Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (10): 1484-1490.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2248
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous curved vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: distribution and leakage rate of injected bone cement
Li Fanjie, Du Yibin, Liu Yiming, Zhang Zhidong, Li Jian, Ma Li, Li Chun, Cheng Yonghong
- Department of Spine Surgery, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230061, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2019-07-15Revised:2019-07-17Accepted:2019-09-02Online:2020-04-08Published:2020-02-14 -
Contact:Du Yibin, Chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230061, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Li Fanjie, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Spine Surgery, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230061, Anhui Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Fanjie, Du Yibin, Liu Yiming, Zhang Zhidong, Li Jian, Ma Li, Li Chun, Cheng Yonghong. Comparison of percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous curved vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: distribution and leakage rate of injected bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(10): 1484-1490.
share this article
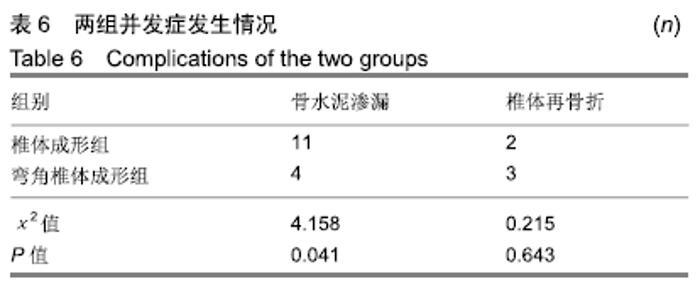
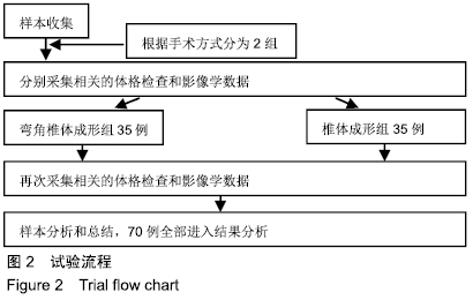
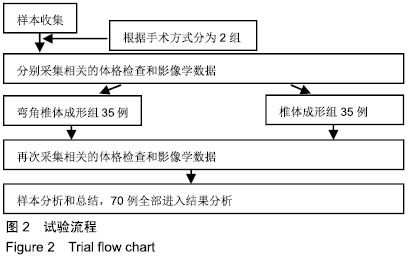
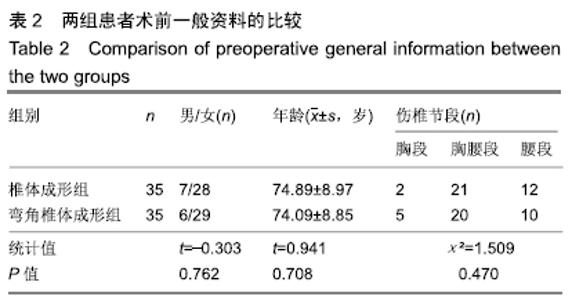
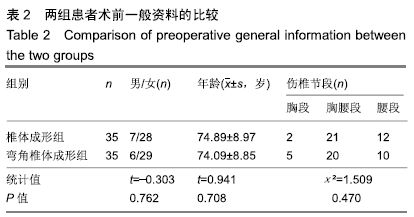
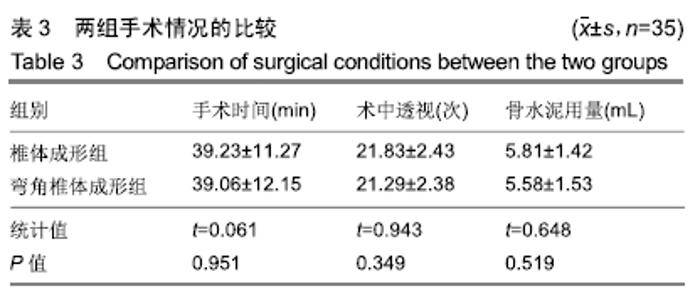
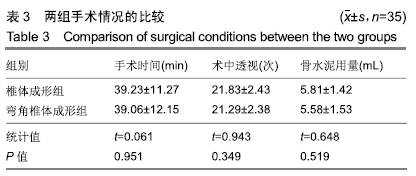
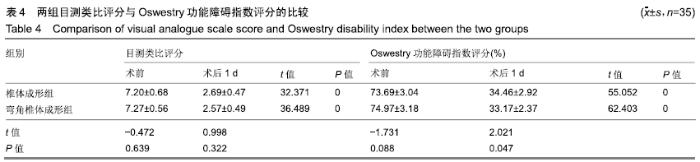
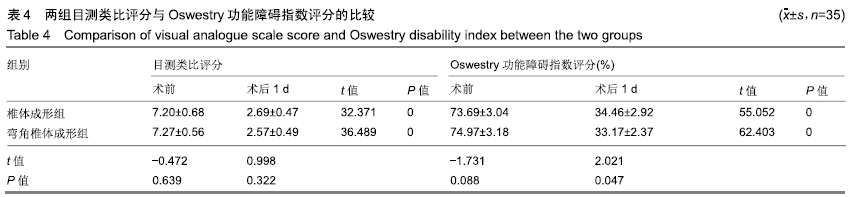
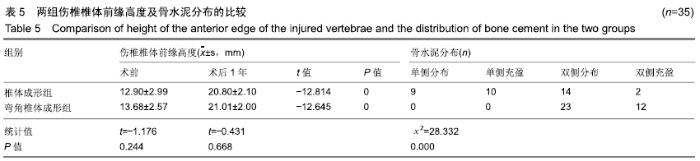
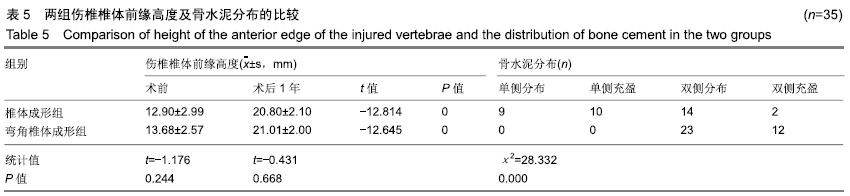
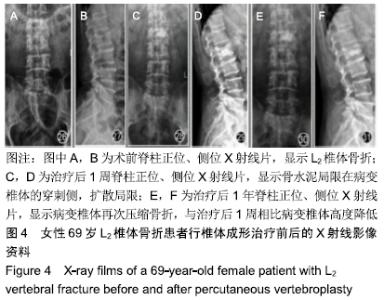
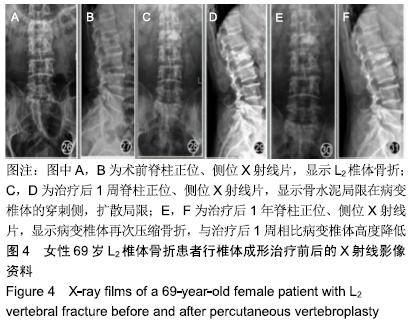
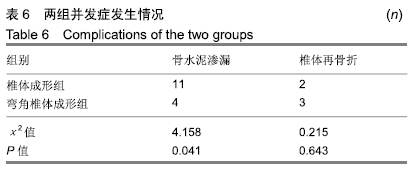
2.7 两组骨水泥弥散程度 由于患者椎体情况不同,故在手术中以尽量获得满意骨水泥分布为基础。两组术中观察及术后CT检测的骨水泥分布差异明显:椎体成形组单侧分布9例,单侧充盈10例,,双侧分布14例,双侧充盈2例;弯角椎体成形组单侧分布0例,单侧充盈0例,双侧分布23例,双侧充盈12例,两组间骨水泥弥散情况比较差异有显著性意义(χ2=28.332,P < 0.05),见表5。 2.8 材料宿主生物相容性 椎体成形组发现骨水泥渗漏11例,总渗漏率为31%;弯角椎体成形组发现骨水泥渗漏4例,总渗漏率为11%,两组总渗漏率比较差异有显著性意义(χ2=4.158,P < 0.05),见表6。由于手术均在C臂定位下进行,且为了获得最佳骨水泥弥散,试验中的椎体均在发现有骨水泥渗漏时停止灌注,所有的骨水泥渗漏均无临床症状,且术后所有个体均未发生感染、栓塞、硬膜外出血等严重并发症。 "
| [1] YE LQ, LIAN G, JIANG XB, et al.Risk Factors for the Occurrence of Insufficient Cement Distribution in the Fractured Area after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures.Pain Physician.2018;21(1):E33-E42. [2] MCCARTHY J, DAVIS A.Diagnosis and Management of Vertebral Compression Fractures. Am Fam Physician. 2016;94(1):44-50. [3] KAN SL, YUAN ZF, CHEN LX, et al.Which is best for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: balloon kyphoplasty, percutaneous vertebroplasty or non-surgical treatment? A study protocol for a Bayesian network meta-analysis.BMJ Open.2017; 7(1):e012937. [4] FENG L, FENG C, CHEN J, et al.The risk factors of vertebral refracture after kyphoplasty in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a study protocol for a prospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):195. [5] SHI C, ZHANG M, CHENG AY, et al.Percutaneous kyphoplasty combined with zoledronic acid infusion in the treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar fractures in the elderly. Clin Interv Aging.2018;13:853-861. [6] ZHAO WT, QIN DP, ZHANG XG, et al.Biomechanical effects of different vertebral heights after augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a three-dimensional finite element analysis.J Orthop Surg Res.2018;13(1):32. [7] ZHOU T, LIN H, WANG H, et al.Comparative study on the biomechanics between improved PVP and traditional PKP in the treatment of vertebral peripheral wall damage-type OVCF. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(1):575-580. [8] YU WB, JIANG XB, LIANG D, et al.Risk factors and score for recollapse of the augmented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Osteoporos Int.2019;30(2):423-430. [9] MANSOUR A, ABDEL-RAZEQ N, ABUALI H, et al.Cement pulmonary embolism as a complication of percutaneous vertebroplasty in cancer patients. Cancer Imaging.2018;18(1): 5. [10] 蒋国强,蒋国强,蔡凯文,等.椎间隙骨水泥渗漏的不同分型对邻椎相邻终板应力分布的影响:三维有限元研究[J].中华骨科杂志, 2019, 39(6):364. [11] YI HJ, JEONG JH, IM SB, et al.Percutaneous Vertebroplasty versus Conservative Treatment for One Level Thoracolumbar Osteoporotic Compression Fracture: Results of an Over 2-Year Follow-up. Pain Physician.2016;19(5):E743-750. [12] SARACEN A, KOTWICA Z.Complications of percutaneous vertebroplasty: An analysis of 1100 procedures performed in 616 patients. Medicine (Baltimore).2016;95(24):e3850. [13] GRASSO G.Does Optimal Volume Fraction in Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Prevent Cement Leakage? World Neurosurg. 2018; 116:489-490. [14] TAKURA T, YOSHIMATSU M, SUGIMORI H, et al. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Compression Fractures.Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(3): E205-E210. [15] SUN H, LU PP, LIU YJ, et al.Can Unilateral Kyphoplasty Replace Bilateral Kyphoplasty in Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pain Physician.2016;19(8):551-563. [16] FIRANESCU CE, De VRIES J, LODDER P, et al. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty is no Risk Factor for New Vertebral Fractures and Protects Against Further Height Loss (VERTOS IV). Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol.2019;42(7): 991-1000. [17] 熊森,毛克亚,韩振川,等.弯角输送装置在体外椎体成形实验中的效果观察[J].军医进修学院学报,2016,37(7):769-772. [18] SOON WC, MATHEW RK, TIMOTHY J.Comparison of vertebroplasty using directional versus straight needle. Acta Radiol Open.2015;4(3):2047981615569268. [19] SI L, WINZENBERG TM, JIANG Q, et al.Projection of osteoporosis-related fractures and costs in China: 2010-2050. Osteoporos Int.2015;26(7):1929-1937. [20] ZHOU X, MENG X, ZHU H, et al.Early versus late percutaneous kyphoplasty for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: A retrospective study.Clin Neurol Neurosurg.2019; 180:101-105. [21] ZUO XH, ZHU XP, AO HG, et al.Network meta-analysis of percutaneous vertebroplasty, percutaneous kyphoplasty, nerve block, and conservative treatment for nonsurgery options of acute/subacute and chronic osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs) in short-term and long-term effects. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(29):e11544. [22] ZAPALOWICZ K, RADEK M. Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of painful vertebral compression fractures: effect on local kyphosis and one-year outcomes in pain and disability. Neurol Neurochir Pol.2015;9(1):11-15. [23] LIU J, LI CS, CHANG CS, et al.Long-term follow-up study of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture treated using balloon kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;23(1):94-98. [24] BAZ AB, AKALIN S, KILICASLAN OF, et al.Efficiency of Balloon Kyphoplasty in the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Kobe J Med Sci. 2016;62(3):E49-54. [25] KANAYAMA M, OHA F, IWATA A, et al.Does balloon kyphoplasty improve the global spinal alignment in osteoporotic vertebral fracture? Int Orthop. 2015;39(6):1137-1143. [26] WANG CH, MA JZ, ZHANG CC, et al.Comparison of high-viscosity cement vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Pain Physician.2015;18(2):E187-194. [27] GAO C, ZONG M, WANG WT, et al.Analysis of risk factors causing short-term cement leakages and long-term complications after percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Acta Radiol. 2018;59(5):577-585. [28] ZHANG H, XUAN J, CHEN TH, et al.Projection of the Most Anterior Line of the Spinal Canal on Lateral Radiograph: An Anatomic Study for Percutaneous Kyphoplasty and Percutaneous Vertebroplasty.J Invest Surg.2018:1-7. [29] LI YX, GUO DQ, ZHANG SC, et al.Risk factor analysis for re-collapse of cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty (PVP) or percutaneous kyphoplasty (PKP).Int Orthop.2018;42(9):2131-2139. [30] LIEBSCHNER MA, ROSENBERG WS, KEAVENY TM.Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1547-1554. [31] BELKOFF SM, MATHIS JM, JASPER LE, et al.The biomechanics of vertebroplasty. The effect of cement volume on mechanical behavior. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1537-1541. |
| [1] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [2] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [3] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [4] | Liu Zhengpeng, Wang Yahui, Zhang Yilong, Ming Ying, Sun Zhijie, Sun He. Application of 3D printed interbody fusion cage for cervical spondylosis of spinal cord type: half-year follow-up of recovery of cervical curvature and intervertebral height [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 849-853. |
| [5] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [6] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [7] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [8] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [9] | Feng Guancheng, Fang Jianming, Lü Haoran, Zhang Dongsheng, Wei Jiadong, Yu Bingbing. How does bone cement dispersion affect the early outcome of percutaneous vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3450-3457. |
| [10] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [11] | Liu Jinlei, Yin Li, Zhang Yi, Wang Haitao, Li Zhuangyan, Xia Peige, Qiao Renqiu. Effects of intravenous tranexamic acid combined with periarticular multipoint injection of tranexamic acid cocktail on blood loss and pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2833-2839. |
| [12] | Sun Yiqiang, Xing Jianqiang, Li Xuecheng, Wang Xin, Tian Shenglan, Zhao Zihao, Geng Xiaopeng. Kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture in the elderly: a comparison of vertebral height recovery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2851-2855. |
| [13] | Li Qiang, Li Jun, Luan Jian, Jin Canghai, Hao Meng, Lin Yong. Bone cement distribution of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2466-2471. |
| [14] | Tian Lin, Shi Xiaoqing, Mao Jun, Zhang Nongshan, Zhang Li, Xing Runlin, Wang Peimin. Meta-analysis of vacuum-sealing drainage combined with antibiotic bone cement in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2618-2624. |
| [15] | Song Min, Lu Chao, Chen Jin, Wu Gaoyi, Li Congcong, Li Anan, Ye Guozhu, Lin Wenzheng, Cai Yuning, Liu Wengang, Xu Weipeng. Application of tourniquet affects thickness of bone cement penetration in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1917-1923. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||