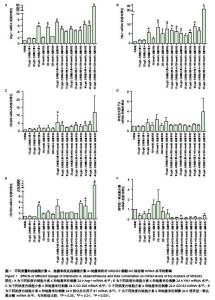
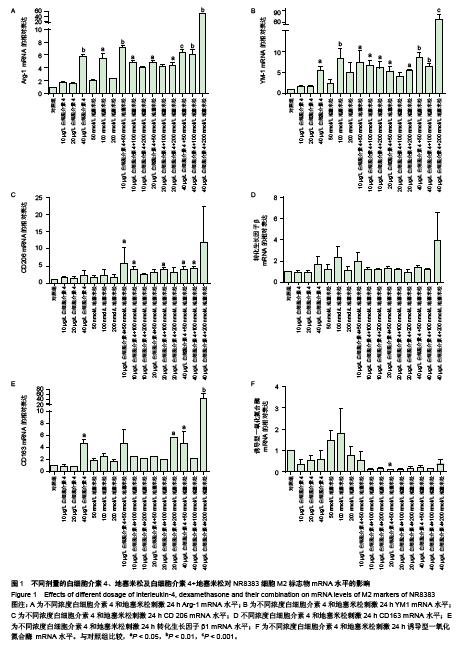
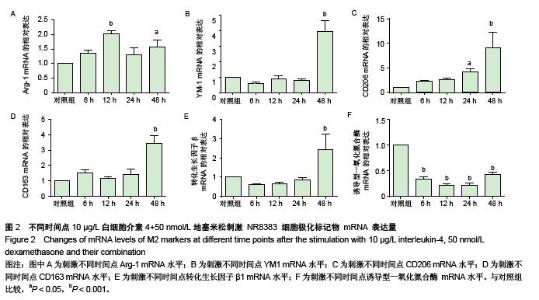
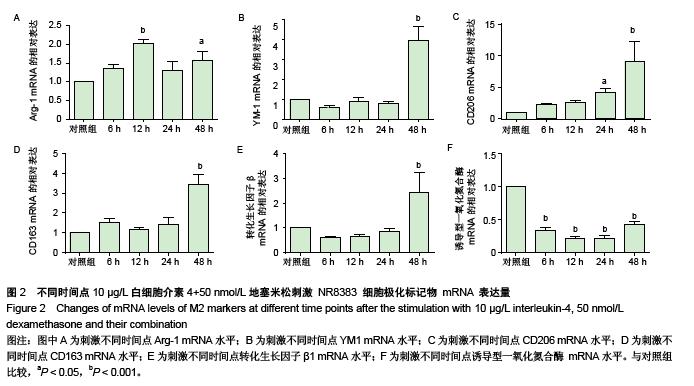
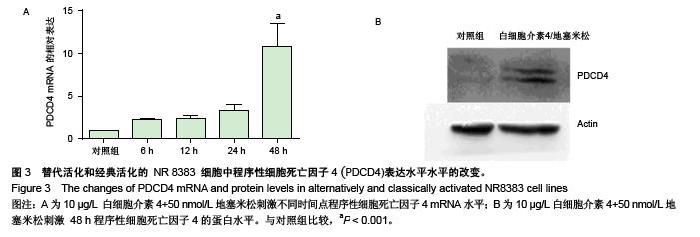
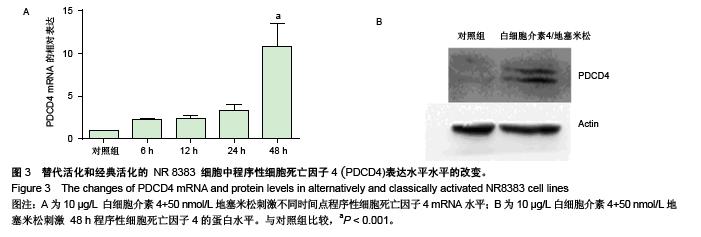
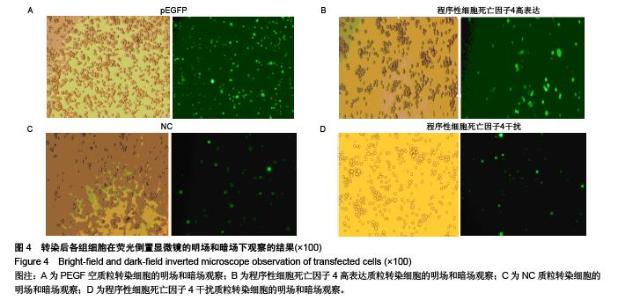
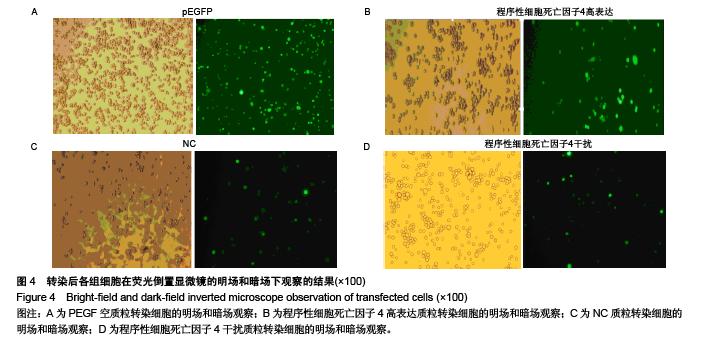
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (51): 8281-8288.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.51.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
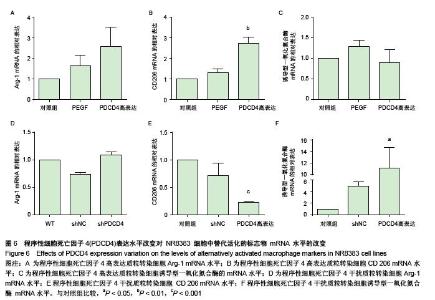
Programmed cell death 4 is a novel molecular marker of alternatively activated macrophages
- 1Micobiology Institute of Shaanxi, Xi’an 710043, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Department of Biochemistry and Molecule Biology, Preclinical College of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China; 3Department of Pharmacology, Preclinical College of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China; 4Department of Pediatrics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710004, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2015-09-25Online:2015-12-10Published:2015-12-10 -
Contact:Yang Xu-dong, M.D., Lecturer, Department of Biochemistry and Molecule Biology, Preclinical College of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Tian Jia, Master, Assistant researcher, Micobiology Institute of Shaanxi, Xi’an 710043, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81370123
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tian Jia, Jiang Xiao-gang Li, Hai-yan, Zhong Bo, Zhang Fu-jun, Ning Qi-lan, Han Yan. Programmed cell death 4 is a novel molecular marker of alternatively activated macrophages[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(51): 8281-8288.
share this article
| [1] Sica A, Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest.2012;122(3): 787-795.
[2] Xue J, Schmidt SV, Sander J, et al.Transcriptome-based network analysis reveals a spectrum model of human macrophage activation.Immunity. 2014;40(2):274-288.
[3] Mantovani A, Sica A, Locati M. Macrophage polarization comes of age. Immunity.2005; 23(4): 344-346.
[4] Vernon MA, Mylonas KJ, Hughes J. Macrophages and renal fibrosis. Semin Nephrol. 2010; 30(3): 302-317.
[5] Whyte CS, Bishop ET, Rückerl D, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)1 is a key determinant of differential macrophage activation and function. J Leukoc Biol.2011; 90(5): 845-854.
[6] Phipps KD, Gebremeskel S, Gillis J, et al. Alternatively activated M2 macrophages improve autologous Fat Graft survival in a mouse model through induction of angiogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg.2015;135(1):140-149.
[7] Okizaki S, Ito Y, Hosono K, et al. Suppressed recruitment of alternatively activated macrophages reduces TGF-β1 and impairs wound healing in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015;70:317-325.
[8] Wilson HM.Macrophages heterogeneity in atherosclerosis- implications for therapy.J Cell Mol Med. 2010; 14(8):2055- 2065.
[9] Wynn TA. Fibrotic disease and the T(H)1/T(H)2 paradigm.Nat Rev Immunol.2004; 4(8): 583-594.
[10] Shibahara K, Asano M, Ishida Y, et al. Isolation of a novel mouse gene MA-3 that is induced upon programmed cell death. Gene. 1995;166(2):297-301.
[11] Palamarchuk A, Efanov A, Maximov V, et al. Akt phosphorylates and regulates Pdcd4 tumor suppressor protein. Cancer Res. 2005; 65 (24):11282-11286.
[12] Lankat-Buttgereit B, Göke R. The tumour suppressor Pdcd4: recent advances in the elucidation of function and regulation. Biol Cell. 2009;101(6):309-317.
[13] White K, Dempsie Y, Caruso P, et al. Endothelial apoptosis in pulmonary hypertension is controlled by a microRNA/ programmed cell death 4/caspase-3 axis. Hypertension. 2014; 64 (1):185-194.
[14] Yasuda M, Schmid T, Rübsamen D, et al. Downregulation of programmed cell death 4 by inflammatory conditions contributes to the generation of the tumor promoting microenvironment. Mol Carcinog. 2010;49(9):837-848.
[15] Wang X, Zhang L, Wei Z, et al. The inhibitory action of PDCD4 in lipopolysaccharide /D-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury. Lab Invest. 2013; 93(3):291-302.
[16] Yasuda M, Schmid T, Rübsamen D, et al. Downregulation of programmed cell death 4 by inflammatory conditions contributes to the generation of the tumor promoting microenvironment. Mol Carcinog. 2010;49(9):837-848.
[17] Hwang SK, Baker AR, Young MR, et al. Tumor suppressor PDCD4 inhibits NF-κB-dependent transcription in human glioblastoma cells by direct interaction with p65. Carcinogenesis. 2014; 35 (7):1469-1480.
[18] Erwig LP, Stewart KN, Rees AJ. Macrophages from inflamed but not normal glomeruli are unresponsive to anti-inflammatory cytokines. Am J Pathol. 2000;156(1): 295-301.
[19] Ke X, Hu G, Fang W,et al. Yin inhibits the LPS-induced activation of the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Int J Mol Med. 2015;35(4):1133-1137.
[20] de Oliveira JR, Favarin DC, Tanaka SC, et al. AT-RvD1 Modulates CCL-2 and CXCL-8 Production and NF-κB, STAT-6,SOCS1, and SOCS3 Expression on Bronchial Epithelial Cells Stimulated with IL-4.Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:178369.
[21] Whyte CS, Bishop ET, Rückerl D, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)1 is a key determinant of differential macrophage activation and function. J Leukoc Biol. 2011; 90(5): 845-854.
|
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||