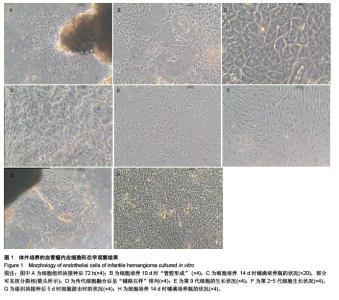
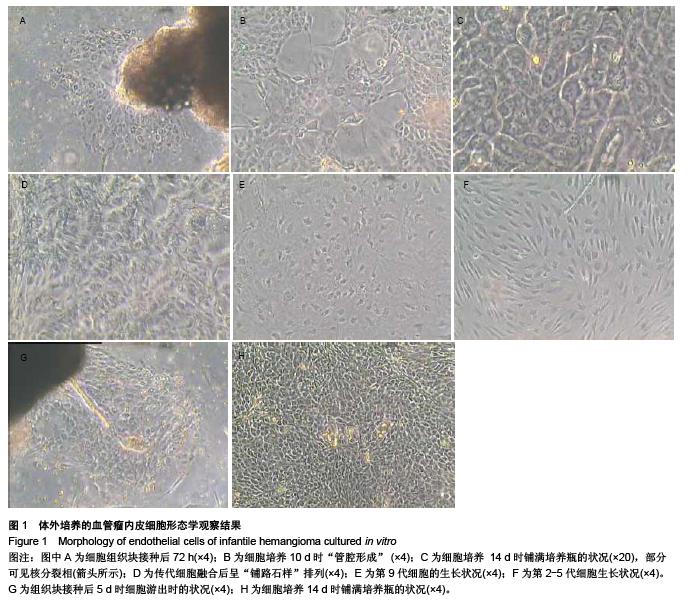
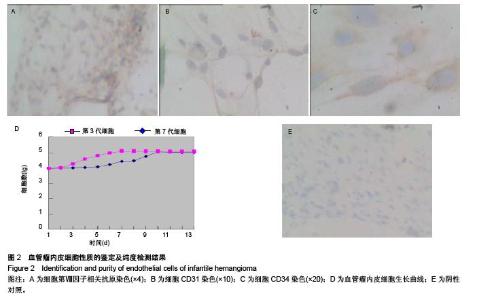
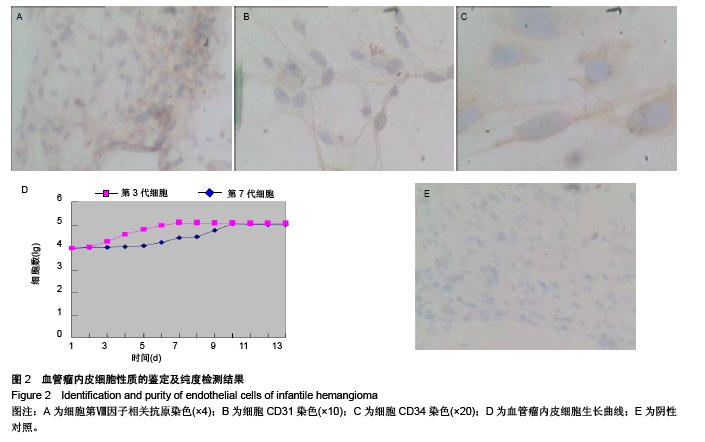
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (51): 8276-8280.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.51.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
Endothelial cells in infantile hemangioma at proliferative phase: culture, identification and growth
Li Pan-deng1, Chen Run-fang2, Zhang Li3, Zhang Yuan-gui1
- 1Department of Burn Plastic Surgery, 2Clinical Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Department of Plastic Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu 233004, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2015-10-06Online:2015-12-10Published:2015-12-10 -
Contact:Chen Run-fang, Laboratorian, Clinical Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Li Pan-deng, Master, Attending physician, Department of Burn Plastic Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou 221002, Jiangsu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Pan-deng, Chen Run-fang, Zhang Li, Zhang Yuan-gui. Endothelial cells in infantile hemangioma at proliferative phase: culture, identification and growth[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(51): 8276-8280.
share this article
| [1] Mulliken JB, Glowacki J. Hemangiomas and vascular malformations in infants and children: a classification based on endothelial characteristics. Plast Reconstr Surg.1982;69: 412-420. [2] 郑家伟,张凌.婴幼儿血管瘤治疗理念与方法的转变[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志:电子版,2015,9(2):91-94. [3] 张莉,张成书,李旭文,等.Survivin、VEGF、Caspase-3在血管瘤不同时期的表达及其相关性研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2010,6(2):89-92. [4] 李静,李小丹,蔡育,等.β受体在婴幼儿血管瘤组织中的表达及意义[J].中华整形外科杂志,2013,29(4):290-292. [5] 黄巧玲,冯晓玲.胰岛素样生长因子-2在婴幼儿血管瘤中的表达及意义[J].中国美容医学,2012,21(5) :769-773. [6] 翟亚楠,宋洪涛,陈少全,等.普萘洛尔凝胶治疗婴幼儿血管瘤的疗效观察[J].中华整形外科杂志,2013,29(1):25-28. [7] 张兰平,李宗良.32P敷贴治疗婴幼儿血管瘤1619例疗效分析[J].海南医学,2013,24(11):1607-1608. [8] Lè auté-Labrè ze C, Dumas de la Roque E, Hubiche T, et al. Propranolol for severe hemangiomas of infancy.N Engl J Med.2008; 358:2649-2651. [9] 牛静静,徐广琪,吕仁荣,等.外涂普萘洛尔软膏治疗浅表型婴幼儿血管瘤疗效观察[J].中华整形外科杂志,2013,29(2):100-103. [10] 郭军,王宇,张毅,等.口服普萘洛尔治疗婴幼儿血管瘤的临床研究[J].重庆医学,2014,43(33):4464-4466. [11] Yu Y, Flint AF, Mulliken JB,et al.Endothelial progenitor cells in infantile hemangioma.Blood.2004;103:1373-1375. [12] 张莉,李攀登,钱景瑜,等.反义Survivin对血管瘤内皮细胞增殖及凋亡的影响[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2011,32(1):1-5. [13] Seghezzi G,Patel S,Ren CJ,et al. Fibroblast growth factor-2(FGF-2)induces vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF) expression in the endothelial cells of forming capillaries:An autocrine mechanism contributing to angiogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1998;141(7):1659-1673. [14] Azizkhan Rg, Azizkhan JC, Zetter BR, et al.Mast cell heparin stimulates migration of capillary endothelial cells in vitro.J ExP Med.1980;152:931-944. [15] 韩承新,肖现民,高解春,等.肝素,干扰素、可的松和雌激素对血管瘤内皮细胞生长影响的体外实验[J].中华小儿外科杂志,1998, 19(1):47. [16] 廖洪跃,邢新,欧阳天祥,等.组织块结合酶消化法培养婴幼儿血管瘤内皮细胞[J].第二军医大学学报,2009,30(2):147-149. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||