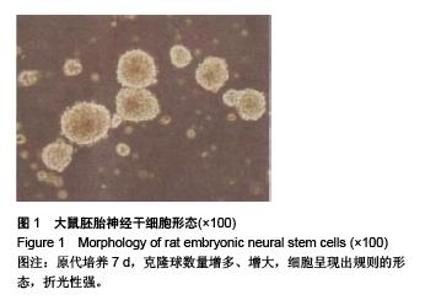
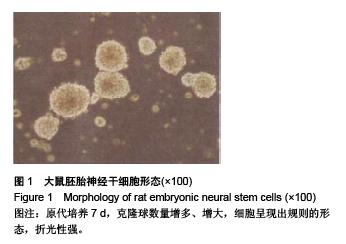
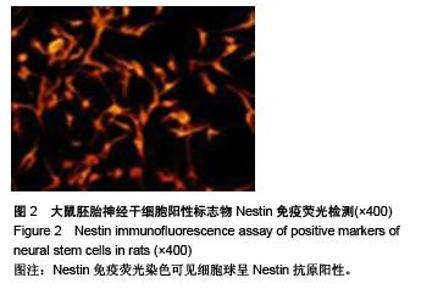
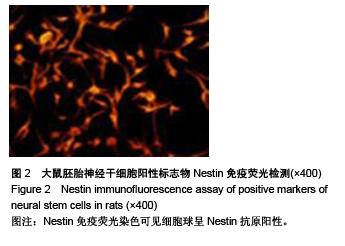
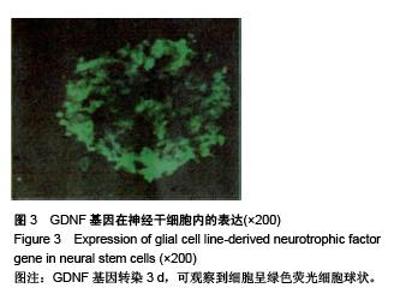
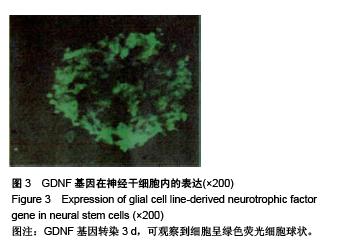
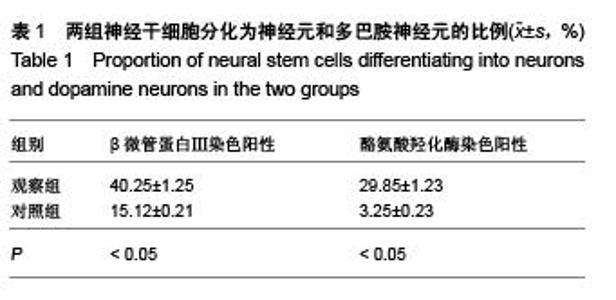
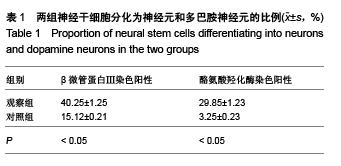
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (50): 8167-8171.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.50.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Differentiation of neural stem cells induced by glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor
He Jia1, Yan Bo2
- 1Department of Neurology, the 363rd Hospital of PLA, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Neurology, West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2015-10-17Online:2015-12-03Published:2015-12-03 -
About author:He Jia, Attending physician, Department of Neurology, the 363rd Hospital of PLA, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81201010
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Jia, Yan Bo. Differentiation of neural stem cells induced by glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(50): 8167-8171.
share this article
| [1] 阮奕文,袁群芳,王传恩,等.NGF/GDNF基因修饰神经干细胞移植对AD模型鼠前脑胆碱能神经元的保护作用[J].解剖学报, 2002,33(2):126-130.[2] 田美玲,金国华,谭雪锋,等.IL-1α及与IL-11、LIF和GDNF联合诱导胚鼠皮质、中脑神经干细胞向多巴胺神经元分化的比较[J].神经解剖学杂志,2005,21(6):656-660.[3] Reynolds BA, Weiss S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science. 1992;255(5052):1707-1710. [4] 罗特坚,丁继固,李光,等.白细胞介素-1β和胶质源性神经营养因子体外诱导鼠胚中脑神经干细胞向酪氨酸羟化酶阳性神经元分化[J].解剖学杂志,2011,34(1):41-44.[5] 陈梅玲,沈岳飞,李清华,等.不同浓度GDNF诱导神经干细胞向多巴胺能神经元分化研究[J].重庆医学,2011,40(22):2185-2187, 2190.[6] 丁继固,丁文杰,李光,等.胶质源性神经营养因子体外诱导小鼠胚胎中脑神经干细胞分化的研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2008, 23(4):341-343.[7] 姚帅辉.ATRA干预培养鼠胚神经干细胞联合GDNF移植对脊髓损伤再生修复的作用[D]. 泸州:泸州医学院,2014.[8] 高明勇,肖建德,郑启新,等.神经干细胞转染胶质细胞源性神经营养因子基因后的分化表现[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(11): 1067-1072.[9] Krasny M, Zadurska M, Cessak G, et al. Analysis of effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on teeth and oral tissues during orthodontic treatment. Report based on literature review. Acta Pol Pharm. 2013;70(3):573-577.[10] Pathak AK, Sharma DS. Biofilm associated microorganisms on removable oral orthodontic appliances in children in the mixed dentition. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2013;37(3):335-339.[11] Iijima M, Brantley WA, Kawashima I, et al. Micro-X-ray diffraction observation of nickel-titanium orthodontic wires in simulated oral environment. Biomaterials. 2004;25(1): 171-176.[12] 陈茂华.HIF-1α基因及GDNF基因修饰神经干细胞移植治疗大鼠脊髓损伤的研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2014.[13] Eppright M, Shroff B, Best AM, et al. Influence of active reminders on oral hygiene compliance in orthodontic patients. Angle Orthod. 2014;84(2):208-213.[14] 谭雪锋,金国华,田美玲,等.白介素-1α及与白介素-11、白血病抑制因子和胶质细胞源性神经生长因子联合诱导人神经干细胞向多巴胺神经元的分化[J].解剖学报,2005,36(4):351-355.[15] Wang F, Kameda M, Yasuhara T, et al. GDNF-pretreatment enhances the survival of neural stem cells following transplantation in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Res. 2011;71(1):92-98.[16] Baricevic M, Mravak-Stipetic M, Majstorovic M,et al. Oral mucosal lesions during orthodontic treatment. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2011;21(2):96-102.[17] Chu K, Kim M, Jeong SW, et al. Human neural stem cells can migrate, differentiate, and integrate after intravenous transplantation in adult rats with transient forebrain ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 2003;343(2):129-133.[18] Lei Z, Jiang Y, Li T, et al. Signaling of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor and its receptor GFRα1 induce Nurr1 and Pitx3 to promote survival of grafted midbrain-derived neural stem cells in a rat model of Parkinson disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2011;70(9):736-747.[19] 贺月秋,陈惠金,钱龙华,等.胶质细胞源性神经营养因子联合神经干细胞移植治疗脑室周围白质软化新生大鼠的疗效观察[J].临床儿科杂志,2009,27(10):963-970.[20] 陈梅玲,沈岳飞,罗彦妮,等.抗坏血酸联合胶质细胞源性神经营养因子诱导神经干细胞向多巴胺能神经元分化的研究[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2009,26(5):523-526.[21] 陈梅玲.神经干细胞体外定向分化为多巴胺能神经元的实验研究[D].南宁:广西医科大学,2008. [22] 贺月秋,陈惠金,钱龙华,等.经脑室神经干细胞移植治疗脑室周围白质软化新生大鼠电镜下脑病理评估[J].实用儿科临床杂志, 2008, 23(20):1610-1612,1629.[23] 徐胜利,周明,陈彪,等.神经营养因子基因修饰的神经干细胞在帕金森病大鼠模型中的治疗作用[J].中华老年医学杂志,2010, 29(1):58-62.[24] 李勇,沈文正,杨春荣,等.大鼠胎儿神经干细胞的分离、培养及诱导分化[J].西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版,2007,35(3): 20-24.[25] Jue SS, Kim JY, Na SH, et al. Localization of ODAM, PCNA, and CK14 in regenerating junctional epithelium during orthodontic tooth movement in rats. Angle Orthod. 2014; 84(3): 534-540.[26] 李凤飞,李升,刘钟,等.胶质细胞源性神经营养因子对培养的胚鼠脑室下区神经干细胞表达Pitx3及酪氨酸羟化酶的影响[J].解剖学杂志,2007,30(3):304-306,354.[27] 姜宇,曾水林,鲁佑瑜,等.胶质细胞源性神经营养因子促进中脑源神经干细胞增殖和向多巴胺能神经元分化[J].神经解剖学杂志, 2010,26(5):537-542.[28] Seehra J, Newton JT, Dibiase AT.Interceptive orthodontic treatment in bullied adolescents and its impact on self-esteem and oral-health-related quality of life. Eur J Orthod. 2013; 35(5): 615-621.[29] Lin YS, Yu JH, Chang YZ, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an orthodontic miniimplant used with revolving (translation and rotation) temporary anchorage device by finite element analysis and experimental testing. Implant Dent. 2013;22(1): 77-82.[30] 邓兴力,王应莉,杨智勇,等.SPIO、EGFP双标GDNF基因修饰中脑神经干细胞移植治疗帕金森病[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2010, 27(2):109-113.[31] Yoo YM, Lee CJ, Kim YJ. Exogenous GDNF increases the migration of the neural stem cells with no protection against kainic acid-induced excitotoxic cell death in rats. Brain Res. 2012;1486:27-38.[32] 靳晓亮,李京红,关方霞,等.大鼠神经干细胞体外培养条件下GDNF及NGF的分泌特点[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2009,4(2): 108-109,113.[33] Ngan ES, Shum CK, Poon HC, et al. Prokineticin-1 (Prok-1) works coordinately with glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) to mediate proliferation and differentiation of enteric neural crest cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008; 1783(3):467-478.[34] Lv Y, Zhao P, Chen G, et al. Effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on cell viability, proliferation and neural differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells-derived neural crest stem cells. Biotechnol Lett. 2013;35(12):2201-2212.[35] Sun NF, Zhong WY, Lu SA, et al. Coexpression of recombinant adenovirus carrying GDNF and EDNRB genes in neural stem cells in vitro. Cell Biol Int. 2013;37(5):458-463.[36] Cherry JF, Bennett NK, Schachner M, et al. Engineered N-cadherin and L1 biomimetic substrates concertedly promote neuronal differentiation, neurite extension and neuroprotection of human neural stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(10):4113-4126.[37] 沈峰,潘庆刚,邓东风,等.GDNF基因转染诱导神经干细胞向神经元分化的作用[J].同济大学学报:医学版,2007,28(5):35-39.[38] 陈立,杜娟,陈丽,等.GDNF及dbcAMP对神经干细胞诱导分化为多巴胺能神经元作用的实验研究[J].中风与神经疾病杂志, 2014, 31(7):580-584. |
| [1] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [4] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Liu-Gao Miyang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Wang Jinxiang, Pan Xinghua. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for traumatic systemic inflammatory response syndrome in tree shrews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3994-4000. |
| [5] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [6] | Chen Lei, Zheng Rui, Jie Yongsheng, Qi Hui, Sun Lei, Shu Xiong. In vitro evaluation of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction combined with osteochondral integrated scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3487-3492. |
| [7] | Wei Qin, Zhang Xue, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Jia Qiyu, Ma Chuang. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [8] | Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li. Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [9] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [10] | Li Congcong, Yao Nan, Huang Dane, Song Min, Peng Sha, Li Anan, Lu Chao, Liu Wengang. Identification and chondrogenic differentiation of human infrapatellar fat pad derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2976-2981. |
| [11] | Gao Yuanhui, Xiang Yang, Cao Hui, Wang Shunlan, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang, Huang Denggao. Comparison of biological characteristics of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells in Wuzhishan inbreed miniature pigs aged two different months [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2988-2993. |
| [12] | Cao Yang, Zhang Junping, Peng Li, Ding Yi, Li Guanghui. Isolation and culture of rabbit aortic endothelial cells and biological characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3000-3003. |
| [13] | Dai Min, Wang Shuai, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Yu Limei, Hu Xiaohua, Yi Jie, Yao Li, Zhang Ligang. Biological characteristics of hypoxic preconditioned human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3004-3008. |
| [14] | Qin Yanchun, Rong Zhen, Jiang Ruiyuan, Fu Bin, Hong Xiaohua, Mo Chunmei. Chinese medicine compound preparation inhibits proliferation of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells and the expression of stemness transcription factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3016-3023. |
| [15] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||