Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (12): 1924-1929.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3791
Previous Articles Next Articles
Fixed-bearing prosthesis versus mobile-bearing prosthesis during total knee arthroplasty for different follow-up periods: a meta-analysis
Wang Xin1, Lin Xiaodong1, Liu Hongliang2, Huang Zexin2, Xu Shuchai2, Chen Bojian2
- 1Second Clinical Medical College, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-05-23Revised:2020-05-27Accepted:2020-07-06Online:2021-04-28Published:2020-12-26 -
Contact:Chen Bojian, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Wang Xin, Master candidate, Second Clinical Medical College, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Xin, Lin Xiaodong, Liu Hongliang, Huang Zexin, Xu Shuchai, Chen Bojian. Fixed-bearing prosthesis versus mobile-bearing prosthesis during total knee arthroplasty for different follow-up periods: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1924-1929.
share this article
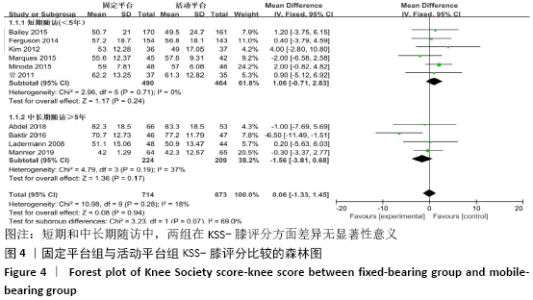
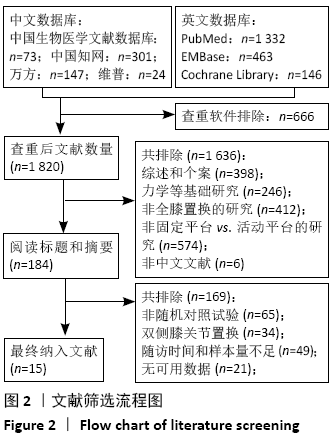
2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 各组KSS-膝评分差异 共有10篇文献报道了KSS-膝评 分[9-10,12-13,15-18,20,22],其中4篇文献随访时间超过5年[9,12,16,22],有6篇文献随访时间不足5年[10,13,15,17-18,20],故按照随访时间长短分为短期随访组(<5年)和中长期随访组(≥5年)2个亚组。亚组异质性检验结果显示,短期随访组(I2=0%,P=0.71)与中长期随访组(I2=37%,P=0.19)组间具有同质性,故采用固定效应模型合并效应量。Meta分析结果显示,短期随访组中,固定平台组与活动平台组在KSS-膝评分方面差异无显著性意义(MD=1.06,95%Cl:-0.71-2.83,P=0.24);中长期随访组中,两组间差异仍无显著性意义(MD=-1.56,95%Cl:-3.81-0.68,P=0.17),见图4。 "
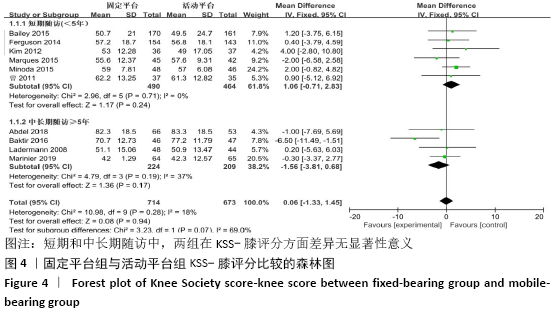
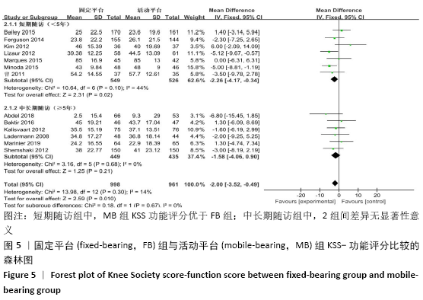
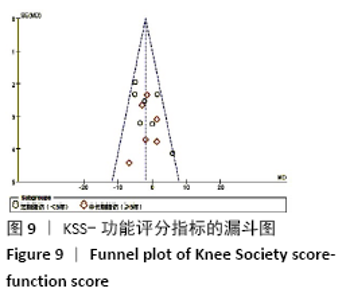
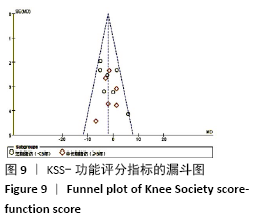
2.3.2 各组KSS-功能评分差异 共有13篇文献报道了KSS-功能评 分[8-13,15-18,20-22],其中6篇文献随访时间超过5年[8-9,12,16,21,23],有7篇文献随访时间不足5年[10-11,13,15,17-18,20],故按照随访时间长短分为短期随访组(<5年)和中长期随访组(≥5年)2个亚组。亚组异质性检验结果显示,短期随访组(I2=44%,P=0.1)与中长期随访组(I2=0%,P=0.68)组间具有同质性,故采用固定效应模型合并效应量。Meta分析结果显示,短期随访组中,活动平台组KSS功能评分优于固定平台组,2组间差异有显著性意义(MD=-2.26,95%Cl:-4.17至-0.34,P=0.02);中长期随访组中,2组间差异无显著性意义(MD=-1.58,95%Cl:-4.06-0.90,P=0.21),见图5。 "

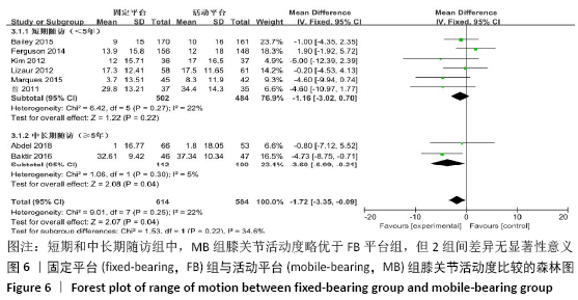
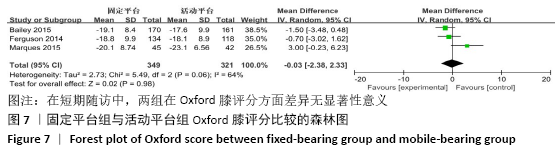
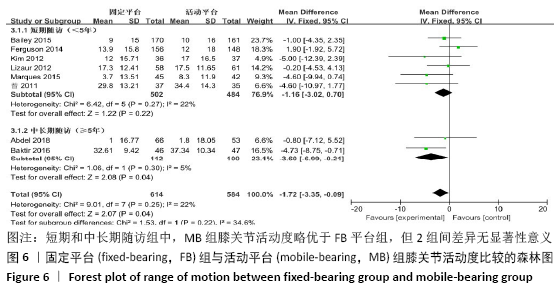
2.3.3 各组膝关节活动度差异 共有8篇文献报道了膝关节活动 度[10-11,13,15-18,22],其中有2篇文献随访时间超过5年[16,22],有6篇文献随访时间不足5年[10-11,13,15,17-18],故按照随访时间长短分为短期随访组(<5年)和中长期随访组(≥5年)2个亚组。亚组异质性检验结果显示,短期随访组(I2=22%,P=0.27)与中长期随访组(I2=5%,P=0.3)组间具有同质性,故采用固定效应模型合并效应量。Meta分析结果显示,短期随访组中,活动平台组膝关节活动度优于固定平台平台组,但组间差异无显著性意义(MD=-1.16,95%Cl: -3.02-0.70,P=0.22);中长期随访组中,活动平台组在膝关节活动度方面优于固定平台组,且2组间差异有显著性意义(MD=-3.60,95%Cl:-6.99至-0.21,P=0.04),见图6。"
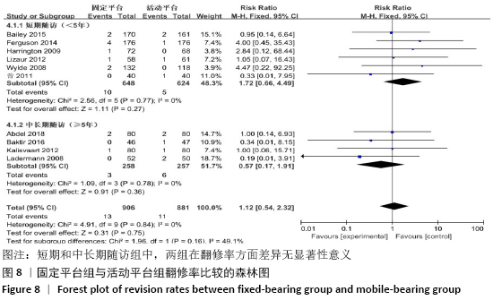
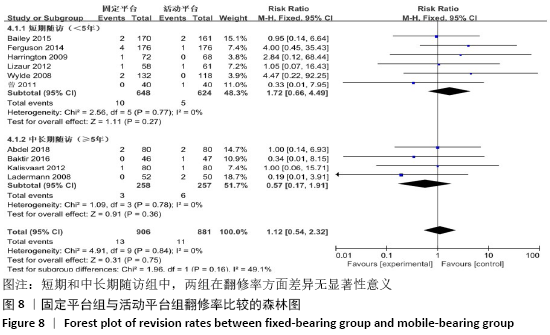
2.3.5 各组翻修率差异 共有10篇文献报道了翻修病例[11-12,14-19,21-22],其中4篇文献随访时间超过5年[12,16,21-22],6篇文献随访时间不足5年[11,14-15,17-19],故按照随访时间长短分为短期随访组(<5年)和中长期随访组(≥5年)2个亚组。亚组异质性检验结果显示,短期随访组(I2=0%,P=0.77)与中长期随访组(I2=0%,P=0.78)组间具有同质性,故采用固定效应模型合并效应量。Meta分析结果显示,短期随访组中,固定平台组在翻修率方面与活动平台组相比差异无显著性意义(RR=1.72,95%Cl:0.66-4.49,P=0.27);中长期随访组中,2组间差异仍无显著性意义(RR=0.57,95%Cl:0.17-1.91,P=0.36),见图8。"
| [1] AGLIETTI P, BALDINI A, BUZZI R, et al. Comparison of mobile-bearing and fixed-bearing total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(2):145-153. [2] HAIDER H, GARVIN K. Rotating platform versus fixed-bearing total knees: an in vitro study of wear. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(11):2677-2685. [3] HO FY, MA HM, LIAU JJ, et al. Mobile-bearing knees reduce rotational asymmetric wear. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;462:143-149. [4] LI YL, WU Q, NING GZ, et al. No difference in clinical outcome between fixed- and mobile-bearing TKA: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(3):565-575. [5] MOSKAL JT, CAPPS SG. Rotating-platform TKA no different from fixed-bearing TKA regarding survivorship or performance: a meta-analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(7):2185-2193. [6] BO ZD, LIAO L, ZHAO JM, et al. Mobile bearing or fixed bearing? A meta-analysis of outcomes comparing mobile bearing and fixed bearing bilateral total knee replacements. Knee. 2014;21(2):374-381. [7] 曹力,龚时国,康雄,等.活动平台与固定平台假体全膝关节置换术疗效的Meta分析[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2009,29(2):97-102. [8] SHEMSHAKI H, DEHGHANI M, ESHAGHI MA, et al. Fixed versus mobile weight-bearing prosthesis in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(12):2519-2527. [9] SAPPEY-MARINIER E, DE ABREU FGA, O’LOUGHLIN P, et al. No difference in patellar position between mobile-bearing and fixed-bearing total knee arthroplasty for medial osteoarthritis: a prospective randomized study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(5):1542-1550. [10] MARQUES CJ, DANIEL S, SUFI-SIAVACH A, et al. No differences in clinical outcomes between fixed- and mobile-bearing computer-assisted total knee arthroplasties and no correlations between navigation data and clinical scores. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(6):1660-1668. [11] LIZAUR-UTRILLA A, SANZ-REIG J, TRIGUEROS-RENTERO MA. Greater satisfaction in older patients with a mobile-bearing compared with fixed-bearing total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(2):207-212. [12] LADERMANN A, LÜBBEKE A, STERN R, et al. Fixed-bearing versus mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomised, clinical and radiological study with mid-term results at 7 years. Knee. 2008;15(3):206-210. [13] KIM D, SEONG SC, LEE MC, et al. Comparison of the tibiofemoral rotational alignment after mobile and fixed bearing total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(2):337-345. [14] HARRINGTON MA, HOPKINSON WJ, HSU P, et al. Fixed- vs mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty: does it make a difference? A prospective randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(6 Suppl):24-27. [15] FERGUSON KB, BAILEY O, ANTHONY I, et al. A prospective randomised study comparing rotating platform and fixed bearing total knee arthroplasty in a cruciate substituting design-outcomes at two year follow-up. Knee. 2014;21(1):151-155. [16] BAKTIR A, KARAASLAN F, YURDAKUL E, et al. Mobile- versus fixed-bearing total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled trial featuring 6-10-year follow-up. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2016;50(1):1-9. [17] BAILEY O, FERGUSON K, CRAWFURD E, et al. No clinical difference between fixed- and mobile-bearing cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(6):1653-1659. [18] 曾赟,曹力,刘阳,等.固定平台型和旋转平台型假体全膝关节置换术后早期疗效的随机对照研究[J].中华医学杂志, 2011,91(11):752-756. [19] WYLDE V, LEARMONTH I, POTTER A, et al. Patient-reported outcomes after fixed-versus mobile-bearing total knee replacement: a multi-centre randomised controlled trial using the Kinemax total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(9):1172-1179. [20] MINODA Y, IWAKI H, IKEBUCHI M, et al. Mobile-bearing prosthesis and intraoperative gap balancing are not predictors of superior knee flexion: a prospective randomized study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(7):1986-1992. [21] KALISVAART MM, PAGNANO MW, TROUSDALE RT, et al. Randomized clinical trial of rotating-platform and fixed-bearing total knee arthroplasty: no clinically detectable differences at five years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(6):481-489. [22] ABDEL MP, TIBBO ME, STUART MJ, et al. A randomized controlled trial of fixed- versus mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty: a follow-up at a mean of ten years. Bone Joint J. 2018; 100-B(7):925-929. [23] MCEWEN HM, BARNETT PI, BELL CJ, et al. The influence of design, materials and kinematics on the in vitro wear of total knee replacements. J Biomech. 2005;38(2):357-365. [24] HASEGAWA M, SUDO A, UCHIDA A. Staged bilateral mobile-bearing and fixed-bearing total knee arthroplasty in the same patients: a prospective comparison of a posterior-stabilized prosthesis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009;17(3):237-243. [25] HUANG CH, LIAU JJ, CHENG CK. Fixed or mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2007;2:1. [26] MATSUDA S, MIZU-UCHI H, FUKAGAWA S, et al. Mobile-bearing prosthesis did not improve mid-term clinical results of total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(10): 1311-1316. [27] HIGUCHI H, HATAYAMA K, SHIMIZU M, et al. Relationship between joint gap difference and range of motion in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomised study between different platforms. Int Orthop. 2009;33(4):997-1000. [28] BHAN S, MALHOTRA R, KIRAN EK, et al. A comparison of fixed-bearing and mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty at a minimum follow-up of 4.5 years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(10): 2290-2296. [29] OH KJ, PANDHER DS, LEE SH, et al. Meta-analysis comparing outcomes of fixed-bearing and mobile-bearing prostheses in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(6):873-884. [30] SMITH TO, EJTEHADI F, NICHOLS R, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes of fixed-versus mobile-bearing total knee replacement: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(3):325-340. [31] 韩俊亮,段王平,高耀祖,等.移动平台型假体与固定平台型假体全膝置换术治疗膝关节炎疗效的Meta分析[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2015,9(3):370-376. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [6] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [7] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [8] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [9] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [10] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [11] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [12] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [13] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [14] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [15] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||