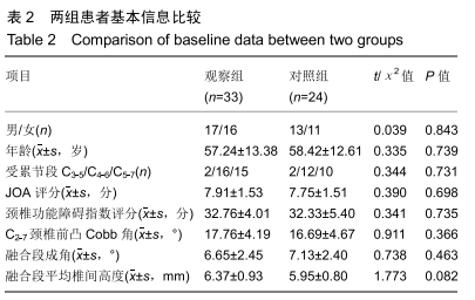
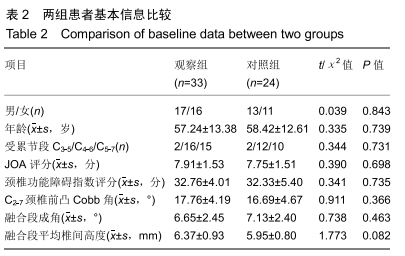
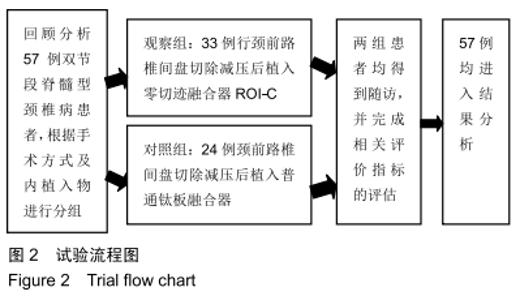
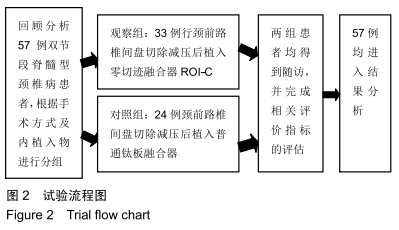
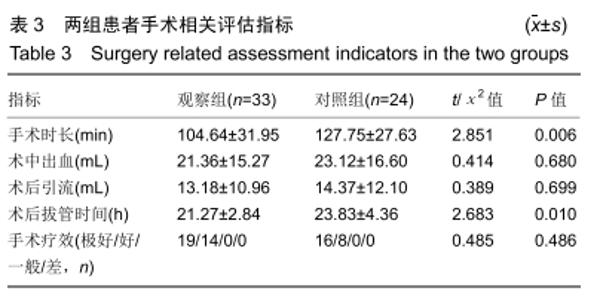
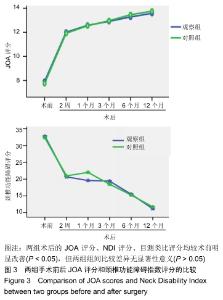
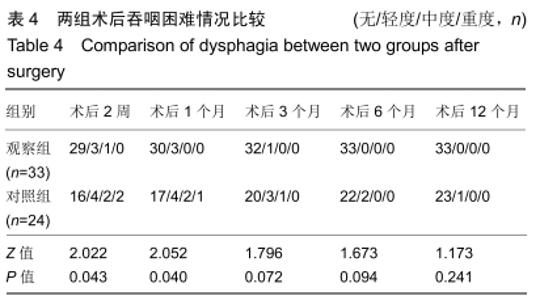
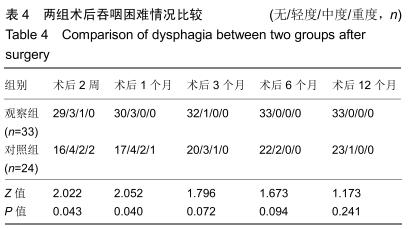
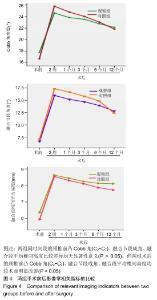
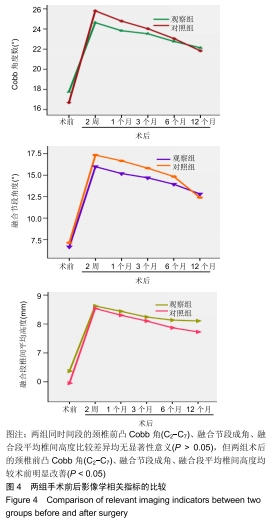
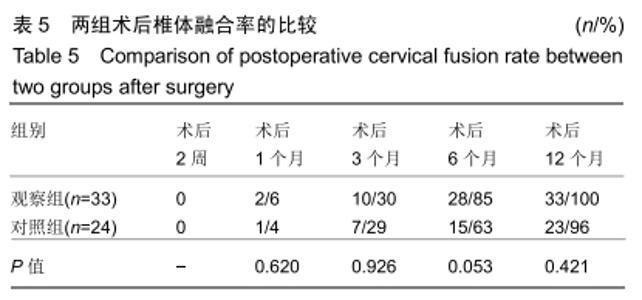
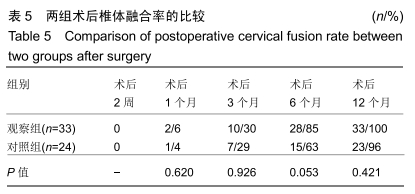
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (21): 3329-3335.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2702
Previous Articles Next Articles
Zero-profile anterior cervical ROI-C cage versus traditional fusion cage combined with titanium plate in treatment of two-level cervical spondylotic myelopathy
Zhang Junhui, Xu Hualiang, Chang Hong, Lin Zhujian, Song Yancheng
- Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2019-10-14Revised:2019-10-19Accepted:2019-11-25Online:2020-07-28Published:2020-04-17 -
Contact:Song Yancheng, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Junhui, Master, Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Innovation Cultivation Project for Guangdong University Students, No. pdjhb0261; the Medical Science and Technology Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. B2019049
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Junhui, Xu Hualiang, Chang Hong, Lin Zhujian, Song Yancheng . Zero-profile anterior cervical ROI-C cage versus traditional fusion cage combined with titanium plate in treatment of two-level cervical spondylotic myelopathy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3329-3335.
share this article
| [1] RAO RD, CURRIER BL, ALBERT TJ, et al. Degenerative Cervical Spondylosis: Clinical Syndromes, Pathogenesis,and Management.Instr Course Lect.2008;57(6):447-469. [2] ZHAO H, DUAN LJ, GAO YS, et al. What is the superior surgical strategy for bi-level cervical spondylosis-anterior cervical disc replacement or anterior cervical decompression and fusion?: A meta-analysis from 11 studies.Medicine.2018; 97(13):1-11. [3] 王莹,董丽娜,钟志伟,等.肌电图在颈椎病诊断中的临床价值[J].中国实验诊断学,2018,22(4):746-748. [4] KWON BK, VACCARO AR, GRAUER JN, et al. The use of rigid internal fixation in the surgical management of cervical spondylosis.Neurosurgery.2007;60(1 Supp1 1):S118-129. [5] SMITH GW, ROBINSON RA. The treatment of certain cervical-spine disorders by anterior removal of the intervertebral disc and interbody fusion.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1958;40-A(3):607. [6] YANG L, GU Y, LIANG L, et al. Stand-alone Anchored Spacer Versus Anterior Plate for Multilevel Anterior Cervical Diskectomy and Fusion.Orthopedics.2012;35(10): e1503-e1510. [7] IKENAGA M, SHIKATA J, TANAKA C. Anterior corpectomy and fusion with fibular strut grafts for multilevel cervical myelopathy.J Neurosurg Spine.2005;3(3):79-85. [8] SUN Z, LIU Z, HU W, et al. Zero-Profile Versus Cage and Plate in Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion with a Minimum 2 Years of Follow-Up: A Meta-Analysis.World Neurosurgery.2018;120:E551-E561. [9] LUO J, HUANG S, GONG M, et al. Two-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion using self-locking stand-alone polyetheretherketone cages with two anchoring clips placed in the upper and lower vertebrae, respectively.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2015;25 Suppl 1:S147-153. [10] CHEN Y, LU G, WANG B, et al. A comparison of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) using self-locking stand-alone polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cage with ACDF using cage and plate in the treatment of three-level cervical degenerative spondylopathy: a retrospective study with 2-year follow-up.Eur Spine J.2016;(25):2255–2262. [11] 杨洋,黎庆初,朱召银,等.双节段前路颈椎自锁式融合器融合术后矢状位影像学参数的变化[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(2): 116-123. [12] 贾斌,栾冠楠,陈宇飞,等.脊髓型颈椎病的发病机制及治疗的研究进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2015,15(19):3766-3769. [13] WANG B, LÜ G, KUANG L. Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with stand-alone anchored cages versus posterior laminectomy and fusion for four-level cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a retrospective study with 2-year follow-up.BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2018;19(1):216. [14] SHAO MH, ZHANG F, YIN J, et al. Titanium cages versus autogenous iliac crest bone grafts in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion treatment of patients with cervical degenerative diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Curr Med Res Opin.2017;33(5):803-811. [15] 张颖,王新伟,陈华江,等.单纯前路手术治疗“钳夹型”颈椎病的疗效[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(8):714-720. [16] 钟远鸣,廖俊城,李嘉琅,等.颈椎前路单椎体次全切融合术后矢状位变化与临床疗效的相关性[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(3): 7-12. [17] NOH SH, ZHANG HY. Comparison among perfect-CR, zero-PR, and plates with a cage in single-level cervical degenerative disc disease.BMC Musculoskel Dis. 2018;19(1): 33. [18] RADCLIFF KE, BENNETT J, STEWART RJ, et al. Change in angular alignment is associated with early dysphagia after anterior cervical diskectomy and fusion.Clin Spine Surg.2016; 29(6):248-254. [19] 宋升,孙振中,姜为民,等, ROI-C与传统融合器联合钛板内固定治疗颈椎病:颈椎稳定性重建及椎间融合的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(28):4474-4478. [20] 王新伟,袁文,吴晓东.颈椎手术并发症现状与新动向[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(2):97-99. [21] YANG JY, SONG HS, LEE M, et al. Adjacent level ossification development after anterior cervical fusion without plate fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2009;34(1):30-33. [22] NJOKU I JR, ALIMI M, LENG LZ, et al.Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with a zero-profile integrated plate and spacer device:a clinical and radiological study. Clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine.2014;21(4):529-537. [23] 戎玉罗,罗勇骏,刘蔚,等.零切迹自稳型颈椎融合器在前路颈椎椎间盘切除融合术中的应用及其对吞咽困难和邻近节段骨化的影响[J].脊柱外科杂志,2019,17(2):73-77. [24] 叶有晨,赵新华,杨永宏.前路颈椎桥形锁定融合器(ROI-C)治疗退变性颈椎间盘疾病的临床应用分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2017,25(3):209-213. [25] STEIN MI, NAYAK AN, GASKINS RB 3RD, et al. Biomechanics of an integrated interbody device versus ACDF anterior locking plate in a single-level cervical spine fusion construct.Spine J.2014;14 (1):128-136. [26] 阮立奇,施建东,ROI-C与钢板联合 cage在单节段脊髓型颈椎病 ACDF术中应用的效果比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018, 33(9):901-904. [27] ZHOU J, LI X, ZHOU X, et al. Anterior decompression and hybrid reconstruction with titanium mesh cage plus plate and self-locking stand-alone cage for the treatment of three-level cervical spondylotic myelopathy.J Clin Neurosci. 2017;43: 196-201. [28] ZHOU J, LI J, LIN H, et al. A comparison of a self-locking stand-alone cage and anterior cervical plate for ACDF: Minimum 3-Year Assessment of Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes.Clin Neurol Neurosur. 2018;(170):73-78. [29] CHEN Y, LIU Y, CHEN H, et al.Comparison of Curvature Between the Zero-P Spacer and Traditional Cage and Plate After 3-Level Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion.Clin Spine Surg.2016;30(8):E1111-E1116. [30] 陈博来,林涌鹏,赵帅,等.零切迹自稳型颈椎融合器(ROI-C)在颈椎前路减压融合术中的安全性与有效性评价[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(10):894-898. |
| [1] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [2] | Zhang Qifu, Ma Yonghong, Wang Tao, Hu Yibo, Zhang Heling, Zong Qunchuan. Effects of anterior corpectomy and fusion versus posterior single open-door laminoplasty on cervical range of motion of patients with multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3870-3874. |
| [3] | Xu Hui, Kang Bingxin, Zhong Sheng, Gao Chenxin, Zhao Chi, Qiu Guowei, Sun Songtao, Xie Jun, Xiao Lianbo, Shi Qi. Pressing local acupoints plus adjustion of the knee joint in a sitting position for treating knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 216-221. |
| [4] | Ma Long, Tan Xiaoxin, Sun Guoshao. A 5-year follow-up on sagittal alignment and radiological outcomes of consecutive three-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion and hybrid surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1879-1885. |
| [5] | Yu Bin, Peng Yinxiao, Xue Li, Qin Hui, Liang Yijian. Comparison between anterior cervical discectomy and fusion using Zero-P and traditional anterior cervical plate plus cage for treating two-level cervical spondylosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1342-1347. |
| [6] | Li Yongtao, Song Wenhui, Liu Changwen, Liang Kaiheng, Zhang Kaixi, Liu Changfeng. Clinical efficacy of calcium sulphate/demineralized bone matrix versus bone allograft in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5478-5485. |
| [7] | Yi Honglei, Chen Xingjie, Chen Xuqiong, Wu Zenghui, Ma Xiangyang, Ai Fuzhi, Wang Jianhua, Zhang Kai, Xia Hong. Relationship between transoral atlantoaxial reduction screw-rod system fixation and oropharyngeal airway stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 354-358. |
| [8] | Wang Wei, Jia Yujie, Cai Hongmei, Wang Wenjuan, Sun Cuicui. Functional patch combined with surface electromyographic biofeedback for post-stroke dysphagia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4697-4701. |
| [9] | Chen Sheng, Liu Jianhang, Liu Bentao, Zhang Zhaojian, Li Benche, Zhang Fan, Li Dongfei. Hot spots of animal models of cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3890-3896. |
| [10] | Song Yancheng, Kang Liqing, Shen Canghai, Liu Fenghai, Feng Yongjian. Application of task-state fMRI in evaluating disease severity and prognosis of cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3341-3346. |
| [11] | Xiao Qiang, Li Xiaodan, Liu Jingli, Zeng Jihuan, Deng Liang. Safety and feasibility of a new 3D printing template designed for bilateral anterior cervical transpedicular screws placements [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2823-2828. |
| [12] |
Zhang Chunlin, Liu Yang, Shang Lijie, Yan Xu, Ning Yongming, Li Dongzhe, Dong Chao, Cao Zhengming.
Observation of herniated
cervical intervertebral disc volume based on quantitative volume measurement “monitoring” based on PACS software |
| [13] | Li You, Zheng Bengbeng, Wang Jiaming, Ma Yongsheng. Research and application of artificial cervical disc [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(12): 1941-1948. |
| [14] | Zhong Qiusheng1, Xia Weichao1, Guo Meizhen1, Zhu Haiqing1, Zhong Cuiqiong1, Shao Jieqi1, He Xiaohong2, Chen Xiumin2. Sandwiched Moxibustion plus Bushen Quhan recipe for treating knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5670-5675. |
| [15] | Cheng Wendan, Wu Han, Zhang Jisen, Zhang Xin, Zhang Shuo, Li Ziyu, Wu Yibo, Bai Wenyi, Jing Juehua. Total hip arthroplasty by direct anterior approach in the lateral position in the treatment of ankylosed hips: early therapeutic effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4429-4434. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||