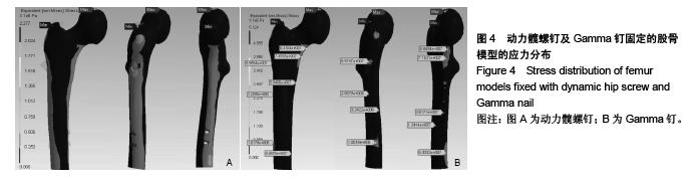
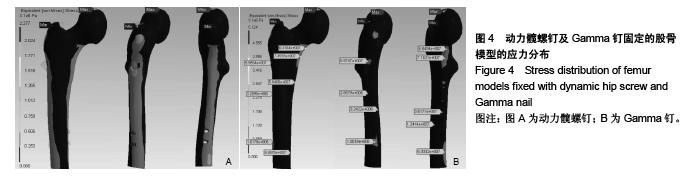
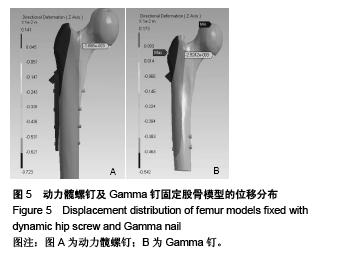
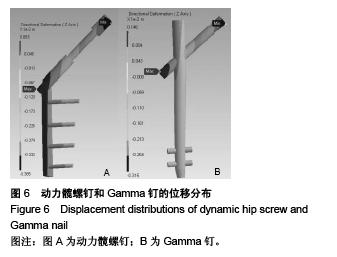
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (53): 8603-8608.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.53.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
Dynamic hip screw and Gamma nail fixation repair unstable intertrochanteric fracture: a three-dimensional finite element analysis
Huang Xiao-wei, Yu Bao-qing, Li Ze-xiang, Ao Rong-guang
- Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Pudong Hospital, Shanghai 201399, China
-
Received:2015-10-13Online:2015-12-24Published:2015-12-24 -
Contact:Corresponding author: Yu Bao-qing, Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Pudong Hospital, Shanghai 201399, China Corresponding author: Li Ze-xiang, Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Pudong Hospital, Shanghai 201399, China -
About author:Huang Xiao-wei, Master, Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Pudong Hospital, Shanghai 201399, China -
Supported by:the Key Program of Health Bureau of Shanghai City, No.20124021; a Project funded by Health System Key Specialty Construction of Shanghai Pudong New Area of China, No. PWZz2013-09
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Xiao-wei, Yu Bao-qing, Li Ze-xiang, Ao Rong-guang. Dynamic hip screw and Gamma nail fixation repair unstable intertrochanteric fracture: a three-dimensional finite element analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(53): 8603-8608.
share this article
| [1] Kukia, Heinz T, Berger G. Gamma nail versus DHS in 120 patients over 60 years: a randomized tiral. Read at the Annual Meeting of the orthopaedic Trauma Asssociation, Vancouver, BC, Canada. 1998. [2] Avila MA, Pereira GJ, Bocchi SC.Informal caregivers of older people recovering surgery for hip fractures caused by a fall: fall prevention. Cien Saude Colet. 2015;20(6):1901-1907.[3] Bae KC, Cho CH, Lee KJ,et al. Bilateral medial tibial plateau fracture after arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligment reconstruction. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2015;27(2):129-132.[4] Yoon RS, Liporace FA, Egol KA. Definitive fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2015;46(3):363-375.[5] Cosenza G, Reif U, Martini FM.Tibial plateau levelling osteotomy in 69 small breed dogs using conically coupled 1.9/2.5 mm locking plates. A clinical and radiographic retrospective assessment. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2015.[Epub ahead of print][6] Çeçen GS, Gülabi D, Pehlivano?lu G, et al. The impact of obesity on teh outcomes of the patients operated on due to Schatzker type I and type II tibial plateau fractures. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2015;21(3): 209-215.[7] Elsoe R, Larsen P, Shekhrajka N, et al.The outcome after lateral tibial plateau fracture treated with percutaneous screw fixation show a tendency towards worse functional outcome compared with a reference population. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg.2015.[Epub ahead of print][8] Su L, Townsend KL, Au J, et al. Comparison of tibial plateau angles in small and large breed dogs. Can Vet J. 2015; 56(6): 610-614.[9] Luitse J, Dunki J, Van der Hart CP. The dynamic hip screw “Goleden standard” in the treatment of pertorchanteric fractures. In: Marti RK, Dunki Jacobs, PB, editors. Proximal femoral fractures. Operative techniques and complications, vol, 2. London: ED. Medical Press; 1993: 409-422.[10] Parker MJ, Handoll H. Extramedullary fixation implants and external fixators for estracapsular hip fractures. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2014.[11] Parker MJ, Tripuraneni G, McGreggor-Riley J. Osteotomy, compression and reaming techniques for internal fixation of extracapsular hip fractures. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(3):CD000522. [12] Aune AK, Ekeland A, Odegaard B. Gamma nail vs compression screw for trochanteric femoral fractures: 15 reoperations in a prospective, randomised study of 378 patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 1994;65: 127-130.[13] Bridle SH, Pstel AD, Bircher M. Fixation of intertrochanteric fractures of the femur: a randomised prospective comparison of the Gamma nail and dynamic hip screw. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73:330-334.[14] Radford PJ, Needoff M, Webb JK. A prospective randomised comparison of the dynamic hip screw and the Gamma locking nail. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993;75: 789-793.[15] Williams WW, Parker BC. Complications associated with the use of the Gamma nail. Injury. 1992;23:291-292.[16] Christopher I, Adams C, Robinson M, et al. Prospective randomised controlled trial of an intramedullary nail versus dynamic screw and plate for intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(6):394-400.[17] Ahrengart L, Tornkvist H, Fornander P. A randomized study of the compressing hip screw and Gamma nail in 426 fractures. Clin Orthop. 2012; 401: 209-222.[18] Sitthiseripratip K, Van Oosterwyck H, Vandar Sloten J. Finite element study of trochanteric Gamma nail for trochanteric fracture. Med Eng Phys. 2013;25:99-106.[19] Taylor ME, Tanner KE, Freeman M. Stress and strain distribution within the intact femur: compression or bending? Med Eng Phys. 1997;2:122-131.[20] Bermann G, Graichen F, Rohlmann A. Hip joint loading during walking and running, measured in two patients. J Biomech. 1993;26:969-990.[21] Shahar R,Banks-Sills L, Eliasy R. Stress and strain distribution in the intact canine femur: finite element analysis. Med Eng Phys. 2003;25:387-395. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||