiang, Yuan Lijun, Tong Zhibin, Cheng Yinjie, Tu Xing. Meta-analysis of tripterygium glycosides combined with methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5710-5717. |
| [10] | Lu Qilin, Cai Xianhua, Shang Ranran, Chen Yanzhao, Xie Wei, Chen Xiongwei, Wu Haiyang. Feasibility of preoperative ratio of C-reactive protein to albumin for assessing the prognosis of older adults with hip fracture undergoing arthroplasty or internal fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4435-4439. |
| [11] | Wang Xinling, Tan Biao, Yin Jiandong, Zuo Biao. Restrictive use and non-use tourniquets during total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4456-4460. |
| [12] | Zang Wenhao, Song Jian, Teng Xueren, Zhang Qiliang. Correlation of local skin temperature of knee joint with C-reactive protein, interleukin 6 and erythrocyte sedimentation rate after primary unilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3773-3779. |
| [13] | Yang Baokuan, Huang Rui, Shi Xinghui. Bracketless invisible orthodontic appliance for treating adult periodontal disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(22): 3451-3455. |
| [14] | Wang Zhi1, Lin Yipeng2, Li Qi3. Biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis: performance analysis of antibodies from serum and synovial fluid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(19): 3102-3108. |
| [15] | Hu Xiaoli, Gu Ying, Cai Yan, Xie Jin, Liu Chan. Assessment of seven joint ultrasound score for early rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(16): 2523-2528. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||