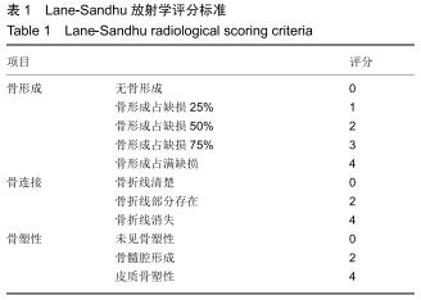
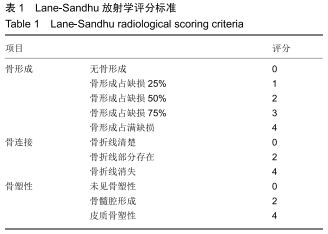
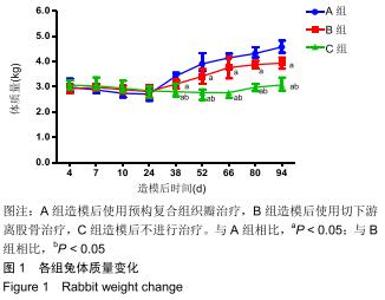
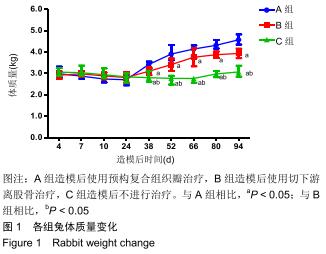
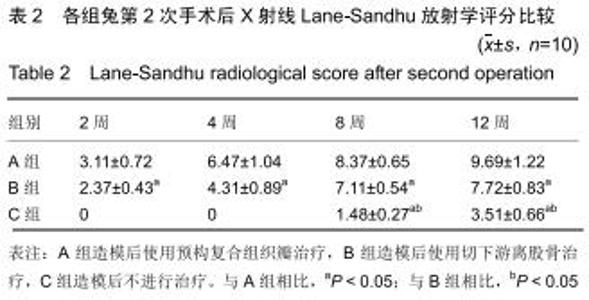
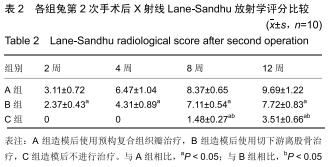
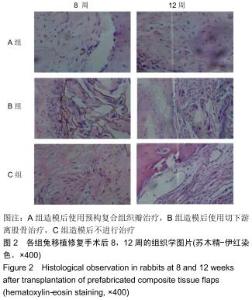
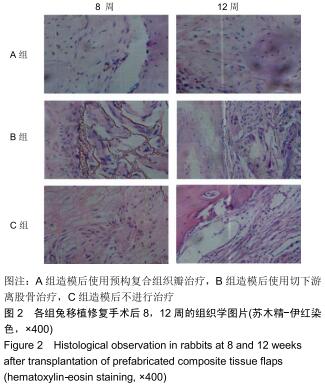
|
[1] 易守红,周武平,何纯青,等.外固定治疗创伤性四肢骨折的疗效及其对术后炎症应激反应的影响[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2019,11(2): 99-103.
[2] 李秋菊,刘婷,马德春.网状脂质水胶体含银敷料在四肢创伤骨折后张力性水泡中的应用[J].吉林医学,2019,40(8):1898-1900.
[3] OWENS BD, KRAGH JJ, MACAITIS J, et al. Characterization of extremity wounds in operation iraqi freedom and operation enduring freedom. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21(4):254-257.
[4] UHRIG BA, CLEMENTS IP, BOERCKEL JD, et al. Characterization of a composite injury model of severe lower limb bone and nerve trauma. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2014;8(6):432-441.
[5] WEN G, ZHOU R, WANG Y, et al. Management of post-traumatic long bone defects: A comparative study based on long-term results. Injury. 2019;50(11):2070-2074.
[6] Physical agents for soft tissue injury. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2016; 46(7):555.
[7] BYRD HS, SPICER TE, CIERNEY GR. Management of open tibial fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985;76(5):719-730.
[8] HO CA, PODESZWA DA, RICCIO AI, et al. Soft tissue injury severity is associated with neurovascular injury in pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 2018;38(9):443-449.
[9] MITCHELL PM, O'NEILL DE, BRANCH E, et al. Calcaneal avulsion fractures: a multicenter analysis of soft tissue compromise and early fixation failure. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33(11):e422-e426.
[10] 徐生根,肖坚,吴维剑.软组织损伤评估处理对跟骨骨折术后感染的意义[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志,2016,22(1):21-23.
[11] 赵刚.四肢软组织损伤评估与救治的几个重要问题[J].创伤外科杂志,2020, 22(1):5-9.
[12] 冯震.预构复合肌骨组织瓣修复肢体严重损伤的动物模型与实验研究[D]. 济南:山东大学, 2008.
[13] 罗远国,覃万安,吴家昌,等.复合组织瓣修复合并静脉功能障碍组织缺损的应用研究[J].微创医学,2017,12(3):331-333.
[14] 李颖,郭力.预制皮瓣的基础研究进展[J].泸州医学院学报,2008,31(2): 214-216.
[15] 马旭,杨大平.预构皮瓣再血管化的研究进展[J].中国美容医学,2011,20(4): 691-693.
[16] ZHANG L, YANG Q, JIANG H, et al. Reconstruction of complex facial defects using cervical expanded flap prefabricated by temporoparietal fascia flap. J Craniofac Surg. 2015;26(6):e472-e475.
[17] NKENKE E, EITNER S. Complex hemimaxillary rehabilitation with a prefabricated fibula flap and cast-based vacuum-formed surgical template. J Prosthet Dent. 2014;111(6):521-524.
[18] PAUCHET D, PIGOT JL, CHABOLLE F, et al. Prefabricated fibula free flap with dental implants for mandibular reconstruction. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2018;135(4):279-282.
[19] NKENKE E, EITNER S. Complex hemimaxillary rehabilitation with a prefabricated fibula flap and cast-based vacuum-formed surgical template. J Prosthet Dent. 2014;111(6):521-524.
[20] 林山,芮钢,胡义,等.数字化珊瑚羟基磷灰石人工骨修复兔胫骨腔隙性骨缺损[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(2):153-156.
[21] 吴翠翠,李艳辉,张新敏,等.小剂量曲马多与右美托咪定对神经病理性疼痛大鼠的抗抑郁效果[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2015,21(9):662-667.
[22] TENFORDE AS, BROOK EM, BROAD E, et al. Prevalence and anatomical distribution of bone stress injuries in the elite para athlete. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2019;98(11):1036-1040.
[23] 孙玲,朱秋红,隋桂英.52例创伤性骨折患者心理因素分析[J].济宁医学院学报,2003,26(2):55-56.
[24] 陈咏霞.心理护理在骨科四肢骨折患者护理中应用及其对疼痛的影响分析[J].实用临床护理学电子杂志,2020,5(3):42.
[25] WANG Y, SUN M, DAI H, et al. Comparison of repair characteristics of artificial dermis composite tissue with traditional prefabricated flap. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2018. doi: 10.7547/16-184.
[26] JIMENEZ MG, MELGOSA-JUAREZ M, PALACIOS-JUAREZ J, et al. Complex upper limb reconstruction using dorsoepigastric flap. Case report of a convenient resource. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2019;62:31-34.
[27] REXITI P, ZHANG TC, BATUER C, et al. Orthopedic treatment for open fracture of lower extremities and soft tissue defects in young children and rapid rehabilitation after operation. Phys Sportsmed. 2019:1-4.
[28] PAUCHET D, PIGOT JL, CHABOLLE F, et al. Prefabricated fibula free flap with dental implants for mandibular reconstruction. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2018;135(4):279-282.
[29] 孙守亮,黄伟. 颞浅筋膜瓣预构皮瓣修复面部大面积瘢痕的临床研究[J]. 中国医疗美容, 2018,8(5):18-20.
[30] PRIBAZ JJ, FINE N, ORGILL DP. Flap prefabrication in the head and neck: a 10-year experience. Plast Reconstr Surg.1999;103(3):808-820.
|