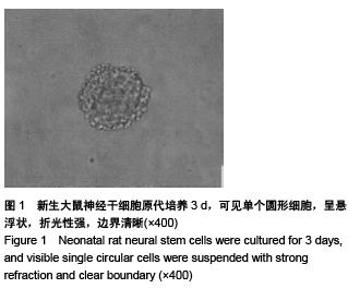
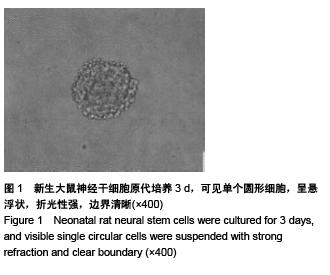
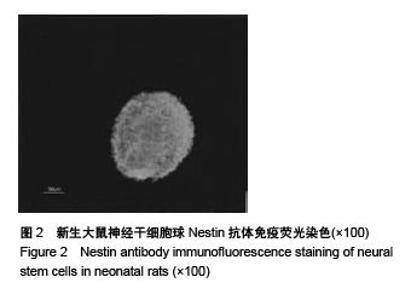
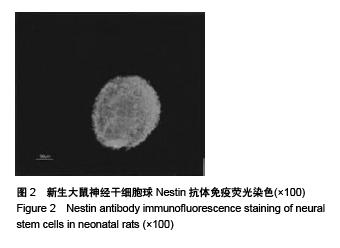
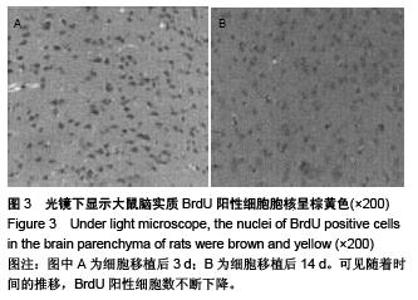
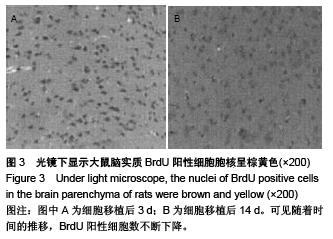
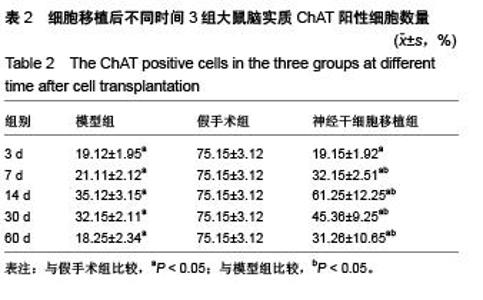
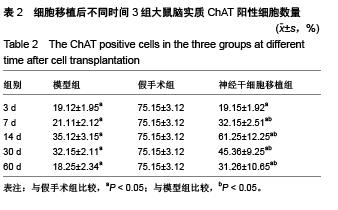
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (50): 8126-8131.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.50.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Changes of cholinergic neurons in the hippocampus of vascular dementia rats after neural stem cell transplantation
Sun Yu-hua, Geng Li-jiao, Zhao Jing-ya, He Wei-ya, Li Bao-ping
- Department of Neurology, Huaihe Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng 475001, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2015-11-03Online:2015-12-03Published:2015-12-03 -
About author:Sun Yu-hua, Associate chief physician, Department of Neurology, Huaihe Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng 475001, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Yu-hua, Geng Li-jiao, Zhao Jing-ya, He Wei-ya, Li Bao-ping. Changes of cholinergic neurons in the hippocampus of vascular dementia rats after neural stem cell transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(50): 8126-8131.
share this article
| [1] 张宏,王玮,郑志竑,等.血管性痴呆大鼠海马神经干细胞移植[J].福建医科大学学报,2003,37(2):128-132.[2] 李肖云,兰希发.粒细胞集落刺激因子对血管性痴呆大鼠海马神经细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(27):5044-5047.[3] 向静,王昌铭,江德鹏,等.脐血干细胞海马移植对VD大鼠脑内Ach及AchE活性的影响[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志,2007,33(7): 389-394.[4] Meguro K, Akanuma K, Meguro M, et al. Prognosis of vascular mild cognitive impairment includes vascular dementia onset and death by cardiovascular disease: reanalysis from the Osaki-Tajiri project. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012;21(7):607-611.[5] Reynolds BA, Weiss S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science. 1992;255(5052):1707-1710. [6] 黄河清,唐军,周振华,等.全脑缺血大鼠海马自体神经干细胞动员与5-HT1A受体表达关系的初步研究[J].重庆医学,2008,37(7): 693-696. [7] 黄河清,唐军,周振华,等.西酞普兰对血管性痴呆大鼠海马DG神经发生和认知障碍影响的初步研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2008, 30(10):946-949.[8] Meguro K, Akanuma K, Meguro M, et al. Prognosis of vascular mild cognitive impairment includes vascular dementia onset and death by cardiovascular disease: reanalysis from the Osaki-Tajiri project. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012;21(7):607-611.[9] 叶建新,王玮,郑志竑,等.移植神经干细胞对血管性痴呆大鼠的行为学效应[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(34):7668-7670. [10] 叶建新,王玮,郑志竑,等.移植神经干细胞对血管性痴呆大鼠海马胆碱能神经元的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2005,11(1): 10-12. [11] Perri R, Fadda L, Caltagirone C, et al. Word list and story recall elicit different patterns of memory deficit in patients with Alzheimer's disease, frontotemporal dementia, subcortical ischemic vascular disease, and Lewy body dementia. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;37(1):99-107.[12] Liu B,Tang J,Zhang JX,et al.Autophagy activation aggravates neuronal injury in the hippocampus of vascular dementia rats. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9 (13): 1288-1296[13] 宋晨晨,张楠,程焱,等.瑞舒伐他汀和美金刚对血管性痴呆大鼠内皮祖细胞的影响[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2015,17(3): 299-302. [14] 马向薇.胚胎干细胞移植治疗脑血管疾病[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(31):5717-5722.[15] 金善,曹秉振,赵忠新,等.间充质干细胞对血管性痴呆大鼠学习记忆能力及海马CA1区突触素表达的影响[J].中国行为医学科学, 2008,17(4):307-309. [16] 金善,赵忠新,邵福源,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对血管性痴呆大鼠海马CA1区突触素表达的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2006,21(8): 683-685,插7. [17] 邢雪松,吕威力,张玉丽,等.行为学训练对血管性痴呆大鼠内源性神经干细胞增殖及肌醇需要因子1蛋白表达的影响[J].解剖学杂志,2014,37(1):63-66,85. [18] 李婷.甲状腺激素促进成年大鼠慢性脑缺血后海马神经祖细胞增殖[D].广州:南方医科大学,2011. [19] 金善,曹秉振,张秀花,等.静脉注射同种异体骨髓间充质干细胞对血管性痴呆大鼠海马区脑组织形态及微管相关蛋白2表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(33):6637-6640. [20] Ekonomou A, Ballard CG, Pathmanaban ON, et al. Increased neural progenitors in vascular dementia. Neurobiol Aging. 2011;32(12):2152-2161.[21] Chen YJ, Deutsch G, Satya R, et al. A semi-quantitative method for correlating brain disease groups with normal controls using SPECT: Alzheimer's disease versus vascular dementia. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2013;37(1):40-47.[22] 邢雪松,吕威力,赵海,等.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子促进血管性痴呆大鼠音猬蛋白的表达[J].解剖学杂志,2014,37(6):771-774. [23] Li H, Xin X. Nitrogen dioxide (NO(2)) pollution as a potential risk factor for developing vascular dementia and its synaptic mechanisms. Chemosphere. 2013;92(1):52-58.[24] 农伟东,莫雪安,阳玉群,等.甘露醇对骨髓间充质干细胞治疗血管性痴呆大鼠行为学及海马CA3区突触素表达水平的影响[J].中华神经科杂志,2013,46(6):408-413. [25] 张泰鹏,莫雪安,刘金萍,等.甘露醇对骨髓间充质干细胞治疗血管性痴呆大鼠行为学及海马胆碱能系统的影响[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2011,28(4):317-320.[26] Meguro K, Tanaka N, Nakatsuka M, et al. Vascular lesions in mixed dementia, vascular dementia, and Alzheimer disease with cerebrovascular disease: the Kurihara Project. J Neurol Sci. 2012;322(1-2):157-160. [27] 李丽杰,孔繁明,张学斌,等.立体定向移植骨髓间充质干细胞改善血管性大鼠的学习记忆能力[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(14):2562-2566. [28] Cervellati C, Romani A, Seripa D, et al. Oxidative balance, homocysteine, and uric acid levels in older patients with Late Onset Alzheimer's Disease or Vascular Dementia. J Neurol Sci. 2014;337(1-2):156-161.[29] Liu B, Tang Y, Shen Y, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid τ protein in differential diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia in Chinese population: a meta-analysis. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2014;29(2):116-122.[30] Chu K, Kim M, Jeong SW, et al. Human neural stem cells can migrate, differentiate, and integrate after intravenous transplantation in adult rats with transient forebrain ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 2003;343(2):129-133.[31] 胡兰兰,姚永杰,苏长雨,等.骨髓间充质干细胞输注对血管性痴呆大鼠海马细胞凋亡的影响[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2014, 16(11):1212-1214.[32] 王昌铭,滕军放,高唱,等.骨髓间充质干细胞颈内动脉移植在血管性痴呆大鼠脑内存活迁移及对胆碱能系统的影响[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2014,16(2):196-199.[33] 黄敬.细胞移植及药物治疗血管性痴呆的实验研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2006.[34] Fu JL, Zhang T, Chang C, et al. The value of diffusion tensor imaging in the differential diagnosis of subcortical ischemic vascular dementia and Alzheimer's disease in patients with only mild white matter alterations on T2-weighted images. Acta Radiol. 2012;53(3):312-317.[35] 井沆,田茂,董艳军,等.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗血管性痴呆大鼠行为学及海马CaM、CaMKⅡ表达水平的影响[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2015,32(2):148-150.[36] 王济潍,陈文,王玉良,等.EGb761对血管性痴呆大鼠海马齿状回神经干细胞增殖分化的影响[J].神经解剖学杂志,2012,28(6): 589-594.[37] 黄燕,王景周,张涛,等.促红细胞生成素对血管性痴呆大鼠神经干细胞增殖分化的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2009,31(9): 805-808.[38] 王菲,常光明,耿鑫,等.BDNF和TERT联合转染BMSCs对血管性痴呆大鼠学习记忆功能恢复及海马CA1区超微结构的影响[J].天津医科大学学报,2014,20(3):172-176.[39] 李莹,张微微,魏微,等.人脐血间充质干细胞海马移植治疗大鼠血管性痴呆的实验研究[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2009,4(4):244- 248.[40] 李莹,王景周.人脐血干细胞海马CA1区移植及GM1腹腔注射治疗大鼠血管性痴呆[J].第三军医大学学报,2008, 30(12): 1154-1158. |
| [1] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [4] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Liu-Gao Miyang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Wang Jinxiang, Pan Xinghua. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for traumatic systemic inflammatory response syndrome in tree shrews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3994-4000. |
| [5] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [6] | Chen Lei, Zheng Rui, Jie Yongsheng, Qi Hui, Sun Lei, Shu Xiong. In vitro evaluation of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction combined with osteochondral integrated scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3487-3492. |
| [7] | Wei Qin, Zhang Xue, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Jia Qiyu, Ma Chuang. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [8] | Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li. Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [9] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [10] | Li Congcong, Yao Nan, Huang Dane, Song Min, Peng Sha, Li Anan, Lu Chao, Liu Wengang. Identification and chondrogenic differentiation of human infrapatellar fat pad derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2976-2981. |
| [11] | Gao Yuanhui, Xiang Yang, Cao Hui, Wang Shunlan, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang, Huang Denggao. Comparison of biological characteristics of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells in Wuzhishan inbreed miniature pigs aged two different months [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2988-2993. |
| [12] | Cao Yang, Zhang Junping, Peng Li, Ding Yi, Li Guanghui. Isolation and culture of rabbit aortic endothelial cells and biological characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3000-3003. |
| [13] | Dai Min, Wang Shuai, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Yu Limei, Hu Xiaohua, Yi Jie, Yao Li, Zhang Ligang. Biological characteristics of hypoxic preconditioned human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3004-3008. |
| [14] | Qin Yanchun, Rong Zhen, Jiang Ruiyuan, Fu Bin, Hong Xiaohua, Mo Chunmei. Chinese medicine compound preparation inhibits proliferation of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells and the expression of stemness transcription factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3016-3023. |
| [15] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||