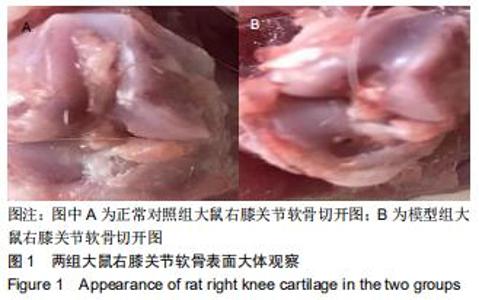
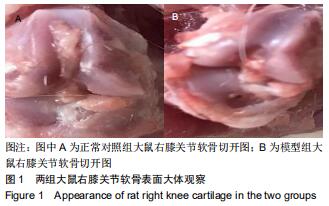
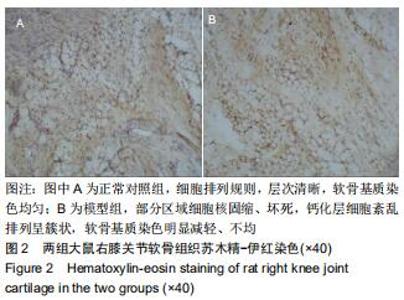
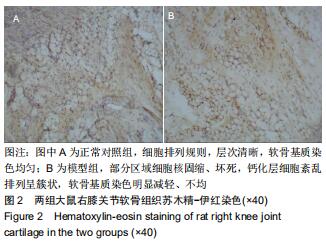
|
[1] THYSEN S, LUYTEN FP, LORIES RJ. Targets, models and challenges in osteoarthritis research. Dis Model Mech. 2015; 8(1):17-30.
[2] FRANK RM, COTTER EJ, NASSAR I, et al. Failure of Bone Marrow Stimulation Techniques. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2017;25(1):2-9.
[3] CHEN N, WANG J, MUCELLI A, et al. Electro-Acupuncture is Beneficial for Knee Osteoarthritis: The Evidence from Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Chin Med. 2017;45(5):965-985.
[4] BAKER K, GRAINGER A, NIU J, et al. Relation of synovitis to knee pain using contrast-enhanced MRIs. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(10):1779-1783.
[5] HOSHINO T, TSUJI K, ONUMA H, et al. Persistent synovial inflammation plays important roles in persistent pain development in the rat knee before cartilage degradation reaches the subchondral bone. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):291.
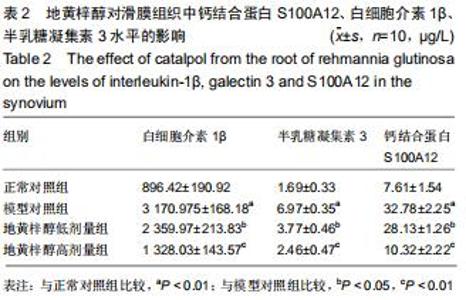
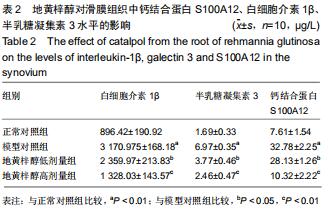
[6] 代凤雷,孙强,张斌,等.髋骨性关节炎滑膜组织中钙结合蛋白(S100A12)的表达及意义[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(1): 27-30,42.
[7] BLOM AB, VAN DER KRAAN PM, VAN DEN BERG WB. Cytokine targeting in osteoarthritis. Curr Drug Targets. 2007; 8(2):283-292.
[8] O'NEIL CK, HANLON JT, MARCUM ZA. Adverse effects of analgesics commonly used by older adults with osteoarthritis: focus on non-opioid and opioid analgesics. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2012;10(6):331-342.
[9] ZHU P, WU Y, YANG A, et al. Catalpol suppressed proliferation, growth and invasion of CT26 colon cancer by inhibiting inflammation and tumor angiogenesis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;95:668-676.
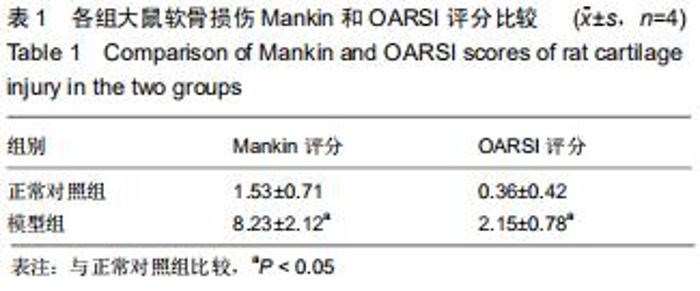
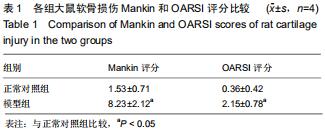
[10] 何强,尹宏,代凤雷,等.早期膝骨性关节炎模型大鼠的建立与验证[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(27):4338-4343.
[11] 申剑,张艳霞,吴国泰,等.黄管秦艽中总环烯醚萜苷对骨关节炎大鼠模型治疗作用研究[J].中药药理与临床,2018,34(3):85-89.
[12] 孙鲁宁,赵燕华,黄桂成,等.木瓜蛋白酶诱导膝关节骨关节炎模型兔滑膜病理变化与药物注射时间的关系[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(50):9311-9313.
[13] 韩冠英,凌沛学,王凤山,等.不同浓度木瓜蛋白酶建立兔膝骨关节炎模型的比较研究[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(5):424-429.
[14] 陈奇.中药药理研究方法学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1993: 33-34.
[15] BASTICK AN, BELO JN, RUNHAAR J, et al. What Are the Prognostic Factors for Radiographic Progression of Knee Osteoarthritis? A Meta-analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(9):2969-2989.
[16] 苏睿.膝关节骨性关节炎治疗进展研究[J].中医临床研究,2016, 8(2):145-146.
[17] 许蓓,许进.骨关节炎发病机制及治疗进展[J].浙江医学,2017, 39(21):1833-1835.
[18] 尹宏,俞宁,钱卫庆.奇正消痛贴治疗膝骨性关节炎临床疗效观察[J].白求恩军医学院学报, 2010,8(6):420-421.
[19] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版) [J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715.
[20] 代凤雷,陈荣国,金雯,等.S100A12在膝关节骨性关节炎中的表达及意义[J].江苏医药,2016,42(24):2680-2682.
[21] DE LANGE-BROKAAR BJ, IOAN-FACSINAY A, YUSUF E, et al. Degree of synovitis on MRI by comprehensive whole knee semi-quantitative scoring method correlates with histologic and macroscopic features of synovial tissue inflammation in knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(10): 1606-1613.
[22] CONAGHAN PG, COOK AD, HAMILTON JA, et al. Therapeutic options for targeting inflammatory osteoarthritis pain. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(6):355-363.
[23] 陈荣国,代风雷,欧先锋,等.血清和关节液中钙结合蛋白(S100A12) 的水平与膝关节骨关节炎严重程度的相关性分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(8):985-988.
[24] CHIEN SY, HUANG CY, TSAI CH, et al. Interleukin-1β induces fibroblast growth factor 2 expression and subsequently promotes endothelial progenitor cell angiogenesis in chondrocytes. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016;130(9): 667-681.
[25] 龙朝阳,李凤珍,梁江洪,等.清毒伸筋汤对胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠血清TNF-α、IL-1β 水平的影响[J].中医学报,2017,32(1):93-95.
[26] REESINK HL, NIXON AJ, SU J, et al. Galectins-1 and-3 Increase in Equine Post-traumatic Osteoarthritis. Front Vet Sci. 2018;5:288.
[27] 何强,尹宏,代凤雷,等.膝骨关节炎大鼠滑膜组织中半乳糖凝集素3(Galectin-3)变化趋势研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2020, 22(2):86-90.
[28] SALAMANNA F, GIAVARESI G, PARRILLI A, et al.Effects of intra-articular hyaluronic acid associated to Chitlac (arty-duo®) in a rat knee osteoarthritis model. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(4): 867-876.
[29] KESSEL C, LIPPITZ K, WEINHAGE T, et al. Proinflammatory Cytokine Environments Can Drive Interleukin-17 Overexpression by γ/δ T Cells in Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69(7):1480-1494.
[30] UCHINO Y, WOODWARD AM, MAURIS J, et al. Galectin-3 is an amplifier of the interleukin-1β-mediated inflammatory response in corneal keratinocytes. Immunology. 2018;154(3): 490-499.
[31] IACOBINI C, BLASETTI FANTAUZZI C, BEDINI R, et al. Galectin-3 is essential for proper bone cell differentiation and activity, bone remodeling and biomechanical competence in mice. Metabolism. 2018;83:149-158.
[32] JHUN JY, NA HS, SHIN JW, et al. Notoginseng Radix and Rehmanniae Radix Preparata Extract Combination (YH23537) Reduces Pain and Cartilage Degeneration in Rats with Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Osteoarthritis. J Med Food. 2018;21(8):745-754.
[33] 国家药典委员会.中国药典2015年版(一部)[S].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2015.
|