Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (14): 2224-2230.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3129
Previous Articles Next Articles
Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu Decoction in the treatment of osteoarthritis: analysis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology
Han Jie1, Zhang Xiaoyun1, 2, Chen Rilan1, Zhang Chi1, Liao Zilong1, Chen Yueping1, Chen Feng1, Liao Jianzhao1
- 1Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Received:2020-04-28Revised:2020-04-30Accepted:2020-05-30Online:2021-05-18Published:2020-12-31 -
Contact:Chen Rilan, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Han Jie, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960908 (to CRL); Guangxi Chinese Medicine/Zhuangyao Pharmaceutical Preparation Improvement Project, No. GZZJ16-07 (to CRL); First-Class Discipline Projects of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2019XK026 (to CYP) and 2019XK029
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Jie, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Rilan, Zhang Chi, Liao Zilong, Chen Yueping, Chen Feng, Liao Jianzhao . Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu Decoction in the treatment of osteoarthritis: analysis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2224-2230.
share this article
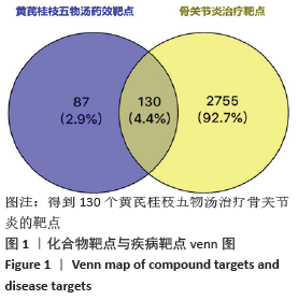
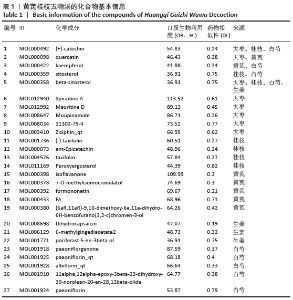
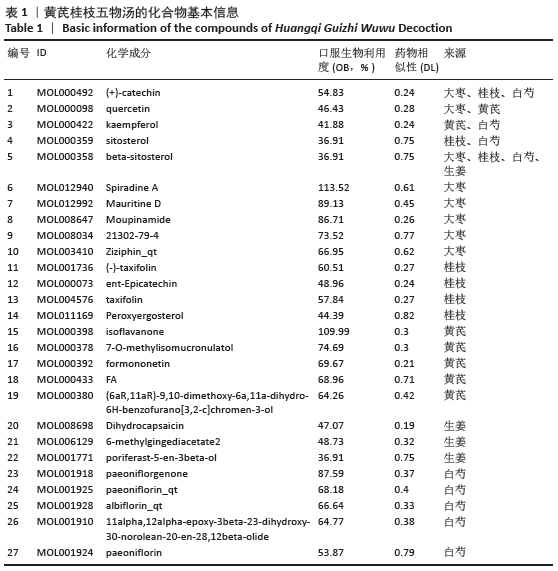
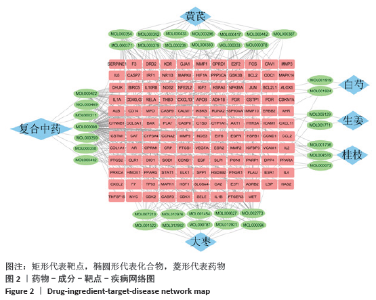
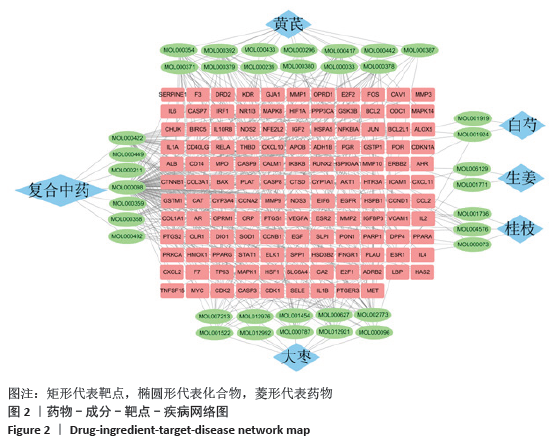
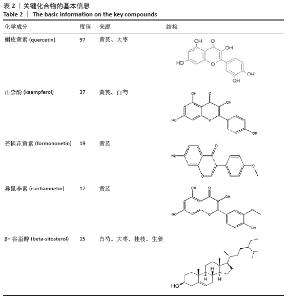
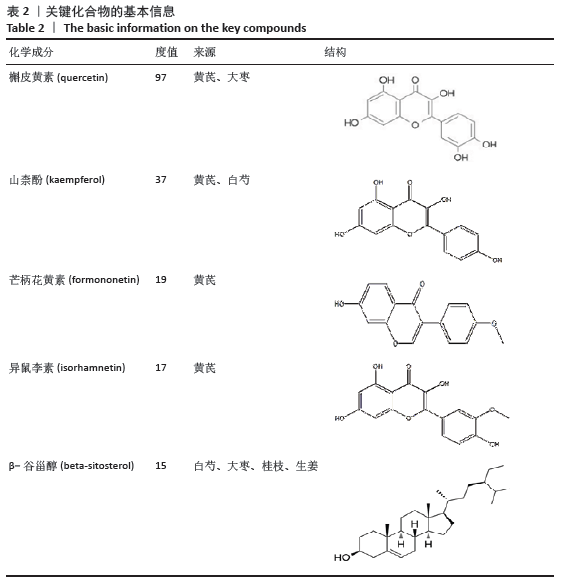
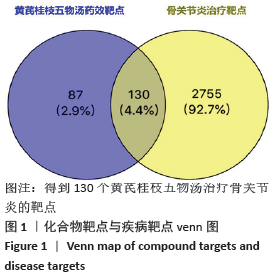
2.1 化合物筛选结果 以口服生物利用度(OB)≥30%且药物相似性(DL)≥0.18作为筛选参数,共得到74个活性化学成分,黄芪的化合物有20个,桂枝的化合物有7个,白芍的化合物有13个,生姜的化合物有5个,大枣的化合物有29个。其中大枣、黄芪、白芍有1个交集化合物,大枣、生姜有1个交集化合物,大枣、桂枝、白芍、生姜有1个交集化合物,大枣、桂枝、白芍有1个交集化合物,大枣、黄芪有1个交集化合物,桂枝、白芍有1个交集化合物,黄芪、白芍有1个交集化合物,删除重复数据后剩余活性化学成分63个,活性成分的基本信息见表 1,由于筛选结果过多,因此仅列出共同作用的活性成分及每味药口服生物利用度(OB)值前5的活性成分。 2.2 预测黄芪桂枝五物汤治疗骨关节炎的靶点结果 根据TCMSP数据库预测得到217个黄芪桂枝五物汤药效靶点。根据OMIM、GeneCards和TTD数据库得到 2 885个骨关节炎的治疗靶点。运用Venny平台将黄芪桂枝五物汤药效靶点与骨关节炎的治疗靶点取交集,得到130个黄芪桂枝五物汤治疗骨关节炎的靶点,如图1。"
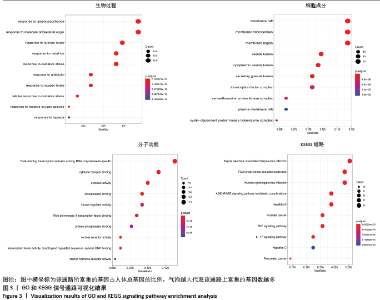
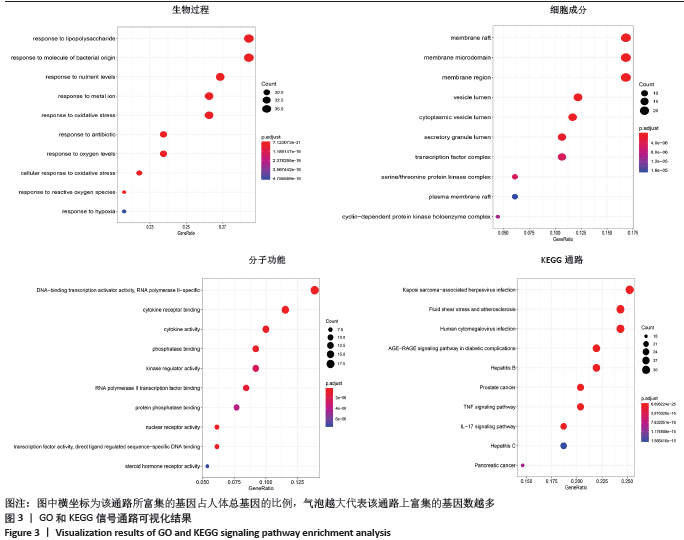
2.4 GO富集分析与KEGG富集分析结果 GO富集分析所得到的GO条目共2 343个(P < 0.05),其中生物过程(BP)条目 2 144个、细胞成分(CC)条目70个、分子功能(MF)条目129个;KEGG通路富集分析共得到146条通路。根据P排序,选取P值最显著的前10个条目以气泡图的形式展现,如图3。分析结果显示,黄芪桂枝五物汤治疗骨关节炎的生物过程主要涉及对脂多糖的反应、对细菌来源分子的反应、对营养水平的反应、氧化应激反应等;细胞成分主要涉及膜筏、膜微区、膜区等;分子功能主要涉及核受体活性、转录因子活性、细胞因子活性等;信号通路主要涉及AGE?RAGE信号通路、MAPK信号通路、核因子κB信号通路、肿瘤坏死因子信号通路、白细胞介素17信号通路等,如图3。 "
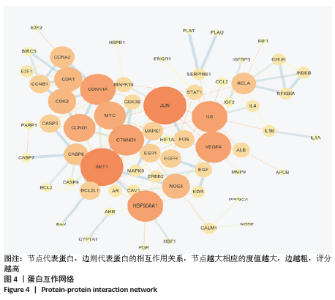
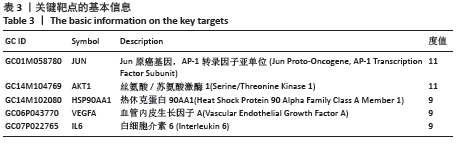
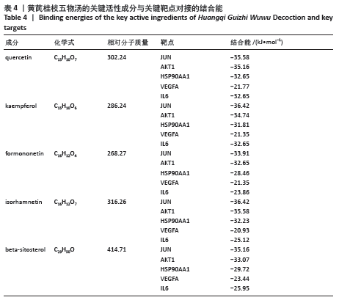
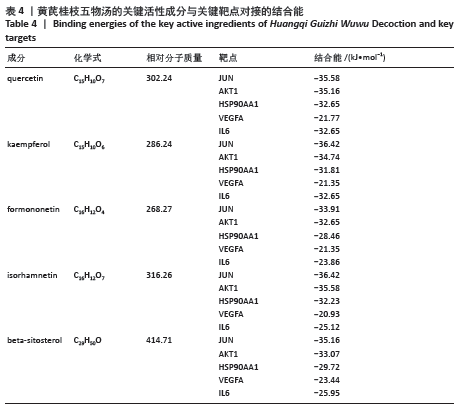
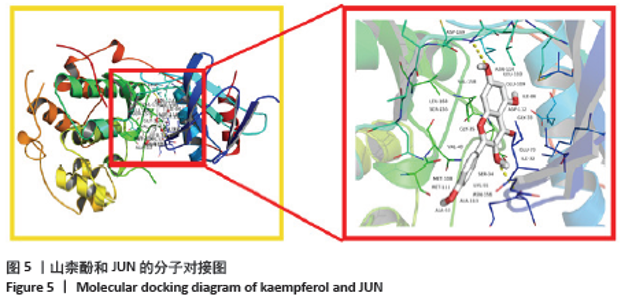
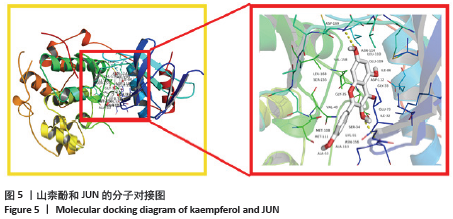
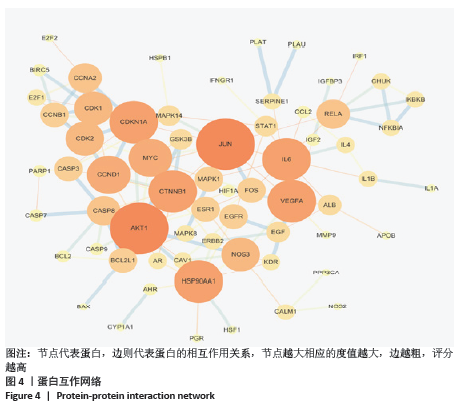
2.5 蛋白互作网络与蛋白模块 借助String数据库和Cytoscape构建PPI网络图,见图4。图中共涉及节点65个、边125条,其中节点代表蛋白,边则代表蛋白的相互作用关系。度值排名前5的蛋白质为Jun原癌基因(Jun Proto-Oncogene,JUN)、AKT丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶1(AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase 1,AKT1)、热休克蛋白90AA1(Heat Shock Protein 90 Alpha Family Class A Member 1,HSP90AA1)、血管内皮生长因子A(Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A,VEGFA)、白细胞介素6(Interleukin 6,IL6)。这些度值较大的蛋白质在整个网络中起着关键的作用,同时这些蛋白所对应的靶点在黄芪桂枝五物汤治疗骨关节炎中具有重要的地位,可能是黄芪桂枝五物汤治疗骨关节炎的关键靶点,其基本信息见表3。 "
| [1] Li D, Li G, Chen Y, et al. Astragaloside IV protects ATDC5 cells from lipopolysaccharide-caused damage through regulating miR-203/MyD88.Pharm Biol. 2020;58(1):89-97. [2] Zhao J, Huang H, Liang G, et al. Effects and safety of the combination of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and hyaluronic acid (HA) in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020; 21(1):224. [3] Liu T. Super-aging and social security for the most elderly in China. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2018;51(1): 105-112. [4] Mol MF, Runhaar J, Bos PK, et al. Effectiveness of intramuscular gluteal glucocorticoid injection versus intra-articular glucocorticoid injection in knee osteoarthritis: design of a multicenter randomized, 24 weeks comparative parallel-group trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):225. [5] 陈日兰,邓凯烽,韦星成,等.电针对膝关节骨性关节炎患者疼痛改善及关节功能影响的荟萃分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(21): 3438-3444. [6] 邓凯烽,尚鑫阳,朱圣旺,等.穴位注射改善膝骨关节炎患者疼痛及关节功能的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(18):2879-2887. [7] 王骥.中医药疗法治疗膝关节骨性关节炎研究进展[J].中国临床医生杂志,2015,43(3): 36-39. [8] 王清.黄芪桂枝五物汤结合关节镜治疗膝骨性关节炎的疗效观察[D]. 昆明:云南中医学院, 2017. [9] 赵乐,李艳彦,王永辉,等.黄芪桂枝五物汤对骨关节炎大鼠血管新生的作用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(3):87-93. [10] Li J, Zhao P, Li Y, et al. Systems pharmacology-based dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Bufei Yishen as an effective treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15290. [11] Ru J, Li P, Wang J, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform. 2014;6:13. [12] 赵乐,李艳彦,王永辉,等.黄芪桂枝五物汤对阳虚寒凝型骨关节炎大鼠免疫相关细胞因子的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2017, 23(7):160-166. [13] 汤晓晨.黄芪甲苷干预人膝骨关节炎退变关节软骨细胞的效应及机制研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学, 2015. [14] 胡鹏飞.芍药苷在骨性关节炎中的作用及其机制研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2017. [15] Wei B, Zhang Y, Tang L, et al. Protective effects of quercetin against inflammation and oxidative stress in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis.Drug Dev Res. 2019;80(3):360-367. [16] Permatasari DA, Karliana D, Iskandarsyah I, et al. Quercetin prevent proteoglycan destruction by inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9, matrix metalloproteinase-13, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs-5 expressions on osteoarthritis model rats. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2019;10(1):2-8. [17] Zhuang Z, Ye G, Huang B. Kaempferol Alleviates the Interleukin-1β-Induced Inflammation in Rat Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes via Suppression of NF-κB.Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:3925-3931. [18] Cho IA, Kim TH, Lim H, et al. Formononetin Antagonizes the Interleukin-1β-Induced Catabolic Effects Through Suppressing Inflammation in Primary Rat Chondrocytes. Inflammation. 2019; 42(4):1426-1440. [19] Zhou F, Mei J, Yuan K, et al. Isorhamnetin attenuates osteoarthritis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and protecting chondrocytes through modulating reactive oxygen species homeostasis. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(6): 4395-4407. [20] Cheng BC, Fu XQ, Guo H, et al. The genus Rosa and arthritis: Overview on pharmacological perspectives. Pharmacol Res.2016;114:219-234. [21] Millerand M, Berenbaum F, Jacques C. Danger signals and inflammaging in osteoarthritis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;120(5):48-56. [22] Rosenberg JH, Rai V, Dilisio MF, et al. Damage-associated molecular patterns in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis:potentially novel therapeutic targets.Mol Cell Biochem. 2017; 434(1-2):171-179. [23] Wei Y, Jin Z, Zhang H, et al. The Transient Receptor Potential Channel, Vanilloid 5, Induces Chondrocyte Apoptosis via Ca2+ CaMKII-Dependent MAPK and Akt/ mTOR Pathways in a Rat Osteoarthritis Model. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(5):2309-2323. [24] Ran J, Ma C, Xu K, et al. Schisandrin B ameliorated chondrocytes inflammation and osteoarthritis via suppression of NF-κB and MAPK signal pathways.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018;12: 1195-1204. [25] Zhou F, Mei J, Han X, et al. Kinsenoside attenuates osteoarthritis by repolarizing macrophages through inactivating NF-κB/MAPK signaling and protecting chondrocytes. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2019;9(5):973-985. [26] Yan S, Ding H, Peng J, et al. Down-regulation of protease-activated receptor 2 ameliorated osteoarthritis in rats through regulation of MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(3):BSR20192620. [27] Chow YY, Chin KY. The Role of Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2020;2020:8293921. [28] Zhang G, Gu M, Xu Y, et al. A comprehensive analysis on the effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 on primary chondrocytes cultured from patients with osteoarthritis. Gene. 2020;730:144322. [29] Gao N, Ding L, Pang J, et al. Metabonomic-Transcriptome Integration Analysis on Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Genomics. 2020;2020:5925126. [30] Gao X, Sun Y, Li X. Identification of key gene modules and transcription factors for human osteoarthritis by weighted gene co-expression network analysis.Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(4): 2479-2490. [31] Qiong J, Xia Z, Jing L, et al. Synovial mesenchymal stem cells effectively alleviate osteoarthritis through promoting the proliferation and differentiation of meniscus chondrocytes.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(4):1645-1655. [32] Xue H, Tu Y, Ma T, et al. Lactoferrin Inhibits IL-1β-Induced Chondrocyte Apoptosis Through AKT1-Induced CREB1 Activation.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(6):2456-2465. [33] Zhao X, Wang T, Cai B, et al. MicroRNA-495 enhances chondrocyte apoptosis, senescence and promotes the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting AKT1.Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(4): 2232-2244. [34] Siebelt M, Jahr H, Groen HC, et al. Hsp90 inhibition protects against biomechanically induced osteoarthritis in rats. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(8):2102-2112. [35] Boehm AK, Seth M, Mayr KG, et al. Hsp90 mediates insulin-like growth factor 1 and interleukin-1beta signaling in an age-dependent manner in equine articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(7): 2335-2343. [36] Guan M, Zhu Y, Liao B, et al.Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound inhibits VEGFA expression in chondrocytes and protects against cartilage degeneration in experimental osteoarthritis.FEBS Open Bio. 2020;10(3):434-443. [37] Takano S, Uchida K, Shoji S, et al. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Is Regulated by the Canonical and Noncanonical Transforming Growth Factor-β Pathway in Synovial Fibroblasts Derived from Osteoarthritis Patients.Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:6959056. [38] Sakata S, Kunimatsu R, Tsuka Y, et al. High-Frequency Near-Infrared Diode Laser Irradiation Attenuates IL-1β-Induced Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines and Matrix Metalloproteinases in Human Primary Chondrocytes. J Clin Med. 2020;9(3):881. [39] Li D, Li G, Chen Y, et al. Astragaloside IV protects ATDC5 cells from lipopolysaccharide-caused damage through regulating miR-203/MyD88. Pharm Biol. 2020;58(1):89-97. |
| [1] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [2] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [3] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [4] | Shen Jinbo, Zhang Lin. Micro-injury of the Achilles tendon caused by acute exhaustive exercise in rats: ultrastructural changes and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1190-1195. |
| [5] | Li Jing, Xie Jianshan, Cui Huilin, Cao Ximei, Yang Yanping, Li Hairong. Expression and localization of diacylglycerol kinase zeta and protein kinase C beta II in mouse back skin with different coat colors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1196-1200. |
| [6] | Chai Le, Lü Jianlan, Hu Jintao, Hu Huahui, Xu Qingjun, Yu Jinwei, Quan Renfu. Signal pathway variation after induction of inflammatory response in rats with acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1218-1223. |
| [7] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [8] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [9] | Tan Jingyu, Liu Haiwen. Genome-wide identification, classification and phylogenetic analysis of Fasciclin gene family for osteoblast specific factor 2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1243-1248. |
| [10] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [11] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [12] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [13] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [14] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [15] | Wang Hanyue, Li Furong, Yang Xiaofei, Hu Chaofeng. Direct reprogramming hepatocytes into islet-like cells by efficiently targeting and activating the endogenous genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1056-1063. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||