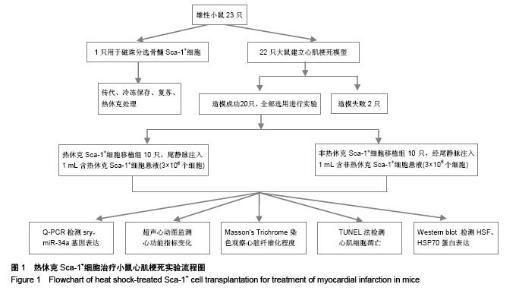
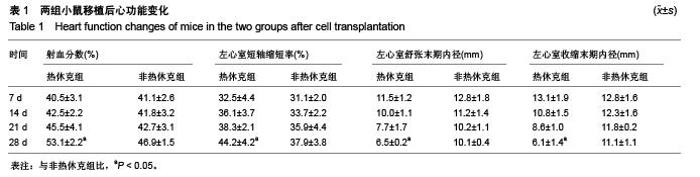
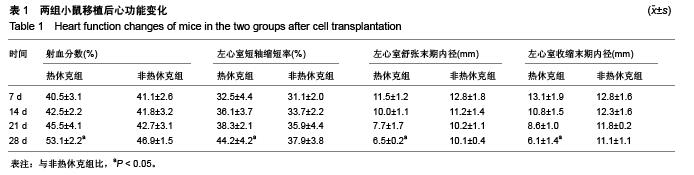
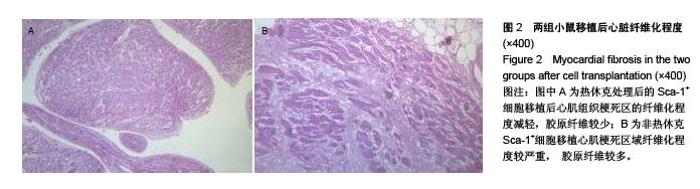
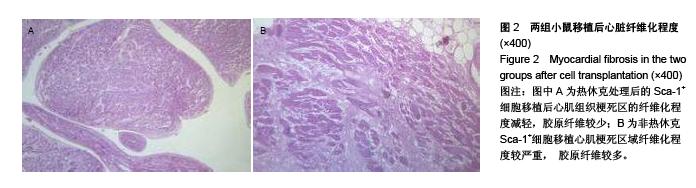
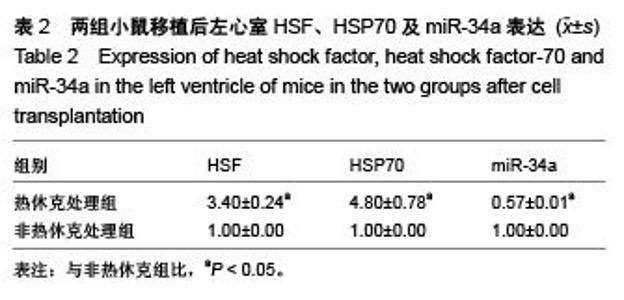
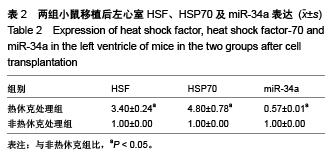
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (50): 8149-8154.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.50.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
Heat shock improves Sca-1+ cell transplantation for treatment of myocardial infarction in mice
Wang Li-hui1, Shen Ya-hui1, Guo Yan-qing1, Zang Bin-bin1, Li Wei2
- 1Intensive Care Unit, Henan Province Hospital of TCM, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China; 2Intensive Care Unit, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2015-10-08Online:2015-12-03Published:2015-12-03 -
About author:Wang Li-hui, Associate chief physician, Intensive Care Unit, Henan Province Hospital of TCM, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Li-hui, Shen Ya-hui, Guo Yan-qing, Zang Bin-bin, Li Wei . Heat shock improves Sca-1+ cell transplantation for treatment of myocardial infarction in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(50): 8149-8154.
share this article
| [1] 包玉梅,赵燕平,周丽华.骨髓干细胞移植与心肌再生的研究进展[J].中国误诊学杂志,2010,10(11):2537-2538.[2] Bhaskar B, Mekala NK, Baadhe RR,et al. Role of signaling pathways in mesenchymal stem cell differentiation.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;9(6):508-512.[3] Tian H, Chen GH, Xu Y,et al. Biological characteristics of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and JAK2 mutation in myeloproliferative neoplasms.Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2012;33(9):701-704.[4] Zhu X, Du J, Liu G. The comparison of multilineage differentiation of bone marrow and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Clin Lab. 2012;58(9-10):897-903.[5] Wang B, Wu SM, Wang T, et al. Pre-treatment with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibits systemic intravascular coagulation and attenuates organ dysfunction in lipopolysaccharide-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation rat model. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012;125(10): 1753-1759.[6] Wu Y, Zhao RC. The role of chemokines in mesenchymal stem cell homing to myocardium. Stem Cell Rev. 2012;8(1): 243-250.[7] Tong J, Ding J, Shen X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation enhancement in myocardial infarction rat model under ultrasound combined with nitric oxide microbubbles. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e80186.[8] Won YW, Patel AN, Bull DA. Cell surface engineering to enhance mesenchymal stem cell migration toward an SDF-1 gradient. Biomaterials. 2014;35(21):5627-5635.[9] 何庚戌,要彤,张浩,等.骨髓间充质干细胞经静脉移植到心肌梗死大鼠体内后的分布[J].心脏杂志,2009,21(2):201-205.[10] Rodrigo SF, van Ramshorst J, Hoogslag GE, et al. Intramyocardial injection of autologous bone marrow-derived ex vivo expanded mesenchymal stem cells in acute myocardial infarction patients is feasible and safe up to 5 years of follow-up. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2013;6(5):816-825.[11] Narita T, Shintani Y, Ikebe C, et al. The use of scaffold-free cell sheet technique to refine mesenchymal stromal cell-based therapy for heart failure. Mol Ther. 2013;21(4):860-867.[12] Tano N, Narita T, Kaneko M, et al. Epicardial placement of mesenchymal stromal cell-sheets for the treatment of ischemic cardiomyopathy; in vivo proof-of-concept study. Mol Ther. 2014;22(10):1864-1871.[13] Chen Y, Teng X, Chen W, et al. Timing of transplantation of autologous bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells for treating myocardial infarction. Sci China Life Sci. 2014;57(2): 195-200.[14] Chullikana A, Majumdar AS, Gottipamula S, et al. Randomized, double-blind, phase I/II study of intravenous allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells in acute myocardial infarction. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(3):250-261. [15] Qu Z, Xu H, Tian Y, et al. Atorvastatin improves microenvironment to enhance the beneficial effects of BMSCs therapy in a rabbit model of acute myocardial infarction. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32(2):380-389.[16] Wang F, Zhou H, Du Z, et al. Cytoprotective effect of melatonin against hypoxia/serum deprivation-induced cell death of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;748:157-65.[17] Liu XB, Wang JA, Ji XY, et al. Preconditioning of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by prolyl hydroxylase inhibition enhances cell survival and angiogenesis in vitro and after transplantation into the ischemic heart of rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(5):111.[18] 温倜,戚勋.生长因子可促进自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗急性心肌梗死[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(19):3017-3022.[19] Tang Y, Gan X, Cheheltani R, et al. Targeted delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor improves stem cell therapy in a rat myocardial infarction model. Nanomedicine. 2014; 10(8):1711-1718.[20] 周卢琨,曹文彬,姚剑峰,等.过表达Akt1 对小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞生物学功能的影响[J].生物医学工程与临床,2014,12(4): 380-385.[21] Chen XQ, Chen LL, Fan L, et al. Stem cells with FGF4-bFGF fused gene enhances the expression of bFGF and improves myocardial repair in rats Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;447(1):145-151.[22] Mao J, Lv Z, Zhuang Y. MicroRNA-23a is involved in tumor necrosis factor-α induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells and myocardial infarction. Exp Mol Pathol. 2014;97(1):23-30.[23] Deng JH, Deng P, Lin SL, et al. Gene silencing in vitro and in vivo using intronic microRNAs. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1218: 321-340.[24] Starega-Roslan J, Koscianska E, Kozlowski P, et al. The role of the precursor structure in the biogenesis of microRNA. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68(17):2859-2871.[25] Kroh EM, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS, et al. Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods. 2010;50(4): 298-301.[26] Fichtlscherer S, De Rosa S, Fox H, et al. Circulating microRNAs in patients with coronary artery disease. Circ Res. 2010;107(5):677-684.[27] Wang R, Li N, Zhang Y, et al. Circulating microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers of acute myocardial infarction. Intern Med. 2011;50(17):1789-1795.[28] Olivieri F, Antonicelli R, Lorenzi M, et al. Diagnostic potential of circulating miR-499-5p in elderly patients with acute non ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167(2): 531-536.[29] Meder B, Keller A, Vogel B, et al. MicroRNA signatures in total peripheral blood as novel biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011;106(1):13-23.[30] Gidlöf O, Andersson P, van der Pals J, et al. Cardiospecific microRNA plasma levels correlate with troponin and cardiac function in patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction, are selectively dependent on renal elimination, and can be detected in urine samples. Cardiology. 2011;118(4):217-226.[31] Matsumoto S, Sakata Y, Nakatani D, et al. A subset of circulating microRNAs are predictive for cardiac death after discharge for acute myocardial infarction Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;427(2):280-284. |
| [1] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [4] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Liu-Gao Miyang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Wang Jinxiang, Pan Xinghua. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for traumatic systemic inflammatory response syndrome in tree shrews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3994-4000. |
| [5] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [6] | Chen Lei, Zheng Rui, Jie Yongsheng, Qi Hui, Sun Lei, Shu Xiong. In vitro evaluation of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction combined with osteochondral integrated scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3487-3492. |
| [7] | Wei Qin, Zhang Xue, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Jia Qiyu, Ma Chuang. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [8] | Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li. Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [9] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [10] | Li Congcong, Yao Nan, Huang Dane, Song Min, Peng Sha, Li Anan, Lu Chao, Liu Wengang. Identification and chondrogenic differentiation of human infrapatellar fat pad derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2976-2981. |
| [11] | Gao Yuanhui, Xiang Yang, Cao Hui, Wang Shunlan, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang, Huang Denggao. Comparison of biological characteristics of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells in Wuzhishan inbreed miniature pigs aged two different months [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2988-2993. |
| [12] | Cao Yang, Zhang Junping, Peng Li, Ding Yi, Li Guanghui. Isolation and culture of rabbit aortic endothelial cells and biological characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3000-3003. |
| [13] | Dai Min, Wang Shuai, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Yu Limei, Hu Xiaohua, Yi Jie, Yao Li, Zhang Ligang. Biological characteristics of hypoxic preconditioned human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3004-3008. |
| [14] | Qin Yanchun, Rong Zhen, Jiang Ruiyuan, Fu Bin, Hong Xiaohua, Mo Chunmei. Chinese medicine compound preparation inhibits proliferation of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells and the expression of stemness transcription factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3016-3023. |
| [15] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||