Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (6): 833-838.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2447
Previous Articles Next Articles
Severity of patellofemoral osteoarthritis does not affect the prognosis of total knee arthroplasty with patella retention
Xu Changbo, Zhang Yi, Yin Li
- Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2019-07-09Revised:2019-07-10Accepted:2019-08-07Online:2020-02-28Published:2020-01-16 -
Contact:Yin Li, MD, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
About author:Xu Changbo, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Changbo, Zhang Yi, Yin Li . Severity of patellofemoral osteoarthritis does not affect the prognosis of total knee arthroplasty with patella retention[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 833-838.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
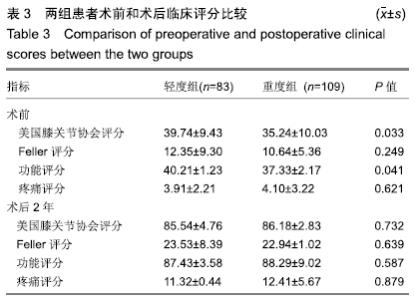
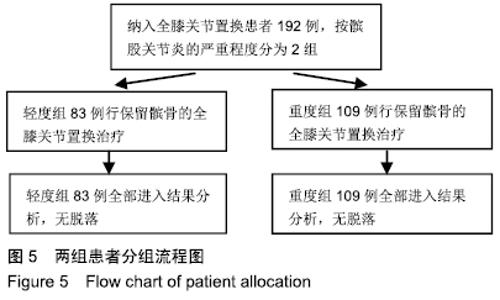
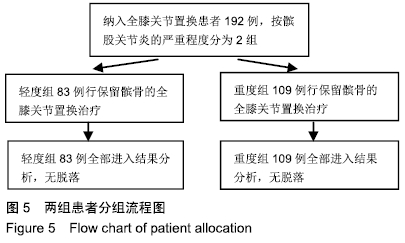
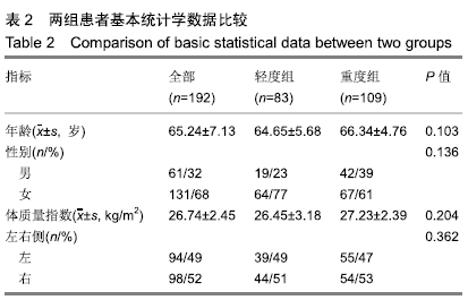
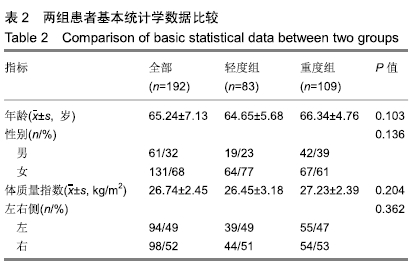
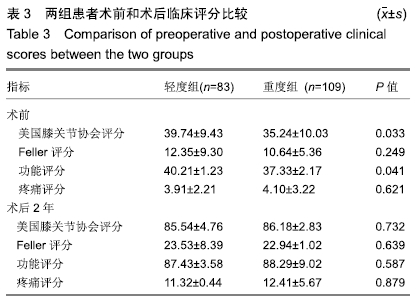
2.4 术前和术后临床评分比较 可以看出2组患者术后临床评分均较术前明显提高,轻度组患者的美国膝关节协会评分、Feller评分、功能评分、疼痛评分较术前分别增加45.80,11.18,47.22,7.41分。重度组的美国膝关节协会评分、Feller评分、功能评分、疼痛评分较术前分别增加50.94,12.30,50.96,8.31分。术前2组美国膝关节协会评分和功能评分差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),而术后美国膝关节协会评分、功能评分、Feller评分、疼痛评分差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。从临床评估方面来说,无论术前髌股骨性关节炎是重还是轻,术后差异均无显著性意义,都可获得良好的结果,详见表3。"
| [1] SHUKLA D, SREEDHAR SK, RASTOGI V. A comparative study of botulinum toxin a with triamcinolone compared to triamcinolone alone in the treatment of osteoarthritis of knee. Anesth Essays Res. 2018;12(1):47-49. [2] BEAUPRE LA, SHARIFI B, JOHNSTON DWC. A randomized clinical trial comparing posterior cruciate-stabilizing vs posterior cruciate-retaining prostheses in primary total knee arthroplasty: 10-year follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(3): 818-823. [3] GRASSI A, COMPAGNONI R, FERRUA P, et al. Patellar resurfacing versus patellar retention in primary total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review of overlapping meta-analyses. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;(6): 1-13. [4] DONG Y, LI T, ZHENG Z, et al. Adding patella resurfacing after circumpatellar electrocautery did not improve the clinical outcome in bilateral total knee arthroplasty in chinese population: a prospective randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2017. [5] ESHNAZAROV KE, SEON JK, SONG EK. Comparison of radiological assessments patellar resurfacing with retention for grade iv osteoarthritis in patellofemoral joint accomplished total knee arthroplasty. Vestn Rentgenol Radiol. 2016;97(1):28-32. [6] ARIRACHAKARAN A, SANGKAEW C, KONGTHARVONSKUL J. Patellofemoral resurfacing and patellar denervation in primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015; 23(6):1770-1781. [7] HA C, WANG B, LI W, et al. Resurfacing versus not-resurfacing the patella in one-stage bilateral total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized clinical trial. Int Orthop. 2019. doi: 10.1007/s00264-019-04361-7. [8] JIA C, NI M, FU J, et al. A comparative study on effectiveness of patellar resurfacing against non-resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty. Chin J Rep Reconstr Surg. 2018; 32(4): 394-399. [9] WANG, JF, LI Z, ZHANG KS, et al. Unilateral patellar resurfacing in bilateral total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled study. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017;49(5):861-866. [10] GRASSI A, COMPAGNONI R, FERRUA P, et al. Patellar resurfacing versus patellar retention in primary total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review of overlapping meta-analyses. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(11):3206-3218. [11] LONGO UG, CIUFFREDA M, MANNERING N, et al. Patellar Resurfacing in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2018; 33(2): 620-632. [12] HE JY, JIANG LS, DAI LY. Is patellar resurfacing superior than nonresurfacing in total knee arthroplasty? A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Knee. 2011;18(3): 137-144. [13] CHEN K, LI G, FU D, et al. Patellar resurfacing versus nonresurfacing in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Int Orthop. 2013;37(6): 1075-1083. [14] PATEL K, RAUT V. Patella in total knee arthroplasty: to resurface or not to--a cohort study of staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2011; 35(3): 349-353. [15] MARADIT-KREMERS H, HAQUE OJ, KREMERS WK, et al. Is selectively not resurfacing the patella an acceptable practice in primary total knee arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(4): S0883540316307409. [16] AUNAN E, NAESS G, CLARKE-JENSSEN J, et al. Patellar resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty: functional outcome differs with different outcome scores: A randomized, double-blind study of 129 knees with 3 years of follow-up. Acta Orthop. 2016;87(2): 158-164. [17] ROBERTS DW, HAYES TD, TATE CT, et al. Selective patellar resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(2): 216-222. [18] HELMY N, ANGLIN C, GREIDANUS NV, et al. To resurface or not to resurface the patella in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(11):2775-2783. [19] SCHIAVONE PANNI A, CERCIELLO S, DEL REGNO C, et al. Patellar resurfacing complications in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2014;38(2):313-317. [20] CHUN KC, LEE SH, BAIK JS, et al. Clinical and radiological results of cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty with the NexGen(R)-CR system: comparison of patellar resurfacing versus retention with more than 14 years of follow-up. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017; 12(1): 144. [21] 王军锋,李沼,张克石,等.双膝关节置换术中髌骨置换与否的左右侧随机对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017,49(5):119-124. [22] AUNAN E, NÆSS G, CLARKE-JENSSEN J, et al. Patellar resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty: functional outcome differs with different outcome scores. Acta Orthopaedica.2015;87(2):1-7. [23] IWANO T, KUROSAWA H, TOKUYAMA H, et al. Roentgenographic and clinical findings of patellofemoral osteoarthrosis. With special reference to its relationship to femorotibial osteoarthrosis and etiologic factors. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;252(252):190-197. [24] CAPLAN N, KADER DF. A comparison of four models of total knee- replacement prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg [Am].1976;58(6):754. [25] CHO WJ, BIN SI, KIM JM, et al. Total knee arthroplasty with patellar retention: the severity of patellofemoral osteoarthritis did not affect the clinical and radiographic outcomes. J Arthroplasty. 2018; 33(7): 2136-2140. [26] AITKEN RC. Measurement of feelings using visual analogue scales. Proc R Soc Med. 1969;62(10): 989-993. [27] CAPLAN N, KADER DF. Roentgenographic analysis of patellofemoral congruence. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56(7): 1391-1396. [28] HEESTERBEEK P, BEUMERS M, JACOBS W, et al. A comparison of reproducibility of measurement techniques for patella position on axial radiographs after total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2007;14(5): 411-416. [29] FENG B, WENG X, LIN J, et al. Long term follow up of clinical outcome between patellar resurfacing and nonresurfacing in total knee arthroplasty: Chinese experience. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014; 127(22):3845-3851. [30] ARBUTHNOT JE, MCNICHOLAS MJ, MCGURTY DW, et al. Total knee replacement and patellofemoral pain. Surgeon. 2004;2(4): 230-233. [31] PETERSEN W, REMBITZKI IV, BRÜGGEMANN GP, et al. Anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty: a narrative review. Int Orthop. 2014;38(2): 319-328. [32] WOOD DJ, SMITH AJ, COLLOPY D, et al. Patellar resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized trial. J Bone Joint Sur Am. 2002; 84-A(2): 187. [33] YASSA R, KHALFAOUI MY, DAVIES AP. Are "patellofemoral symptoms" truly related to the patellofemoral joint? Knee Surg Relat Res. 2016;28(1): 68-74. [34] BEAUPRE L, SECRETAN C, JOHNSTON D, et al. A Randomized controlled trial comparing patellar retention versus patellar resurfacing in primary total knee arthroplasty: 5-10 year follow-up. Bmc Research Notes. 2012;5(1): 273-273. [35] HAN I, CHANG CB, LEE S, et al. Correlation of the condition of the patellar articular cartilage and patellofemoral symptoms and function in osteoarthritic patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(8):1081. [36] MAYMAN D, BOURNE RB, RORABECK CH, et al. Resurfacing versus not resurfacing the patella in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(5): 541-545. [37] BURNETT RS, HAYDON CM, RORABECK CH, et al. Patella resurfacing versus nonresurfacing in total knee arthroplasty: results of a randomized controlled clinical trial at a minimum of 10 years' followup. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;428(428):12-25. [38] SEO SS, KIM CW, MOON SW. A comparison of patella retention versus resurfacing for moderate or severe patellar articular defects in total knee arthroplasty: minimum 5-year follow-up results. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2011; 23(3):142-148. [39] WHITESIDE LT. Effect of femoral component design on unresurfaced patellas in knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;410(410):189-198. [40] RODRIGUEZ-MERCHAN EC, GOMEZ-CARDERO P. The outerbridge classification predicts the need for patellar resurfacing in TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(5):1254-1257. [41] GUPTA S, AUGUSTINE A, HOREY L, et al. Electrocautery of the patellar rim in primary total knee replacement: beneficial or unnecessary? Bone Joint J. 2010; 92(9): 1259. [42] PULAVARTI RS, RAUT W, MCLAUCHLAN GJ. Patella denervation in primary total knee arthroplasty-a randomized controlled trial with 2 years of follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(5): 977-981. |
| [1] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [2] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [3] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [4] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [5] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [6] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [7] | Gao Yan, Zhao Licong, Zhao Hongzeng, Zhu Yuanyuan, Li Jie, Sang Deen. Alteration of low frequency fluctuation amplitude at brain-resting state in patients with chronic discogenic low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1160-1165. |
| [8] | Wu Xun, Meng Juanhong, Zhang Jianyun, Wang Liang. Concentrated growth factors in the repair of a full-thickness condylar cartilage defect in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1166-1171. |
| [9] | Li Jiacheng, Liang Xuezhen, Liu Jinbao, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Differential mRNA expression profile and competitive endogenous RNA regulatory network in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1212-1217. |
| [10] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [11] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [12] | Wu Gang, Chen Jianwen, Wang Shilong, Duan Xiaoran, Liu Haijun, Dong Jianfeng. Simple HyProCure subtalar stabilization in treatment of adolescent flexible flatfoot combined with painful accessory navicular bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 901-905. |
| [13] | Liu Lihua, Sun Wei, Wang Yunting, Gao Fuqiang, Cheng Liming, Li Zirong, Wang Jiangning. Type L1 steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head through femoral head and neck junction decompression by fenestration: a single-center prospective clinical study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 906-911. |
| [14] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [15] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||