Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (53): 8022-8031.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.53.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Different doses of rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of safety and efficacy
Wei Zhi-hui, Zhang Ming-hua, Zhao Bo, Min Jing, Qiu Hao, Lu Min-peng
- Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Yongchuan Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 402160, China
-
Revised:2016-09-29Online:2016-12-23Published:2016-12-23 -
Contact:Zhang Ming-hua, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Yongchuan Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 402160, China -
About author:Wei Zhi-hui, Master, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Yongchuan Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 402160, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing City, No. cstc2012jjA10029
Cite this article
Wei Zhi-hui, Zhang Ming-hua, Zhao Bo, Min Jing, Qiu Hao, Lu Min-peng. Different doses of rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of safety and efficacy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(53): 8022-8031.
share this article
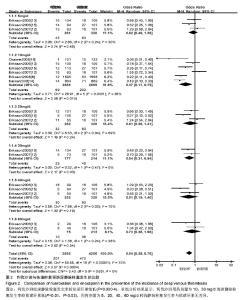
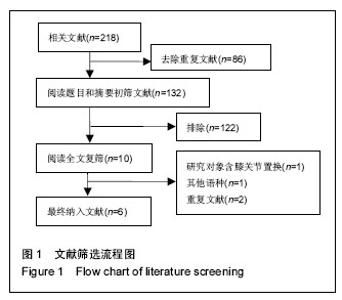
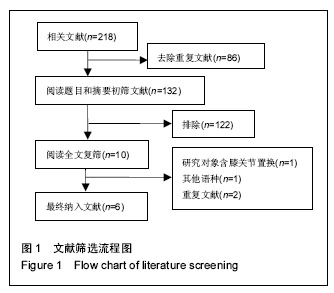
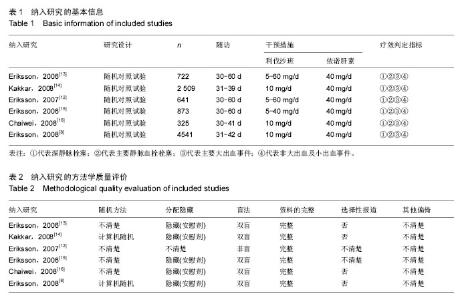
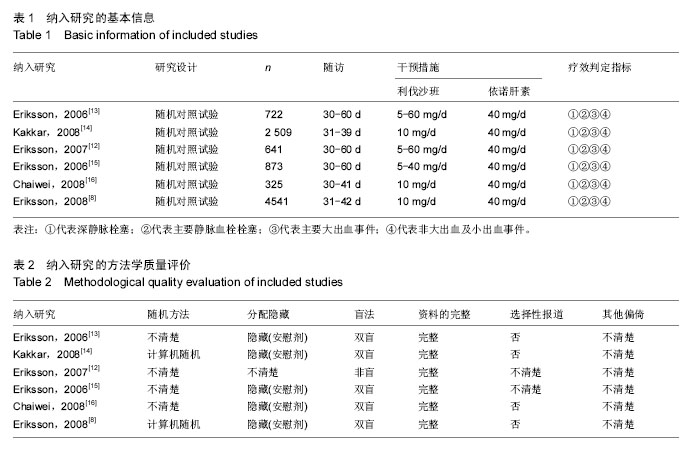
2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 深静脉栓塞 将利伐沙班按照不同用药剂量进行亚组分析。各研究结果间有统计学异质性(P=0.000 01,I2=70%),选用随机效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,利伐沙班组深静脉栓塞发生率较依诺肝素组低[OR=0.54,95%CI(0.38,0.76),P=0.000 4]。亚组分析结果显示,利伐沙班用药剂量为10,30 mg/d的深静脉栓塞发生率较依诺肝素低[OR=0.37,95%CI(0.17,0.79),P=0.01;OR=0.5495%CI(0.31,0.94),P=0.03];用药剂量为5,20,40,60 mg/d时,静脉栓塞发生率与依诺肝素比较差异无显著性意义[OR=0.82,95%CI(0.49,1.38),P=0.46;OR=0.61,95%CI(0.26,1.41),P=0.24;OR=0.51,95%CI(0.19,1.40),P=0.19;OR=0.73,95%CI(0.28,1.96),P=0.54],见图2。"

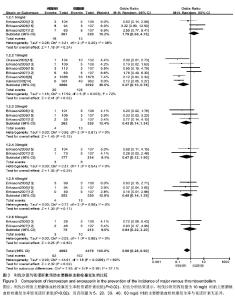
2.3.2 主要静脉血栓栓塞 将利伐沙班按照不同用药剂量进行亚组分析。各研究结果间有统计学异质性(P=0.000 5,I2=60%),选用随机效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,利伐沙班组主要静脉血栓栓塞发生率较依诺肝素组低[OR=0.50,95%CI(0.28,0.90),P=0.02]。亚组分析结果显示,利伐沙班用药剂量为10 mg/d 时,主要静脉血栓栓塞发生率较依诺肝素低[OR=0.27,95%CI(0.10,0.78),P=0.02];用药剂量为5,20,30, 40,60 mg/d 时的主要静脉血栓栓塞发生率与依诺肝素无差异[OR=1.79,95%CI(0.68,4.75),P=0.24;OR=0.43,95%CI(0.14,1.34),P=0.15;OR=0.47,95%CI(0.12,1.90),P=0.29;OR=0.45,95%CI(0.14,1.39),P=0.17;OR=0.84,95%CI(0.22,3.20),P=0.80],见图3。"
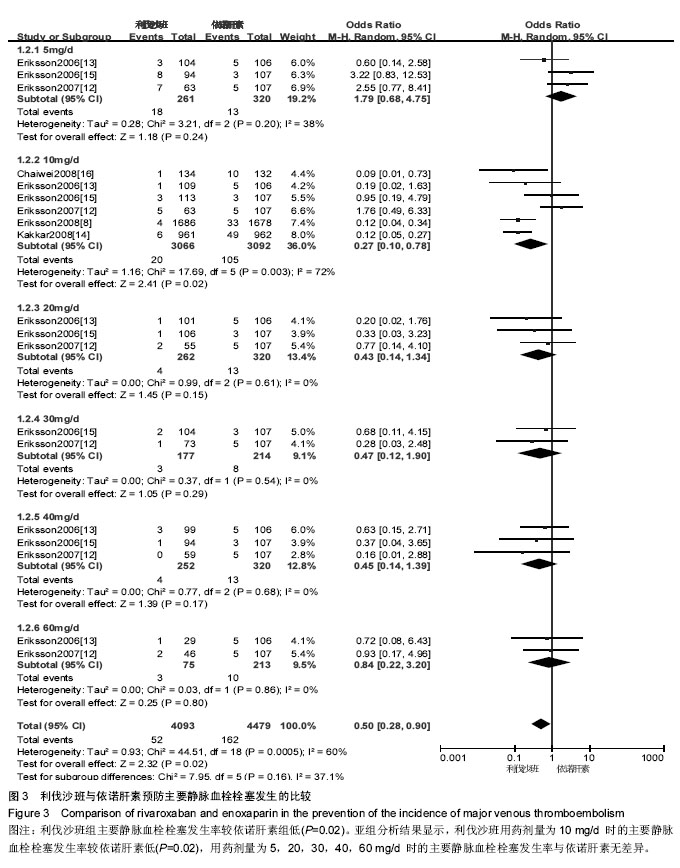
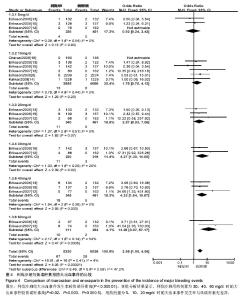
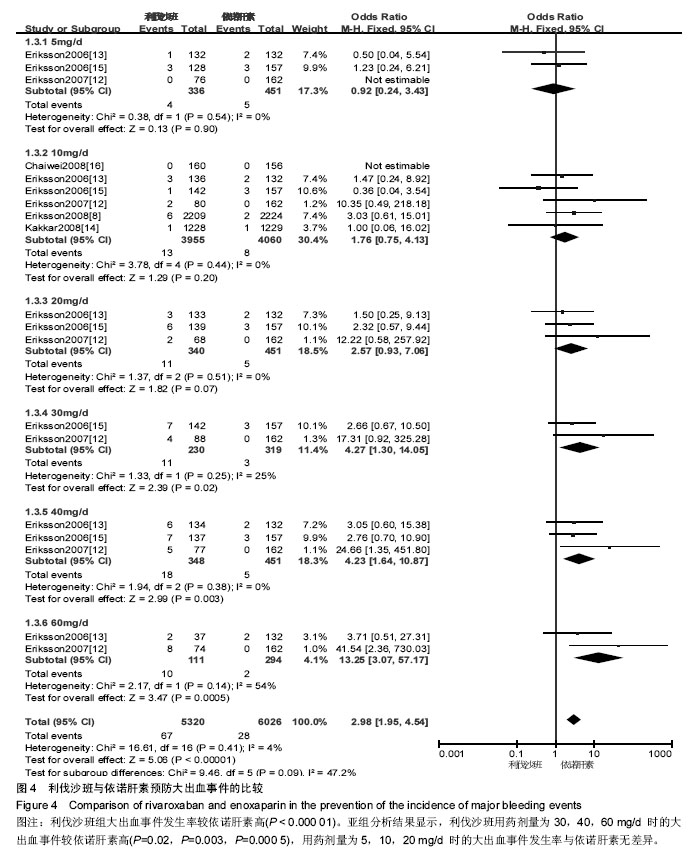
2.3.3 大出血事件 将利伐沙班按照不同用药剂量进行亚组分析。各研究结果间无统计学异质性(P=0.41,I2=4%),选用固定效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,利伐沙班组大出血事件发生率较依诺肝素组高[OR=2.98,95%CI(1.95,4.54),P < 0.000 01]。亚组分析结果显示,利伐沙班用药剂量为30,40,60 mg/d时的大出血事件较依诺肝素高[OR=4.27,95%CI(1.30,14.05),P=0.02;OR=4.23,95%CI(1.64,10.87),P=0.003;OR=13.25,95%CI(3.07,57.17),P=0.000 5];用药剂量为5,10,20 mg/d 时的大出血事件发生率与依诺肝素无差异[OR=0.92,95%CI(0.29,3.43),P=0.90;OR=1.76,95%CI(0.75,4.13),P=0.20;OR=2.57,95%CI(0.93,7.06),P=0.07],见图4。"
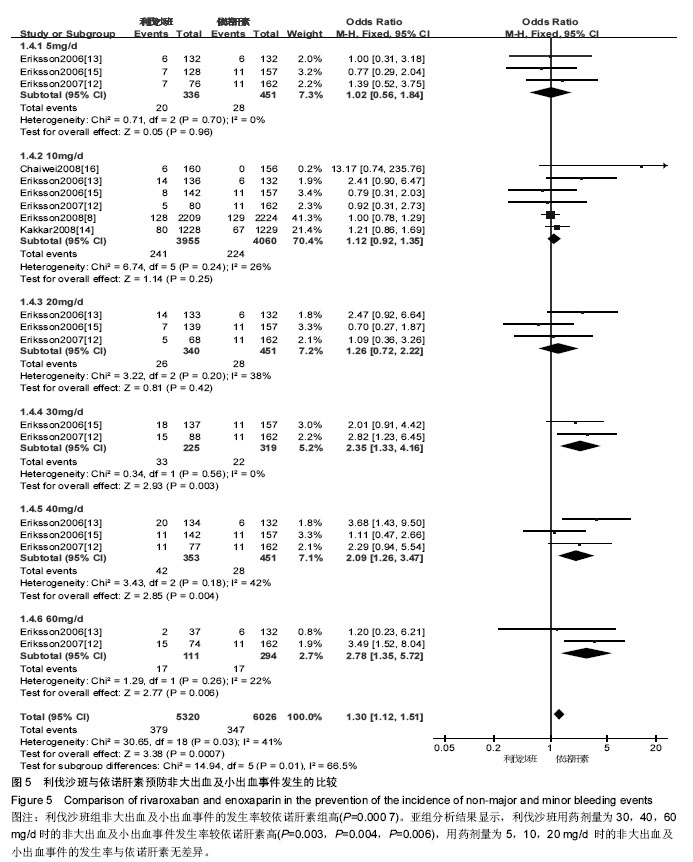
2.3.4 非大出血及小出血事件 将利伐沙班按照不同用药剂量进行亚组分析。各研究结果间无统计学异质性(P=0.03,I2=41%),选用固定效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,利伐沙班组非大出血及小出血事件的发生率较依诺肝素组高[OR=1.30,95%CI(1.12,1.51),P=0.000 7]。亚组分析结果显示,利伐沙班用药剂量为30,40,60 mg/d时的非大出血及小出血事件发生率较依诺肝素高[OR=2.35,95%CI(1.33,4.16),P=0.003;OR=2.09,95%CI(1.26,3.47),P=0.004;OR=2.78,95%CI(1.35,5.72),P=0.006],用药剂量为5,10,20 mg/d 时的非大出血及小出血事件发生率与依诺肝素无差异[OR=1.02,95%CI(0.56,1.84),P=0.96;OR=1.12,95%CI(0.92,1.35),P=0.25;OR=1.26,95%CI(0.72,2.22),P=0.42],见图5。"
| [1] Falck-Ytter Y,Francis CW,Johanson NA,et al.Prevention of VTE in orthopedic surgery patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2 Suppl):e278S-325S.[2] Geerts WH,Bergqvist D,Pineo GF,et al.Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest.2008;133(6 Suppl): 381S-453S.[3] 吕厚山.人工关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成和肺栓塞的防治[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2007,9(3):201-204.[4] 李佩佳,高玉镭,王东辰,等.利伐沙班与低分子肝素在预防人工全髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成的分析[J],中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(11):998-1000.[5] 邱贵兴,戴尅戎,杨庆铭,等.预防骨科大手术后深静脉血栓形成的专家建议[J].中国临床医生,2006,34(1):27-28. [6] Eriksson BI,Rosencher N,Friedman RJ,et al.Concomitant use of medication with antiplatelet effects in patients receiving either rivaroxaban or enoxaparin after total hip or knee arthroplasty.Thromb Res,2012;130(2):147-151.[7] 邱贵兴.中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2009,3(3):380-383.[8] Eriksson BI,Borris LC,Friedman RJ,et al. Rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after hip arthroplasty.N Engl J Med.2008;358(26):2765-2775.[9] Gomez-Outes A,Terleira-Fernandez AI,Suarez-Gea ML,et al.Dabigatran, rivaroxaban, or apixaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after total hip or knee replacement: systematic review, meta-analysis, and indirect treatment comparisons.BMJ.2012; 14(344): e3675.[10] 钟文昭,吴一龙,谷力加. Review Manager (RevMan)-临床医生通向Meta分析的桥梁[J].循证医学,2013,3(4): 234-246.[11] Harris RP,Helfand M,Woolf SH,et al.Methods Work Group,Third U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Current methods of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.A review of the process.Am J Prev Med.2001; 20(Suppl 3):21-35.[12] Eriksson BI,Borris LC,Dahl OE,et al.Dose-escalation study of rivaroxaban (BAY 59-7939)--an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor--for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in patients undergoing total hip replacement.Thromb Res. 2007;120(5): 685-693.[13] Eriksson BI,Borris L,Dahl OE,et al.Oral, direct Factor Xa inhibition with BAY 59-7939 for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip replacement. J Thromb Haemost.2006;4(1): 121-128.[14] Kakkar AK,Brenner B,Dahl OE,et al.Extended duration rivaroxaban versus short-term enoxaparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip arthroplasty: a double-blind, randomised controlled trial.Lancet.2008;372(9632): 31-39.[15] Eriksson BI,Borris LC,Dahl OE,et al. A once-daily, oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor, rivaroxaban (BAY 59-7939), for thromboprophylaxis after total hip replacement. Circulation.2006;114(22):2374-2381.[16] 柴伟.利伐沙班预防成人全髋关节置换术后静脉血栓栓塞的有效性及安全性研究[D].中国人民解放军军医进修学院,2008.[17] 马骊,王欣,蒋丽华.人工髋关节置换后的深静脉血栓形成:发生因素及其预防策略[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(9):1677-1680.[18] Harder S.Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of rivaroxaban: considerations for the treatment of venous thromboembolism. Thromb J.2014;12(1):22.[19] 张晟,解笑宸,姚粤峰,等.全髋关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成的4项危险因素[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(13):1969-1973.[20] 林梅清,古艳,何晓薇,等.彩色多普勒超声诊断下肢深静脉血栓形成的分析和探讨[J].中国医学创新, 2012, 7(25):157-158.[21] Parisi R,Visonà A,Camporese G,et al.Isolated distal deep vein thrombosis: efficacy and safety of a protocol of treatment. Treatment of Isolated Calf Thrombosis (TICT) Study.Int Angiol.2009;28(1): 68-72.[22] Weitz JI,Hirsh J,Samama MM,et al. New antithrombotic drugs: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition).Chest. 2008;133(6 Suppl): 234S-256S.[23] Turpie AG.Oral, direct factor Xa inhibitors in development for the prevention and treatment of thromboembolic diseases. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2007;27(6): 1238-1247.[24] 程丈俊,王俊文,任义军,等.利伐沙班与低分子量肝素在初次全髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成防治中的比较研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,6(14):480-483.[25] Turpie AG,Kreutz R,Llau J,et al.Management consensus guidance for the use of rivaroxaban--an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor.Thromb Haemost. 2012; 108:876-886.[26] Mueck W,Becka M,Kubitza D,et al.Population model of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban--an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor-in healthy subjects.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;45: 335-344.[27] Kubitza D,Becka M,Wensing G,et al.Safety, pharmacodynamics and phar-macokinetics of BAY 59-7939 - an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor - after multiple dosing in healthy male subjects.Eur J Clin Pharmacol.2005;61:873-880.[28] 靖光武,叶树楠,杨述华.髋关节置换后利伐沙班与低分子肝素预防下肢深静脉血栓的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(22):4028-4031.[29] 廖朝雨,付金玉.利伐沙班预防全髋关节置换术后静脉血栓的近期疗效及安全性[J].中外医疗,2015,35(24): 132-134.[30] 王炜,翁习生,林进,等.单侧全膝关节置换术后依诺肝素与利伐沙班抗凝效果的随机对照研究[J].中国骨与关节外科,2012,5(3):198-202.[31] Huisman MV,Quinlan DJ,Dahl OE,et al.Enoxaparin versus dabigatran or rivaroxaban for thromboprophylaxis after hip or knee arthroplasty:results of separate pooled analyses of phase III multicenter randomized trials.Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes.2010; 3(6):652-660.[32] Cao YB,Zhang JD,Shen H,et al.Rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after total hip or knee arthroplasty:a meta analysis of randomized controlled trials.Eur J Clin Pharmacol.2010;66(11): 1099-1108.[33] Kubitza D,Becka M,Voith B,et al.Safety, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of single doses of BAY 59-7939, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor.Clin Pharmacol Ther.2005;78(4):412-421.[34] 李军,王健,史占军,等.全髋关节置换后应用利伐沙班安全性的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(9): 1618-1621. |
| [1] | Liang Xin, Wang Heng, Li Xian-rong. Preoperative application of alprazolam for patients with anxiety and depression and pain after total knee arthroplasty: its safety and effectiveness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 985-992. |
| [2] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [3] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [4] | Lu Yao-jia, Xiong Chuan-zhi, Li Xiao-lei, Hu Han-sheng, Chen Gang, Wang Qiang, Lu Zhi-hua. Comparison of two methods for reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1004-1008. |
| [5] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [6] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [7] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [8] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [9] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [10] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [11] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [12] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [13] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [14] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [15] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||