Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (30): 4818-4823.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2822
Previous Articles Next Articles
A new minimally invasive spreader combined with less invasive stabilization system for proximal tibial fractures
Huang Junming, Liu Xiaoming, Li Jiman, Zhong Weibin, Liu Yu, Zhu Haodong
- Department of Orthopedics (Part 1), Fifth Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510730, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2019-12-12Revised:2019-12-14Accepted:2020-02-26Online:2020-10-28Published:2020-09-19 -
Contact:Zhu Haodong, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics (Part 1), Fifth Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510730, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Huang Junming, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics (Part 1), Fifth Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510730, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Junming, Liu Xiaoming, Li Jiman, Zhong Weibin, Liu Yu, Zhu Haodong. A new minimally invasive spreader combined with less invasive stabilization system for proximal tibial fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(30): 4818-4823.
share this article
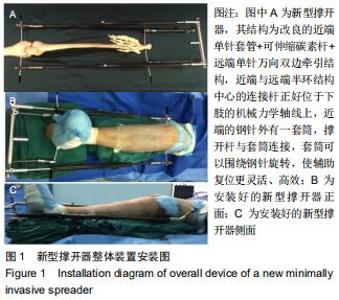
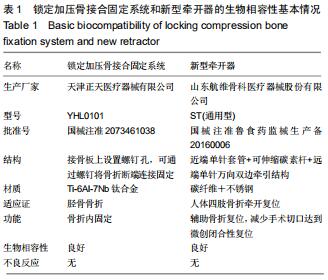
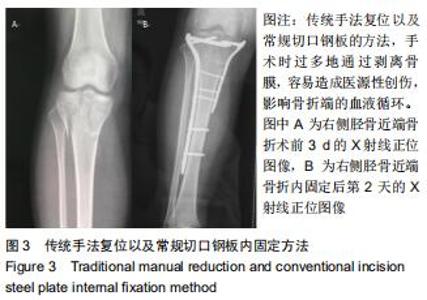
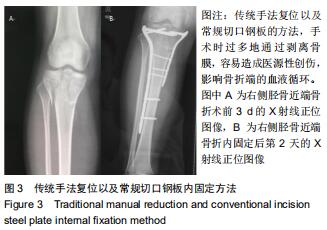
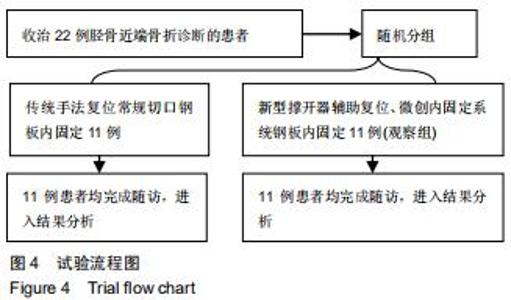
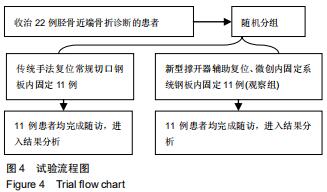
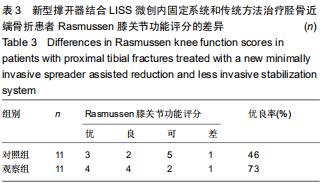
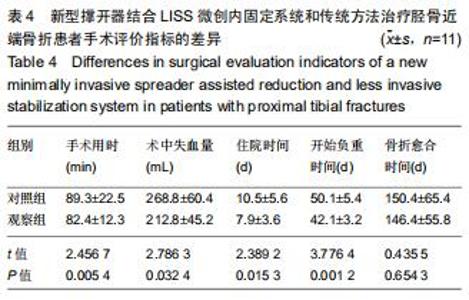
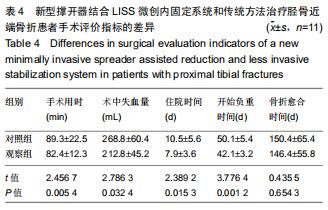
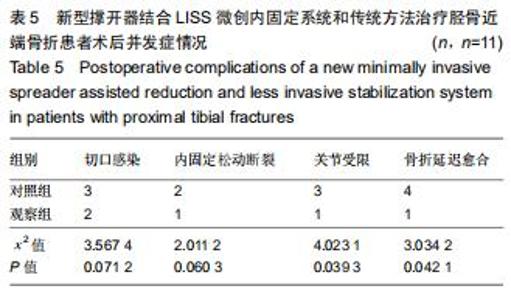
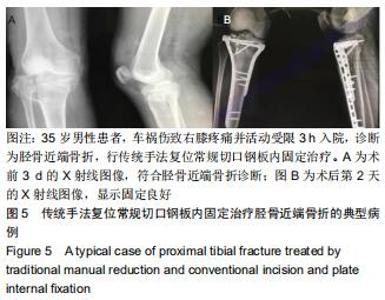
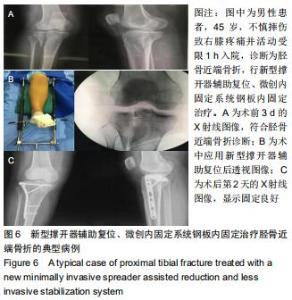
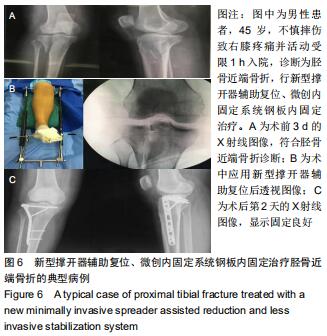
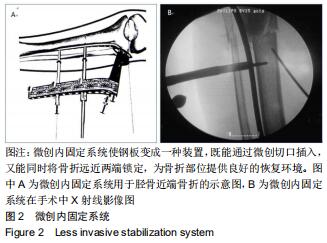
1.5.2 新型微创撑开器辅助复位及微创切口微创内固定系统治疗 采用单侧硬脊膜外腔麻醉,患肢上止血带。先安装新型撑开器,在术中透视下,调整双边牵引撑开程度,确认恢复膝关节的胫股正常力线后锁定撑开器。应用前外侧切口,从Gerdy结节向远端行一长约4 cm的弧形切口,仔细分离胫前肌近端附着处,逐层分离,清除关节内积血,清洗后充分暴露胫骨近端关节面,在牵引撑开器辅助下,微调骨折对位、对线复位。若仍发现关节面不平整,则于关节面下方约2 cm处凿出一骨窗,应用复位顶棒将关节面撑顶复位,经透视关节面平整后取自体髂骨或人工骨植入,再次透视确定关节面平整。沿胫骨轴线经骨膜外向远端分离出一软组织隧道,预计钢板需要的长度,要保证骨折线远端的钢板最少有三四个螺钉孔固定。把合适长度的微创内固定系统-锁定钢板安装在导向器上,在透视的引导下将钢板经隧道穿行至胫骨远端。将配套的带螺纹的克氏针固定导向器的近端孔里,侧位透视确认钢板远端位置准确后,用克氏针固定导向器远端孔,皮外行小切口暴露钢板远端钉孔。再次透视确定钢板位置满意,远近端分别置入锁定螺钉,拔除克氏针、导向器。术毕拆除微创撑开器,冲洗切口,放置引流管,逐层缝合,加压包扎伤口。存在合并症的二期关节镜下再处理,见图1,2。 "
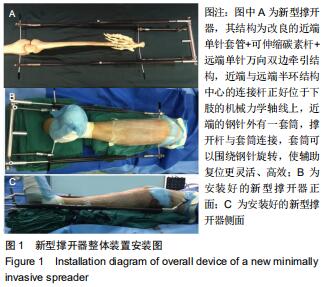
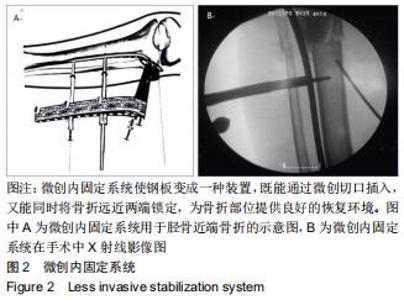
1.5.2 新型微创撑开器辅助复位及微创切口微创内固定系统治疗 采用单侧硬脊膜外腔麻醉,患肢上止血带。先安装新型撑开器,在术中透视下,调整双边牵引撑开程度,确认恢复膝关节的胫股正常力线后锁定撑开器。应用前外侧切口,从Gerdy结节向远端行一长约4 cm的弧形切口,仔细分离胫前肌近端附着处,逐层分离,清除关节内积血,清洗后充分暴露胫骨近端关节面,在牵引撑开器辅助下,微调骨折对位、对线复位。若仍发现关节面不平整,则于关节面下方约2 cm处凿出一骨窗,应用复位顶棒将关节面撑顶复位,经透视关节面平整后取自体髂骨或人工骨植入,再次透视确定关节面平整。沿胫骨轴线经骨膜外向远端分离出一软组织隧道,预计钢板需要的长度,要保证骨折线远端的钢板最少有三四个螺钉孔固定。把合适长度的微创内固定系统-锁定钢板安装在导向器上,在透视的引导下将钢板经隧道穿行至胫骨远端。将配套的带螺纹的克氏针固定导向器的近端孔里,侧位透视确认钢板远端位置准确后,用克氏针固定导向器远端孔,皮外行小切口暴露钢板远端钉孔。再次透视确定钢板位置满意,远近端分别置入锁定螺钉,拔除克氏针、导向器。术毕拆除微创撑开器,冲洗切口,放置引流管,逐层缝合,加压包扎伤口。存在合并症的二期关节镜下再处理,见图1,2。"
|
[1] MEHIN R, O'BRIEN P, BROEKHUYSE H, et al. Endstage arthritis following tibia plateau fractures: average 10-year follow-up. Can J Surg. 2012;55(2):87-94.
[2] 王建伟,杨星光,王韬,等,微创内固定系统治疗胫骨近端复杂骨折[J].中国临床医学,2007,14(4):554-557.
[3] 陈新宇.微创内固定技术与传统手术对胫骨平台骨折患者膝关节功能的影响对比[J].中国实用医药,2013,8(10)43-44. [4] KRIEG JC. Proximal tibial fractures: current treatment, results, and problems. Injury. 2003;34 Suppl 1:A2-A10.
[5] SCHANDELMAIER P, PARTENHEIMER A, KOENEMANN B, et al. Distal femoral fractures and LISS stabilization. Injury. 2001;32 Suppl 3: SC55-SC63.
[6] GOESLING T, FRENK A, APPENZELLER A, et al. LISS PLT: design, mechanical and biomechanical characteristics. Injury. 2003;34 Suppl 1:A11-A15.
[7] 李浩,徐龙伟,季卫平,等LISS钢板在胫骨近端骨折中的应用[J].实用骨科杂志,2007,13(1):45-47.
[8] SCHÜTZ M, KÄÄB MJ, HAAS N. Stabilization of proximal tibial fractures with the LIS-System: early clinical experience in Berlin. Injury. 2003;34 Suppl 1:A30-A35.
[9] STANNARD JP, WILSON TC, VOLGAS DA, et al. Fracture stabilization of proximal tibial fractures with the proximal tibial LISS: early experience in Birmingham, Alabama (USA). Injury. 2003;34 Suppl 1:A36-A42.
[10] 骆锦强,袁权华,陈振宇,等.LISS钢板在胫骨近端骨折中的应用研究[J].中国医学创新,2009,6(22):25-26.
[11] GRALA P, TWARDOSZ W, TONDEL W, et al. Large bone distractor for open reconstruction of articular fractures of the calcaneus. Int Orthop. 2009;33(5):1283-1288.
[12] 吴煌,廖瑛,范伟杰,等.SchatzkerⅤⅥ型胫骨平台骨折的手术治疗与疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(12):891-893.
[13] RASMUSSEN PS. Tibial condylar fractures. Impairment of knee joint stability as an indication for surgical treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973;55(7):1331-1350.
[14] 胡超,张桃根,蔡林.胫骨平台骨折的治疗现状[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2012,27(2):191-192.
[15] 王庆鹏,孙永明.胫骨平台骨折及其伴随损伤的诊断[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(11):953.
[16] BAREI DP, NORK SE, MILLS WJ, et al. Functional outcomes of severe bicondylar tibial plateau fractures treated with dual incisions and medial and lateral plates. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(8):1713-1721.
[17] 徐云钦,李强,申屠刚,等.三种手术方法在复杂胫骨平台骨折中的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(3):281-283.
[18] 王星华,姚振均,张庆华,等.带锁髓内钉治疗胫骨骨折38例报告[J].中国临床医学,2003,10(1):47-49.
[19] SAFRAN O, LIEBERGALL M, SEGAL D, et al. Proximal tibial fractures-should we nail them?. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2001; 30(9):681-684.
[20] 曾庆敏,丁磊,张键.交锁髓内钉治疗胫骨近端骨折26例分析[J].中国临床医学,2008,15(4):545-546.
[21] 王海滨,卢旭华.有限内固定结合外固定架在胫骨骨折治疗中的应用进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,14(14):1074-1076.
[22] VEITCH SW, STROUD RM, TOMS AD. Compaction bone grafting in tibial plateau fracture fixation. J Trauma. 2010;68(4):980-983.
[23] 苏琦,陈芒.锁定钢板治疗胫骨平台骨折中的应用[J].临床骨科杂志,2010, 13(6):654-655.
[24] 王亦.骨与关节损伤[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2007:736.
[25] 王永宏,戴守达,董小雄,等.双钢板支撑治疗Scliatzker V及VI型胫骨平台骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(2):157.
[26] 罗从风,陈云丰,高洪,等.改良双钢板法治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2004,24(6):326-329.
[27] WILSON W, VAN RIETBERGEN B, VAN DONKELAAR CC, et al. Pathways of load-induced cartilage damage causing cartilage degeneration in the knee after meniscectomy. J Biomech. 2003;36(6): 845-851.
[28] 胡超,蔡林,王建平等.复杂性胫骨平台骨折的手术治疗[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(8):749-750.
[29] 李翔,范卫民,刘锋,等.LISS在复杂胫骨平台骨折中的应用[J].江苏医药, 2007,33(2):140-142.
[30] 张经纬,何贤峰,朱李梅,等.股骨LISS钢板外固定治疗胫骨骨折116例体会[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(8):874-875.
[31] 姜新峰,陈华.股骨撑开器辅助复位治疗不稳定型胫骨平台骨折疗效分析[J].江苏医药,2016,7(2):1151-1152. [32] 张志伟.长骨撑开器于胫骨平台骨折手术中的应用[J].中国医学工程,2015, 23(11):71-72. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [3] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [4] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [5] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [6] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [7] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [8] | Xiang Feifan, Ye Junwu, Zhang Xihai, Ge Jianhua, Tang Lian, Yang Yunkang. Comparison of three different internal fixation methods in treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 403-408. |
| [9] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of multiple implants in treatment of traumatic dislocation of sternoclavicular joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 443-448. |
| [10] | Nie Shaobo, Li Jiantao, Sun Jien, Zhao Zhe, Zhao Yanpeng, Zhang Licheng, Tang Peifu. Mechanical stability of medial support nail in treatment of severe osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 329-333. |
| [11] | Tan Jiachang, Yuan Zhenchao, Wu Zhenjie, Liu Bin, Zhao Jinmin. Biomechanical analysis of elastic nail combined with end caps and wire fixation for long oblique femoral shaft fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 334-338. |
| [12] | Chen Lu, Zhang Jianguang, Deng Changgong, Yan Caiping, Zhang Wei, Zhang Yuan. Finite element analysis of locking screw assisted acetabular cup fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 356-361. |
| [13] | Li Kun, Li Zhijun, Zhang Shaojie, Gao Shang, Sun Hao, Yang Xi, Wang Xing, Dai Lina . A 4-year-old child model of occipito-atlanto-axial joints established by finite element dynamic simulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3773-3778. |
| [14] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||