Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (22): 4099-4106.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.22.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis on the relationship between femoral intercondylar notchsize and anterior cruciate ligament injury
Wei Jie1, Zeng Chao2, Gao Shu-guang2, Yang Tu-bao1, Lei Guang-hua2
- 1 School of Public Health, Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China
2 Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China
-
Online:2013-05-28Published:2013-05-28 -
Contact:Yang Tu-bao, School of Public Health, Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China 394345006@qq.com -
About author:Wei Jie, Studying for master’s degree, School of Public Health, Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China weijie_612@sina.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wei Jie, Zeng Chao, Gao Shu-guang, Yang Tu-bao, Lei Guang-hua. Meta-analysis on the relationship between femoral intercondylar notchsize and anterior cruciate ligament injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(22): 4099-4106.
share this article
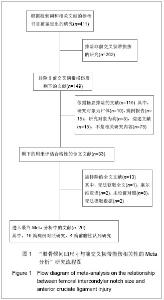
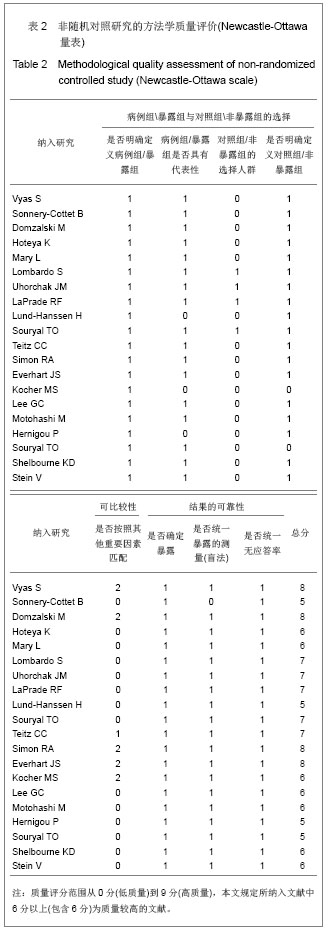
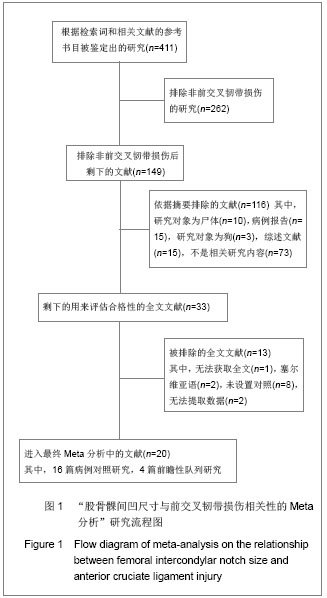
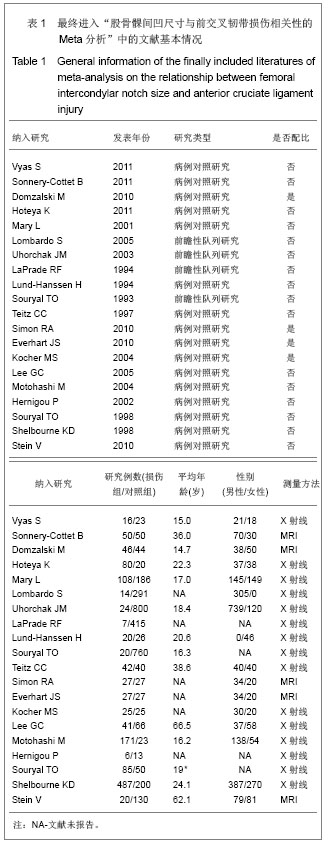
2.1检索结果及纳入文献的质量评价 最开始计划在这项Meta分析中纳入随机对照试验(RCT)的研究,但是在研究检索的最后阶段,发现没有与这个主题相关的随机对照试验研究,最后,将符合纳入标准的前瞻性和回顾性对照研究作为主要纳入文献进行合并分析。 图1显示了依据文献纳入和排除标准来检索相关文献。通过检索前文提到的这些数据库,一共检索出了411篇可能符合纳入标准的文献。首先排除了262篇非前交叉韧带损伤的文献,另有116篇没有满足纳入标准的文献被排除。阅读了剩下的33篇文献全文,13篇文献被排除。最后剩余20篇文献纳入最终研究[5-24] ,见图1。 纳入的20个研究中,16个为病例对照研究,4个为前瞻性队列研究,具体见表1。这20个研究均按照非随机对照研究的方法学质量评价(Newcastle-Ottawa量表)进行了严格的方法学质量评价,结果为16个研究的得分在6分或6分以上,为较高质量的文献,具体见表2。"
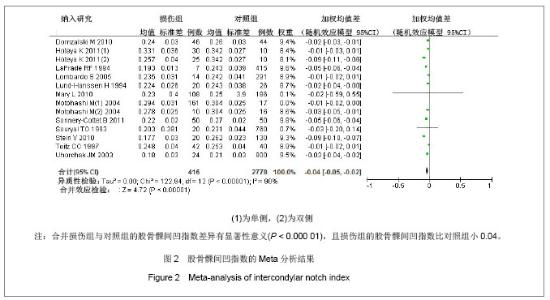
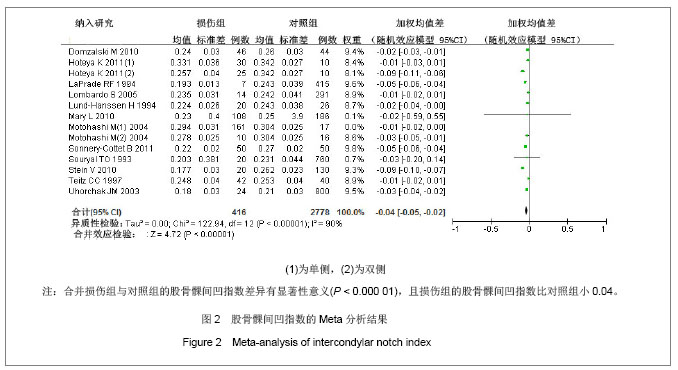
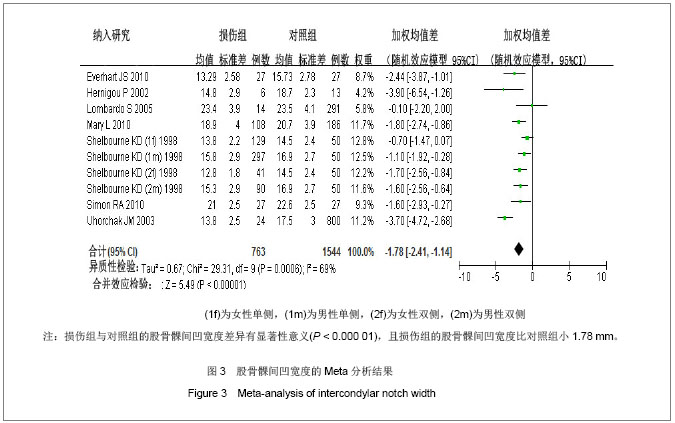
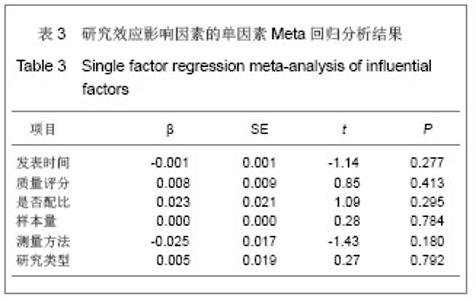
2.2 Meta分析结果 2.2.1 股骨髁间凹指数 12篇文献报道了损伤组与对照组的股骨髁间凹指数的均值和标准差[6-15,20,24] ,累计研究对象1 823例,损伤组577例,对照组2 795例。由图2可知,各研究间存在异质性(P < 0.05,I2=91%),采用随机效应模型的Meta分析,合并统计结果显示:损伤组与对照组的股骨髁间凹指数的合并加权均值差为-0.04,95%CI:(-0.05,-0.02),Z=4.56,P< 0.05,说明损伤组与对照组的股骨髁间凹指数的差异有显著性意义,且损伤组的股骨髁间凹指数比对照组小0.04。对纳入的每个研究剔除一次做合并分析,敏感性分析显示对结果影响不大,WMD的范围为-0.03(-0.05,-0.02)到-0.04(-0.05,-0.02)。对发表时间、质量评分、是否配比、样本量、测量方法以及研究类型分别进行单因素Meta回归,结果显示未找出可能的异质性来源,见表3。经Begg秩相关和Egger线性回归(Begg,P=0.584;Egger,P=0.739)检验发表偏倚,均显示所纳入的有关股骨髁间凹指数与前交叉韧带损伤相关性的文献不存在发表偏倚。以上研究说明Meta分析结果的稳定性好。"
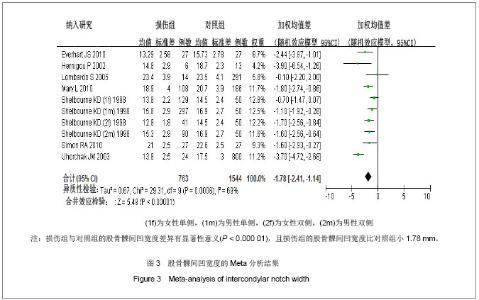
对纳入的每个研究剔除一次做合并分析,敏感性分析显示当剔除了Uhorchak等[11]的研究,加权均值差为-1.47,95%CI:(-1.92,-1.02),Z=6.36,P < 0.05,异质性检验I2=34%,提示Uhorchak等[11]可能为本研究异质性的重要来源之一。经Begg秩相关和Egger线性回归(Begg,P=0.074;Egger,P=0.542)检验发表偏倚,Begg秩相关检验显示所纳入的有关股骨髁间凹宽度与前交叉韧带损伤相关性的文献可能存在发表偏倚,提示结果不一定可靠,下结论时需谨慎。 另有4篇文献无法提取数据[5,19-20,22] ,未进行统计分析。Vyas等[5]的研究结果显示损伤组和对照组的股骨髁间凹指数差异无显著性意义;Lee等[19]的研究结果显示前交叉韧带损伤组与胫骨脊柱骨折组的股骨髁间凹指数差异有显著性意义;Motohashi等[20]的研究结果显示损伤组和对照组的股骨髁间凹宽度差异有显著性意义;Shelbourne等[23]的研究结果显示损伤组和对照组的股骨髁间凹指数差异无显著性意义。"
| [1]Simon RA, Everhart JS, Nagaraja HN, et al. A case-control study of anterior cruciate ligament volume, tibial plateau slopes and intercondylar notch dimensions in ACL-injured knees. J Biomech. 2010;43(9):1702-1707.[2]Lee JJ, Choi YJ, Shin KY,et al. Medial meniscal tears in anterior cruciate ligament-deficient knees: effects of posterior tibial slope on medial meniscal tear. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2011;23(4):227-230.[3]Chung SC, Chan WL, Wong SH. Lower limb alignment in anterior cruciate ligament-deficient versus -intact knees.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2011;19(3):303-308.[4]Kimura Y, Ishibashi Y, Tsuda E,et al. Increased knee valgus alignment and moment during single-leg landing after overhead stroke as a potential risk factor of anterior cruciate ligament injury in badminton.Br J Sports Med. 2012;46(3): 207-213.[5]Vyas S, van Eck CF, Vyas N,et al. Increased medial tibial slope in teenage pediatric population with open physes and anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(3):372-377.[6]Sonnery-Cottet B, Archbold P, Cucurulo T, et al. The influence of the tibial slope and the size of the intercondylar notch on rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(11):1475-1478. [7]Domzalski M, Grzelak P, Gabos P. Risk factors for Anterior Cruciate Ligament injury in skeletally immature patients: analysis of intercondylar notch width using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Int Orthop. 2010;34(5):703-707.[8]Hoteya K, Kato Y, Motojima S,et al. Association between intercondylar notch narrowing and bilateral anterior cruciate ligament injuries in athletes. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011; 131(3):371-376.[9]Ireland ML, Ballantyne BT, Little K, et al. A radiographic analysis of the relationship between the size and shape of the intercondylar notch and anterior cruciate ligament injury. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2001;9(4):200-205.[10]Lombardo S, Sethi PM, Starkey C. Intercondylar notch stenosis is not a risk factor for anterior cruciate ligament tears in professional male basketball players: an 11-year prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(1):29-34.[11]Uhorchak JM, Scoville CR, Williams GN, et al. Risk factors associated with noncontact injury of the anterior cruciate ligament: a prospective four-year evaluation of 859 West Point cadets. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31(6):831-842.[12]LaPrade RF, Burnett QM 2nd. Femoral intercondylar notch stenosis and correlation to anterior cruciate ligament injuries. A prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1994;22(2):198-202.[13]Lund-Hanssen H, Gannon J, Engebretsen L, et al. Intercondylar notch width and the risk for anterior cruciate ligament rupture. A case-control study in 46 female handball players. Acta Orthop Scand. 1994;65(5):529-532.[14]Souryal TO, Freeman TR. Intercondylar notch size and anterior cruciate ligament injuries in athletes. A prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1993;21(4):535-539.[15]Teitz CC, Lind BK, Sacks BM. Symmetry of the femoral notch width index. Am J Sports Med. 1997;25(5):687-690.[16]Simon RA, Everhart JS, Nagaraja HN, et al. A case-control study of anterior cruciate ligament volume, tibial plateau slopes and intercondylar notch dimensions in ACL-injured knees. J Biomech. 2010;43(9):1702-1707. [17]Everhart JS, Flanigan DC, Simon RA, et al. Association of noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injury with presence and thickness of a bony ridge on the anteromedial aspect of the femoral intercondylar notch. Am J Sports Med. 2010; 38(8):1667-1673.[18]Kocher MS, Mandiga R, Klingele K, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament injury versus tibial spine fracture in the skeletally immature knee: a comparison of skeletal maturation and notch width index. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004;24(2):185-188.[19]Lee GC, Cushner FD, Vigoritta V, et al. Evaluation of the anterior cruciate ligament integrity and degenerative arthritic patterns in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(1):59-65.[20]Motohashi M. Profile of bilateral anterior cruciate ligament injuries: a retrospective follow-up study.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2004;12(2):210-215.[21]Hernigou P, Garabedian JM. Intercondylar notch width and the risk for anterior cruciate ligament rupture in the osteoarthritic knee: evaluation by plain radiography and CT scan. Knee. 2002;9(4):313-316.[22]Souryal TO, Moore HA, Evans JP. Bilaterality in anterior cruciate ligament injuries: associated intercondylar notch stenosis. Am J Sports Med. 198816(5):449-454.[23]Shelbourne KD, Facibene WA, Hunt JJ. Radiographic and intraoperative intercondylar notch width measurements in men and women with unilateral and bilateral anterior cruciate ligament tears. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 1997; 5(4):229-233.[24]Stein V, Li L, Guermazi A, et al. The relation of femoral notch stenosis to ACL tears in persons with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(2):192-199.[25]Begg CB, Mazumdar M.Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. 1994;50(4): 1088-1101.[26]Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, et al. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315(7109):629-634.[27]Palmer I. On the injuries to the ligaments of the knee joint, A clinical study. Acta Chir Scand Suppl.1938;53:1-28.[28]Souryal TO, Freeman TR. Intercondylar notch size and anterior cruciate ligament injuries in athletes. A prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 1993;21(4):535-539.[29]Boden BP, Dean GS, Feagin JA Jr, et al. Mechanisms of anterior cruciate ligament injury.Orthopedics. 2000; 23(6): 573-578.[30]Dienst M, Schneider G, Altmeyer K, et al. Correlation of intercondylar notch cross sections to the ACL size: a high resolution MR tomographic in vivo analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007;127(4):253-260.[31]Muneta T, Takakuda K, Yamamoto H. Intercondylar notch width and its relation to the configuration and cross-sectional area of the anterior cruciate ligament. A cadaveric knee study. Am J Sports Med. 1997;25(1):69-72.[32]Bjordal JM, Arn?y F, Hannestad B, et al. Epidemiology of anterior cruciate ligament injuries in soccer. Am J Sports Med. 1997;25(3):341-345.[33]Toth AP, Cordasco FA. Anterior cruciate ligament injuries in the female athlete. J Gend Specif Med. 2001;4(4):25-34.[34]Ruedl G, Webhofer M, Helle K,et al. Leg dominance is a risk factor for noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injuries in female recreational skiers. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(6): 1269-1273.[35]Ageberg E, Forssblad M, Herbertsson P,et al. Sex differences in patient-reported outcomes after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: data from the Swedish knee ligament register. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(7):1334-1342.[36]Wolters F, Vrooijink SH, Van Eck CF, et al. Does notch size predict ACL insertion site size. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19 Suppl 1:S17-S21.[37]van Eck CF, Martins CA, Lorenz SG,et al. Assessment of correlation between knee notch width index and the three-dimensional notch volume. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(9):1239-1244. |
| [1] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [2] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [3] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [4] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [5] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [6] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [7] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [8] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [9] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [10] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [11] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [12] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [13] | Zeng Zhen, Hu Jingwei, Li Xuan, Tang Linmei, Huang Zhiqiang, Li Mingxing. Quantitative analysis of renal blood flow perfusion using contrast-enhanced ultrasound in rats with hemorrhagic shock during resuscitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1201-1206. |
| [14] | Chai Le, Lü Jianlan, Hu Jintao, Hu Huahui, Xu Qingjun, Yu Jinwei, Quan Renfu. Signal pathway variation after induction of inflammatory response in rats with acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1218-1223. |
| [15] | Chen Jiming, Wu Xiaojing, Liu Tianfeng, Chen Haicong, Huang Chengshuo. Effects of silymarin on liver injury and bone metabolism induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1224-1228. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||