Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (21): 3438-3444.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2605
Effect of electro-acupuncture on pain relief and joint function in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis
Chen Rilan1, Deng Kaifeng2, Wei Xingcheng2, Wang Hengsheng2, Feng Jiaoqun2, Yan Jiaxing2, Gao Qianqian2, Ma Yinglu2, Zhu Ying1
- 1Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2019-08-22Revised:2019-08-26Accepted:2019-10-09Online:2020-07-28Published:2020-04-20 -
Contact:Zhu Ying, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Chen Rilan, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960908; Guangxi Medical and Health Technology Development and Promotion Project of Guangxi Health and Family Planning Commission, No. S2017057; Graduate Education Innovation Program of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. YCSY20190095
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Rilan, Deng Kaifeng, Wei Xingcheng, Wang Hengsheng, Feng Jiaoqun, Yan Jiaxing, Gao Qianqian, Ma Yinglu, Zhu Ying. Effect of electro-acupuncture on pain relief and joint function in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3438-3444.
share this article
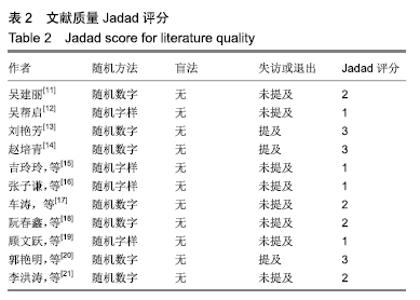
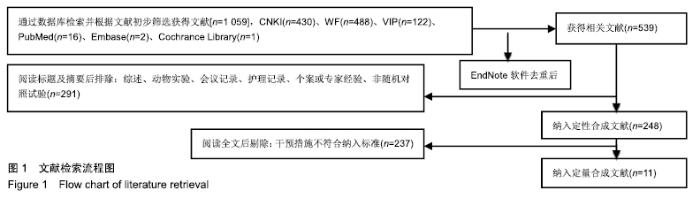
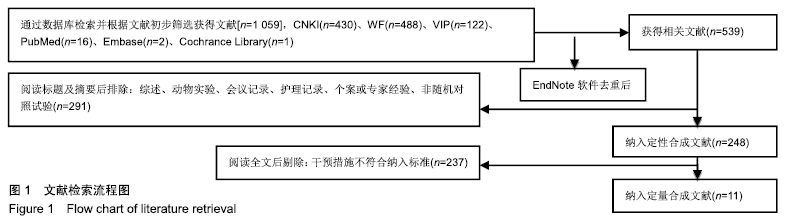
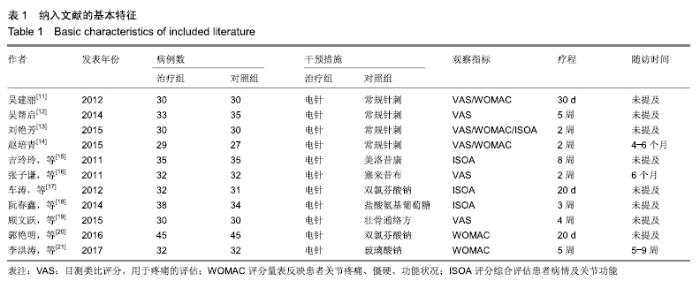
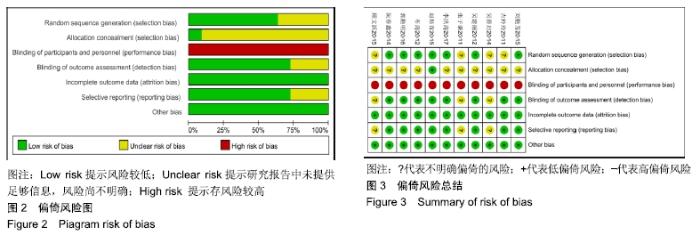
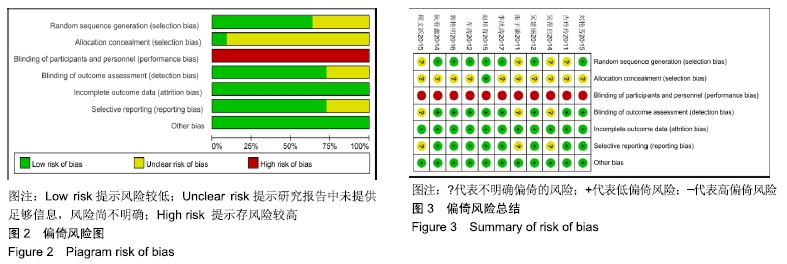
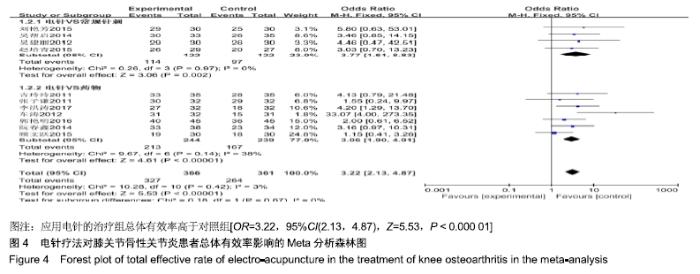
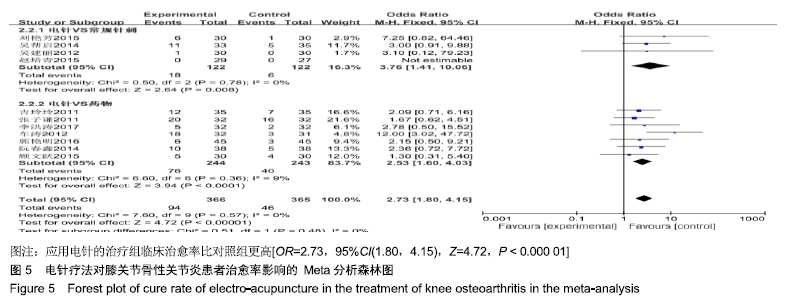
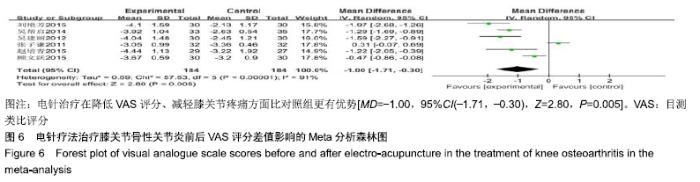
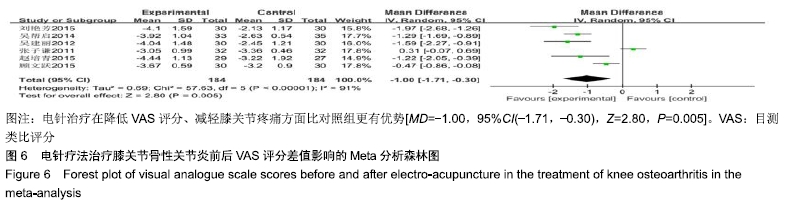
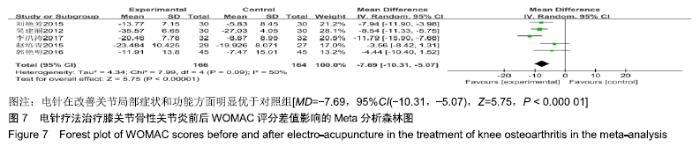
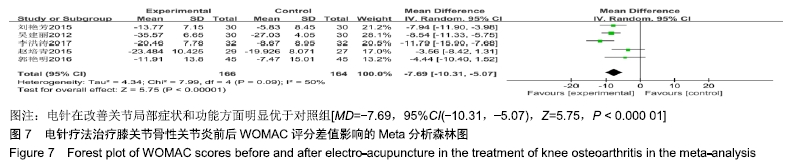
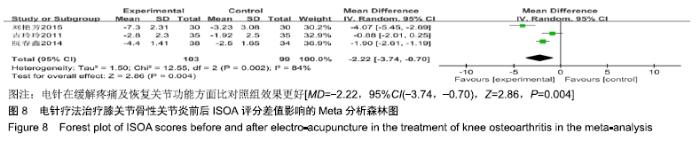
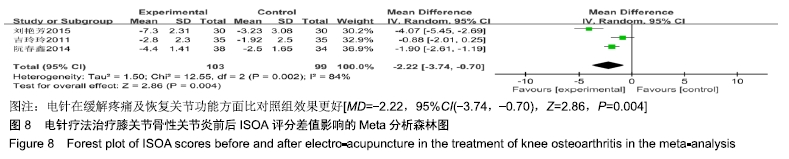
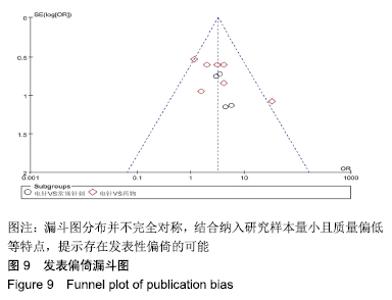
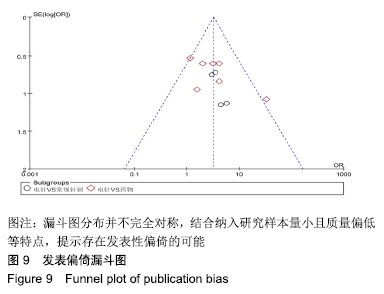
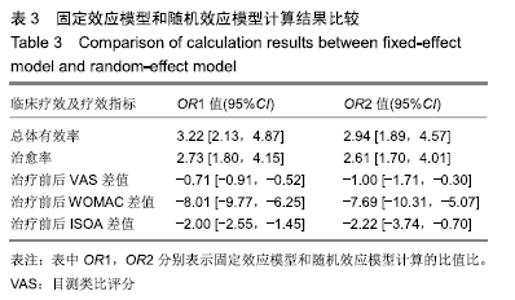
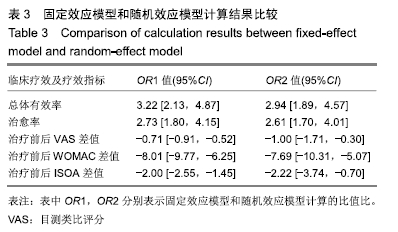
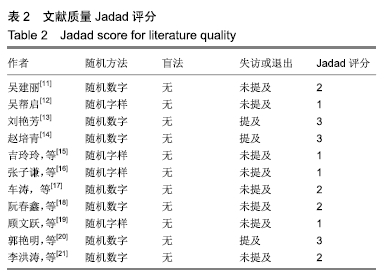
2.3 纳入研究的质量评价 采用Jadad评分量表(≤2分判定为低质量,≥3分判定为高质量)对纳入的11项研究进行评估。结果显示有3项为高质量研究[13-14,20],得分均为3分;其余8项均为低质量研究[11-12,15-19,21],4项研究得分为2分[11,17-18,21],4项研究得1分[12,15-16,19]。7项试验使用随机数字表法[11,13-14,17-18,20-21],其余4项只提及了随机字样[12,15-16,19]。有3项试验提及随访时间[14,6,21],所有的研究皆报告了两组之间基线相似性一致。但是,以上文献均未将原始数据进行呈现,只能通过研究者的总结报告进行评价,使分析存在信息偏倚的可能。由于电针疗法本身治疗方式特殊,难以对研究人员以及受试人员施盲,导致实施性偏倚风险评估均为high risk。详见表2,图2,3。 "
| [1] LAWRENCE RC, FELSON DT, HELMICK CG, et al.Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States:Part Ⅱ. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(1):26-35. [2] TAO J, LIU J, EGOROVA N, et al.Increased hippocampus-medial prefrontal cortex resting-state functional connectivity and memory function after Tai Chi Chuan Practice in elder adults.Front Aging Neurosci.2016;8(2):25-26. [3] FEJER R, RUHE A.What is the prevalence of musculoskeletal problems in the elderly population in developed countries?.A systematic critical literature review. Chiropr Man Therap. 2012;20(1): 31-32. [4] COLES LS, FRIES JF, KRAINES RG, et al. From experiment to experience: side effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.Am J Med.1983;74(5):820-828. [5] CLIVE DM, STOFF JS. Renal syndromes associated with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs.N Engl J Med.1984;310(9):563-572. [6] 李丽,李宁,吴滨.针灸治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的文献计量学分析[J].中国针灸,2007,27(11):862-864. [7] AHSIN S, SALEEM S, BHATTI AM, et al. Clinical and endocrinological changes after electroacupuncture treatment in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee.Pain.2009;147(1-3):60-66.. [8] Chinese Rheumatology Association.Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis(protocol).Zhonghua Feng Shi Bing Xue Za Zhi.2003;7(11):702-704. [9] 郑筱萸.中药新药临床研究指导原则[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2002: 349. [10] JADAD AR, MOORE RA, CARROLL D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials:is blinding necessary?.Control Clin Trials.1996;17(1):1-12. [11] 吴建丽.电针治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的临床观察[D].哈尔滨:黑龙江中医药大学,2012. [12] 吴帮启.电针治疗膝骨性关节炎33例[J].山东中医杂志,2014,33(9):750-752. [13] 刘艳芳.电针结筋点治疗膝关节骨性关节的临床疗效观察[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2015. [14] 赵培青.电针治疗膝骨性关节炎的临床研究[D].沈阳:辽宁中医药大学, 2015. [15] 吉玲玲,欧阳八四.电针治疗膝骨关节炎疗效观察[J].上海针灸杂志,2011, 30(9):620-621. [16] 张子谦,姚红,陈建雄电针治疗早期膝关节炎的近远期疗效观察[J].光明中医,2011,26(8):1616-1618. [17] 车涛,裘敏蕾,孙剑.电针治疗膝骨关节炎疗效观察[J].上海针灸杂志,2012, 31(8):595-596. [18] 阮春鑫,陈兴奎.电针治疗膝骨关节炎疗效及对股四头肌表面肌电信号的影响[J].上海针灸杂志,2014,33(8):745-747. [19] 顾文跃,陈健花,沈丹.针药并施治疗退行性膝关节炎的临床研究[J].浙江中医杂志,2015,50(2):96-97. [20] 郭艳明,梁永瑛,顾钧青.电针围刺治疗早中期膝骨关节炎[J].吉林中医药, 2016,36(1):91-93+107. [21] 李洪涛,刘昊,杨方军.电针治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的临床疗效分析[J].中医药学报,2017,45(1):110-113. [22] DEMOLY P, BOUSQUET PJ, MESBAH K, et al.Visual analogue scale in patients treated for allergic rhinitis: an observational prospective study in primary care: asthma and rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2013; 43(8):881-888. [23] BELLAMY N, BUCHANAN WW, GOLDSMITH CH, et al.Validation study of WOMAC:a health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee.J Rheumatol.1988; 15(12):1833-1840. [24] LEQUESNE MG, MERY C, SAMSON M, et al.Indexes of severity for osteoarthritis of the hip and knee. Validation--value in comparison with other assessment tests.Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1987;65:85-89. [25] 王道海,包飞,吴志宏,等.针刺对膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨白细胞介素-1β及肿瘤坏死因子-α表达的影响[J].中国骨伤,2011,24(9):775-778. [26] 刘苗苗,韦芳,潘超安,等.电针对膝骨关节炎MIA模型大鼠滑膜组织中MMP-3/TIMP-1表达的影响[J].针灸临床杂志, 2014,30(6):70-75. [27] 周景辉,吴耀持,张峻峰,等.电针干预膝骨关节炎大鼠转化生长因子β含量的变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(24):4690-4695. [28] 乔鸿飞.超短波联合电针疗法对家兔膝关节骨性关节炎自由基代谢的影响[J].中医杂志,2010,51(1):53-54. [29] 白晓东,李顺月,宋晓晶,等.针灸治疗仪作用原理及其临床应用[J].中华中医药杂志,2015(2):488-491. [30] RUIXIN Z, LIXING L, KE R, et al.Berman.mechanisms of acupuncture- electroacupuncture on persistent pain.Anesthesiology.2014;120(2): 482-503. [31] 叶国平.电针膝眼穴调控RhoA/ROCK信号通路抑制膝骨性关节炎软骨退变的机制研究[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2019. [32] YUSUF E, BIJSTERBOSCH J, SLAGBOOM PE, et al.Association between several clinical and radiological determinants with long-term clinical progression and good prognosis of lower limb osteoarthritis. PLoS One. 2011;6:e25426. [33] 林洁,付长龙,李俐,等.电针治疗膝骨性关节炎疗效的系统评价[J].康复学报,2016,26(4):52-58. [34] 姚阿玲.发表偏倚对Meta分析结果影响的模拟研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2015. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [4] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [5] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [6] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [7] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [8] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [9] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [10] | Gao Yan, Zhao Licong, Zhao Hongzeng, Zhu Yuanyuan, Li Jie, Sang Deen. Alteration of low frequency fluctuation amplitude at brain-resting state in patients with chronic discogenic low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1160-1165. |
| [11] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [12] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [13] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [14] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [15] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||