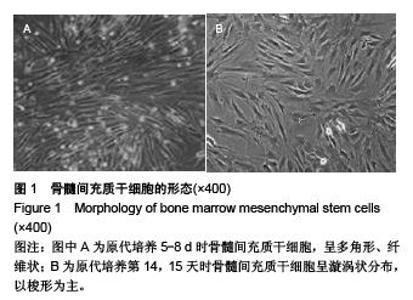
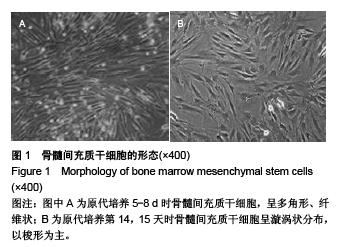
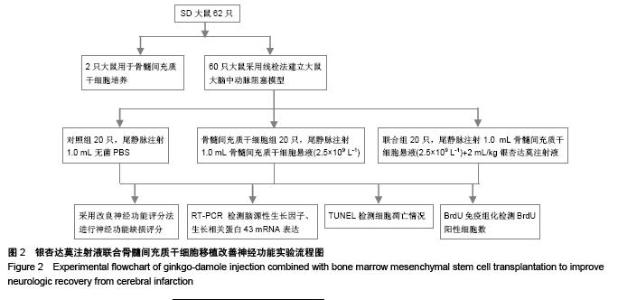
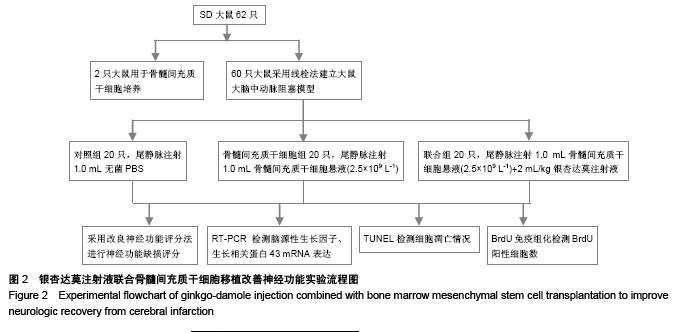
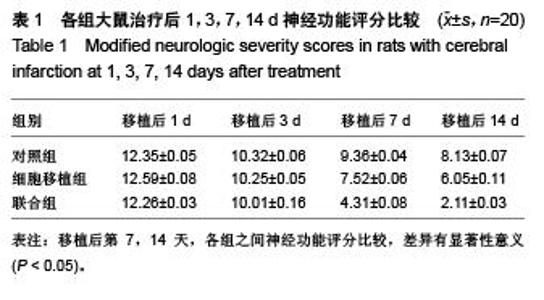
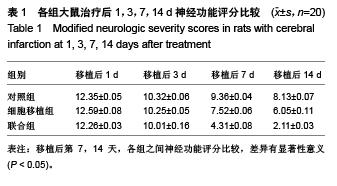
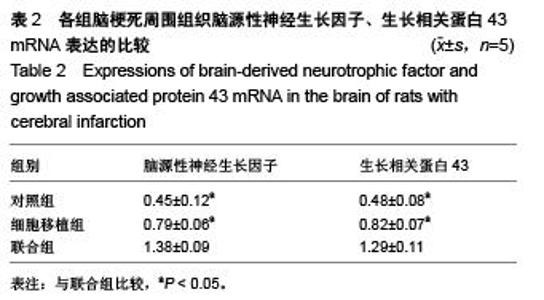
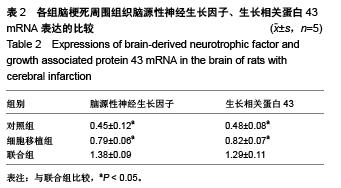
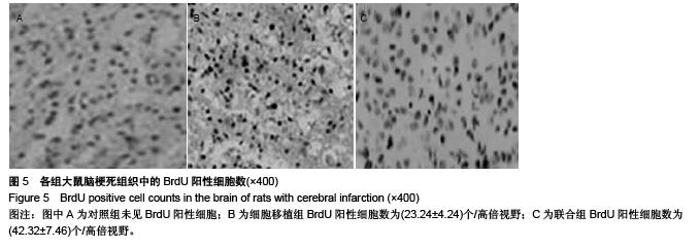
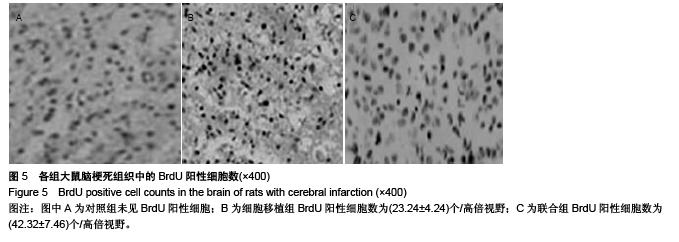
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (50): 8108-8113.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.50.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ginkgo-damole injection combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation improves neurologic recovery from cerebral infarction
Yang Chao-yang
- Department of General Internal Medicine, Jiyuan Municipal People’s Hospital, Jiyuan 454000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2015-10-19Online:2015-12-03Published:2015-12-03 -
About author:Yang Chao-yang, Associate chief physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Jiyuan Municipal People’s Hospital, Jiyuan 454000, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Chao-yang. Ginkgo-damole injection combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation improves neurologic recovery from cerebral infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(50): 8108-8113.
share this article
| [1] Zheng W, Honmou O, Miyata K, et al. Therapeutic benefits of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow after global cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2010;1310:8-16.
[2] Akiyama K, You YO, Yamaza T, et al. Characterization of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells in suspension. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012;3(5):40.
[3] Yip HK, Chang LT, Chang WN, et al. Level and value of circulating endothelial progenitor cells in patients after acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2008;39(1):69-74.
[4] 杨志华,徐凤霞,彭烈标,等.BMSCs移植后梗死灶周围及室管膜下区神经元增殖促进大鼠神经功能恢复[J].中华神经医学杂志, 2014,13(4):348-352.
[5] Barbosa da Fonseca LM, Gutfilen B, Rosado de Castro PH, et al. Migration and homing of bone-marrow mononuclear cells in chronic ischemic stroke after intra-arterial injection. Exp Neurol. 2010;221(1):122-128.
[6] Li Z, Tian X, Yuan Y, et al. Effect of cell culture using chitosan membranes on stemness marker genes in mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2013;7(6):1945-1949.
[7] Hokari M, Kuroda S, Chiba Y, et al. Synergistic effects of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor on bone marrow stromal cell transplantation for mice cerebral infarct. Cytokine. 2009; 46(2):260-266.
[8] Kawabori M, Kuroda S, Ito M, et al. Timing and cell dose determine therapeutic effects of bone marrow stromal cell transplantation in rat model of cerebral infarct. Neuropathology. 2013;33(2):140-148.
[9] 吴涛,安锐,张斌青,等.131I-FIAU/TK报告基因系统监测大鼠脑梗死模型中移植细胞的研究[J].中华核医学杂志,2011,31(5): 301-305.
[10] Wakabayashi K, Nagai A, Sheikh AM, et al. Transplantation of human mesenchymal stem cells promotes functional improvement and increased expression of neurotrophic factors in a rat focal cerebral ischemia model. J Neurosci Res. 2010;88(5):1017-1025.
[11] Komatsu K, Honmou O, Suzuki J, et al. Therapeutic time window of mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow after cerebral ischemia.Brain Res. 2010;1334:84-92.
[12] Solaroglu I, Cahill J, Tsubokawa T, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor protects the brain against experimental stroke via inhibition of apoptosis and inflammation. Neurol Res. 2009;31(2):167-172.
[13] 郭振宇,郑芹,雷俊霞,等.不同品系小鼠骨髓问质干细胞扩增能力及细胞表型差异的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008, 47(12)-9257-9260.
[14] Caplan AI, Correa D. The MSC: an injury drugstore. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;9(1):11-15.
[15] Charbord P, Livne E, Gross G, et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: a systematic reappraisal via the genostem experience. Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(1):32-42.
[16] Hicks AU, Lappalainen RS, Narkilahti S, et al. Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived neural precursor cells and enriched environment after cortical stroke in rats: cell survival and functional recovery. Eur J Neurosci. 2009;29(3): 562-574.
[17] Li Y, Chopp M. Marrow stromal cell transplantation in stroke and traumatic brain injury. Neurosci Lett. 2009;456(3): 120-123.
[18] 吴晓牧,屈新辉,张洪连,等.颈动脉移植骨髓间充质干细胞治疗脑梗死大鼠[J].中华神经科杂志,2011,44(7):487-492.
[19] Buffo A, Rolando C, Ceruti S. Astrocytes in the damaged brain: molecular and cellular insights into their reactive response and healing potential. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010;79(2):77-89.
[20] Zhang D, Fan GC, Zhou X, et al. Over-expression of CXCR4 on mesenchymal stem cells augments myoangiogenesis in the infarcted myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;44(2):281-292.
[21] Higuchi T, Anton M, Saraste A, et al. Reporter gene PET for monitoring survival of transplanted endothelial progenitor cells in the rat heart after pretreatment with VEGF and atorvastatin. J Nucl Med. 2009;50(11):1881-1886.
[22] Ben Azouna N, Jenhani F, Regaya Z, et al. Phenotypical and functional characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow: comparison of culture using different media supplemented with human platelet lysate or fetal bovine serum. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012;3(1):6.
[23] Knoop K, Schwenk N, Dolp P, et al. Stromal targeting of sodium iodide symporter using mesenchymal stem cells allows enhanced imaging and therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Gene Ther. 2013;24(3):306-316.
[24] Liu Z, Li Y, Zhang ZG, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells enhance inter- and intracortical axonal connections after ischemic stroke in adult rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010;30(7):1288-1295.
[25] Yu YL, Chou RH, Shyu WC, et al. Smurf2-mediated degradation of EZH2 enhances neuron differentiation and improves functional recovery after ischaemic stroke. EMBO Mol Med. 2013;5(4):531-547.
[26] Raghavan A, Shah ZA. Repair and regeneration properties of Ginkgo biloba after ischemic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9 (11): 1104-1107.
[27] Xia W, Li H, Wang Z, et al. Human platelet lysate supports ex vivo expansion and enhances osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Biol Int. 2011;35(6):639-643.
[28] Wang JW,Chen W,Wang YL.A ginkgo biloba extract promotes proliferation of endogenous neural stem cells in vascular dementia rats.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(18): 1655-1662
[29] 王雪松, 阮旭中,刘买利. 银杏叶提取物(GBE)对大鼠局灶性脑缺血后细胞间黏附分子-1及其mRNA表达的影响[J].中国现代应用药学,2008,20(6):441-444.
[30] 张勇,程敬亮,王娟,等.SHU555A标记大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的磁敏感加权成像[J].实用放射学杂志,2010,26(5):736-739.
[31] Wang H, Cao F, De A, et al. Trafficking mesenchymal stem cell engraftment and differentiation in tumor-bearing mice by bioluminescence imaging. Stem Cells. 2009;27(7):1548-1558. |
| [1] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [4] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Liu-Gao Miyang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Wang Jinxiang, Pan Xinghua. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for traumatic systemic inflammatory response syndrome in tree shrews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3994-4000. |
| [5] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [6] | Chen Lei, Zheng Rui, Jie Yongsheng, Qi Hui, Sun Lei, Shu Xiong. In vitro evaluation of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction combined with osteochondral integrated scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3487-3492. |
| [7] | Wei Qin, Zhang Xue, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Jia Qiyu, Ma Chuang. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [8] | Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li. Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [9] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [10] | Li Congcong, Yao Nan, Huang Dane, Song Min, Peng Sha, Li Anan, Lu Chao, Liu Wengang. Identification and chondrogenic differentiation of human infrapatellar fat pad derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2976-2981. |
| [11] | Gao Yuanhui, Xiang Yang, Cao Hui, Wang Shunlan, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang, Huang Denggao. Comparison of biological characteristics of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells in Wuzhishan inbreed miniature pigs aged two different months [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2988-2993. |
| [12] | Cao Yang, Zhang Junping, Peng Li, Ding Yi, Li Guanghui. Isolation and culture of rabbit aortic endothelial cells and biological characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3000-3003. |
| [13] | Dai Min, Wang Shuai, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Yu Limei, Hu Xiaohua, Yi Jie, Yao Li, Zhang Ligang. Biological characteristics of hypoxic preconditioned human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3004-3008. |
| [14] | Qin Yanchun, Rong Zhen, Jiang Ruiyuan, Fu Bin, Hong Xiaohua, Mo Chunmei. Chinese medicine compound preparation inhibits proliferation of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells and the expression of stemness transcription factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3016-3023. |
| [15] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||